BK101
Knowledge Base
Information Literacy - Analyzing Information

Information Literacy is a set of abilities that helps you to locate, evaluate, and filter information, and also recognize when more information or data is needed, and then be able to use that information effectively in order to solve a problem or to make a more accurate decision. Information literacy includes skepticism, judgment, free thinking, questioning, and understanding. Information literacy are competencies that every informed citizen of an information society ought to possess in order to participate intelligently and actively with in a society.
Imagine being in another country and not being able to speak a foreign language, you would have no idea what other people were saying. Now imagine being able to speak the same language as someone else, a conversation would be much easier. But what if someone were lying to you, or what if someone were telling you something that manipulated your understanding, then you would still have a communication problem. So even if you speak the same language as someone else, there's no guarantee that the information that you're receiving is accurate. If you never learn what certain words mean, like when a Doctor try's to explain to you a medical condition, you might not understand the meaning of certain words. This is when you will not fully understand the message. Welcome to information literacy.
Truth - Objective - Validation - Opinions - Lies - Denial
Thinking in Layers - Processing Speed - Information Overload
Big Data - Data - Digital - Data Bases
Wikipedia Information Sources - Social Networks - Information Bubbles
Media Literacy and Information Literacy are corresponding subjects and skills that work together in unison.
Reading Comprehension is also similar, and coincides within the characteristics of Information Literacy.
Problem Solving and Information Literacy also are closely related and used in unison.
Validation - How true or how accurate is the information?
Freedom of Information - Rights to Access Information. Knowledge Management - Database
Education Reform - Teaching students to understand information.
The ability to analyze information is every humans most valuable skill. So learning the knowledge and skills that helps define the processes that are used to analyze information are extremely important. And then those skills need to be measured, confirmed, maintained and updated accordingly. How information is conveyed is extremely important. Certain information takes more the just a title and an introduction. Information sometimes needs multiple mediums and many different explanations in order for it to be understood by a wide range of people with many different levels of education and understanding. You must then organize and categorize information so that people can easily navigate through all the knowledge and associations that are related to that particular information. You don't have to know all the details to every bit of knowledge, you just need to know when that knowledge is important and when to seek more of that particular Knowledge. Information also needs to be easily transferable into snippets and manageable chunks so that people can take and use this information for their own educational needs.
Information needs a certain level of accuracy, and it is also needs a certain level of relevance. Artificial or not, you must always be aware of information whether it comes from AI or a human. Information is information. It's not about the source of the information, because the true source of the information can not always be verified. So information first. Is the Information relevant? Does the Information have value? If it does, then how does knowing the source of this Information change anything? Life could have never survived if life did not have a source for information. Life did not say "Who are you?" Life only said thank you for the information, I will see if there is a use for this information and let you know what I have learned. Instructions.
Bottom Line Is: It's very important to know how information is being processed and understood by the person receiving the information. It's also important to know what the output and the effects will be after that information is processed and understood. Are behaviors being modified or improved? Are a persons actions more effective and more efficient now then they were before? Or is the opposite happening. Never take learning for granted.
Information - A Collection of Facts
Information is a collection of facts from which conclusions may be drawn. Information is a message received and understood. Information is knowledge acquired through study or experience or instruction. Information is something that informs or gives an answer to a question. Information is a detectable pattern of some form of energy that can be measured and then translated into a language that a receiver can understand. Information is any type of signal or symbol that can be interpreted and understood. Information is meaning conveyed by symbolism and language. Information is a product of measurement that is subjective until we give it meaning, like with zeros or ones or on or off. Information is something that data and knowledge can be derived from. Data represents values attributed to parameters, and knowledge signifies understanding of real things or abstract concepts. Information's existence is not always coupled to a cognitive observer. In order to accurately receive a signal, the receiver must know how to interpret the signal and then be able to translate that information into the appropriate action.
Energy is information, God is information and Humans are information, and humans have only deciphered less then 1% of the total information being transmitted in our universe. And preserving our deciphered information is extremely important, because without our information, we will not survive, and starting over this time would be nearly impossible. Information doesn't require a human in order to exist, but humans need information in order to exist. Information needs information. And when we lose information, we lose part of ourselves. The information is still there, it's just that we can't detect that information anymore using the information that we have left. This means that we would have to start over, again. Without Information, Life would not exist.
Most signals are a consistent pattern with a set of rules and order. Life can not exist without the sending and receiving of information. The human sperm and egg cells contain all the information and instructions needed to develop and grow into an adult human. Systematically assemble itself. Information also needs instructions on how to interpret the information and also how to use the information so that it can be utilized. All information needs a receiver that can interpret the Signal. When we find old text on stone we need to decipher the meaning of the Symbols, if we can't, then the information is never understood or utilized. We started out sending information using sounds that our mouths made. These unique and unusual sounds helped us communicate. Then we started using the 3D world to send and receive information signals, using paper and stone that had symbols. Then when we discovered electricity, a few years later we were able to use it to send information signals.
When Information is first Detected. First you have to understand the source of the information and how it came to be, what is the cause of this information? Then second, you have to understand, process and interpret this information, what are the effects of this information and is the root message being transmitted by this information? Then third you have to understand the correct action to take and why the decision you're making is the best decision at this moment? Then the outcome, did your decision have the effect that you were planning for? Detected - Realized.
 Information Management (IM) concerns a cycle of
organizational activity: the acquisition of information from one or more
sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to
those who need it, and its ultimate disposition through archiving or
deletion.
Information Management (IM) concerns a cycle of
organizational activity: the acquisition of information from one or more
sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to
those who need it, and its ultimate disposition through archiving or
deletion.Backup - Knowledge Preservation
Structured Analysis are methods for analyzing and converting business requirements into specifications and ultimately, computer programs, hardware configurations and related manual procedures.
Information Asymmetry deals with the study of decisions in transactions where one party has more or better information than the other. This creates an imbalance of power in transactions, which can sometimes cause the transactions to go away, a kind of market failure in the worst case. Examples of this problem are adverse selection, moral hazard, and information monopoly.
Complete Information is when knowledge about participants is available to all participants. Common knowledge gives equal power of knowledge to everyone thus reduces unfair practices or criminal activity that results from people knowing more then you, and then exploiting your ignorance in their favor.
Minimum Information Standards is a set of guidelines for reporting data derived by relevant methods in biosciences. If followed, it ensures that the data can be easily verified, analyzed and clearly interpreted by the wider scientific community. Keeping with these recommendations also facilitates the foundation of structuralized databases, public repositories and development of data analysis tools.
Informatics involves the practice of information processing, and the engineering of information systems. The field considers the interaction between humans and information alongside the construction of interfaces, organizations, technologies and systems.
Information Systems is any organized system for the collection, organization, storage and communication of information. More specifically, it is the study of complementary networks that people and organizations use to collect, filter, process, create and distribute data. In a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure (or roles), and technology. Any specific information system aims to support operations, management and decision-making. An information system is the information and communication technology (ICT) that an organization uses, and also the way in which people interact with this technology in support of business processes. The six components that must come together in order to produce an information system are: (Information systems are organizational procedures and do not need a computer or software, this data is erroneous, i.e., an accounting system in the 1400's using a ledger and ink utilizes an information system). Hardware: The term hardware refers to machinery. This category includes the computer itself, which is often referred to as the central processing unit (CPU), and all of its support equipment. Among the support, equipment are input and output devices, storage devices and communications devices. Software: The term software refers to computer programs and the manuals (if any) that support them. Computer programs are machine-readable instructions that direct the circuitry within the hardware parts of the system to function in ways that produce useful information from data. Programs are generally stored on some input/output medium, often a disk or tape. Data: Data are facts that are used by programs to produce useful information. Like programs, data are generally stored in machine-readable form on disk or tape until the computer needs them. Procedures: Procedures are the policies that govern the operation of a computer system. "Procedures are to people what software is to hardware" is a common analogy that is used to illustrate the role of procedures in a system. People: Every system needs people if it is to be useful. Often the most overlooked element of the system are the people, probably the component that most influence the success or failure of information systems. This includes "not only the users, but those who operate and service the computers, those who maintain the data, and those who support the network of computers." Feedback: it is another component of the IS, that defines that an IS may be provided with a feedback (Although this component isn't necessary to function). Data is the bridge between hardware and people. This means that the data we collect is only data until we involve people. At that point, data is now information. A computer(-based) information system is essentially an IS using computer technology to carry out some or all of its planned tasks. The basic components of computer-based information systems are: Hardware- these are the devices like the monitor, processor, printer and keyboard, all of which work together to accept, process, show data and information. Software- are the programs that allow the hardware to process the data. Databases- are the gathering of associated files or tables containing related data. Networks- are a connecting system that allows diverse computers to distribute resources. Procedures- are the commands for combining the components above to process information and produce the preferred output. A computer-based information system, following a definition of Langefors, is a technologically implemented medium for: recording, storing, and disseminating linguistic expressions, as well as for drawing conclusions from such expressions. Geographic information systems, land information systems, and disaster information systems are examples of emerging information systems, but they can be broadly considered as spatial information systems. System development is done in stages which include: Problem recognition and specification, Information gathering. Requirements specification for the new system. System design. System construction. System implementation. Review and maintenance.
Information Technology is the application of computers and internet to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data, or information, often in the context of a business or other enterprise. IT is considered a subset of information and communications technology (ICT).
Information Technology - Knowledge Management (Technology Education)
Information Technology Management is the discipline whereby all of the information technology resources of a firm are managed in accordance with its needs and priorities. These resources may include tangible investments like computer hardware, software, data, networks and data centre facilities, as well as the staff who are hired to maintain them.
Information Communications Technology (ICT) is an extended term for information technology (IT) which stresses the role of unified communications.
TAFIM - Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management.
Strategic Information Systems are developed in response to corporate business initiative. They are intended to give competitive advantage to the organization. They may deliver a product or service that is at a lower cost, that is differentiated, that focuses on a particular market segment, or is innovative.
Information Architecture is the structural design of shared information environments; the art and science of organizing and labeling websites, intranets, online communities and software to support usability and findability; and an emerging community of practice focused on bringing principles of design and architecture to the digital landscape.
Information Security - Information Science
Physical Information refers generally to the information that is contained in a physical system. Its usage in quantum mechanics (i.e. quantum information) is important, for example in the concept of quantum entanglement to describe effectively direct or causal relationships between apparently distinct or spatially separated particles. Physical information is a form of information. In physics, it refers to the information of a physical system. Physical information is an important concept used in a number of fields of study in physics. For example, in quantum mechanics, the form of physical information known as quantum information is used in many descriptions of quantum phenomena, such as quantum observation, quantum entanglement and the causal relationship between quantum objects that carry out either or both close and long-range interactions with one another. In a general sense, information is that which resolves uncertainty, which is due to the fact that it describes the details of that which is associated with the uncertainty. The description itself is, however, divorced from any type of language. When clarifying the subject of information, care should be taken to distinguish between the following specific cases: The phrase instance of information refers to the specific instantiation of information (identity, form, essence) that is associated with the being of a particular example of a thing. (This allows for the reference to separate instances of information that happen to share identical patterns.) A holder of information is a variable or mutable instance that can have different forms at different times (or in different situations). A piece of information is a particular fact about a thing's identity or properties, i.e., a portion of its instance. A pattern of information (or form) is the pattern or content of an instance or piece of information. Many separate pieces of information may share the same form. We can say that those pieces are perfectly correlated or say that they are copies of each other, as in copies of a book. An embodiment of information is the thing whose essence is a given instance of information. A representation of information is an encoding of some pattern of information within some other pattern or instance. An interpretation of information is a decoding of a pattern of information as being a representation of another specific pattern or fact. A subject of information is the thing that is identified or described by a given instance or piece of information. (Most generally, a thing that is a subject of information could be either abstract or concrete; either mathematical or physical.) An amount of information is a quantification of how large a given instance, piece, or pattern of information is, or how much of a given system's information content (its instance) has a given attribute, such as being known or unknown. Amounts of information are most naturally characterized in logarithmic units. As the above usages are all conceptually distinct from each other, overloading the word "information" (by itself) to denote (or connote) several of these concepts simultaneously can lead to confusion. Accordingly, this article uses more detailed phrases, such as those shown in bold above, whenever the intended meaning is not made clear by the context.
Information Theory studies the quantification, storage, and communication of information. It was originally proposed by Claude Shannon in 1948 to find fundamental limits on signal processing and communication operations such as data compression, in a landmark paper titled "A Mathematical Theory of Communication". The field is at the intersection of probability theory, statistics, computer science, statistical mechanics, information engineering, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (with two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a die (with six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measures in information theory are mutual information, channel capacity, error exponents, and relative entropy. Important sub-fields of information theory include source coding, algorithmic complexity theory, algorithmic information theory, and information-theoretic security. Applications of fundamental topics of information theory include lossless data compression (e.g. ZIP files), lossy data compression (e.g. MP3s and JPEGs), and channel coding (e.g. for DSL). Its impact has been crucial to the success of the Voyager missions to deep space, the invention of the compact disc, the feasibility of mobile phones and the development of the Internet. The theory has also found applications in other areas, including statistical inference, cryptography, neurobiology, perception, linguistics, the evolution and function of molecular codes (bioinformatics), thermal physics, quantum computing, black holes, information retrieval, intelligence gathering, plagiarism detection, pattern recognition, anomaly detection and even art creation.
Processing Information
Processing is to perform mathematical and logical operations on data according to programmed instructions. To put information through a prescribed procedure in order to prepare information for a particular purpose. To subject information to a treatment with the aim of readying it for some purpose, or to improve something or to remedy a condition. To deal with something in a routine way.
Data Processing is the collection and manipulation of items of data to produce meaningful information. In this sense it can be considered a subset of information processing, the change of information in any manner detectable by an observer. A series of operations on data by a computer in order to retrieve or transform or classify information.
Data Analysis is a process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, as well as suggesting conclusions and supporting decision-making.
Information Processing is the change of information in any manner detectable by an observer. As such, it is a process that describes everything that happens in the universe, from the falling of a rock or a change in position or the printing of a text file from a digital computer system. In the latter case, an information processor is changing the form of presentation of that text file. Interpretation.
Information Processing System is a system which takes information in a sequence of enumerated symbols or states in one form and processes or transforms it into another form, e.g. to statistics, by an algorithmic process. An information processing system is made up of four basic parts, or sub-systems: Input, Processor, Storage, Output. Speed. (information can be electrical, mechanical or biological).
Thinking Fast is when you have the ability to answer questions quickly and recall information fast without hesitation.
Quick Decisions (Split Second Decision Making) - Processing Speed
Dual Process Theory provides an account of how thought can arise in two different ways, or as a result of two different processes. Often, the two processes consist of an implicit (automatic), unconscious process and an explicit (controlled), conscious process. Verbalized explicit processes or attitudes and actions may change with persuasion or education; though implicit process or attitudes usually take a long amount of time to change with the forming of new habits. Dual process theories can be found in social, personality, cognitive, and clinical psychology. It has also been linked with economics via prospect theory and behavioral economics, and increasingly in sociology through cultural analysis. Dual processing theory indicates that our ability to process information for decision making purposes happens in two distinct ways. Implicit processing is unconscious, fast, guided by lived experiences and bias, and requires no special intellect. Multitasking.
Signal Processing concerns the analysis, synthesis, and modification of signals, which are broadly defined as functions conveying "information about the behavior or attributes of some phenomenon", such as sound, images, and biological measurements. For example, signal processing techniques are used to improve signal transmission fidelity, storage efficiency, and subjective quality, and to emphasize or detect components of interest in a measured signal.
Use is to put something into service and make it work for a particular purpose or use as designed. Seek or achieve an end by using to one's advantage. Spend time doing something so that less or no time is left. Use in economics is the utilization of economic goods to satisfy needs or in manufacturing. Use in psychology is an automatic pattern of behavior in reaction to a specific situation; may be inherited or acquired through frequent repetition.
Information Literacy - The Big Six Skills
 1. Goal - The first step in the
information literacy strategy is
to clarify and understand the requirements
of the
problem or task for which
information is
sought.
Conceptual
abstractions may be formed by
filtering the information
content of a concept or an observable phenomenon,
selecting only the
aspects which are relevant for a particular purpose.
Big 6 Skills
- Problem
Solving - Goals.
1. Goal - The first step in the
information literacy strategy is
to clarify and understand the requirements
of the
problem or task for which
information is
sought.
Conceptual
abstractions may be formed by
filtering the information
content of a concept or an observable phenomenon,
selecting only the
aspects which are relevant for a particular purpose.
Big 6 Skills
- Problem
Solving - Goals. Basic questions asked at this stage.
1. What is known about the topic? (well-formed statements and all questions considered).
2. What information is needed? - Information Visualization - Needs - Thinking Styles.
3. Where can the information be found? Information Sources - Human Search Engine.
2. Locating - The second step is to identify sources of information and to find those resources. Depending upon the task, sources that will be helpful may vary. Sources may include books, encyclopedias, maps, almanacs, etc. Sources may be in electronic, print, social bookmarking tools, or other formats. Information Retrieval - Evidence - Reliable Sources - Extenuating Circumstances - Data - Facts - Validation - Doubt - Bias.
3. Selecting - Analyzing - Step three involves examining the resources that were found. The information must be determined to be useful or not useful in solving the problem. Processing. The useful resources are selected and the inappropriate resources are rejected. Science - Deconstruction.
Image Differencing is an image processing technique used to determine changes between images.
Verification - Validation - Analysis - Authentication - Factoid.
4. Organizing - Synthesizing - It is in the fourth step this information which has been selected is organized and processed so that Knowledge and solutions are developed.
Examples of basic steps in this stage are:
1. Discriminating between Fact and Opinion. Cryptography - Inference.
2. Basing comparisons on similar characteristics. Mutual Information - Understanding.
3. Noticing various interpretations of data. Pattern Recognition - Meanings - Labels.
4. Finding more information if needed. Internet Searches - Requirements Elicitation.
5. Organizing ideas and information logically. Consequentialism - Coincidence.
5. Creating - Presenting - In step five the information or solution is presented to the appropriate udience in an appropriate format. A paper is written. A presentation is made. Drawings, illustrations, and Graphs are presented. Info-Graphics - Digital Technology - Disclaimer.
6. Evaluation - The final step in the Information Literacy strategy involves the critical evaluation of the completion of the task or the new understanding of the concept. Was the problem solved? Was new Knowledge found? What could have been done differently? What was done well?
Intelligence Analysis - Analyze - Profiling Practices - Cryptography - Translations - Media Literacy
Learning Methods - Knowledge Management - Data Visualization - Scientific Examinations
Self Directed Learning - Information Stations - Information Knowledge Base - Information Sources.
Data - Set of Values
 Data is a set of values of
qualitative or quantitative
variables. Pieces of data are individual pieces of information.
Data
is a collection of
facts from which
conclusions may be drawn.
An item of factual information
derived from
measurement or
research or from the
senses.
Data is a set of values of
qualitative or quantitative
variables. Pieces of data are individual pieces of information.
Data
is a collection of
facts from which
conclusions may be drawn.
An item of factual information
derived from
measurement or
research or from the
senses.Datum is an item of factual information derived from measurement or research.
