BK101
Knowledge Base
Sustainable - Staying Strong and Not Weakening
Sustainable Living is all about creating an easy to manage life so that everyone has more free time to enjoy life and also live peacefully. You don't have to work hard or work long hours. Everyone can have easy jobs with shorter hours because everyone will be working smarter and not just harder or more effectively. Equilibrium is life's sweet spot, and that's where we're headed. But to get there we will have to work hard and long for some time. But remember, we have everything to gain and nothing to lose. Having balance is absolutely necessary.
 Sustainability is when
biological systems remain
diverse and
productive indefinitely.
Sustainability is when
biological systems remain
diverse and
productive indefinitely.Sustained is to be maintained at length without interruption or weakening.
Sustain is to lengthen or extend in duration or space and to provide and supply with nourishment and necessities and support, and carry the weight of vulnerabilities. Sustain also means to establish or strengthen as with new evidence or facts and admit as valid.
Sustainable Design is the designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of social, economic, and ecological sustainability to eliminate negative environmental impact completely through skillful, sensitive design.
Resilient - Longevity - Return on Investment
Earth Overshoot Day is the calculated illustrative calendar date on which humanity's resource consumption for the year exceeds Earth’s capacity to regenerate those resources that year. Earth Overshoot Day is calculated by dividing the world bio-capacity or the amount of natural resources generated by Earth that year, by the world ecological footprint (humanity's consumption of Earth's natural resources for that year), and multiplying by 365, the number of days in one Gregorian common calendar year. Earth Overshoot Day falls on July 29, 2019, which means that humanity is currently using nature 1.75 times faster than our planet's ecosystems can regenerate.
Carrying Capacity is the maximum population size of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment. Collapse.
Don't Bite off More than you can Chew - Live within your Means - Offset
Seven Generation Sustainability is a concept that urges the current generation of humans to live and work for the benefit of the seventh generation into the future. It is believed to have originated with the Iroquois – Great Law of the Iroquois – which holds appropriate to think seven generations ahead (about 140 years into the future) and decide whether the decisions they make today would benefit their children seven generations into the future. It is frequently associated with the modern, popular concept of environmental stewardship or 'sustainability' but it is much broader in context. "In every deliberation, we must consider the impact on the seventh generation... even if it requires having skin as thick as the bark of a pine." This is an often repeated saying, however, despite a common belief, it is not contained in the Constitution of the Iroquois Nation. Instead, the only passage mentioning the number seven talks about qualities that Iroquois leaders should have, while the end of the passage advises them to consider the welfare of future generations. "We now do crown you with the sacred emblem of the deer's antlers, the emblem of your Lordship. You shall now become a mentor of the people of the Five Nations. The thickness of your skin shall be seven spans — which is to say that you shall be proof against anger, offensive actions, and criticism. Look and listen for the welfare of the whole people and have always in view not only the present but also the coming generations, even those whose faces are yet beneath the surface of the ground -- the unborn of the future Nation." Knowledge Preservation.
Two-Way Street is a mutually beneficial, mutually enjoyable, and mutually sacrificial experience. A lifestyle that is not a contradiction.
Compatible Coexistence - Ecological Economics - Weak vs Strong Sustainability - Human Centered Design
Renewable Resource is a resource which can be used repeatedly and replaced naturally.
Draw in a chess game is when two players agree that neither player can win because they are evenly matched no matter how many moves either person makes. So the game ends in a draw with no winners, and no time is wasted trying to win a game that could never be won. This way the players can either start a new game, or, just stop playing the game and do something else.
Sustainable Farming - Sustainable Landscaping (lawns) - Permaculture
Sustainability Reporting gives information about economic, environmental, social and governance performance.