Raw Data or primary data, is data collected from a source, such as numbers, instrument readings, figures, and so on. In the context of examinations, the raw data might be described as a raw score. If a scientist sets up a computerized thermometer which records the temperature of a chemical mixture in a test tube every minute, the list of temperature readings for every minute, as printed out on a spreadsheet or viewed on a computer screen are "raw data". Raw data have not been subjected to processing, "cleaning" by researchers to remove outliers, obvious instrument reading errors or data entry errors, or any analysis (e.g., determining central tendency aspects such as the average or median result). As well, raw data have not been subject to any other manipulation by a software program or a human researcher, analyst or technician. They are also referred to as primary data. Raw data is a relative term (see data), because even once raw data have been "cleaned" and processed by one team of researchers, another team may consider these processed data to be "raw data" for another stage of research. Raw data can be inputted to a computer program or used in manual procedures such as analyzing statistics from a survey. The term "raw data" can refer to the binary data on electronic storage devices, such as hard disk drives (also referred to as "low-level data").
Data Management comprises all the disciplines related to managing data as a valuable resource.
Big Data - Database (dataset) - Memory - Storage - Patterns - Software
Slowly Changing Dimension in data management and data warehousing contain relatively static data about such entities as geographical locations, customers, or products. Data captured by Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCDs) change slowly but unpredictably, rather than according to a regular schedule.
Data Governance is a control that ensures that the data entry by an operations team member or by an automated process meets precisely standards, such as a Business rule, a data definition and data integrity constraints in the data model. The data governor uses data quality monitoring against production data to communicate errors in data back to operational team members, or to the technical support team, for corrective action. Data governance is used by organizations to exercise control over processes and methods used by their data stewards and data custodians in order to improve data quality.
Information Governance - Knowledge Management
Data Structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. Data structures can implement one or more particular abstract data types (ADT), which specify the operations that can be performed on a data structure and the computational complexity of those operations. List of Data Structures (wiki)
Unstructured Data refers to information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Structure.
Structured Data Analysis is the statistical data analysis of structured data. This can arise either in the form of an a priori structure such as multiple-choice questionnaires or in situations with the need to search for structure that fits the given data, either exactly or approximately. This structure can then be used for making comparisons, predictions, manipulations etc.
Persistent Data denotes information that is infrequently accessed and not likely to be modified. The opposite of this is dynamic data (also known as transactional data) where information is asynchronously changed as further updates to the information become available. Updates to dynamic data may come at any time, with periods of inactivity in between.
Persistent Data Structure is a data structure that always preserves the previous version of itself when it is modified. Such data structures are effectively immutable, as their operations do not (visibly) update the structure in-place, but instead always yield a new updated structure. A data structure is partially persistent if all versions can be accessed but only the newest version can be modified. The data structure is fully persistent if every version can be both accessed and modified. If there is also a meld or merge operation that can create a new version from two previous versions, the data structure is called confluently persistent. Structures that are not persistent are called ephemeral or lasting a very short time.
Cold Data is data that is not frequently accessed or actively used. It is data that may get collected and sit for a long time in some virtual container without being retrieved, analyzed or transferred to another part of the system.
Digital - Representing Numbers and Information
Zero or One - On or Off - Pulse or No Pulse - Stop or Go - Long Wave or Short Wave - Low Voltage or High Voltage - Up or Down - Spin Right or Spin Left - Vertical Polarization or Horizontal Polarization - Matter or No Matter - Molecule or No Molecule - Chemical or No Chemical - Punch Hole or No Hole - Circle or Claviform - Source - Gate - Drain, if the Gate is open and the current flows then that equals the number one. If the current doesn't flow because the gate is closed, then that equals the number zero. Extraction.
Digital Data are discrete, discontinuous representations of information or works, as contrasted with continuous, or analog signals which behave in a continuous manner, or represent information using a continuous function. The words digit and digitus (the Latin word for finger), as fingers are often used for discrete counting.
Digital Media are any media that are encoded in a machine-readable format. Digital media can be created, viewed, distributed, modified and preserved on digital electronics devices. Computer programs and software; digital imagery, digital video; video games; web pages and websites, including social media; data and databases; digital audio, such as mp3s; and e-books are examples of digital media. Digital media are frequently contrasted with print media, such as printed books, newspapers and magazines, and other traditional or analog media, such as pictures, film or audio tape.
Digital Electronics are electronics that handle digital signals – discrete bands of analog levels – rather than by continuous ranges as used in analog electronics. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. Because of this discretization, relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.
Digital refers to something using digits, particularly binary digits.
Digital Physics is a collection of theoretical perspectives based on the premise that the universe is, at heart, describable by information. Therefore, according to this theory, the universe can be conceived of as either the output of a deterministic or probabilistic computer program, a vast, digital computation device, or mathematically isomorphic to such a device.
Materialism matter is the fundamental substance in nature, and that all phenomena, including mental phenomena and consciousness, are results of material interactions.
Digital Divide is an economic and social inequality with regard to access to, use of, or impact of information and communication technologies. Knowledge Divide.
Boolean Function describes how to determine a Boolean value output based on some logical calculation from Boolean inputs. Such functions play a basic role in questions of complexity theory as well as the design of circuits and chips for digital computers. The properties of Boolean functions play a critical role in cryptography, particularly in the design of symmetric key algorithms. Logic Gate.
Boolean Data Type is a data type, having two values (usually denoted true and false), intended to represent the truth values of logic and Boolean algebra.
Boolean Algebra is the branch of algebra in which the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0.
Truth Table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is, for each combination of values taken by their logical variables (Enderton, 2001). In particular, truth tables can be used to show whether a propositional expression is true for all legitimate input values, that is, logically valid. A truth table has one column for each input variable (for example, P and Q), and one final column showing all of the possible results of the logical operation that the table represents (for example, P XOR Q). Each row of the truth table contains one possible configuration of the input variables (for instance, P=true Q=false), and the result of the operation for those values. See the examples below for further clarification. Ludwig Wittgenstein is often credited with inventing the truth table in his Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus, though it appeared at least a year earlier in a paper on propositional logic by Emil Leon Post.
Base 10 System. Decimal number system, Decimal number system, also called Hindu-Arabic, or Arabic, number system, in mathematics, positional numeral system employing 10 as the base and requiring 10 different numerals, the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. It also requires a dot (decimal point) to represent decimal fractions.
Base-2 Numeral System or binary numeral system, which uses only two symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one). The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2.
Units of Information is the capacity of some standard data storage system or communication channel, used to measure the capacities of other systems and channels. In information theory, units of information are also used to measure the information contents or entropy of random variables.
Block in data storage is a sequence of bytes or bits, usually containing some whole number of records, having a maximum length, a block size. Data thus structured are said to be blocked. The process of putting data into blocks is called blocking, while deblocking is the process of extracting data from blocks. Blocked data is normally stored in a data buffer and read or written a whole block at a time. Blocking reduces the overhead and speeds up the handling of the data-stream. For some devices such as magnetic tape and CKD disk devices blocking reduces the amount of external storage required for the data. Blocking is almost universally employed when storing data to 9-track magnetic tape, to NAND flash memory, and to rotating media such as floppy disks, hard disks, and optical discs. Storage.
 Bit is the basic
unit of information
in computing and digital communications, can have only one of
two
values. A two-state device represented as
0 and 1. (ON=1 / OFF=0) Quantum
- Code.
Bit is the basic
unit of information
in computing and digital communications, can have only one of
two
values. A two-state device represented as
0 and 1. (ON=1 / OFF=0) Quantum
- Code.
256 Possible Combinations of ones and zeros for 8 bits (2^8). Each bit has 2 possibilities.
Binary Number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, which uses only two symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one).
Binary File is a computer file that is not a text file. The term "binary file" is often used as a term meaning "non-text file", being a sequence of bytes, which means the binary digits (bits) are grouped in eights.
Binary is a number system having 2 as its base. Consisting of two units or components or elements or terms. Binary Data.
Binary Code - Voltages used as a Language.
1 Byte = 8 Bits.
1 Kilobyte = 1000 bytes.
1 Megabyte = 1000 Kbytes (1,000,000 bytes (million) (average large digital photograph is 1.5 Megabytes).
1 Gigabyte = 1000 Megabytes (1,000,000,000 bytes (billion).
1 Terabyte = 1000 Gigabytes (1,000,000,000,000 bytes (trillion).
1 Petabyte = 1000000000000000B = 1000 terabytes.
1 Exabyte = 1 Billion Gigabytes (one quintillion bytes).
1 Zettabyte = 1000 Exabytes.
1 Yottabyte = 1000 Zettabytes.
Qubit is a unit of quantum information.
Memory Cell in binary is the fundamental building block of computer memory. The memory cell is an electronic circuit that stores one bit of binary information and it must be set to store a logic 1 (high voltage level) and reset to store a logic 0 (low voltage level). Its value is maintained/stored until it is changed by the set/reset process. The value in the memory cell can be accessed by reading it.
Signed Number Representations are required to encode negative numbers in binary number systems. Negative numbers in any base are represented by prefixing them with a minus ("−") sign. However, in computer hardware, numbers are represented only as sequences of bits, without extra symbols. The four best-known methods of extending the binary numeral system to represent signed numbers are: sign-and-magnitude, ones' complement, two's complement, and offset binary. Some of the alternative methods use implicit instead of explicit signs, such as negative binary, using the base −2. Corresponding methods can be devised for other bases, whether positive, negative, fractional, or other elaborations on such themes.
How much Data is there?
Sizes (small to big) - Large Numbers
Digital Curation and Preservation
Digital Asset Management
Born-Digital refers to materials that originate in a digital form.
A Bit of History on Data (youtube)
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (wiki) - De Arte Combinatoria (wiki)
Forward Error Correction In telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction (FEC) or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels.
Line Code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for transmitting a digital signal down a line. Line coding is often used for digital data transport.
Data Knowledge - Life is Digital - Building Blocks of Life
Flash-Drives - Organizing - Computer Knowledge
3 Digit Combination Lock has 1,000 possible combinations between 000 and 999. 10 choices for the first digit, you have 10 choices for the 2nd digit, and you have 10 choices for the 3rd digit giving you 10x10x10 = 1000 in all.
4 Digit Combination Lock has 10,000 possible combinations.
"Knowing the reasons for your question will always help you ask the right question, just being inquisitive is not enough."
Socrates argued that the attitude of wanting one’s ideas to be always ‘validated’ and not questioned is intellectually stagnating and is a mark of ‘ignorance’. He pointed this out in his idea of ‘wisdom’. A wise person is one who is always willing to ‘learn’. Such a person assumes tentatively that she does not know. She is willing to methodologically suspend her belief and question it for the purpose of exploring it, to expand her knowledge. The process of questioning—for the purpose of eliciting information and adequate justifications—represents an epistemic attitude which is necessary for critical thinking. Such attitude is often what teachers want to engender in students as critical thinkers. More about Questioning.
Information Extraction - Retrieval
Information Extraction is the task of automatically extracting structured information from unstructured and/or semi-structured machine-readable documents. In most of the cases this activity concerns processing human language texts by means of natural language processing. Recent activities in multimedia document processing like automatic annotation and content extraction out of images/audio/video could be seen as information extraction.
Extract is to remove or take out and separate something.
Extracting is to remove something with some force or effort. To obtain something from a substance, as by mechanical action. To get something despite difficulties or obstacles. To deduce a principle or to construe a meaning.
Extraction the process of obtaining something from a mixture or compound by chemical or physical or mechanical means.
Abstraction (data scraping) - Extensive Reading - Data Extraction - Knowledge Extraction - Filtering
Public Knowledge - Enlightenment - Learning - Search Engine
Information Retrieval is the activity of obtaining information system resources relevant to an information need from a collection of information resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for metadata that describe data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Document Retrieval.
Retrieve is regaining something or saving something that may be in danger of becoming lost. To get back or recover something. To reach or to gain access to information.
Text Retrieval is defined as the matching of some stated user query against a set of free-text records. These records could be any type of mainly unstructured text, such as newspaper articles, real estate records or paragraphs in a manual. User queries can range from multi-sentence full descriptions of an information need to a few words.
Image Retrieval a computer system for browsing, searching and retrieving images from a large database of digital images. Most traditional and common methods of image retrieval utilize some method of adding metadata such as captioning', keywords, or descriptions to the images so that retrieval can be performed over the annotation words.
Information Assurance is the practice of assuring information and managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information or data and the systems and processes used for those purposes. Information assurance includes protection of the integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation and confidentiality of user data.
Quantum Information Science is an area of study based on the idea that information science depends on quantum effects in physics.
Information Theory studies the quantification, storage, and communication of information. Claude Shannon is the father of information theory.
Information Integration describe and model how a person integrates information from a number of sources in order to make an overall judgment.
Information Entropy is defined as the average amount of information produced by a probabilistic stochastic source of data. The measure of information entropy associated with each possible data value is the negative logarithm of the probability mass function for the value. Thus, when the data source has a lower-probability value (i.e., when a low-probability event occurs), the event carries more "information" ("surprisal") than when the source data has a higher-probability value. The amount of information conveyed by each event defined in this way becomes a random variable whose expected value is the information entropy. Generally, entropy refers to disorder or uncertainty, and the definition of entropy used in information theory is directly analogous to the definition used in statistical thermodynamics.
Entropy in information theory is where systems are modeled by a transmitter, channel, and receiver. The transmitter produces messages that are sent through the channel. The channel modifies the message in some way. The receiver attempts to infer which message was sent. In this context, entropy (more specifically, Shannon entropy) is the expected value (average) of the information contained in each message. 'Messages' can be modeled by any flow of information. UC Merced Cognitive and Information Sciences.
Knowledge Extraction is the creation of knowledge from structured (relational databases, XML) and unstructured (text, documents, images) sources. The resulting knowledge needs to be in a machine-readable and machine-interpretable format and must represent knowledge in a manner that facilitates inferencing.
Information Extraction - Information Retrieval - Data Extraction - Enlightenment
Information Literacy the ability to know when there is a need for information, to be able to identify, locate, evaluate, and effectively use that information for the issue or problem at hand.
Extraction of Data
Data Extraction is the act or process of retrieving data out of unstructured or poorly structured data sources for further data processing or data storage (data migration). The import into the intermediate extracting system is thus usually followed by data transformation and possibly the addition of metadata prior to export to another stage in the data workflow. Extracts data from similar or dissimilar data sources. Information Extraction.
Extract, Transform, Load is the general procedure of copying data from one or more sources into a destination system which represents the data differently from the source(s) or in a different context than the source(s).
Data Acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms DAS or DAQ, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include: Sensors, to convert physical parameters to electrical signals. Signal conditioning circuitry, to convert sensor signals into a form that can be converted to digital values. Analog-to-digital converters, to convert conditioned sensor signals to digital values. Data acquisition applications are usually controlled by software programs developed using various general purpose programming languages such as Assembly, BASIC, C, C++, C#, Fortran, Java, LabVIEW, Lisp, Pascal, etc. Stand-alone data acquisition systems are often called data loggers. There are also open-source software packages providing all the necessary tools to acquire data from different hardware equipment. These tools come from the scientific community where complex experiment requires fast, flexible and adaptable software. Those packages are usually custom fit but more general DAQ package like the Maximum Integrated Data Acquisition System can be easily tailored and is used in several physics experiments worldwide. H.S.E.
Data Feed is a mechanism for users to receive updated data from data sources. It is commonly used by real-time applications in point-to-point settings as well as on the World Wide Web. The latter is also called web feed.
Data Transformation – transforms the data for storing it in the proper format or structure for the purposes of querying and analysis.
Data Compression - Memory (storage)
Data Loading – loads it into the final target (database, more specifically, operational data store, data mart, or data warehouse). Since the data extraction takes time, it is common to execute the three phases in parallel. While the data is being extracted, another transformation process executes. It processes the already received data and prepares it for loading. As soon as there is some data ready to be loaded into the target, the data loading kicks off without waiting for the completion of the previous phases. ETL systems commonly integrate data from multiple applications (systems), typically developed and supported by different vendors or hosted on separate computer hardware. The disparate systems containing the original data are frequently managed and operated by different employees. For example, a cost accounting system may combine data from payroll, sales, and purchasing.
Science of Information Libraries
Library Science is an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary field that applies the practices, perspectives, and tools of management, information technology, education, and other areas to libraries; the collection, organization, preservation, and dissemination of information resources; and the economy of information.
Information Science is concerned with the analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Information Science.
Information Sciences Institute is a component of the University of Southern California that specializes in research and development in information processing, computing, and communications technologies.
Library and Information Sciences is a merging of library science and information science.
Library in computing is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications.
Information Technology Infrastructure Library is a set of practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business.
Network Science - Ontology
Archival Science is the study and theory of building and curating archives, which are collections of recordings and data storage devices. To build and curate an archive, one must acquire and evaluate recorded materials, and be able to access them later. To this end, archival science seeks to improve methods for appraising, storing, preserving, and cataloging recorded materials. An archival record preserves data that is not intended to change. In order to be of value to society, archives must be trustworthy. Therefore, an archivist has a responsibility to authenticate archival materials, such as historical documents, and to ensure their reliability, integrity, and usability. Archival records must be what they claim to be; accurately represent the activity they were created for; present a coherent picture through an array of content; and be in usable condition in an accessible location. An archive curator is called an archivist; the curation of an archive is called archive administration.
Information Literacy Forum
Philosophy of Information
Information Institute
Tag Metadata is a non-hierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information (such as an Internet bookmark, digital image, or computer file). This kind of metadata helps describe an item and allows it to be found again by browsing or searching. Tags are generally chosen informally and personally by the item's creator or by its viewer, depending on the system.
Information Lifecycle Management refers to a wide-ranging set of strategies for administering storage systems on computing devices.
Information Literacy is mastering the ability to gather appropriate facts and then creatively leverage those facts towards a Learning Objective. A distinct skill set of competencies to intelligently and actively Recognize when information is needed and have the ability to locate, acquire, Collate, evaluate, and use effectively the needed Information for any situation. Acquire needed information using Books, Digital Technology, Visual Images, Mathematics, Communication Tools, Networks, Libraries, Universities and so on. The student who is information literate accesses information efficiently and effectively, Evaluates Information Critically and competently and uses Information accurately and Creatively. You also need to effectively filter Noise.
De-identification is the process used to prevent a person’s identity from being connected with information.
Information Literacy is about giving people the ability to quickly understand information without being distracted by the information, or overwhelmed by the information, or manipulated by the information. This way people can quickly and accurately measure progress, goals and daily operations, which will leave more time for people to enjoy life, while continuing to learn, and continually making improvements. There is no need to complicate things more then they need to be, or make something more difficult or confusing by causing it to be more complex. Knowledge Management.
Information Governance
Information Governance is the set of multi-disciplinary structures, policies, procedures, processes and controls implemented to manage information at an enterprise level, supporting an organization's immediate and future regulatory, legal, risk, environmental and operational requirements. Data Governance.
Information Technology Governance is a subset discipline of corporate governance, focused on information and technology (IT) and its performance and risk management. The interest in IT governance is due to the ongoing need within organizations to focus value creation efforts on an organization's strategic objectives and to better manage the performance of those responsible for creating this value in the best interest of all. Open Government.
Information Market providers and users exchanging information in place of sellers and buyers trading goods and services, respectively.
 Information Society -
Information Age -
Comprehension
Information Society -
Information Age -
ComprehensionCertified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) is a globally recognized certification in the field of audit, control and security of information systems.
Units of Information - Communication - Processing - Processor
Information Stations - Information Processing
Information Action Ratio indicate the relationship between a piece of information and what action, if any, a consumer of that information might reasonably be expected to take once learning it.
Information Gain Ratio is a ratio of information gain to the intrinsic information. It is used to reduce a bias towards multi-valued attributes by taking the number and size of branches into account when choosing an attribute.