Sustainable Calculators - Reusable Containers - Sustainable Consumption
Sustainability Measurement is the quantitative basis for the informed management of sustainability. The metrics used for the measurement of sustainability (involving the sustainability of environmental, social and economic domains, both individually and in various combinations) are still evolving: they include indicators, benchmarks, audits, indexes and accounting, as well as assessment, appraisal and other reporting systems. They are applied over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Some of the best known and most widely used sustainability measures include corporate sustainability reporting, Triple Bottom Line accounting, and estimates of the quality of sustainability governance for individual countries using the Global Green Economy Index (GGEI), Environmental Sustainability Index and Environmental Performance Index. An alternative approach, used by the United Nations Global Compact Cities Programme and explicitly critical of the triple-bottom-line approach is Circles of Sustainability. Environmental sustainability indicators: Global warming potential. Acidification potential. Ozone depletion potential. Aerosol optical depth. Eutrophication potential. Ionization radiation potential. Photochemical ozone potential. Waste treatment. Freshwater use. Energy resources use. Economic indicators: Gross domestic product. Trade balance. Local government income. Profit, value and tax. Investments. Social indicators: Employment generated. Equity. Health and safety. Education. Housing/living conditions. Community cohesion. Social security.
Circles of Sustainability is a method for understanding and assessing sustainability, and for managing projects directed towards socially sustainable outcomes. It is intended to handle 'seemingly intractable problems' such as outlined in sustainable development debates. The method is mostly used for cities and urban settlements. Image Graph.
Homeostasis is the property of a system to remain stable and relatively constant despite changes that would otherwise change, or disturb, the value of the variable. A variable (such as the concentration of a substance in solution, or its temperature etc.) is actively regulated (or controlled) inside a defined environment (mostly within a living organism’s body). Homeostasis in biology is the state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This dynamic state of equilibrium is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as that of the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: a receptor, integrating center, and effector. Hypothalamus.
Potential Theory is the study of harmonic functions, which is a twice continuously differentiable function.
Symbiosis - Gaia Philosophy - B-Corp - Adaptation - Resilience
Harmony is a mutually beneficial agreement that is compatible with reality.
Well Being is a contented state of being happy and healthy and prosperous.
Allostasis is the process of achieving stability, or homeostasis, through physiological or behavioral change. Allostasis is essential in order to maintain internal viability amid changing conditions. Organisms are designed to be efficient
Efficiency requires reciprocal trade-offs. Efficiency also requires being able to predict future needs. Such prediction requires each sensor to Adapt to the expected range of input. Prediction also demands that each effector adapt its output to the expected range of demand. Predictive regulation depends on behavior whilst neural mechanisms also adapt.
Autopoiesis refers to a system capable of reproducing and maintaining itself.
Ecological Stability is a type of stability in a continuum ranging from regeneration via resilience (returning quickly to a previous state), to constancy to persistence. Zero Point Energy.
Steady State is a system or process that is unchanging over time.
Sustainable is being able to Maintain a quality of Life at a certain rate or level without stealing resources from future generations, and without sacrificing lives or infringing on personal freedoms. Growing beyond nonrenewable production and consuming more then we need is not sustainable. We need to Live Life in Balance while providing necessities and support. Maintaining at length without interruption or weakening. Establishing or strengthening as with new evidence or facts. Able to be upheld or defended. Sustainability is the capacity to endure by working in harmony with biological systems so as to remain diverse and productive indefinitely. Progress - Forever - Fairness - Transient State
Biophilia hypothesis suggests that humans possess an innate tendency to seek connections with nature and other forms of life. Biophilia means the love of life or living systems. Biophilic design is a sustainable design strategy that incorporates reconnecting people with the natural environment. It may be seen as a necessary complement to Green Architecture, which decreases the environmental impact of the built world but does not address human reconnection with the natural world. Biophilia is defined as the inherent human inclination to affiliate with nature. The moral imperative of biophilia is that we cannot flourish as individuals or as a species without a compassionate and considerate relationship to the world beyond ourselves of which we are a part. Biophilic design, an extension of biophilia, incorporates natural materials, natural light, vegetation, nature views and other experiences of the natural world into the modern built environment.
Sustainability Science is examining the interactions between human, environmental, and engineered systems to understand and contribute to solutions for complex challenges that threaten the future of humanity and the integrity of the life support systems of the planet, such as climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution and land and water degradation.
Sustainable Development Goals are a collection of 17 global goals set by the United Nations General Assembly. Goal 1: No Poverty. Goal 2: Zero Hunger. Goal 3: Good Health and Well-Being. Goal 4: Quality Education. Goal 5: Gender Equality. Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation. Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy. Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth. Goal 9: Infrastructure, Industrialization. Goal 10: Inequality. Goal 11: Cities. Goal 12: Sustainable Consumption and Production. Goal 13: Climate Change. Goal 14: Oceans. Goal 15: Biodiversity, Forests, Desertification. Goal 16: Peace, Justice Strong Institutions. Goal 17: Partnerships.
Millennium Declaration - Five Pillars Development
Green Chemistry is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the designing of products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances. Whereas environmental chemistry focuses on the effects of polluting chemicals on nature, green chemistry focuses on technological approaches to preventing pollution and reducing consumption of nonrenewable resources.
Sustainable Management takes the concepts from sustainability and synthesizes them with the concepts of management. Sustainability has three branches: the environment, the needs of present and future generations, and the economy. Using these branches, it creates the ability to keep a system running indefinitely without depleting resources, maintaining economic viability, and also nourishing the needs of the present and future generations. From this definition, sustainable management has been created to be defined as the application of sustainable practices in the categories of businesses, agriculture, society, environment, and personal life by managing them in a way that will benefit current generations and future generations.
Sustainable Land Management refers to practices and technologies that aim to integrate the management of land, water, biodiversity, and other environmental resources to meet human needs while ensuring the long-term sustainability of ecosystem services and livelihoods. The term sustainable land management is used, for example, in regional planning and soil or environmental protection, as well as in property and estate management.
Environmental Management Scheme is a mechanism by which landowners and other individuals and bodies responsible for land management can be incentivized to manage their environment. Trees.
Green Infrastructure is a network providing the “ingredients” for solving urban and climatic challenges by building with nature. The main components of this approach include storm water management, climate adaptation, less heat stress, more biodiversity, food production, better air quality, sustainable energy production, clean water and healthy soils, as well as the more anthropocentric functions such as increased quality of life through recreation and providing shade and shelter in and around towns and cities. Green infrastructure also serves to provide an ecological framework for social, economic and environmental health of the surroundings.
Sustainable Architecture is architecture that seeks to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings by efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, and development space and the ecosystem at large. Sustainable architecture uses a conscious approach to energy and ecological conservation in the design of the built environment. The idea of sustainability, or ecological design, is to ensure that our actions and decisions today do not inhibit the opportunities of future generations.
Sustainability Dictionary - Green Living Tips - Biodiversity - Remediation (restore)
Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales. ICAEW was formed in 1880 to secure trust in business and that remains our mission. We ensure our members have the skills, knowledge and influence to help build economies that are sustainable, accountable and fair. ICAEW is playing its part by becoming carbon neutral this September, and stimulating the debate on global recovery.
Regenerative Agriculture is an approach to food and farming systems that rejects pesticides, artificial fertilizers and aims to regenerate topsoil, increase biodiversity, improve water cycles, enhance ecosystem services, increase resilience to climate fluctuation and strengthen the health and vitality of farming and ranching communities. Regenerative agriculture is based on applied research and thinking that integrates organic farming, permaculture, agroecology, agroforestry, restoration ecology, Keyline design and holistic management. On a regenerative farm biological production and ecological structure grow more complex over time. Yields increase while external inputs decrease.
Equilibrium
Equilibrium is a stable or balanced situation in which forces cancel one another. Equality of distribution. Symmetry.
Types of Equilibrium is a list of various types of equilibrium, the condition of a system in which all competing influences are Balanced.
Reflective Equilibrium is a state of balance or coherence among a set of beliefs arrived at by a process of deliberative mutual adjustment among general principles and particular judgments. An approach to justifying the principles of inductive logic.
Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics
Dynamic Equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction ceases to change its ratio of reactants/products, but substances move between the chemicals at an equal rate, meaning there is no net change It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. In thermodynamics a closed system is in thermodynamic equilibrium when reactions occur at such rates that the composition of the mixture does not change with time. Reactions do in fact occur, sometimes vigorously, but to such an extent that changes in composition cannot be observed. Equilibrium constants can be expressed in terms of the rate constants for elementary reactions.
Cynicism as a philosophy states that the purpose of life is to live in virtue, in agreement with nature. As reasoning creatures, people can gain happiness by rigorous training and by living in a way which is natural for themselves, rejecting conventional desires like greed, the abuse of power, or the pitfalls of fame. Instead, they pursue to lead a simple life free from most possessions and always looking for ways to reduce waste while at the same time maximizing productivity and always making sure that there is always some free time each day so that you can relax, live and explore.
Linear System typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications.
Overconsumption is a situation where resource use has outpaced the sustainable capacity of the ecosystem. A prolonged pattern of overconsumption leads to environmental degradation and the eventual loss of resource bases.
Building Sustainably
Sustainable Development is a process for meeting human development goals while sustaining the ability of natural systems to continue to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services upon which the economy and society depend.
Sustainable Development (united nations) - Limits to Growth - Progress Trap - Social Trap
Sustainable Habitat is an ecosystem that produces food and shelter for people and other organisms, without resource depletion and in such a way that no external waste is produced. Thus the habitat can continue into future tie without external infusions of resource. Such a sustainable habitat may evolve naturally or be produced under the influence of man. A sustainable habitat that is created and designed by human intelligence will mimic nature, if it is to be successful. Everything within it is connected to a complex array of organisms, physical resources and functions. Organisms from many different biomes can be brought together to fulfill various ecological niches. The term often refers to sustainable human habitats, which typically involve some form of green building or environmental planning.
Seventh Generation Sustainability is a concept that urges the current generation of humans to live and work for the benefit of the seventh generation into the future. It originated with the Iroquois - Great Law of the Iroquois - which holds appropriate to think seven generations ahead (about 140 years into the future) and decide whether the decisions they make today would benefit their children seven generations into the future. It is frequently associated with the modern, popular concept of environmental stewardship or 'sustainability'. Tomorrows Child - Environmental Sayings.
Green Building (smart homes) - Energy Plus Homes
Organic Architecture is a philosophy of architecture which promotes harmony between human habitation and the natural world. This is achieved through design approaches that aim to be sympathetic and well-integrated with a site, so buildings, furnishings, and surroundings become part of a unified, interrelated composition.
Sustainable City is a City designed with consideration of environmental impact, inhabited by people dedicated to minimization of required inputs of energy, water and food, and waste output of heat, air pollution - CO2, methane, and water pollution.
Sustainable Development (city management)
Principles of Intelligent Urbanism planning is composed of a set of ten axioms intended to guide the formulation of city plans and urban designs. These axioms include environmental sustainability, heritage conservation, appropriate technology, infrastructure-efficiency, placemaking, social access, transit-oriented development, regional integration, human scale, and institutional integrity.
Autonomous Building is a building designed to be operated independently from infrastructural support services such as the electric power grid, gas grid, municipal water systems, sewage treatment systems, storm drains, communication services, and in some cases, public roads. Advocates of autonomous building describe advantages that include reduced environmental impacts, increased security, and lower costs of ownership. Some cited advantages satisfy tenets of green building, not independence per se (see below). Off-grid buildings often rely very little on civil services and are therefore safer and more comfortable during civil disaster or military attacks. (Off-grid buildings would not lose power or water if public supplies were compromised for some reason.) Ecovillage.
Smart Growth is an urban planning and transportation theory that concentrates growth in compact walkable urban centers to avoid sprawl. It also advocates compact, transit-oriented, walkable, bicycle-friendly land use, including neighborhood schools, complete streets, and mixed-use development with a range of housing choices. The term 'smart growth' is particularly used in North America.
Urban Planning is a technical process concerned with the development and use of land, protection and use of the environment, public welfare, and the design of the urban environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks.