Mutual Information of two random Variables is a measure of the mutual dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the "amount of information" (in units such as bits) obtained about one random variable, through the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intricately linked to that of entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory, that defines the "amount of information" held in a random variable.
Database - Organized Collections of Data
Database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modeling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies. Rows and Columns.
Database Management System is a computer software application that interacts with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data. A general-purpose DBMS is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, Sybase, SAP HANA, MemSQL and IBM DB2.
Data Storage (backup data center)
Database Administrator includes capacity planning, installation, configuration, database design, migration, performance monitoring, security, troubleshooting, as well as backup and data recovery. Uses specialized software to store and organize data.
Database Indexing is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time a database table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records.
Database Dump contains a record of the table structure and/or the data from a database and is usually in the form of a list of SQL statements. A database dump is most often used for backing up a database so that its contents can be restored in the event of data loss. Corrupted databases can often be recovered by analysis of the dump. Database dumps are often published by free software and free content projects, to allow reuse or forking of the database.
Database Connection is the means by which a database server and its client software communicate with each other. The term is used whether or not the client and the server are on different machines. The client uses a database connection to send commands to and receive replies from the server. A database is stored as a file or a set of files on magnetic disk or tape, optical disk, or some other secondary storage device. The information in these files may be broken down into records, each of which consists of one or more fields. Fields are the basic units of data storage, and each field typically contains information pertaining to one aspect or attribute of the entity described by the database. Records are also organized into tables that include information about relationships between its various fields. Although database is applied loosely to any collection of information in computer files, a database in the strict sense provides cross-referencing capabilities. Connections are a key concept in data-centric programming. Since some DBMSs require considerable time to connect, connection pooling is used to improve performance. No command can be performed against a database without an "open and available" connection to it.
Database Transaction symbolizes a unit of work performed within a database management system (or similar system) against a database, and treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions. A transaction generally represents any change in a database. Transactions in a database environment have two main purposes: To provide reliable units of work that allow correct recovery from failures and keep a database consistent even in cases of system failure, when execution stops (completely or partially) and many operations upon a database remain uncompleted, with unclear status. To provide isolation between programs accessing a database concurrently. If this isolation is not provided, the programs' outcomes are possibly erroneous. In a Database Management System, a transaction is a single unit of logic or work, sometimes made up of multiple operations. Any logical calculation done in a consistent mode in a database is known as a transaction. One example is a transfer from one bank account to another: the complete transaction requires subtracting the amount to be transferred from one account and adding that same amount to the other. A database transaction, by definition, must be atomic, consistent, isolated and durable. Database practitioners often refer to these properties of database transactions using the acronym ACID. Transactions provide an "all-or-nothing" proposition, stating that each work-unit performed in a database must either complete in its entirety or have no effect whatsoever. Further, the system must isolate each transaction from other transactions, results must conform to existing constraints in the database, and transactions that complete successfully must get written to durable storage.
Atomicity in database systems or an atomic transaction is an indivisible and irreducible series of database operations such that either all occur, or nothing occurs. A guarantee of atomicity prevents updates to the database occurring only partially, which can cause greater problems than rejecting the whole series outright. As a consequence, the transaction cannot be observed to be in progress by another database client. At one moment in time, it has not yet happened, and at the next it has already occurred in whole (or nothing happened if the transaction was cancelled in progress).
Types of Databases (wiki) - Big Data
Database Design is the process of producing a detailed data model of database. This data model contains all the needed logical and physical design choices and physical storage parameters needed to generate a design in a data definition language, which can then be used to create a database. A fully attributed data model contains detailed attributes for each entity.
Database Schema of a database system is its structure described in a formal language supported by the database management system (DBMS). The term "schema" refers to the organization of data as a blueprint of how the database is constructed (divided into database tables in the case of relational databases). The formal definition of a database schema is a set of formulas (sentences) called integrity constraints imposed on a database.
Database Engine is the underlying software component that a database management system (DBMS) uses to create, read, update and delete (CRUD) data from a database. Most database management systems include their own application programming interface (API) that allows the user to interact with their underlying engine without going through the user interface of the DBMS. The term "database engine" is frequently used interchangeably with "database server" or "database management system". A 'database instance' refers to the processes and memory structures of the running database engine.
Compose
Database Model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relational model, which uses a table-based format.
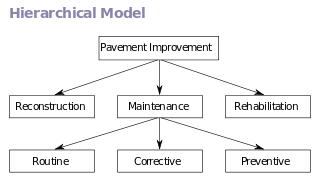 Hierarchical Database Model is a data model in which the
data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data is stored as
records which are connected to one another through links. A record is a
collection of fields, with each field containing only one value. The
entity type of a record defines which fields the record contains. A record
in the hierarchical database model corresponds to a row (or tuple) in the
relational database model and an entity type corresponds to a table (or
relation).The hierarchical database model mandates that each child record
has only one parent, whereas each parent record can have one or more child
records. In order to retrieve data from a hierarchical database the whole
tree needs to be traversed starting from the root node. This model is
recognized as the first database model created by IBM in the 1960s.
Hierarchical Database Model is a data model in which the
data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data is stored as
records which are connected to one another through links. A record is a
collection of fields, with each field containing only one value. The
entity type of a record defines which fields the record contains. A record
in the hierarchical database model corresponds to a row (or tuple) in the
relational database model and an entity type corresponds to a table (or
relation).The hierarchical database model mandates that each child record
has only one parent, whereas each parent record can have one or more child
records. In order to retrieve data from a hierarchical database the whole
tree needs to be traversed starting from the root node. This model is
recognized as the first database model created by IBM in the 1960s.Intelligent Database: 1. high level tools, 2. the user interface and 3. the database engine. The high level tools manage data quality and automatically discover relevant patterns in the data with a process called data mining. This layer often relies on the use of artificial intelligence techniques. The user interface uses hypermedia in a form that uniformly manages text, images and numeric data. The intelligent database engine supports the other two layers, often merging relational database techniques with object orientation.
Integrating AI Database Systems (PDF)
Relational Database is a collection of data items organized as a set of formally-described tables from which data can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganize the database tables. Relation database (wiki) - Attributes (categories)
Relational Database Management System is a database management system (DBMS) that is based on the relational model.
Relational Model is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, where all data is represented in terms of tuples, grouped into relations. A database organized in terms of the relational model is a relational database. The purpose of the relational model is to provide a declarative method for specifying data and queries: users directly state what information the database contains and what information they want from it, and let the database management system software take care of describing data structures for storing the data and retrieval procedures for answering queries.
Navigational Database s a type of database in which records or objects are found primarily by following references from other objects. Websites
Comparing - Associations - Associative Learning
Data Set is a collection of data. Most commonly a data set corresponds to the contents of a single database table, or a single statistical data matrix, where every column of the table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given member of the data set in question. The data set lists values for each of the variables, such as height and weight of an object, for each member of the data set. Each value is known as a datum, which is an item of factual information derived from measurement or research. The data set may comprise data for one or more members, corresponding to the number of rows. The term data set may also be used more loosely, to refer to the data in a collection of closely related tables, corresponding to a particular experiment or event. An example of this type is the data sets collected by space agencies performing experiments with instruments aboard space probes. Data sets that are so large that traditional data processing applications are inadequate to deal with them are known as big data.
Data Modeling is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modeling techniques.
Data Matrix is a matrix of data of dimension n-by-p, where n is the number of samples observed, and p is the number of variables (features) measured in all samples.
Computer Data Storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
Computer Memory refers to the computer hardware devices used to store information for immediate use in a computer; it is synonymous with the term "primary storage". Computer memory operates at a high speed, for example random-access memory (RAM), as a distinction from storage that provides slow-to-access program and data storage but offers higher capacities. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to secondary storage, through a memory management technique called "virtual memory". An archaic synonym for memory is store.
Distributed Data Store is a computer network where information is stored on more than one node, often in a replicated fashion. It is usually specifically used to refer to either a distributed database where users store information on a number of nodes, or a computer network in which users store information on a number of peer network nodes.
Cluster Analysis is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data mining, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including machine learning, pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, and computer graphics.
Levels (thinking)
Object Database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are table-oriented. Object-relational databases are a hybrid of both approaches.
Comparison of Object Database Management Systems (wiki)
Objectivity
Shard Database Architecture is a horizontal partition of data in a database or search engine. Each individual partition is referred to as a shard or database shard. Each shard is held on a separate database server instance, to spread load. Some data within a database remains present in all shards, but some appears only in a single shard. Each shard (or server) acts as the single source for this subset of data.
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system.
SQL or Structured Query Language, is a domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS).
Database Platforms
Data Architecture is composed of models, policies, rules or standards that govern which data is collected, and how it is stored, arranged, integrated, and put to use in data systems and in organizations. Data is usually one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture or solution architecture.
Database-Centric Architecture has several distinct meanings, generally relating to software architectures in which databases play a crucial role. Often this description is meant to contrast the design to an alternative approach. For example, the characterization of an architecture as "database-centric" may mean any combination of the following: Using a standard, general-purpose relational database management system, as opposed to customized in-memory or file-based data structures and access methods. With the evolution of sophisticated DBMS software, much of which is either free or included with the operating system, application developers have become increasingly reliant on standard database tools, especially for the sake of rapid application development. Using dynamic, table-driven logic, as opposed to logic embodied in previously compiled programs. The use of table-driven logic, i.e. behavior that is heavily dictated by the contents of a database, allows programs to be simpler and more flexible. This capability is a central feature of dynamic programming languages. See also control tables for tables that are normally coded and embedded within programs as data structures (i.e. not compiled statements) but could equally be read in from a flat file, database or even retrieved from a spreadsheet. Using stored procedures that run on database servers, as opposed to greater reliance on logic running in middle-tier application servers in a multi-tier architecture. The extent to which business logic should be placed at the back-end versus another tier is a subject of ongoing debate. For example, Toon Koppelaars presents a detailed analysis of alternative Oracle-based architectures that vary in the placement of business logic, concluding that a database-centric approach has practical advantages from the standpoint of ease of development and maintainability. Using a shared database as the basis for communicating between parallel processes in distributed computing applications, as opposed to direct inter-process communication via message passing functions and message-oriented middleware. A potential benefit of database-centric architecture in distributed applications is that it simplifies the design by utilizing DBMS-provided transaction processing and indexing to achieve a high degree of reliability, performance, and capacity. For example, Base One describes a database-centric distributed computing architecture for grid and cluster computing, and explains how this design provides enhanced security, fault-tolerance, and scalability. An overall enterprise architecture that favors shared data models over allowing each application to have its own, idiosyncratic data model.
Secondary Data refers to data that was collected by someone other than the user. Common sources of secondary data for social science include censuses, information collected by government departments, organisational records and data that was originally collected for other research purposes. Primary data, by contrast, are collected by the investigator conducting the research. Secondary data analysis can save time that would otherwise be spent collecting data and, particularly in the case of quantitative data, can provide larger and higher-quality databases that would be unfeasible for any individual researcher to collect on their own. In addition, analysts of social and economic change consider secondary data essential, since it is impossible to conduct a new survey that can adequately capture past change and/or developments. However, secondary data analysis can be less useful in marketing research, as data may be outdated or inaccurate.
Historical Data - Bibliographic Database - Sharing Open Data
Data Processing (EDP) can refer to the use of automated methods to process commercial data. Typically, this uses relatively simple, repetitive activities to process large volumes of similar information.
Electronic Data Processing can refer to the use of automated methods to process commercial data. Typically, this uses relatively simple, repetitive activities to process large volumes of similar information. For example: stock updates applied to an inventory, banking transactions applied to account and customer master files, booking and ticketing transactions to an airline's reservation system, billing for utility services. The modifier "electronic" or "automatic" was used with "data processing" (DP), especially c. 1960, to distinguish human clerical data processing from that done by computer.
Processing - Evaluation - Statistics
Data Clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data mining, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including machine learning, pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, and computer graphics.
Data Model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to properties of the real world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner. The term data model is used in two distinct but closely related senses. Sometimes it refers to an abstract formalization of the objects and relationships found in a particular application domain, for example the customers, products, and orders found in a manufacturing organization. At other times it refers to a set of concepts used in defining such formalizations: for example concepts such as entities, attributes, relations, or tables. So the "data model" of a banking application may be defined using the entity-relationship "data model". This article uses the term in both senses. Overview of data modeling context: Data model is based on Data, Data relationship, Data semantic and Data constraint. A data model provides the details of information to be stored, and is of primary use when the final product is the generation of computer software code for an application or the preparation of a functional specification to aid a computer software make-or-buy decision. A data model explicitly determines the structure of data. Data models are specified in a data modeling notation, which is often graphical in form. A data model can sometimes be referred to as a data structure, especially in the context of programming languages. Data models are often complemented by function models, especially in the context of enterprise models.
Networks (computers)
Data Documentation Initiative is an international standard for describing surveys, questionnaires, statistical data files, and social sciences study-level information. This information is described as metadata by the standard.
Logical Data Model is a data model of a specific problem domain expressed independently of a particular database management product or storage technology (physical data model) but in terms of data structures such as relational tables and columns, object-oriented classes, or XML tags. This is as opposed to a conceptual data model, which describes the semantics of an organization without reference to technology.
Tibco Software in Cloud Computing is an American company that provides integration, analytics and events processing software for companies to use on-premises or as part of cloud computing environments. The software manages information, decisions, processes and applications for over 10000 customers.
Data Transfer is the transfer of data (a digital bit stream or a digitized analog signal) over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal.
Big Data - Data Mining - Over-Load
Metadata (privacy) - Data Compression (noise)
Two-Phase Locking is a concurrency control method that guarantees serializability. It is also the name of the resulting set of database transaction schedules (histories). The protocol utilizes locks, applied by a transaction to data, which may block (interpreted as signals to stop) other transactions from accessing the same data during the transaction's life. By the 2PL protocol, locks are applied and removed in two phases: Expanding phase: locks are acquired and no locks are released. Shrinking phase: locks are released and no locks are acquired. Two types of locks are utilized by the basic protocol: Shared and Exclusive locks. Refinements of the basic protocol may utilize more lock types. Using locks that block processes, 2PL may be subject to deadlocks that result from the mutual blocking of two or more transactions.
Raw Data also known as primary data, is data (e.g., numbers, instrument readings, figures, etc.) collected from a source. If a scientist sets up a computerized thermometer which records the temperature of a chemical mixture in a test tube every minute, the list of temperature readings for every minute, as printed out on a spreadsheet or viewed on a computer screen is "raw data". Raw data has not been subjected to processing, "cleaning" by researchers to remove outliers, obvious instrument reading errors or data entry errors, or any analysis (e.g., determining central tendency aspects such as the average or median result). As well, raw data has not been subject to any other manipulation by a software program or a human researcher, analyst or technician. It is also referred to as primary data. Raw data is a relative term (see data), because even once raw data has been "cleaned" and processed by one team of researchers, another team may consider this processed data to be "raw data" for another stage of research. Raw data can be inputted to a computer program or used in manual procedures such as analyzing statistics from a survey. The term "raw data" can refer to the binary data on electronic storage devices, such as hard disk drives (also referred to as "low-level data").
Fragmentation (hos)
Open Data is the idea that some data should be freely available to everyone to use and republish as they wish, without restrictions from copyright, patents or other mechanisms of control. The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other "open" movements such as open source, open hardware, open content and open access. The philosophy behind open data has been long established (for example in the Mertonian tradition of science), but the term "open data" itself is recent, gaining popularity with the rise of the Internet and World Wide Web and, especially, with the launch of open-data government initiatives such as Data.gov and Data.gov.uk.
International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics
Data Stream is a sequence of digitally encoded coherent signals (packets of data or data packets) used to transmit or receive information that is in the process of being transmitted.
Data Hierarchy refers to the systematic organization of data, often in a hierarchical form. Data organization involves fields, records, files and so on. Power Hierarchy.
Anomaly Detection is the identification of items, events or observations which do not conform to an expected pattern or other items in a dataset. Typically the anomalous items will translate to some kind of problem such as bank fraud, a structural defect, medical problems or errors in a text. Anomalies are also referred to as outliers, novelties, noise, deviations and exceptions.
Usability - First-Order Logic - Predicate
Data Science is an interdisciplinary field about scientific methods, processes and systems to extract knowledge or insights from data in various forms, either structured or unstructured, similar to Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD).
Data Storage
Data Center is a large group of networked computer servers typically used by organizations for the remote storage, processing, or distribution of large amounts of data. A Datacenter facility is used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes redundant or backup power supplies, redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression) and various security devices. Large data centers are industrial scale operations using as much electricity as a small town. Cloud.
Data Farming is the process of using designed computational experiments to “grow” data, which can then be analyzed using statistical and visualization techniques to obtain insight into complex systems. These methods can be applied to any computational model.
Server Farm is a collection of computer servers - usually maintained by an organization to supply server functionality far beyond the capability of a single machine. Server farms often consist of thousands of computers which require a large amount of power to run and to keep cool. At the optimum performance level, a server farm has enormous costs (both financial and environmental) associated with it. Server farms often have backup servers, which can take over the function of primary servers in the event of a primary-server failure. Server farms are typically collocated with the network switches and/or routers which enable communication between the different parts of the cluster and the users of the cluster. Server farmers typically mount the computers, routers, power supplies, and related electronics on 19-inch racks in a server room or data center.
Server Room is a room, usually air-conditioned, devoted to the continuous operation of computer servers. An entire building or station devoted to this purpose is a data center. The computers in server rooms are usually headless systems that can be operated remotely via KVM switch or remote administration software, such as Secure Shell (ssh), VNC, and remote desktop. Climate is one of the factors that affects the energy consumption and environmental impact of a server room. In areas where climate favors cooling and an abundance of renewable electricity, the environmental effects will be more moderate. Thus countries with favorable conditions, such as: Canada, Finland, Sweden, and Switzerland, are trying to attract more companies to site their server rooms there.
Data Defined Storage is a marketing term for managing, protecting, and realizing value from data by uniting application, information and storage tiers. This is achieved through a process of unification, where users, applications and devices gain access to a repository of captured metadata that empowers organizations to access, query and manipulate the critical components of the data to transform it into information, while providing a flexible and scalable platform for storage of the underlying data. The technology abstracts the data entirely from the storage, allowing full transparent access to users.
Storage Resource Management involves optimizing the efficiency and speed with which a storage area network (SAN) utilizes available drive space. Data growth averages around 50% to 100% per year. Organizations face rising hardware-costs and the increased costs of managing their storage. Storage professionals who face out-of-control data-growth are looking at SRM to help them navigate the storage environment. SRM identifies underutilized capacity, identifies old or non-critical data that could be moved to less-expensive storage, and helps predict future capacity requirements.
Data Warehouse is a system used for reporting and data analysis, and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place and are used for creating analytical reports for knowledge workers throughout the enterprise. Examples of reports could range from annual and quarterly comparisons and trends to detailed daily sales analysis.
Aggregate Data Warehouse are used in dimensional models of the data warehouse to produce dramatic positive effects on the time it takes to query large sets of data. At the simplest form an aggregate is a simple summary table that can be derived by performing a Group by SQL query. A more common use of aggregates is to take a dimension and change the granularity of this dimension. When changing the granularity of the dimension the fact table has to be partially summarized to fit the new grain of the new dimension, thus creating new dimensional and fact tables, fitting this new level of grain.
Aggregate Data are data combined from several measurements. When data are aggregated, groups of observations are replaced with summary statistics based on those observations.
Terra Scale data center is a global green infrastructure development firm that designs, engineers, builds and operates large scale, sustainable data centers and digital infrastructure projects to meet the needs of our planet’s future. TerraScale is focused on large scale projects in the following verticals: Government, Data Centers, Technology, Logistics, Distribution, and Warehousing, Research.
Data Logging is the recording of collected data over a period of time. Data Logger.
Colocation Centre is a type of data center where equipment, space, and bandwidth are available for rental to retail customers. Colocation facilities provide space, power, cooling, and physical security for the server, storage, and networking equipment of other firms—and connect them to a variety of telecommunications and network service providers—with a minimum of cost and complexity.
Web Hosting Service is a type of Internet hosting service that allows individuals and organizations to make their website accessible via the World Wide Web. Web hosts are companies that provide space on a server owned or leased for use by clients, as well as providing Internet connectivity, typically in a data center. Web hosts can also provide data center space and connectivity to the Internet for other servers located in their data center, called colocation, also known as Housing in Latin America or France.
Internet Hosting Service is a service that runs Internet servers, allowing organizations and individuals to serve content to the Internet. There are various levels of service and various kinds of services offered. A common kind of hosting is web hosting. Most hosting providers offer a combination of services; e-mail hosting, for example. DNS hosting service is usually bundled with domain name registration. Generic kinds of Internet hosting provide a server where the clients can run anything they want (including web servers and other servers) and have Internet connections with good upstream bandwidth.
"The Data is not the Source of Data"
Dark Data is operational data that is not being used. Information assets that organizations collect, process and store in the course of their regular business activity, but generally fail to use for other purposes.
Big Data - Storing Lots of Details
 We can use Data in many positive ways that can benefit people by
improving services, products and making better decisions.
But of course there are
criminals who want to
use information to
manipulate people, as they do
now with stolen information. Any tool that can be abused will be
abused by criminals, just
like money is. The fact that corporations are
collecting personal information and
selling peoples personal information is criminal and extremely dangerous.
This scam allows corporations to waste time, people, resources, energy and
money so that corporations can harass people with mindless
advertising that try's to force
useless products on unsuspecting consumers. The value of big data that
corporations speak about refers to how much
money they can steal from people, and not about how much this data can
be used to benefit people. These criminals are also
using big data to profile people,
instead of helping people.
We can use Data in many positive ways that can benefit people by
improving services, products and making better decisions.
But of course there are
criminals who want to
use information to
manipulate people, as they do
now with stolen information. Any tool that can be abused will be
abused by criminals, just
like money is. The fact that corporations are
collecting personal information and
selling peoples personal information is criminal and extremely dangerous.
This scam allows corporations to waste time, people, resources, energy and
money so that corporations can harass people with mindless
advertising that try's to force
useless products on unsuspecting consumers. The value of big data that
corporations speak about refers to how much
money they can steal from people, and not about how much this data can
be used to benefit people. These criminals are also
using big data to profile people,
instead of helping people.Big Data is an awesome tool. Big data can help us make better decisions, but we will still have to make those decisions ourselves because big data will not make decisions for us. Big data could create jobs if used correctly. Because it was never about having enough jobs, it was always about having enough intelligent people to understand what type of jobs are needed. Job is a word that describes a positive action that a life form must take in order to sustain life. A job is not just something that a person does, a job is something that needs to be done for the survival of life, and not just for the survival of the individual.
Big Data is a term for data sets that are so large or complex that traditional data processing application software is inadequate to deal with them. Challenges include capture, storage, analysis, data curation, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating and information privacy. The term "big data" often refers simply to the use of predictive analytics, user behavior analytics, or certain other advanced data analytics methods that extract value from data, and seldom to a particular size of data set.
Information Overload
Data Mining is the computational process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics, and database systems. The overall goal of the data mining process is to extract information from a data set and transform it into an understandable structure for further use. Aside from the raw analysis step, it involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. Data mining is the analysis step of the "knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD.
Big Data - Little Data - Data Backup (preserve) - Data Protection
How much Information are we Generating?
Development (science) - Code - Operating Systems
Information communication technology is projected to account for 20% of total energy consumption in the United States by 2020. Data centers are processing data and dispensing the results at astonishing rates and such robust systems require a significant amount of energy.
Making a Difference (future jobs)
An Unbiased Approach for sifting through Big Data. MENet helps build the Optimal Information Network (OIN) which indicates the most useful information to accurately characterize systemic health maximum transfer entropy," which probabilistically measures the strength of relationships between multiple variables over time.
Data Brokers and the Hidden Data Ecosystem. The fact that countless companies are tracking millions of people around the web and on their phones is disturbing enough, but what is even more disturbing about my Quantcast data is the extent to which the company relies on data brokers, credit referencing agencies, and even credit card companies in ways that are impossible for the average consumer to know about or escape. Advertising companies and data brokers have been quietly collecting, analysing, trading, and selling data on people for decades. What has changed is the granularity and invasiveness at which this is possible. Data brokers buy your personal data from companies you do business with; collect data such as web browsing histories from a range of sources; combine it with other information about you (such as magazine subscriptions, public government records, or purchasing histories); and sell their insights to anyone that wants to know more about you. Even though these companies are on the whole non-consumer facing and hardly household names, the size of their data operations is astounding. Acxiom’s Annual report of 2017, for instance, states that they offer data “on approximately 700 million consumers worldwide, and our data products contain over 5,000 data elements from hundreds of sources.” Part of the problem is that this data can be used to target, influence, and manipulate each and every one of us ever more precisely. How precisely? A few years ago, an advertising company from Massachusetts in the US targeted “abortion-minded women” with anti-abortion messages while there were in hospital. Laws in the US are very different from what is legal in the EU, yet the example shows what it technically possible: to target very precise groups of people, at particular times and particular places. This is the reality of what targeted advertisement looks like today. While uncannily accurate data can be used against us, inaccurate data is no less harmful, especially when data that most of us don’t even know exists and have very little control over is used to make decisions about us. An investigation by Big Brother Watch in the UK, for instance, showed how Durham Police in the UK were feeding Experian’s Mosaic marketing data into their ‘Harm Assessment Risk Tool’, to predict whether a suspect might be at low, medium or high risk of reoffending in order to guide decisions as to whether a suspect should be charged or released onto a rehabilitation program. Durham Police is not the only police force in England and Wales that uses Mosaic service. Cambridgeshire Constabulary, and Lancashire Police are listed as having contracts with Experian for Mosaic. Privacy International has filed complaints against seven data brokers (Acxiom, Oracle), ad-tech companies (Criteo, Quantcast, Tapad), and credit referencing agencies (Equifax, Experian) with data protection authorities in France, Ireland, and the UK. These companies do not comply with the Data Protection Principles, namely the principles of transparency, fairness, lawfulness, purpose limitation, data minimisation, and accuracy. They also do not have a legal basis for the way they use people's data, in breach of GDPR. The world is being rebuilt by companies and governments so that they can exploit data. Without urgent and continuous action, data will be used in ways that people cannot now even imagine, to define and manipulate our lives without us being to understand why or being able to effectively fight back. We urge the data protection authorities to investigate these companies and to protect individuals from the mass exploitation of their data, and we encourage journalists, academics, consumer organisations, and civil society more broadly, to further hold these industries to account. Switch Data Center.
Profiling - Marketing Abuses - Personal Information
It's no longer news that our data is for sale. Data brokers often use online browsing records to create digital consumer profiles that are then sold to marketers as pre-defined audiences for targeted advertising. It is often assumed that the tools used to analyze and categorize customer data are so sophisticated that marketers can reliably fine-tune messaging and targeting. But new research has revealed that the process for creating those digital profiles may not be as reliable as many may assume. International Association for Professionals in operations Research and Analytics. Researchers lift the curtain behind the 'black box' of data broker records. New study reveals key strengths and weaknesses of data records.
The greatest thing about Big Data is that we can analyze huge amounts of clinical information to correctly analyze diseases and produce better treatments.
Fast machines for DNA sequencing will be capable of producing 85 petabytes of data this year worldwide, twice that much in 2019.
Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics, mathematics, and engineering to study and process biological data.
Palantir Technologies is a private American software company that specializes in big data analytics. Headquartered in Palo Alto, California. The company's name is derived from The Lord of the Rings: a palantír is an artifact used to communicate with or see faraway parts of the world. The company is known for three projects in particular: Palantir Gotham, Palantir Metropolis and Palantir Foundry. Palantir Gotham is used by counter-terrorism analysts at offices in the United States Intelligence Community (USIC) and United States Department of Defense, fraud investigators at the Recovery Accountability and Transparency Board, and cyber analysts at Information Warfare Monitor, while Palantir Metropolis is used by hedge funds, banks, and financial services firms. Palantir Foundry is used by corporate clients such as Morgan Stanley, Merck KGaA, Airbus, and Fiat Chrysler Automobiles NV. Palantir's original clients were federal agencies of the USIC. It has since expanded its customer base to serve state and local governments, as well as private companies in the financial and healthcare industries.
How the Large Hadron Collider stores all the Information The sensors generate about one petabyte of data every second. 530 Million Gigabytes stored on nearline magnetic tape. The detectors that record particle collisions have 100 million read-out channels and take 14 million pictures per second. It's akin to saving 14 million selfies with every tick of a watch's second hand. CERN Open Lab.
Information Overload
Information Overload occurs when the amount of input to a system exceeds its processing capacity.
Too much information depends on how you look at it. Most of the time it's usually a unique set of circumstances or relevance that is understood by your perception and skill level at a particular time and place. It's not too much information, it's not being able to effectively and efficiently filter information, and utilize the information that is available to you at a given time. This is one of the main reasons why we have created computers and advanced software. If you have lots of information that needs to be processed and calculated, information that would help you make a logical decision, then you will need all the technology tools and people available to quickly analyze information so that an accurate decision can be made in timely manner. If you don't have the resources and the time to utilize all the information available, then you will have to make a decision based on the experience and knowledge that you have on hand. If you have time to make a decision, then you should learn as much as you can first. If you don't have the time to make a decision, then you have to make do with what you have. Information overload is not the same as over thinking or being overwhelmed with useless information, or overwhelmed by unorganized information, or overwhelmed by irrelevant information, or overwhelmed by information that cannot be understood, because then you can easily be overwhelmed. But, as long as you can properly filter information and specify the needed information, you can then avoid a so called information overload. The bottom line is that you can have a lot of information and still not have enough. It's not the volume of information that's important, it's the quality and the accuracy and the value of the information. So you could never learn too much, you can only misunderstand what you have learned, which means that you haven't learned enough. We can use artificial intelligence to look for patterns in huge amounts of data using algorithms, while humans can focus on things that are more important.
Cognitive Load refers to the measure of perceived mental effort that's being used in the working memory and the way that information or tasks are presented to a learner. The experience of cognitive load is not the same in everyone. Intrinsic cognitive load is the inherent level of difficulty associated with a specific instructional topic. Extraneous cognitive load is generated by the manner in which information is presented to learners and is under the control of instructional designers. Germane cognitive load is that load devoted to the processing, construction and automation of schemas.
Analysis Paralysis is the state of over-analyzing or over-thinking a situation so that a decision or action is never taken, in effect paralyzing the outcome. A decision can be treated as over-complicated, with too many detailed options, so that a choice is never made, rather than try something and change if a major problem arises. A person might be seeking the optimal or "perfect" solution upfront, and fear making any decision which could lead to erroneous results, while on the way to a better solution.
Sensory Overload occurs when one or more of the body's senses experiences over-stimulation from the environment. There are many environmental elements that impact an individual.
Superfluous is getting more than is needed, desired, or required. Unnecessary, especially through being more than enough. Serving no useful purpose; having no excuse for being. Spam - Abusive Advertising.
Inundate is to overwhelm someone with too many tasks, details or things to be dealt with. To flood or fill quickly beyond capacity.
Unstructured Data is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, numbers, and facts as well. This results in irregularities and ambiguities that make it difficult to understand using traditional programs as compared to data stored in fielded form in databases or annotated (semantically tagged) in documents. Fragmented.
Information Explosion is the rapid increase in the amount of published information or data and the effects of this abundance. As the amount of available data grows, the problem of managing the information becomes more difficult, which can lead to information overload.
Parallel Processing is the ability of the brain to simultaneously process incoming stimuli of differing quality. With vision, the brain divides what it sees into four components: color, motion, shape, and depth. These are individually analyzed and then compared to stored memories, which helps the brain identify what you are viewing. The brain then combines all of these into the field of view that you see and comprehend.
Parallel Computing is a type of computation in which many calculations are carried out simultaneously
Cognitive Off-Loading - Multi-Tasking - Big Data
Throughput is the rate of production or the rate at which something can be processed.
Additive-Increase/Multiplicative-decrease (AIMD) algorithm is a feedback control algorithm best known for its use in TCP congestion control. AIMD combines linear growth of the congestion window with an exponential reduction when a congestion takes place. Multiple flows using AIMD congestion control will eventually converge to use equal amounts of a contended link. The related schemes of multiplicative-increase/multiplicative-decrease (MIMD) and additive-increase/additive-decrease (AIAD) do not converge.
Flow Control in data is the process of managing the rate of data transmission between two nodes to prevent a fast sender from overwhelming a slow receiver. It provides a mechanism for the receiver to control the transmission speed, so that the receiving node is not overwhelmed with data from transmitting node. Flow control should be distinguished from congestion control, which is used for controlling the flow of data when congestion has actually occurred. Flow control mechanisms can be classified by whether or not the receiving node sends feedback to the sending node. Flow control is important because it is possible for a sending computer to transmit information at a faster rate than the destination computer can receive and process it. This can happen if the receiving computers have a heavy traffic load in comparison to the sending computer, or if the receiving computer has less processing power than the sending computer.
Having good Awareness is very important when examining information as well as having excellent Reading Comprehension Skills. Focus on what's important. Remember the most important aspects, and learn from them.
The Information Age - Internet of Things
Organizing Knowledge Base - Information Visualization
Preserving Information - Knowledge Management - How Much is There?
Spatial Intelligence - Thinking Levels
It would be ignorant to say that we have too much information and it is impossible to filter it all. That's like walking into a library and saying that there's too many books. You don't have to read every book moron. You just have to know which books to read, why you should read them, and when you should read them. This is not an Information Paradox for this goes beyond Physical Information. We should be thankful that we have an abundance of information. Our task, and the task that I have taken, is to filter the information, narrow it down and Organize it into Categories and Manageable Chunks. Our information and knowledge is priceless. This is the world’s greatest and most valuable asset. So information and knowledge needs our full attention and understanding so that Information does not become Abused or Misused.
Saying that there is too much to read is like saying that eating food is too much work. "I have to find food, I have to prepare food, I have to chew food, I have to swallow food, I have to digest food, and I have to poop out my food, it's too much work." What a moron, right. That is why you eat the healthiest food. That is why you read the most beneficial knowledge that has been written. Don't waste time, make time, time to enjoy, instead of creating time just to suffer. Consume Knowledge
Information Overload Research Group - Social Knowledge
Information overload is a Contradiction, like the The Paradox of Choice.
Oxymoron's List - Knowing Enough
Too much of anything of course is bad, and of course too much of something that you don't have the intelligence or understanding to handle is extremely bad. So a person needs not only ‘Information Literacy’, a person also needs to fully understand balance, variety and Self-Discipline.
Web 3.0 (video)
You don't need a Low Information Diet, all you need is a healthy information diet, one that provides you with just enough information to increase your knowledge of yourself and the world around you so that you continue to mature at a steady pace. If you to choose you information sources wisely so that you can filter out the enormous amount of misinformation and bullshit that is being forced on citizens through the main stream media. There are so many distractions, if you are not skilled enough or knowledgeable enough to protect yourself, you will be overwhelmed and abused to a point were you will be unable to function normally, an you will not be able to understand the world accurately enough to make good decisions, you will be lost, and you will not even know that you are lost.
How can we have so much information and still only have just 5 percent of the data needed to preserve the world’s biodiversity. Answer: Ignorance, corruption and bad prioritizing.
Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020, including Aichi Biodiversity Targets
Filling in biodiversity threat gaps
Threatened Island Biodiversity Database
"It's not so important knowing "who generated the information", what's more important is knowing if the information is accurate and relevant?
Don't judge the Messenger, Judge only the Message."
"The collector is the true resident of the interior.....The collector dreams his way not only into a distant or bygone world but also into a better one". - Walter Benjamin
"When a man's knowledge is not in order, the more of it he has the greater will be his confusion." Herbert Spencer
"With the internet, if you are not plugged in, that means you are unplugged. And things that are unplugged, are most likely to be thrown away or ignored."
Information Sources - Information Sayings
I didn't learn everything from the Internet, but I did learn a lot about a lot of things, because of the internet.
They say "Knowledge is Power". But only if knowledge is distributed equally will power will be equal to all, which in turn will make knowledge a blessing instead of a curse."
I can't fight every battle that comes my way, for if I did, I would be fighting all day"
Fight or Flight?
"Information overload is really just ignorance overload, so it's not that there's too much information, it's that there's too much ignorance. Ignorance that struggles to process information correctly."
OS Error? - Need a Patch?
"You are not here to waste time, you are here to use time, and that time that you use is from the time that I saved you, now it's your turn to save time for someone else."
More Information and Internet Quotes
We have created a lot of information and knowledge. We also have answers to most of our important questions. So now is the time to put it all together, organize it, categorize it, continually update it and make it available to everyone. more...
Our most difficult problem is how to safely store and preserve our most valuable information and knowledge.
Libraries will always be needed because we need to store hard copies of our books and printed history. But everything will eventually move to digital. So now you have no constraints on how to organize your books. You will see the book isle, you will see the categories, but now you will also see everything that's related, because you have no constraints on space, physical space. You can see everything in the library without moving your physical self. Able to flow effortlessly through information, with the ability to ask a question anytime that you need an answer, without having to look for a librarian, who might or might not know the answer. Being connected to almost every book ever written in the last 2,000 years in human history is amazing. But there is one problem. Just being connected to enormous amount of information and knowledge does not mean that it is being used effectively. People are not being educated enough in order to effectively utilize our enormous treasure trove of information and knowledge. But once people do get up to speed, amazing things will happen, and everything will improve. Not over night, but it sure will seem like that.
Search Engines are very limited and too easy to manipulate. So we need a central database that is a Human Search Engine that is also a forum that has 24-hour live assistance from operators who have extensive knowledge in the subject that you are interested in. Every question will be documented and every answer will be documented in the central database. Every question will have the number of times it has been asked and how many times the same answer was given to that question. If the answer was changed the new updated answer will be listed as well as the old answer and the reason why the old answer was changed and updated. You will also see how many people agree with that particular answer and how many disagree. The top 3 answers will be given based on how many people who agree with that answer and the top 3 answers will be given based on how many people who disagree with that answer. The database will also list other relevant questions of similar importance. So if the user asks a question they will see other relevant questions that may have to be asked and answered so that a full understanding of the question can be accomplished. Other relevant questions will also list how many times users referenced these other relevant questions and the reason why they used them.
Database Operators will scan blogs, news channels, News-papers, books, comments, forums, search engines and websites for information and knowledge that could be added to particular answers as addition references. References Will list the date that the information was created, who created it and where it was created on what book page number, blog, forum, news source, website and so on and so on.
Information Stations - Knowledge Management - Open Curriculum
Future Cities - 24/7 Information Operators - Having a Central Database
Wikipedia - Wiki Stats - Social Networking - Social Network Statistics
Disinhibition
Digital content on track to equal half 'Earth's mass' by 2245. As we use resources to power massive computer farms and process digital information, our technological progress is redistributing Earth's matter from physical atoms to digital information. Eventually, we will reach a point of full saturation, a period in our evolution in which digital bits will outnumber atoms on Earth, a world 'mostly computer simulated and dominated by digital bits and computer code,' according to a new article.
The procedures and the platform that the database operates on will be available for public review. This way if the procedures change or the platform changes people will be aware of these changes and also learn why the database operates the way it does.
Valid - Validation - Validity
Valid is something that is confirmed and well grounded in logic, fact, truth or having legal force and legally acceptable.
Validity guarantees the truth of an argument's conclusion. A formula is valid if and only if it is true under every interpretation, and an argument form (or schema) is valid if and only if every argument of that logical form is valid. Something right and good.
Validation is getting the recognition or affirmation that your feelings or opinions are valid or worthwhile. Validating is the action of checking or proving the validity or accuracy of something. The action of making or declaring something legally or officially acceptable. Repeatable.
Legitimacy is credibility and the quality of being believable or trustworthy.
Criterion Validity refers to a comparison between the measure in Question and an outcome assessed at the same time.
Construct Validity is when a test measures what it claims, or purports, to be measuring.
Test Validity accurately measures what it is supposed to measure. Evidence.
Content Validity refers to the extent to which a measure represents all facets of a given construct.
Concurrent Validity is a type of evidence that can be gathered to defend the use of a test for predicting other outcomes.
Predictive Validity is the extent to which a score on a scale or test predicts scores on some criterion measure.
Discriminant Validity tests whether concepts or measurements that are not supposed to be related are, in fact, unrelated.
Convergent Validity refers to the degree to which two measures of constructs that theoretically should be related, are in fact related.
Validity in statistics is the extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and corresponds accurately to the real world.
External Validity is the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other situations and to other people.
Internal Validity is the extent to which a causal conclusion based on a study is warranted, which is determined by the degree to which a study minimizes systematic error (or 'bias'). It contrasts with external validity, the degree to which it is warranted to generalize results to other contexts.
Face Validity is the extent to which a test is subjectively viewed as covering the concept it purports to measure. It refers to the transparency or relevance of a test as it appears to test participants. In other words, a test can be said to have face validity if it "looks like" it is going to measure what it is supposed to measure. For instance, if a test is prepared to measure whether students can perform multiplication, and the people to whom it is shown all agree that it looks like a good test of multiplication ability, this demonstrates face validity of the test. Face validity is often contrasted with content validity and construct validity.
Statistical Conclusion Validity is the degree to which conclusions about the relationship among variables based on the data are correct or ‘reasonable’.
Ecological Validity is when the methods, materials and setting of the study must approximate the real-world that is being examined.
Subjective Validation is a cognitive Bias by which a person will consider a statement or another piece of information to be correct if it has any personal meaning or significance to them. In other words, a person whose opinion is affected by subjective validation will perceive two unrelated events (i.e., a coincidence) to be related because their personal belief demands that they be related. Closely related to the Forer effect, subjective validation is an important element in cold reading.
Fallacies - Morally Sound - Accuracy
Verificationism is the philosophical doctrine which maintains that only statements that are empirically verifiable or verifiable through the senses are cognitively meaningful, or else they are truths of logic. Verificationism thus rejects as cognitively "meaningless" statements specific to entire fields such as metaphysics, theology, ethics and aesthetics. Such statements may be meaningful in influencing emotions or behavior, but not in terms of truth value, information or factual content. Verificationism was a central thesis of Logical Positivism. Logical Positivism asserts that only statements verifiable through direct observation or logical proof are meaningful. Reality - Consciousness.
Tautology is a formula or assertion that is true in every possible interpretation.
Verification and Validation are independent procedures that are used together for checking that a product, service, or system meets requirements and specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose. These are critical components of a quality management system such as ISO 9000.
Authentication is the act of confirming the truth of an attribute of a single piece of data (a datum) claimed true by an entity. In contrast with identification which refers to the act of stating or otherwise indicating a claim purportedly attesting to a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of actually confirming that identity. It might involve confirming the identity of a person by validating their identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product is what its packaging and labeling claim to be. In other words, authentication often involves verifying the validity of at least one form of identification.
Certified is something endorsed authoritatively as having met certain requirements. Holding appropriate documentation and officially on record as qualified to perform a specified function or practice a specified skill.
Necessity and Sufficiency is the assertion that one statement is a necessary and sufficient condition of another means that the former statement is true if and only if the latter is true. That is, the two statements must be either simultaneously true or simultaneously false.
Certainty is perfect knowledge that has total security from error, or the mental state of being without doubt. Objectively defined, certainty is total continuity and validity of all foundational inquiry, to the highest degree of precision. Something is certain only if no skepticism can occur.
Verified is something that is proven to be true. Confirm the truth of. To declare or affirm solemnly and formally as true. Provide evidence for. Evidence is an indication that makes something evident. Verifiability - Errors.
Confirm is to establish or strengthen as with new evidence or facts. Establish the validity of something. Demonstrate by Math.
Confirmation is additional proof that some fact, hypothesis or theory is correct. Information that confirms or verifies. Making something valid by formally ratifying or confirming it. Consensus (Peer Review) - Confirmation Hearing.
Affirm is to establish or strengthen as with new evidence or Facts. Oath.
Asserting is to to declare or affirm solemnly and formally as true. State categorically.
Emphatically is something that is believed to be without question or beyond doubt.
Declaration is a formal public statement that is emphatic and explicit that is either spoken or written.
Acknowledged is to declare to be true or admit the existence or reality or truth of. Generally accepted. Accept as legally binding and valid.
Knowledge-Based Trust Score - Lazy Truth
Learning how a Court of Law treats Evidence is good training for debating and researching.
Evidence is having witnesses, expert testimony and physical evidence or any material object that proves a fact in issue based on the object's demonstrable physical characteristics. Evidence (science) - Peer Review
Proof in truth is sufficient evidence or a sufficient argument for the truth of a proposition.
Proofs and Refutations is a book written as a series of Socratic dialogues involving a group of students who debate the proof of the Euler characteristic defined for the polyhedron. A central theme is that definitions are not carved in stone, but often have to be patched up in the light of later insights, in particular failed proofs. This gives mathematics a somewhat experimental flavour. At the end of the Introduction, Lakatos explains that his purpose is to challenge formalism in mathematics, and to show that informal mathematics grows by a logic of "proofs and refutations".
Consensus - Statistics
Epistemic is relating to knowledge or to the degree of its validation.
Media Literacy - Lying
Understanding is the capacity for rational thought or inference or discrimination. Characterized by understanding based on comprehension and discernment and empathy. To know and comprehend the nature or meaning of something and perceive an idea or situation mentally.
Wisdom is accumulated knowledge, erudition or enlightenment. The trait of utilizing knowledge and experience with common sense and insight. Ability to apply knowledge or experience or understanding or common sense and insight. The quality of being prudent and sensible.
Sympathetic is expressing or feeling sympathy or compassion and understanding and generosity. A relation of affinity or harmony between people and having similar disposition and tastes. Whatever affects one correspondingly affects the other. Love.
Intelligence - Problem Solving - Math - Science - Information Literacy
Witnessed is someone who sees an event and reports what happened. Expert - Judge (courts).
Documented is something that was recorded or written in detail, documents that support or supply references.
References are short notes that recognize a source for the information presented, or states the persons name of a quoted passage.
Agreements (diplomacy)
Pertinent is having precise or logical relevance to the matter at hand. Being of striking appropriateness and pertinence. Rightness. Appropriate conduct; doing the right thing. The quality of being specially suitable. According with conscience or Morality.
Legal is something that has been established by or founded upon Law or official or accepted Rules.
Human Rights - Justice - Judge - Laws - Legal Terms
Authority is the power or right to give orders or make decisions. Person or persons who exercise administrative control over others. An expert whose views are taken as definitive. Freedom from doubt and a belief in yourself and your abilities. An administrative unit of Government Official permission or approval. Authority is the right to exercise power given by the State.
Authorization is a document giving an official instruction or command. The power or right to give orders or make decisions. Authorization is the function of specifying access rights to resources related to information security and computer security in general and to access control in particular.
Accurate
Accuracy is the quality of being near to the true value and has been measured, calibrated and compared. Valid.
Accuracy and Precision is a description of systematic errors and a measure of statistical bias that causes a difference between a result and a "true" value. ISO calls this trueness. Alternatively, ISO defines accuracy as describing a combination of both types of observational error above random and systematic, so high accuracy requires both high precision and high trueness. In simplest terms, given a set of data points from repeated measurements of the same quantity, the set can be said to be precise if the values are close to each other, while the set can be said to be accurate if their average is close to the true value of the quantity being measured. The two concepts are independent of each other, so a particular set of data can be said to be either accurate, or precise, or both, or neither. Accuracy and Precision (PDF)
Observational Error - Bias - Eliminating Errors
Correct is something that is accurate and free from error and is considered to be fact or truth, as well as being in accord with accepted standards of usage or procedure.
Dot the i's and Cross the t's is to pay great attention to every small detail in a task. To be meticulous and precise.
Precise is characterized by perfect conformity to fact or truth; strictly correct. Sharply exact, accurate or delimited.
Precision is the degree of being precise; the quality of having high accuracy and consistency.
Thorough is being extremely attentive to accuracy and detail. Performed comprehensively and completely. Being careful.
Objective
Objectivity is judgment based on facts and reality and not influenced by emotions or personal prejudices. Objectivity is without biases that are caused by feelings, ideas or opinions.
Objective is belonging to immediate experience of actual things or events. Emphasizing or expressing things as perceived without distortion of personal feelings, insertion of fictional matter, or personal interpretation. Using Facts and Knowledge to understand.
Object is a tangible and visible entity. The focus of cognitions. The goal intended to be attained. Object can also mean an objection.
Objectification is the act of dehumanizing a person like a woman, or disrespecting an animal, as if object or a thing, without rights, justifiable reasoning or respect.
Indifference is an unbiased or impartial unconcern. Apathy demonstrated by an absence of emotional reactions. The trait of lacking enthusiasm for something or lacking interest in things generally. The trait of remaining calm and seeming not to care; a casual lack of concern.
Impartial is showing a lack of favoritism and free from undue bias or preconceived opinions. Not Polarized or Partisan.
Subjective
Subjectivity is judgment based on individual personal impressions and feelings and opinions rather than external facts. Subjectivity is some information, idea, situation, or physical thing that is considered to be true from the perspective of a subject or subjects. Something being a subject that acts upon or wields power over some other entity or object. An individual who possesses conscious experiences, such as perspectives, feelings, beliefs, and desires. Agency.
Subjective is something taking place within the mind and modified by individual bias. Of a mental act performed entirely within the mind. The opposite of being Objective.
Subjectivism is our own mental activity is the only unquestionable fact of our experience and that knowledge is merely subjective and that there is no external or objective truth.
Subject is some situation or event that is the focus of a conversation or discussion and likely to be affected by something. A branch of knowledge. A subject can also mean a person who is subjected to experimental or other observational procedures; someone who is an object of investigation. Refer for judgment or consideration.
Subjunctive Mood is a way of speaking that allows people to express their attitude toward what they are saying, found in many languages. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality such as wish, emotion, possibility, judgment, opinion, obligation, or action that have not yet occurred; the precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is an irrealis mood (one that does not refer directly to what is necessarily real) – it is often contrasted with the indicative, which is a realis mood (used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact).
Cynic is a person who believes that people are motivated purely by self-interest rather than acting for honorable or unselfish reasons. Critic.
Anecdotal is something not necessarily true or reliable, because it's based on personal accounts rather than facts or research. Denial.
Anecdote is a brief small narrative, revealing account of an individual person or an incident.
Agreement - Diplomacy
Compatibility is the capability of existing or performing in harmonious or congenial combination that is suitable to your needs.
Facts - Proven Verified Information
Fact is a piece of information about circumstances that exist or events that have occurred. A fact is statement or assertion of verified information about something that is the case or has happened. An event known to have happened or something known to have existed. A concept whose truth can be proven. Fact is something that has really occurred or something that is actually the case and has been documented or verified or witnessed by a credible source.
Scientific Fact is information that is repeatable and verified by careful observation of measurements, experiments and testing. The usual test for a statement of fact is verifiability and whether it can be demonstrated to correspond to experience. Standard reference works are often used to check facts.
Fact Checking (watch dogs) - Honesty (trust)
De Facto is existing in fact whether with lawful authority or not. In reality or fact.
Correct is something free from error and adhering to fact or truth. Having truthful opinions or making the right judgment. Something that is socially appropriate or approved and in accord with accepted standards of usage or procedure. To alter or regulate so as to achieve accuracy or to be in line with a standard.
Irrefutable is information that is impossible to deny or to disprove.
Veracity is the quality of being truthful and close to the true value. Unwillingness to tell lies.
No Two Ways About It is used to convey that there can be no doubt about something.
Detail is an isolated fact that can be considered separately from the whole or as one of the contributing factors.
Minutia is a small or minor detail.
Gory Details are the details and small facts or pieces of information about something that are unpleasant or shocking to some people who are uncomfortable with seeing or hearing about serious injuries or violence. Gory means covered with blood.
Particulars are facts about some part of something, as opposed to something general. A proposition that asserts something. A small part that can be considered separately from the whole.
Element is a statement of fundamental facts or principles. An artifact that is one of the individual parts of which a composite entity is made up, especially a part that can be separated from or attached to a system. Known Substances.
Specific Facts that can be expressed using words with rational inferences from those facts.
Mental Facts include such things as perceptions, feelings, and judgments. Mental facts are ultimately caused by physical facts, in that mental facts depend on physical and biological functions which are required for consciousness. The physical and biological processes which are necessary for consciousness enable conscious individuals to recognize physical and mental facts. Thus, mental facts are based on physical facts, and both physical and mental facts are required for the construction of social reality.
Specifics are the facts that surround some part of something, and not a general statement.
Specified is something clearly defined and explicitly stated. Decide upon definitely; give a value. Determine the essential quality of. Unspecified is something not stated explicitly or explained in detail.
Evidence (science) - Validity - Accuracy - Precision - Observations - Lying
Legitimate is based on known statements or events or conditions and is in accordance with recognized or accepted standards, principles or laws. Expert Witness.
Affirm is to establish or strengthen a statement with new evidence or more facts. To declare or affirm solemnly and formally as true. To say yes to.
Affirmation is a statement asserting the existence or the truth of something. The act of affirming, asserting or stating something. Affirmation in religion is a solemn declaration that serves the same purpose as an oath. Affirmation in law is a judgment by a higher court that the judgment of a lower court was correct and should stand. Affirmative is a yes reply.
Preponderance is the quality or fact of being greater in number, quantity, or importance.
Fact-Finding is the job of a person or group of persons in a judicial or administrative proceeding that has or have the responsibility of determining the facts relevant to decide a controversy. The term trier of fact generally denotes the same function. The process is an extremely important part of the communication process. Trier of Fact is a person, or group of persons, who determines facts in a legal proceeding, usually a trial. To determine a fact is to decide, from the evidence, whether something existed or some event occurred. Various aspects of a case that are not in controversy may be the "facts of the case" and are determined by the agreement of the separate parties; the trier of fact need not decide such issues.
Literary Realism attempts to represent subject-matter truthfully, avoiding speculative fiction and supernatural elements. Literary realism attempts to represent familiar things as they are. Realist authors chose to depict everyday and banal activities and experiences.
Characteristic is a feature or quality that belongs to a person, place, or thing that helps to identify it.
Properties are those physical quantities which directly describe the physical attributes of the system.
Fundamental is something serving as an essential component and being or involving basic facts or principles. Any factor that could be considered important to the understanding of a particular business. Far-reaching and thoroughgoing in effect especially on the nature of something.
Pragmatic is concerned with practical matters. Guided by practical experience and observation rather than theory.
Pragmatism is the attribute of accepting the facts of life and favoring practicality and literal truth. Pragmatism in philosophy is the doctrine that practical consequences are the criteria of knowledge and meaning and value. Pragmatism is the doctrine that practical consequences are the criteria of knowledge and meaning and value. Philosophy.
Parameters are those combinations of the properties which suffice to determine the response of the system. Properties can have all sorts of dimensions, depending upon the system being considered; parameters are dimensionless, or have the dimension of time or its reciprocal.
Parameter is any factor that defines a system and determines or limits its performance. A quantity such as the mean or variance that characterizes a statistical population and that can be estimated by calculations from sample data. Parameter in computer science is a reference or value that is passed to a function, procedure, subroutine, command, or program.
Property in philosophy is a characteristic of an object. The property may be considered a form of object in its own right, able to possess other properties. A property, however, differs from individual objects in that it may be instantiated, and often in more than one thing. It differs from the logical/mathematical concept of class by not having any concept of extensionality, and from the philosophical concept of class in that a property is considered to be distinct from the objects which possess it. Understanding how different individual entities (or particulars) can in some sense have some of the same properties is the basis of the problem of universals. The terms attribute and quality have similar meanings.
Correlation does not prove something is right or correct.
Indicative is something serving as a sign or an indication of something. Pointing out something or revealing something clearly. Denoting a mood of verbs expressing simple statement of a fact. A grammatically unmarked mood that represents the act or state as an objective fact.
Indication is something that serves to indicate or suggest something. The act of indicating or pointing out something by name. Something as a course of action that is indicated as being expedient or necessary. A datum about some physical state that is presented to a user by a meter or similar instrument.
Realis Mood is a grammatical mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact; in other words, to express what the speaker considers to be a known state of affairs, as in declarative sentences.
Let the Facts Speak for Themselves means that the things that have happened or the things that someone has done is evidence that something is true. Facts connected with a matter can make the matter more clear. Facts of a particular situation can provide true information about it and help come to a logical conclusion.
Truth - True
Truth is a fact that has been verified and is in line with reality or actuality. Valid - Accurate - Honest.
Truth is most often used to mean being in accord with fact or reality, or fidelity to an original or standard. Truth may also often be used in modern contexts to refer to an idea of "truth to self," or authenticity.
True is something consistent with fact or Reality and is not false. Worthy of being depended on. Having a legally established claim. Worthy of reliance or trust. Have confidence or faith in. Certainty based on past experience.
Truth is Debatable because when you don't know all the details it could be a Lie or Propaganda.
Bona Fide is not counterfeit or copied. Undertaken in good faith.
Being Frank means that you're being direct in manner of speech without being subtle or evasive. Being blunt, candid, forthright or plainspoken, or just trying to be honest without beating around the bush.
From the Bottom of My Heart means that you are being sincere.
Straight Talk refers to the practice of speaking in a very honest and truthful manner without being cruel or insensitive.
Good Faith is a sincere intention to be fair, open, and honest, regardless of the outcome of the interaction.
Axiom is a saying that states that something is widely accepted and known, so it is assumed to be true and self-evident without the need for proof or disproof.
Consistency is doing something that does not contain a contradiction.
Consistent is Reliable and capable of being reproduced. The same throughout in structure or composition and relation of parts. Acting or done in the same way over time, especially so as to be fair or accurate. Logic.
Repeatable - Symmetry - Synchronicity
Uniform is always the same and showing a single form or character in all occurrences. The same throughout in structure or composition. But not without being able to Adapt and Develop.
Synchronicity - Uniformity and Order
Truth Value sometimes called a logical value, is a value indicating the relation of a proposition to truth.
Veracity is the unwillingness to tell lies. Honest.
Morals - Words to Describe Intelligence
Correspondence theory of Truth states that the truth or falsity of a statement is determined only by how it relates to the world and whether it accurately describes that world. Regards truth as coherence within some specified set of sentences, propositions or beliefs.
Infinite Regress in a series of propositions arises if the truth of proposition P1 requires the support of proposition P2, the truth of proposition P2 requires the support of proposition P3, ... , the truth of proposition Pn−1 requires the support of proposition Pn, ad infinitum. Distinction is made between infinite regresses that are "vicious" and those that are not.
Legal Fiction is a fact assumed or created by courts which is then used in order to apply a legal rule. Typically, a legal fiction allows the court to ignore a fact that would prevent it from exercising its jurisdiction, by simply assuming that the fact is different.
Objective Approach to an issue means having due regard for the known valid evidence (relevant facts, logical implications and viewpoints and human purposes) pertaining to that issue. If relevant valid evidence is denied or falsified, an objective approach is impossible. An objective approach is particularly important in science, and in decision-making processes which affect large numbers of people (e.g. politics).
Universality in philosophy is the notion that universal facts can be discovered and is therefore understood as being in opposition to relativism.
Universal Truth is considered to be universal if it is valid in all times and places. Seen as eternal or as absolute.
Truth by Consensus is the process of taking statements to be true simply because people generally agree upon them.
Consensus Theory of Truth is the process of taking statements to be true simply because people generally agree upon them.
As Scary as that may Sound, it's the truth.
You Can't Handle the Truth, that's because you were denied the knowledge and information that would have given you the ability to understand the truth. So the truth be told, you're just ignorant. But once you learn about the knowledge and information that helps you to define truth, then truth will never be a problem, it will only be the solution.
Revelation is the revealing or disclosing of some form of truth or knowledge through communication with a deity or other supernatural entity or entities.
Propositional Formula is a type of syntactic formula which is well formed and has a truth value. If the values of all variables in a propositional formula are given, it determines a unique truth value.
Finicky is being demanding about one's needs or requirements. Showing or requiring great attention to detail.
“Truth reveals itself in degrees, and we can progress from an incomplete to a more and ever more complete comprehension of truth. Truth is not a thing, not an object that we either have in entirety or have not at all.” - Goethe
Coherentism There are two distinct types of coherentism. One is the coherence theory of truth; the other, the coherence theory of justification. Coherent truth is divided between an anthropological approach, which applies only to localized networks ('true within a given sample of a population, given our understanding of the population'), and an approach that is judged on the basis of universals, such as categorical sets. The anthropological approach belongs more properly to Correspondence theory, while the universal theories are a small development within Analytic philosophy. The coherentist theory of justification, which may be interpreted as relating to either theory of coherent truth, characterizes epistemic justification as a property of a belief only if that belief is a member of a coherent set. What distinguishes coherentism from other theories of justification is that the set is the primary bearer of justification. As an epistemological theory, coherentism opposes dogmatic foundationalism and also infinitism through its insistence on definitions. It also attempts to offer a solution to the regress argument that plagues correspondence theory. In an epistemological sense, it is a theory about how belief can be proof-theoretically justified. Coherentism is a view about the structure and system of knowledge, or else justified belief. The coherentist's thesis is normally formulated in terms of a denial of its contrary, such as dogmatic foundationalism, which lacks a proof-theoretical framework, or correspondence theory, which lacks universalism. Counterfactualism, through a vocabulary developed by David K. Lewis and his Many worlds theory although popular with philosophers, has had the effect of creating wide disbelief of universals amongst academics. Many difficulties lie in between hypothetical coherence and its effective actualization. Coherentism claims, at a minimum, that not all knowledge AND justified belief rest ultimately on a foundation of noninferential knowledge OR justified belief. To defend this view, they may argue that conjunctions (AND) are more specific, and thus in some way more defensible, than disjunctions (OR).
Honesty - Trust
Honest is being a person of value, someone who does not cheat or defraud, or is deceptive or fraudulent, or unfairly judgmental. A person worthy of being depended on, without pretensions. Someone who has gained or earned without cheating or stealing. Honesty refers to a facet of moral character and connotes positive and virtuous attributes such as integrity, truthfulness, straightforwardness, including straightforwardness of conduct, along with the absence of lying, cheating, theft, etc. Furthermore, honesty means being trustworthy, loyal, fair, and sincere.
Don't Break your Word - Moral - Reliable Source - Reputation
Sincere is being open and genuine and not deceitful. Sincerity is the virtue of one who speaks and acts truly about his or her own feelings, beliefs, thoughts, and desires.
Earnest is a firm and humorless belief in the validity of your opinions. Sincerely intended and with strong feeling. Not distracted by anything unrelated to the goal. Something of value given by one person to another to bind a contract. Unassuming.
Trustworthy is someone who is worthy of trust or belief. Taking responsibility for one's conduct and obligations.
Credibility is the quality of being believable or trustworthy. Credible is capable of being believed. Appearing to merit belief or acceptance. Ratings - Profiling.
Veracity is the unwillingness to tell lies. Not being corrupt or negligent.
Trust is to have confidence or faith in someone. Certainty based on past experience. To confer a trust upon. Extend credit to. Allow without fear. Expect and wish. Trust is having faith in someone that is based on past experiences with that person and information and knowledge that you know about, without being gullible or assuming that nothing could go wrong. Trust is also when one party (trustor) is willing to rely on the actions of another party (trustee); the situation is directed to the future. In addition, the trustor (voluntarily or forcedly) abandons control over the actions performed by the trustee. As a consequence, the trustor is uncertain about the outcome of the other's actions; they can only develop and evaluate expectations. The uncertainty involves the risk of failure or harm to the trustor if the trustee will not behave as desired.
Trust Metric is a measurement of the degree to which one trusts another social actor or an individual or a group. Trust metrics may be abstracted in a manner that can be implemented on computers.
Reliable is something or someone worthy of reliance or trust. Conforming to fact and therefore worthy of belief. Worthy of being depended on. Consistent and dependable. Something that is known and witnessed to always work the same way. Like the laws of physics, not a guarantee, but highly probable and most likely to happen time and time again.
Reliability (odds) - Probability - Consistent - Predictable (assurance)
Dependable is worthy of reliance or trust. Consistent in performance or behavior. (ensure, insure)
Live Up to Your End of the Bargain is to do you promised to do in an agreement or in a bargain. To carry through with what one agreed to do.
Benefit of the Doubt is to trust someone temporarily and not assume that the person is lying or doing something bad. You're giving someone a favorable judgment in the absence of evidence that proves otherwise. You're not looking the other way, you're just giving someone a chance to do what is right and a chance to do what is good.
Certain is having no doubt and confident and being sure that something is destined or inevitable to happen
Definite is something established beyond doubt or question and is definitely known for certain and clearly defined.
Explicit is something precisely and clearly expressed or readily observable and leaving nothing to implication.
Precise is something exact or accurate and characterized by fact or truth.
Guarantee is a written assurance that some product or service will be provided or will meet certain specifications. An unconditional commitment that something will happen or that something is true. A promise to do something, to stand behind the quality, accuracy, or condition of something and assume responsibility if it fails.
Solemn is being dignified and somber in manner or character and committed to keeping promises. Characterized by a firm and humorless belief in the validity of your opinions.
Promise is a commitment in advance by one person to another agreeing to do something or not to do something in the future. Promise Manifesto.
Promise Ring is a sign of commitment between two people. Exchanging promise rings can be a symbol of a joint commitment which is not always related to love.
Pre-Engagement Ring is a ring worn to signify a commitment to a monogamous relationship and a promise for an engagement in the future.
Purity Ring is a ring worn to signify a pledge to sexual abstinence until marriage.
Commitment is binding yourself intellectually or emotionally to a course of action. To make a pledge or a contract stating your obligation.
Assured is to make a promise or commitment to something. Security - Insurance
Worthy is having worth or merit or value and being honorable or admirable. Having the qualities or abilities that merit recognition in some way.
Fair is doing something that is free from favoritism or self-interest or bias or deception. Doing something that follows established standards or rules. To gain or earn something without cheating or stealing. Human Rights.
Genuine, Authentic, Sincere is when you are adhering to facts and therefore worthy of belief. Something that is not counterfeit or copied, or deceitful, and not pretended. Something sincerely felt or expressed.
Vouch for someone is to support, backup or confirm someone's good character, that is usually based on your personal knowledge and experience with that person.
Straight Shooter means to be an honest and forthright person. But it could also mean a person who is blunt, sometimes to the point of being harsh or offensive. (You don't have to be rude or insensitive in order to be honest, because rudeness is not being honest, that's just being disrespectable because your ignorant and you don't know how to explain something accurately).
The Battle Hymn of the Republic (youtube) - Glory, glory, Hallelujah! Glory, glory, Hallelujah! Glory, glory, Hallelujah! His truth is marching on.
On the Up and Up is being honest or sincere. steadily improving or becoming more successful.
Mistakes Happen - Something's are not a Given.
Trust No One. Not to say to be paranoid or to think that everyone is lying to you, it's just better to listen carefully and don't always believe everything that you hear or see. You need to ask these two important questions, "If something is possibly true then what are the benefits and what are the risks in believing that it is true? And if something is possibly a lie, then what are the benefits and what are the risks in believing that it is a lie?" Is it everything to gain and nothing top lose, or nothing to gain and everything to lose? (trustno1). Don't Expect Trust. Don't be docile, gullible, passive, too trusting or easily indoctrinated.
Misplaced Loyalty is loyalty placed in other persons or organizations where that loyalty is not acknowledged or respected; is betrayed or taken advantage of. It can also mean loyalty to a malignant or misguided cause.
Loyalty is devotion and faithfulness to a cause, country, group, or person. The act of binding yourself intellectually or emotionally to a course of action. Ethics.
Honesty and Accuracy are two different things, because telling the truth is not always accurate. Just because you're honest does not mean that you are correct. To say to someone that they are ugly is subjective. You can say that the person looks different then you, and what those differences mean should be discussed in a way that does not make assumptions, but only makes sense of the concerns that may be a sign of an underlying health issue. Like saying to someone that their breath stinks, to be more correct you should say that I smell your breath, and was wondering if everything is ok?
Confide is to reveal personal information in private or tell someone confidentially because you confer a trust upon them.
Confiding is willing to entrust personal matters with someone. A proxy.
Confide in Someone is to tell someone about something very private or secret, especially a personal problem, because you feel you can trust them. Attorney–Client Privilege.
To Give Someone the Benefit of the Doubt is to decide that you will believe someone, even though you are not sure that what the person is saying is true.
Betrayal is not always a sign of moral weakness, betrayal is mostly a combination of several things like ignorance, fear and stress. You can still count on people, you just can't count on what happens to people when they are under pressure or under the influence by ignorance. Traitors are everywhere, and betrayal breaks more than just promises. Judas Iscariot (wiki).
It's best not to totally count on someone or expect things to happen in the exact way that you want them to. Sometimes there will be circumstances and things happening that you did not plan for. So always have a Plan B. And always investigate why Plan A did not succeed, and do that without blaming anyone. Keep Learning.
I honestly don't know what to say. Sometimes being honest is saying nothing at all. Just because you believe that you're being honest, does not mean that your honesty is relevant or necessary. Something's are better left unsaid, unless you are positive that the benefits of your honesty out ways the dangers of someone misunderstanding your intentions.
Truth is Debatable
You can't just say "that's the truth", all you can say is this.."This is all the information that I have so far that pertains to this particular occurrence, it's not all the information, it's just the information that I have access to, and how I understood that particular information to be. The truth can only be determined when all the facts are known and accurately understood, and that is as close you can get to knowing the truth. The word 'truth' does not explain anything. To say "I know the truth" only says that you know a few details, which means that a discussion is in order. "To tell it like it is, you have to know what it is."
Too Good to be True (being fooled) - What We Know So Far - Legal Challenge (repeal) - Edit (revise)
Factual Relativism argues that truth itself is relative, and that context and meaning should be without generalizing, or ignoring the fact that things are connected and a bigger picture exists.
John 8:32 - "And you will know the truth, and the truth will set you free.”
There might be some truth in certain things, but if you never investigate and search for truth, the truth will never be found.
Question of Law is a question that must be answered by applying relevant legal principles to interpretation of the law. Such a question is distinct from a question of fact, which must be answered by reference to facts and evidence as well as inferences arising from those facts. Answers to questions of law are generally expressed in terms of broad legal principles and can be applied to many situations rather than be dependent on particular circumstances or factual situations. An answer to a question of law as applied to the particular facts of a case is often referred to as a "conclusion of law." In several civil law jurisdictions, the highest courts consider questions of fact settled by the lower court and will only consider questions of law. They thus may refer a case back to a lower court to re-apply the law and answer any fact-based evaluations based on their answer on the application of the law. International courts such as the Benelux Court of Justice and the European Court of Justice will only answer questions of law, asked by judges of national courts if they are not certain about the interpretation of the law of multilateral organizations. While questions of fact are resolved by a trier of fact, which in the common law system is often a jury, questions of law are always resolved by a judge or equivalent. Whereas findings of fact in a common law legal system are rarely overturned by an appellate court, conclusions of law are more readily reconsidered. In law, a question of fact, also known as a point of fact, is a question that must be answered by reference to facts and evidence as well as inferences arising from those facts. Such a question is distinct from a question of law, which must be answered by applying relevant legal principles. The answer to a question of fact (a "finding of fact") usually depends on particular circumstances or factual situations. All questions of fact are capable of proof or disproof by reference to a certain standard of proof. Depending on the nature of the matter, the standard of proof may require that a fact be proven to be "more likely than not" (there is barely more evidence for the fact than against, as established by a preponderance of the evidence) or true beyond reasonable doubt. In most common law jurisdictions, the general concept and analysis of fact reflects fundamental principles of jurisprudence, and is supported by several well-established standards. Matters of fact have various formal definitions under common law jurisdictions. These include: an element required in legal pleadings to demonstrate a cause of action; The determinations of the finder of fact after evaluating admissible evidence produced in a trial or hearing; A potential ground of reversible error forwarded on appeal in an appellate court; And any of various matters subject to investigation by official authority to establish whether a crime has been perpetrated, and to establish culpability.
"If it sounds to good to be true, it usually isn't" - Ponzi - Occam's Razor.
So you don't know the truth about a lot of things. The truth is hard to swallow, the truth is hard to believe, truth is sometimes stranger then fiction, the truth is a lie, the truth hurts, the truth is painful, the truth is sometimes devastating. But knowing the truth doesn't have to hurt. When you receive more information about a particular occurrence, it will either help you understand the occurrence more, or it will create more questions then answers. So you most likely have more to learn. And emotions are never beneficial when accurately analyzing information. You must keep learning and be in control of your emotions. The truth is not free. The truth takes effort. Deliberate learning and Discussions.
Pluralism in philosophy is the doctrine of multiplicity. Pluralism in ontology refers to different ways, kinds, or modes of being. Pluralism in epistemology is the position that there is not one consistent means of approaching truths about the world. Pluralism in logic is the view that there is no one correct logic, or alternatively, that there is more than one correct logic. Pluralism in metaphysics states that there are many different substances in nature that constitute reality.
Factoid is either a false statement presented as a fact or a true, but brief or trivial item of news or information.
"I agree, there are certain times when you do learn things that you wish you didn't know. But that's only your emotional reaction to this new information, that is not reality. Information is either relevant or irrelevant at that particular time. Like learning about something new on your death bed, what's the point? It's better to let someone die in peace. But if someone is expected to live for years, then they are expected to learn, especially the truth. Learning is a responsibility that no one should ever ignore or take for granted."
Remember that most words have more than one definition, and there is always more to a story, and there is always more then what meets the eye. In order to fully understand what you see, hear or read, you have to know how to navigate through all the different levels of information underneath the surface, if not, then you will never see the whole picture or understand the whole picture. And this is where ignorance does the most damage to people and to the world, and that is the truth. "So put that in your pipe and smoke it".
Why do people say that you should always speak the truth, especially knowing that when speaking the truth you can sometimes get into serious trouble. And sometimes not saying anything at all can also get into serious trouble, and sometimes it's worse. Speak the truth, but wait for the best time to do it, that's if you can wait, if not, then no regrets, at least you spoke the truth. And make sure that you know it is true, and that the truth is accurately measuring all the important factors. What is the value of this information, is the information fair? Facts can be confirmed, but the truth is debatable. If it were just information, how valuable would this information be? And can you measure the value of this information accurately? The truth is debatable. That is why we have courts. So that we can openly debate the value of information, and not just what people believe to be the truth. So the truth is you don't know the complete truth, so how can it be true? Even having all the necessary information, the facts themselves can also be debated. So even reality is debatable. Which is another great reason why educating students to be effective communicators is extremely important, because valuable communication skills will benefit them for their entire life.
To say "I'm speaking the truth", is a lie. All you can say is this, "what I believe to be true is this". Just because you think something is true does not make it the truth. All it can be is your interpretation of certain information. So unless you have facts and witnesses that back up what you say, all you can say is "as far as I know".
There is no such thing as "Nothing but the Truth", there is only truth as far as you can tell to a certain point, which is based on your experiences, empirical evidence and facts. There is no whole truth. Never pretend to know the whole truth.
False Positives and False Negatives where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. A false positive error, or in short false positive, commonly called a "false alarm", is a result that indicates a given condition has been fulfilled, when it has not. I.e. erroneously a positive effect has been assumed. In the case of "crying wolf" – the condition tested for was "is there a wolf near the herd?"; the result was that there had not been a wolf near the herd. The shepherd wrongly indicated there was one, by calling "Wolf, wolf!". A false positive error is a type I error where the test is checking a single condition, and results in an affirmative or negative decision usually designated as "true or false". A false negative error, or in short false negative, is where a test result indicates that a condition failed, while it was successful. I.e. erroneously no effect has been assumed. A common example is a guilty prisoner freed from jail. The condition: "Is the prisoner guilty?" is true (yes, the prisoner is guilty). But the test (a court of law) failed to realize this, and wrongly decided the prisoner was not guilty. A false negative error is a type II error occurring in test steps where a single condition is checked for and the result can either be positive or negative.
Most of the time people change their thinking and modify their point of view when they find out the truth about something. But not everyone understands truth in the exact the same way. Some people react differently to truth because they have a particular level of knowledge and a unique set of experiences that they had in their past. In order for people to process information uniformly, every person must have similar knowledge and information that gives them the ability to accurately analyze information logically and in the most effective way possible. Life could not exist if DNA information was not consistent at least 99% of the time. If DNA reproduced Randomly, their would be no life. This is another reason why we need a consistent and complete education curriculum. One that guarantees intelligence and the full potential of human ability.
Consistent
Postmodernism articulates that the world is in a state of perpetual incompleteness and permanent unresolve. Postmodernism promotes the notion of radical pluralism; that there are many ways of knowing, and many truths to a fact.
Gödel's Incompleteness Theorems are two theorems of mathematical logic that demonstrate the inherent limitations of every formal axiomatic system containing basic arithmetic. These results, published by Kurt Gödel in 1931, are important both in mathematical logic and in the philosophy of mathematics. The theorems are widely, but not universally, interpreted as showing that Hilbert's program to find a complete and consistent set of axioms for all mathematics is impossible. The first incompleteness theorem states that no consistent system of axioms whose theorems can be listed by an effective procedure (i.e., an algorithm) is capable of proving all truths about the arithmetic of the natural numbers. For any such formal system, there will always be statements about the natural numbers that are true, but that are unprovable within the system. The second incompleteness theorem, an extension of the first, shows that the system cannot demonstrate its own consistency. Employing a diagonal argument, Gödel's incompleteness theorems were the first of several closely related theorems on the limitations of formal systems. They were followed by Tarski's undefinability theorem on the formal undefinability of truth, Church's proof that Hilbert's Entscheidungsproblem is unsolvable, and Turing's theorem that there is no algorithm to solve the halting problem.
No Guarantees, only more probable and less probable. Know the Risks.
False in logic, or untrue, is the state of possessing negative truth value or a nullary logical connective. In a truth-functional system of propositional logic it is one of two postulated truth values, along with its negation, truth.
Principle of Bivalence states that every declarative sentence expressing a proposition (of a theory under inspection) has exactly one truth value, either true or false. A logic satisfying this principle is called a two-valued logic or bivalent logic.
Deconstructionism is a theory of literary criticism that questions traditional assumptions about certainty, identity, and truth; asserts that words can only refer to other words; and attempts to demonstrate how statements about any text subvert their own meanings. Words have meaning only because of contrast-effects with other words.
The Truth will set you Free, but only if you are positively sure that you know exactly what the truth is, and only if the truth can be accurately analyzed and confirmed. The truth is sometimes your own personal interpretation of the truth. So unless you have others who have also experienced this truth, and can agree with you, then you are alone. But being alone does not mean that you are wrong, it means that you may be alone in what you think. So, are you sure you know what the truth is? We will listen to you, if you listen to us. The truth is debatable.
Law is Debatable (that is why we have courts)
 The women on the right is making a joke of course, because you would never say that. The point
is, you should not be afraid to speak the truth, especially when
you're sure that you know the truth, and that the
truth can be understood correctly and not be
misinterpreted. She does care what people think, because everyone
can have something valuable to say at any time. If it isn't valuable,
you should either let the person know that their opinion reveals no useful information, or just say nothing.
Freedom of Speech is a
responsibility and not just a right.
The women on the right is making a joke of course, because you would never say that. The point
is, you should not be afraid to speak the truth, especially when
you're sure that you know the truth, and that the
truth can be understood correctly and not be
misinterpreted. She does care what people think, because everyone
can have something valuable to say at any time. If it isn't valuable,
you should either let the person know that their opinion reveals no useful information, or just say nothing.
Freedom of Speech is a
responsibility and not just a right.I would never say "Always Speak the Truth" because the truth has to be relative to the time and the place as well as be relative to the person and the situation. But don't commit perjury, especially when lying hurts innocent people. You should speak the truth when your heart tells you to speak the truth, and when your head agrees with your heart, and when your gut also agrees with both your head and heart and says, "Lets do this, let's tell the truth".
Truth sometimes depends on the person, place or thing. Because even though lies are illogical, they do offer some benefits when used in certain circumstances. If a lie is considered to be protective, then people feel comfortable and sometimes justified for telling a lie, especially when that person feels that they cannot explain the truth effectively enough for other people to understand? Or worse, the truth that they thought they knew was right, turned out to be wrong. After all, to think that you know the truth is to think that you know everything, and we know that you don't. Every truth is debatable. Let us never think that we know the truth, we must always question, as history has taught us, the truth sometimes changes. But even knowing that, we know for a fact that people learn a lot more from telling the truth then they would from telling a lie. It's almost impossible to learn anything if you don't know the truth. Speaking the truth has many benefits, but only if you know the truth, and have lots of evidence to prove it. Understanding how important truth is gives everyone the opportunity to have a more productive and more meaningful conversation. Truth has many benefits, and truth is logical 99.9% of the time...so the odds are in the favor of speaking the truth. Let us begin.
Half Truth is a deceptive statement that includes some element of truth. The statement might be partly true, the statement may be totally true but only part of the whole truth, or it may use some deceptive element, such as improper punctuation, or double meaning, especially if the intent is to deceive, evade, blame or misrepresent the truth.
Necessary and Sufficient Condition are implicational relationships between statements. The assertion that one statement is a necessary and sufficient condition of another means that the former statement is true if and only if the latter is true. That is, the two statements must be either simultaneously true or simultaneously false.
Truth Function is a function from a set of truth values to truth values. Classically the domain and range of a truth function are {truth, falsehood}, but they may have any number of truth values, including an infinity of these.
Truth Value sometimes called a logical value, is a value indicating the relation of a proposition to truth.
You should use all your senses and knowledge when making decisions. You have senses and knowledge for a reason. Trillions of cells in your body are counting on you, and I'm sure they would like to have a say in the decisions that you make, since everyone is affected.
Opinions - Vague Ideas
Opinion is a personal belief or judgment that is not founded on proof or certainty. A message expressing a belief about something, but not factual. An opinion is the expression of a belief that is held with some confidence but not substantiated by positive knowledge or proof. A belief or sentiment shared by most people; the voice of the people. A vague idea in which some confidence is placed. Opinion is a judgment, viewpoint, or statement that is not conclusive.
Point of View - Bias - Pretending to Know
Observation without an explanation is meaningless most of the time. It's like using words that have no definitions. You are not saying anything. If you leave things open to interpretation, it's like sending a message with no purpose or relevance.
Some opinions can be narrow minded and not based on clear evidence that is relevant to the current subject. An opinion can sometimes lack important information that would help to explain someone's opinion clearly enough so that it can be accurately understood by other people. A difference of opinion could mean that someone doesn't care about your opinion, or that someone is in denial about their own opinion. Both sides can be wrong, and both sides can be right. And one person can be wrong, and one person can be right. You need to explain the purpose of your opinion? You need to explain why you think your opinion is important? Can you justify your reasoning or show any evidence or any proof that would help validate your opinion or make your opinion more believable? If you don't care enough to explain and verify your opinion, then you really don't have an opinion. You only have some vague understanding of something that you're trying to express using a few vague words. When people are not seeing eye to eye it can mean that someone is either ignoring information or not seeing the whole picture. So you will need to ask a few questions. Then you need to ask what would the most logical answer be? What is the most fair decision to make? And what is the right thing to do based on the current situation and the current level of knowledge and information available?
Subjectivity - Objectivity - Popularity - Truth - World View - Ignorance - Criticism - Opinions in News - General Statements.
Majority Opinion is a judicial opinion agreed to by more than half of the members of a court. A majority opinion sets forth the decision of the court and an explanation of the rationale behind the court's decision.
Concurring Opinion is in certain legal systems a written opinion by one or more judges of a court which agrees with the decision made by the majority of the court, but states different (or additional) reasons as the basis for his or her decision. When no absolute majority of the court can agree on the basis for deciding the case, the decision of the court may be contained in a number of concurring opinions, and the concurring opinion joined by the greatest number of judges is referred to as the plurality opinion.
Plurality Opinion is in certain legal systems the opinion from a group of judges, often in an appellate court, in which no single opinion supports a majority of the court. The plurality opinion did not receive the support of more than half the justices, but received more support than any other opinion, excluding those dissenting from the holding of the court.
That's one way of looking at it. And if the way you're looking at something is a good way or a bad way, you still need to have a conversation. Just believing something, just doesn't cut it, because people can easily jump to conclusions. You need to explain what you mean instead of pretending that you know what you mean.
There is always another way at looking at something. That is why a second opinion can be extremely valuable.
Second Opinion is getting another opinion from another person or from another source who might have more information or may have more knowledge about a subject than the first opinion. A second opinion may be someone who has a unique point of view based on personal experiences, they may have information that could be valuable to you and can also help you to make a better a decision. Diversity can be valuable in many ways, or confusing when things contradict or when peoples opinions seem biased.
My Take on Things is my point of view or my opinion that is based on my knowledge of the past, as well as my understanding of things when they are combined with the knowledge that I have of the current situation.
Claim is to state that something is true or assert that something is the case, sometimes without providing evidence or proof. An assertion of the truth of something, typically one that is disputed or in doubt. To claim also means to assert one's legal right to property, title or something due. False Advertising.
Statement of Claim is a written statement of the initiating litigant, called a plaintiff, in which he/she must state their case and the facts on which they intend to rely upon and the relief they seek, to the defendant and for the public record, for which they seek a civil trial and judicial determination. False Evidence.
Assertion is the act of stating something. To claim something.
Assert is to declare or formally state that something is true and insist on having one's opinions and rights recognized.
Implication is something that is inferred, deduced or entailed or implied. A meaning that is not expressly stated but can be inferred. An accusation that brings into intimate and usually incriminating connection. A logical relation between propositions p and q of the form 'if p then q'; if p is true then q cannot be false. A relation implicated by virtue of involvement or close connection, especially an incriminating involvement.
Implied is to express something or state something indirectly and suggest as a logically necessary consequence. To suggest that someone is guilty. To incriminate and bring an accusation against someone. Have as a necessary feature.
Accuse is to bring an accusation against someone or charge someone with a crime. To blame someone for something and make a claim of wrongdoing or misbehavior.
Affirm is to establish or strengthen as with new evidence or facts. To say yes to something or agree with something.
Relativism is the concept that points of view have no absolute truth or validity within themselves, but rather only relative, subjective value according to differences in perception and consideration.
It's All Relative is not an answer, it's a question. You're better off saying "Please specify an example to better clarify your point of view." It's all relative doesn't mean that it can't be relative, so make it relative. Yes it's subjective, ambiguous, and it all depends on how you look at it, and depending on circumstances, there can be several explanations, so start talking or start listening.
Concern is something that interests you because it is important or affects you. Be relevant to. A feeling of sympathy for someone or something. Sharing the feelings of others. (But still you must be able to validate, calculate or measure this affect). Having a Concern about something is different then having an Opinion about something.
Arbitrary is the trait of acting unpredictably and more from whim or caprice than from reason or judgment. Based on or subject to individual discretion or preference or sometimes impulse or caprice. Arbitrariness is the quality of being "determined by chance, whim, or impulse, and not by necessity, reason, or principle". Something's have no apparent effect on the subject in question.
Conjecture is a hypothesis that has been formed by speculating or conjecturing (usually with little hard evidence). A message expressing an opinion based on incomplete evidence. Reasoning that involves the formation of conclusions from incomplete evidence. To believe especially on uncertain or tentative grounds. Conjecture is a conclusion or proposition based on incomplete information, for which no proof has been found.
Propaganda (someone is hacking your brain)
Theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena. A tentative insight into the natural world; a concept that is not yet verified but that if true would explain certain facts or phenomena. A belief that can guide behavior.
Guess is a message expressing an opinion based on incomplete evidence. An estimate based on little or no information.
Belief - Believing
Agnostic is someone who is doubtful or noncommittal about something and uncertain of all claims to knowledge. A person who claims that they cannot have true knowledge about the existence of God, but does not deny that God might exist.
Denying - Bias
Opine is to express one's opinion openly and without fear or hesitation. Expect to be true or to believe.
Advice is a form of relating personal or institutional opinions, belief systems, values, recommendations or guidance about certain situations relayed in some context to another person, group or party often offered as a guide to action and/or conduct. Put a little more simply, an advice message is a recommendation about what might be thought, said, or otherwise done to address a problem, make a decision, or manage a situation.
There's a big difference between questioning something and believing that you know the answer to something. When you don't have an answer, you either look for an answer, or just stick with the things that you can answer. Don't pretend to know the answer to something, because that never helps, and usually makes things worse, mostly because no one is learning anything valuable.
Lying - False - Deception
Lie is a statement that deviates from fact and reality in a way that it perverts the truth. A lie is to tell an untruth. A lie is to pretend with intent to deceive. A lie is a statement that the stating party believes to be false and that is made with the intention to deceive. The practice of communicating lies is called lying, and a person who communicates a lie may be termed a Liar.
Deceive is to be false to or to be dishonest with someone and cause someone to believe an untruth or a lie. Deceitful.
Wrong is not right and not correct or not accurate.
False is not in accordance with fact or reality or actuality. Arising from error. Not genuine or real or not correct or proper.
Falseness is being false or untrue. Unfaithfulness by virtue of being unreliable, treacherous, deceitful or hypocritical. The quality of not being open or truthful.
Falsehood is a false statement. The act of rendering something false as by fraudulent changes. (falsehood is a word that news people use as a nice way of saying that someone is a lying scumbag).
Ponzi - Imposter - Fraud - False Pretenses - Breaking your Word - Denial
Lying is giving an intentionally false statement to a person or group made by another person or group who knows it is not the whole truth. A fabrication is a lie told when someone submits a statement as truth without knowing for certain whether or not it actually is true. Half-Truth is a deceptive statement that includes some element of truth. The statement might be partly true, the statement may be totally true but only part of the whole truth, or it may employ some deceptive element, such as improper punctuation, or double meaning, especially if the intent is to deceive, evade, blame, or misrepresent the truth. Honest Lie or confabulation is defined by verbal statements or actions that inaccurately describe history, background, and present situations.
Pathological Lying is a behavior of habitual or compulsive lying. It's when an individual consistently lies, sometimes for no personal gain. (Compulsive Liar, Chronic Liar or Habitual Liar). Trump told 13,435 lies or false or misleading claims in just the last four years since 2016.
Congenital Liar is constant lying as the result of a specific genetic defect.
Perjury is the act of lying or making verifiably false statements on a material matter under oath or affirmation in a court of law, or in any of various sworn statements in writing. White lies are minor lies which could be considered to be harmless, or even beneficial, in the long term. Perjury - Abuse of Power.
False Dilemma is a type of informal fallacy in which something is falsely claimed to be an either/or situation, when in fact there is at least one additional option. Mistakes.
False Positive Paradox is a statistical result where false positive tests are more probable than true positive tests, occurring when the overall population has a low incidence of a condition and the incidence rate is lower than the false positive rate. The probability of a positive test result is determined not only by the accuracy of the test but by the characteristics of the sampled population. When the incidence, the proportion of those who have a given condition, is lower than the test's false positive rate, even tests that have a very low chance of giving a false positive in an individual case will give more false than true positives overall. So, in a society with very few infected people—fewer proportionately than the test gives false positives—there will actually be more who test positive for a disease incorrectly and don't have it than those who test positive accurately and do. The paradox has surprised many.
False Negatives are concepts analogous to type I and type II errors in statistical hypothesis testing, where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences in detail and interpretation.
Double Negation in propositional logic, double negation is the theorem that states that "If a statement is true, then it is not the case that the statement is not true." This is expressed by saying that a proposition A is logically equivalent to not (not-A), or by the formula A ~(~A) where the sign expresses logical equivalence and the sign ~ expresses negation.
Doubt is the state of being unsure of something. Uncertainty about the truth, factuality or existence of something. Lack confidence and consider something to be unlikely.
Suspicion is having doubt about someone's honesty. Being of a suspicious nature. The state of being suspected. An impression that something might be the case.
Bluffing is deceive an opponent by a bold bet on an inferior hand with the result that the opponent withdraws a winning hand. Frighten someone by pretending to be stronger than one really is.
Far Fetched is something that is unlikely, unconvincing or implausible. Something that does not seem to be true or factual. "You can't make this stuff up, oh yes you can".
Deluding is to be false and dishonest with yourself or to others.
Ruse is a deceptive maneuver, especially to avoid capture.
Fantasy - "You couldn't be farther from the truth."
Myth is a false Belief or a Lie.
Insincere is lacking truth and seriousness. Being deceitful or hypocritical.
Prevarication is when someone tells a lie, especially in a sneaky way. A child might use prevarication to avoid telling the whole truth about how the kitchen window got broken.
Fib is a trivial lie or a relatively insignificant lie.
Kidding is to tell false information to for fun. Be silly or tease one another.
Child Lying refers to children displaying varying degrees of deceptive behavior in a social situation. Children have been observed lying as early as age 2 and their deceptive skills increase sharply as they mature into adolescence. Children who have advanced cognitive skills for their age have an increased tendency to begin lying at earlier ages. Children may lie for various reasons including, but not limited to, escaping punishment for not obeying a task (such as eating a cookie when told not to), through observation of their parents and peers, or lacking a comprehensive understanding of basic morality. Relative.
The Lie detector could be a Lie in itself because the body does not always tell the truth, just like the mind may not always tell the truth, as above so below. A simple yes or no is never that simple. This is why people plead the fifth.
Polygraph measures and records several physiological indices such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a person is asked and answers a series of questions. The belief underpinning the use of the polygraph is that deceptive answers will produce physiological responses that can be differentiated from those associated with non-deceptive answers. There are, however, no specific physiological reactions associated with lying, making it difficult to identify factors that separate liars from truth tellers. Polygraph examiners also prefer to use their own individual scoring method, as opposed to computerized techniques, as they may more easily defend their own evaluations.
Lie Detection is an assessment of a verbal statement with the goal to reveal a possible intentional deceit. Lie detection may refer to a cognitive process of detecting deception by evaluating message content as well as non-verbal cues. It also may refer to questioning techniques used along with technology that record physiological functions to ascertain truth and falsehood in response.
Contradictions - Corruption - Propaganda - Assuming
How to Spot a Liar - Body Language - Perjury
Do you solemnly (swear/affirm) that you will tell the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the truth, (so help you God/under pains and penalties of perjury)? Sworn Testimony - Oaths.
Deliberately Deceptive is to cause someone to believe an untruth. Deceptive or fraudulent; disposed to cheat or defraud or deceive. Designed to deceive or mislead either deliberately or inadvertently. Causing one to believe what is not true or fail to believe what is true. False Statements (perjury).
Counterintuitive is a proposition that does not seem likely to be true when assessed using intuition, common sense, or gut feelings.
Liar Paradox is the statement of a liar who states that they are lying: for instance, declaring that "I am lying" or "everything I say is false". If they are indeed lying, they are telling the truth, which means they are lying. In "this sentence is a lie" the paradox is strengthened in order to make it amenable to more rigorous logical analysis. It is still generally called the "liar paradox" although abstraction is made precisely from the liar themself. Trying to assign to this statement, the strengthened liar, a classical binary truth value leads to a contradiction. If "this sentence is false" is true, then the sentence is false, but if the sentence states that it is false, and it is false, then it must be true, and so on.
Coercive Logic is asking questions with only one truthful answer. Possibly the simplest example is “Yes or Yes?”, forcing a ‘yes’ answer. A better example is “Will you answer no to this question?”, which is a yes-or-no question which forces the answerer to lie.
Some lies are that not bad, especially when they are use to protect someone. Sometimes it's better to explain the truth at another time or place. Sometimes the truth is more embarrassing then then lie itself, so people will lie. It's understandable, but it can also be dangerous and risky. When people don't know the truth, mistakes can happen and opportunities can be lost. You will hear people say, why didn't you just tell me the truth? If I knew the truth I could have helped you, and we could have also avoided making unnecessary mistakes or assumptions. So be extremely careful. It sometimes hard to tell the truth, especially when the truth makes you look bad. So knowing how to tell the truth is just as important as telling the truth itself.
Guilt is realizing that you're wrong or realizing that something you're doing is bad. A conscience comes from learning valuable knowledge and information that gives you the ability to analyze yourself and the world accurately.
When stubbornness and ignorance becomes illogical, and a problem...Excuses without Reasoning is a lie.
Freudian Slip an unintentional error regarded as revealing subconscious feelings. Parapraxis is an error in speech, memory, or physical action that occurs due to the interference of an unconscious subdued wish or internal train of thought. The concept is part of classical psychoanalysis. Classical examples involve slips of the tongue, but psychoanalytic theory also embraces misreadings, mishearings, temporary forgettings, and the mislaying and losing of objects. Linguistic slips can represent a sequencing conflict in grammar production.
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that are claimed to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method.
Errors - Incorrectness
Error is a wrong action attributable to bad judgment or ignorance or inattention. Departure from what is ethically acceptable. A misconception resulting from incorrect information. Part of a statement that is not correct. Error is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect.
Erroneous is something that contains or is characterized by error. Mistake - Assumption - Lie - Awareness
Human Error is a mistake in judgment and a deviation from intention, expectation or desirability. Something having been done that was not intended and not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits.
Pilot Error is an accident in which an action or decision made by the pilot was the cause or a contributing factor that led to the accident, but also includes the pilot's failure to make a correct decision or take proper action. Errors are intentional actions that fail to achieve their intended outcomes. Cockpit task management includes: Task initiation – when appropriate conditions exist. Task monitoring – assessment of task progress and status. Task prioritization – relative to the importance and urgency for safety. Resource allocation – assignment of human and machine resources to tasks which need completion. Task interruption – suspension of lower priority tasks for resources to be allocated to higher priority tasks. Task resumption – continuing previously interrupted tasks. Task termination – the completion or incompletion of tasks.
Out of Practice Errors - Certification Renewal - Procedures
New drivers ages 15-25 cause nearly 1/2 of the 1 million+ road deaths worldwide. A new study suggests that driver ed programs use of fear-based messaging doesn't reduce risky driving and may even lead young drivers to take more chances.
Latent Human Error is a term used in safety work and accident prevention, especially in aviation, to describe human errors which are likely to be made due to systems or routines that are formed in such a way that humans are disposed to making these errors. Latent human errors are frequently components in causes of accidents. The error is latent and may not materialize immediately, thus, latent human error does not cause immediate or obvious damage. Discovering latent errors is therefore difficult and requires a systematic approach. Latent human error is often discussed in aviation incident investigation, and contributes to over 70% of the accidents. By gathering data about errors made, then collating, grouping and analyzing them, it can be determined whether a disproportionate amount of similar errors are being made. If this is the case, a contributing factor may be disharmony between the respective systems/routines and human nature or propensities. The routines or systems can then be analyzed, potential problems identified, and amendments made if necessary, in order to prevent future errors, incidents or accidents from occurring. Two Man Rule.
User Error is an error made by the human user of a complex system, usually a computer system, in interacting with it. Although the term is sometimes used by human–computer interaction practitioners, the more formal human error term is used in the context of human reliability.
Error-Tolerant Design is one that does not unduly penalize user or human errors. It is the human equivalent of fault tolerant design that allows equipment to continue functioning in the presence of hardware faults, such as a "limp-in" mode for an automobile electronics unit that would be employed if something like the oxygen sensor failed.
Human Reliability Errors: Assumptions – A condition taken for granted or accepted as true without verification of the facts. Habit – An unconscious pattern of behavior acquired through frequent repetition. Confirmation bias – The reluctance to abandon a current solution. Similarity bias – The tendency to recall solutions from situations that appear similar. Frequency bias – A gamble that a frequently used solution will work. Availability bias – The tendency to settle on solutions or courses of action that readily come to mind. Limited Working Memory - The mind's short-term memory is the “workbench” for problem solving and decision-making. Limited Attention Resources - The limited ability to concentrate on two or more activities challenges the ability to process information needed to solve problems. Mind-Set People tend to focus more on what they want to accomplish (a goal) and less on what needs to be avoided because human beings are primarily goal-oriented by nature. As such, people tend to “see” only what the mind expects, or wants, to see. Difficulty Seeing One's Own Error - Individuals, especially when working alone, are particularly susceptible to missing errors. Limited Perspective - Humans cannot see all there is to see. The inability of the human mind to perceive all facts pertinent to a decision challenges problem-solving. Susceptibility To Emotional/Social Factors - Anger and embarrassment adversely influence team and individual performance. Fatigue - People get tired. Physical, emotional, and mental fatigue can lead to error and poor judgment. Presenteeism - Some employees will be present in the need to belong to the workplace despite a diminished capacity to perform their jobs due to illness or injury.
Team Error refers to errors that occur in settings where multiple people are working together. Dependency increases the likelihood of human error due to interactions with other seemingly independent defense mechanisms. Engaging multiple people to perform a task does not ensure that the task will be done correctly. One potential dependency is team error, an error of one or more members that allows other individual members of the same group to make a mistake.
Technique for Human Error-Rate Prediction is a technique used in the field of human reliability assessment (HRA), for the purposes of evaluating the probability of a human error occurring throughout the completion of a specific task.
Type I - Type II Errors is the incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis (a "false positive"), while a type II error is incorrectly retaining a false null hypothesis (a "false negative"). More simply stated, a type I error is detecting an effect that is not present, while a type II error is failing to detect an effect that is present.
Margin of Error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in a survey's results. It asserts a likelihood (not a certainty) that the result from a sample is close to the number one would get if the whole population had been queried. The likelihood of a result being "within the margin of error" is itself a probability, commonly 95%, though other values are sometimes used. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that the poll's reported results are close to the true figures; that is, the figures for the whole population. Margin of error applies whenever a population is incompletely sampled.
Standard Error can be seen to depict the relationship between the dispersion of individual observations around the population mean (the standard deviation), and the dispersion of sample means around the population mean (the standard error). Different samples drawn from that same population would in general have different values of the sample mean, so there is a distribution of sampled means (with its own mean and variance). The relationship with the standard deviation is defined such that, for a given sample size, the standard error equals the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. As the sample size increases, the dispersion of the sample means clusters more closely around the population mean and the standard error decreases. Inferior (deficient).
Errors and Residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "theoretical value". The error (or disturbance) of an observed value is the deviation of the observed value from the (unobservable) true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean), and the residual of an observed value is the difference between the observed value and the estimated value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals.
Error Detection and Correction are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Forward Error Correction (wiki)
Noise (digital) - Algorithm - Memory Errors - Ignorance
Patch in computing is a piece of software designed to update a computer program or its supporting data, to fix or improve it. This includes fixing security vulnerabilities and improving the usability or performance.
Being wrong is the same as making a mistake. You need to learn from your mistake and you need to change what is wrong.
Denial - Refusing to Except the Facts - Not Listening
Denial is when a person is faced with a fact that is too uncomfortable to accept and rejects it instead, insisting that it is not true despite what may be overwhelming evidence. To be ignorant of the facts. Unwilling to listen to someone else's view. Denial is refusing to see your responsibility or refusing to see that a problem exists at all.
Deny is to refuse to accept something, or not to believe something, or to declare something to be true or untrue without providing any evidence for your belief. To refuse to recognize, acknowledge or reason with someone even when you are contradicting yourself. To refuse to grant, as of a petition or a request. Denying can also mean to deny oneself of something and restrain oneself, especially from indulging in some pleasure. Not Having an Open Mind - Not Seeing the Whole Picture.
Hardliner is a member of a group who adheres uncompromisingly to a set of ideas or policies. Partisan.
Ignoring is refuse to acknowledge or listen. Fail to notice. Give little or no attention to. Be ignorant of or in the dark about.
Disavow is to deny any knowledge of or the responsibility for or the association with somebody or something. Refuse to acknowledge. To disclaim knowledge of or association with.
Dismissive is showing indifference or disregard. Refuse to acknowledge. Willful lack of care and attention. Refuse. Reject. Ignore. Censorship.
Not Listening - Not Confessing - Negligence - Lack of Empathy - Selfish - Extremist
Disavowal is the denial of any connection with or knowledge of.
Disregard is to refuse to acknowledge and a willful lack of care and attention.
Refuse is to not accept something and show unwillingness. To not allow someone to have something. To deny entrance or membership. To elude or avoid, especially in a baffling way.
Repudiate is to refuse to acknowledge, ratify, or recognize something as valid. Reject as untrue, unfounded, or unjust.
Repudiation is rejecting, disowning or disclaiming something as invalid. The exposure of falseness or pretensions. Refusal to acknowledge or pay a debt or honor a contract.
Oppose is to be against or to express opposition to something. Fight against or resist strongly. Set into opposition or rivalry.
Contentious is someone who is likely to cause controversy, or someone who likes to dispute or disagree and engage in frivolous law suits.
Defiance is intentionally having a lack of respect and a hostile behavior or intimidating attitude.
Intolerance is the unwillingness to recognize and respect differences in opinions or beliefs of other people.
Impatience is having a lack of patience and being irritated with anything that causes delay.
Maladaptation is a trait that is more harmful than helpful, in contrast with an adaptation, which is more helpful than harmful.
Self Delusion is the action of deluding oneself; failure to recognize reality.
Self-Deception is a process of denying or rationalizing away the relevance, significance, or importance of opposing evidence and logical argument. Self-deception involves convincing oneself of a truth (or lack of truth) so that one does not reveal any self-knowledge of the deception.
Ecological Trap are scenarios in which rapid environmental change leads organisms to prefer to settle in poor-quality habitats. The concept stems from the idea that organisms that are actively selecting habitat must rely on environmental cues to help them identify high-quality habitat. If either the habitat quality or the cue changes so that one does not reliably indicate the other, organisms may be lured into poor-quality habitat. Evolutionary Mismatch refers to evolved traits that were once advantageous but became maladaptive due to changes in the environment.
Self-Deception is a process of denying or rationalizing away the relevance, significance, or importance of opposing evidence and logical argument. Self-deception involves convincing oneself of a truth (or lack of truth) so that one does not reveal any self-knowledge of the deception.
Bias - Over Confidence - Pretending to Know - Pride - Arrogance
Willful Blindness describe a situation in which a person seeks to avoid civil or criminal liability for a wrongful act by intentionally keeping himself or herself unaware of facts that would render him or her liable. Passive.
Compartmentalization in psychology is a subconscious psychological defense mechanism used to avoid cognitive dissonance, or the mental discomfort and anxiety caused by a person's having conflicting values, cognitions, emotions, beliefs, etc. within themselves. Compartmentalization allows these conflicting ideas to co-exist by inhibiting direct or explicit acknowledgement and interaction between separate compartmentalized self states. Displacement - Fantasize.
Defense Mechanisms are used to manipulate, deny, or distort reality in order to defend against feelings of anxiety and unacceptable impulses and to maintain one's self-schema.
Graded Absolutism. Moral absolutism is the ethical view that certain actions are absolutely right or wrong regardless of other contexts such as their consequences or the intentions behind them. (nothing is absolute, only debated).
Stubborn is being unwilling or marked by tenacious unwillingness to yield. Uncompromising and stuck in there ways.
Inexorable is being impervious to pleas, persuasion, requests, reason. Not to be placated or appeased or moved by entreaty or Earnest or urgent request. Extremist.
"Sometimes there's no amount of evidence that can persuade an idiot."
Relentless is oppressively constant and continuing without pause or interruption. Harsh or inflexible. Not to be confused with Determination.
Reluctant is the unwillingness to do something contrary to your custom. Conservative.
Incorrigible is someone who is not able to be corrected, improved, or reformed, even when corrected by punishment.
Close-Minded is when a person is not willing to consider other ideas and opinions that are different from their own. They are unreceptive to new ideas or arguments. Not having an open mind.
Narrow-Minded is when someone's opinion is based on only a few irrelevant details, and they do not consider other evidence or consider other relevant information that would help them to make their opinion more accurate and more complete. Narrow minded is to express an opinion that it is usually vague and considered propaganda. If someone is not willing to listen to other people, or tolerate other people's views, they may come across as being prejudice or biased, or they may not be informed enough and may be just pretending to know what they are talking about. Refusing to see the whole picture and only seeing what they want to see will always leave you in the dark and always be confusing. Thinking outside the box will help you to avoid information bubbles. Narrow Minded is not the same thing as Blinders for Horses, which are used to help keep the horse focused on what is in front of them, and also help the horse from being distracted by crowds outside their field of view.
Single Minded is when a person only focuses on only one aim or on one purpose while ignoring other important factors. Focusing on one thing at the expense of anything else. A person who cares about their happiness while ignoring other people happiness. Selfish.
Simple Minded is a person showing very little intelligence or judgment. Someone who lacks insight and can't understand or grasp most concepts.
Talking to a Wall is when you are talking to someone but they refuse to listen or respond to your message.
Talk to the Hand is a sarcastic way of saying to someone that you do not want to hear what they are speaking or saying.
My Way or the Highway suggests an ultimatum like "take it or leave it" or "do or die", which indicates that the listener(s) (who are typically not in a position to challenge the options, e.g. employees or those lacking money) must totally accept the speaker's decision or suffer negative consequences such as being fired, asked to leave, or receive nothing.
Mind is Made Up is when someone has made a decision and will not change it, and will not consider other alternatives or options.
No Ifs Ands or Buts is an expression sometimes used when the speaker will not entertain any arguments to the contrary. The phrase no ifs, ands, or buts is a list of words that are often used to begin a sentence that is an explanation or excuse for bad behavior or for not fulfilling an obligation. Two Sides to Every Story.
Bigot is a prejudiced person who is intolerant of any opinions that differs from their own. A person who is biased and blames other people for the same faults that they have.
Bigotry is a habitual state of mind that includes an obstinate, irrational, or unfair intolerance of ideas, opinions, or beliefs that differ from their own, and intolerance of the people who hold them. Bigotry is a term of abuse aimed at a prejudiced or closed-minded person, especially one who is intolerant or hostile towards different social groups (especially, and originally, other religious groups), and especially one whose own beliefs are perceived as unreasonable or excessively narrow-minded, superstitious, or hypocritical or contradictory.
Shallow is someone who is superficial or lacking depth and insight and mostly concerned with silly, irrelevant or inconsequential things. A deep person means having profound insights and understanding.
Stonewalling is a refusal to communicate or cooperate. Such behavior occurs in situations such as marriage guidance counseling, diplomatic negotiations, politics and legal cases. Body language may indicate and reinforce this by avoiding contact and engagement with the other party. People use deflection in a conversation in order to render a conversation pointless and insignificant. Tactics in stonewalling include giving sparse, vague responses, refusing to answer questions, or responding to questions with additional questions. In most cases, stonewalling is used to create a delay, rather than to put the conversation off forever. Filibuster.
When we feel attacked, it's hard to hear what another person has to say with an open mind. Instead, our first thought is to defend ourselves. Or we may try to turn the tables by pointing out flaws in the other person's behavior. By the end of the conversation, it's likely no one feels heard. Criticism can feel painful, especially from the people we feel closest to, even when it's meant to help us. But defensiveness keeps us closed off from building supportive relationships. Learning to spot defensive behavior in ourselves and others can help us have better conversations that result in solutions instead of pointing fingers.
Defensiveness is when we try to counter or deny criticisms in areas in which we feel sensitive. For many, this is a way to emotionally protect ourselves. Our brain instinctively kicks into "fight or flight" mode when we think we are in trouble, which can lead to overwhelming emotions like anger and anxiety. Even if we aren't in bodily danger, we can feel under attack when it seems like someone is threatening our sense of identity or worth. We might not always interpret threats accurately.
Shrewd is being hardheaded and serving one's own interests in an unemotional, analytical manner.
Low-life is a term for a person who is considered unfair and morally unacceptable by his or her community.
If you stubbornly refuse to change your mind about something, you are adamant about it.
Adamant and similar words are used to refer to any especially hard substance, whether composed of diamond, some other gemstone, or some type of metal.
Rigidity in psychology refers to an obstinate inability to yield or a refusal to appreciate another person's viewpoint or emotions characterized by a lack of empathy. It can also refer to the tendency to perseverate, which is the inability to change habits and the inability to modify concepts and attitudes once developed.
Toxic Leadership - Bullying - Jealousy
You want to be firm but not stubborn. You want to be firm with the facts and stand by your reasoning, but not so much that you stop taking in new information. If stubbornness stops you from learning, that's when being stubborn will do the most damage.
To say something isn't true without any evidence or facts, could be Biased or just a Lie?
Placated is to cause to be more favorably inclined.
Cognitive Distortion - Naivety - Fallacies - Psychosis
Minimisation in psychology is a type of deception involving denial coupled with rationalization in situations where complete denial is implausible. Minimisation downplays the dangers and risks of things while over exaggerating the benefits.
Nihilism is the point of view that suspends belief in any or all general aspects of human life, which are culturally accepted.
life is without objective meaning, purpose, or intrinsic value. Denial of objective reality; a sense that everything is unreal. Complete denial of all established authority and institutions.
Covering up your ears and making noises so that you don't hear something that you don't want to listen to. Dumb and Dumber - la la la (youtube).
Loath is the unwillingness to do something contrary to your custom. To be strongly opposed or antipathetic.
Antipathy is a feeling of intense dislike. The object of a feeling of intense aversion or something to be avoided.
Aversion is a feeling of intense dislike. The act of turning yourself or your gaze away.
Reaction Formation is a defensive process (defense mechanism) in which emotions and impulses which are anxiety-producing or perceived to be unacceptable are mastered by exaggeration (hypertrophy) of the directly opposing tendency.
When you have Nothing to Gain but Everything to Lose, then denying is not only illogical, it's extremely dangerous.
Anger (getting mad) - Hate - Prejudice
Obstinate is stubbornly refusing to change one's opinion or chosen course of action, despite attempts to persuade one to do so. Synonyms: stubborn, unyielding, inflexible, unbending, intransigent, intractable, obdurate, mulish, bullheaded, stubborn as a mule, pigheaded, self-willed, strong-willed, headstrong, willful, contrary, perverse, recalcitrant, refractory, uncooperative, unmanageable, stiff-necked, rigid, uncompromising, implacable, unrelenting, immovable, unshakable; More persistent, tenacious, pertinacious, dogged, single-minded. Antonyms: Diplomatic.
Hedges is an intentionally noncommittal or ambiguous statement. Avoid or try to avoid fulfilling, answering, or performing (duties, questions, or issues) Trying to cover up Lies or criminal behavior. Ignorance.
Devolution is the notion that species can revert into more "primitive" forms over time.
"Denying or disavowing the facts does not remove these facts from reality. It only allows a person to use this sad excuse to continue with its illogical behavior."
Projection is attributing or blaming your own thoughts and feelings to another person (e.g., "I'm not angry, you're angry").
Acting out is having an overblown response (like breaking something) instead of expressing the problem.
Rationalization is bending the truth to justify a behavior. Invalid Argument.
Displacement is taking out our frustration from another problem on someone not involved (e.g., getting in a fight with your partner because of trouble at work).
Intellectualizing is only focusing on the facts of a situation while ignoring their emotional significance.
It's one of these three things or a combination of: 1: You refuse to acknowledge your ignorance. 2: You are not aware of your ignorance. 3: You don't care that you're ignorant.
Neurosis is having excessive and irrational anxiety or obsession. Neurosis is a class of functional mental disorders involving chronic distress but neither delusions nor hallucinations.
Neuroticism is someone who responds worse to stressors and are more likely to interpret ordinary situations as threatening and minor frustrations as hopelessly difficult. They are often self-conscious and shy, and they may have trouble controlling urges and delaying gratification. They can be moody and can experience such feelings as anxiety, worry, fear, anger, frustration, envy, jealousy, guilt, depressed mood, and loneliness.
Related Subjects - Fallibilism - Bias - Subjectivity - Opinion - Objectivity - Reasoning - Knowing - Reality - Learning Methods - Scientific Examinations - Knowledge Graph - Knowledge Vault - Verificationism - Popularity.