Alternative Natural Materials is a general term that describes natural materials like rock or adobe that are not as commonly in use as materials such as wood or iron. Alternative natural materials have many practical uses in areas such as sustainable architecture and engineering. The main purpose of using such materials is to minimize the negative effects that our built environment can have on the planet while increasing the efficiency and adaptability of the structures.
Sustainable Spaces - Sustainable Living - Sustainable Living Wise
Sustainable is living without the fear of running out of resources, or without the fear of future generations running out of resources. You have a life because other people in your past did not steal from you, so don't steal from people in the future.
Green Development is a land use planning concept that includes consideration of community-wide or regional environmental implications of development, as well as site-specific green building concepts. This includes city planning, environmental planning, architecture, landscape architecture and community building.
Green Economy is defined as an Economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. Green Building.
Ecological Design is a form of design that minimizes environmentally destructive impacts by integrating itself with living processes.
Environmental Design is the process of addressing surrounding environmental parameters when devising plans, programs, policies, buildings, or products.
Eco-Efficiency is creating more goods and services while using fewer resources and creating less waste and pollution.
Regenerative Design - Restoration
Green Schools (learning to live in harmony)
Viable System Model is a model of the organizational structure of any autonomous system capable of producing itself. A viable system is any system organized in such a way as to meet the demands of surviving in the changing environment. One of the prime features of systems that survive is that they are adaptable. The VSM expresses a model for a viable system, which is an abstracted cybernetic (regulation theory) description that is applicable to any organization that is a viable system and capable of autonomy
Ecological Economics refers to both a transdisciplinary and interdisciplinary field of academic research that aims to address the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems over time and space.
Differentiation Sociology is a term in system theory (found in sociology.) From the viewpoint of this theory, the principal feature of modern society is the increased process of system differentiation as a way of dealing with the complexity of its environment. This is accomplished through the creation of subsystems in an effort to copy within a system the difference between it and the environment. The differentiation process is a means of increasing the complexity of a system, since each subsystem can make different connections with other subsystems. It allows for more variation within the system in order to respond to variation in the environment. Increased variation facilitated by differentiation not only allows for better responses to the environment, but also allows for faster evolution (or perhaps sociocultural evolution), which is defined sociologically as a process of selection from variation; the more differentiation (and thus variation) that is available, the better the selection.
Low Impact Development (LID)
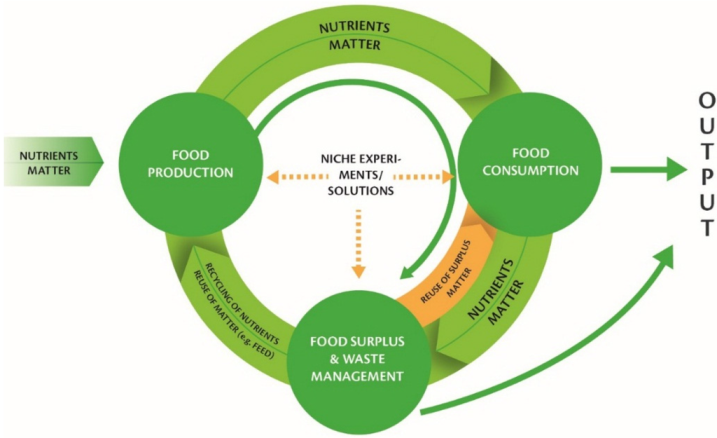
Low-impact Development
Waste
Low Impact Development
Sustainable Livelihoods
Gist Advisory
Teeb Web
Green Schools
Eco-innovation is the development of products and processes that contribute to sustainable development, applying the commercial application of knowledge to elicit direct or indirect ecological improvements. This includes a range of related ideas, from environmentally friendly technological advances to socially acceptable innovative paths towards sustainability. The field of research that seeks to explain how, why, and at what rate new "ecological" ideas and technology spread is called eco-innovation diffusion. EPA
Ecosophy is a philosophy of ecological harmony or equilibrium.
Building Ideas (intelligent buildings)
Environmental Governance is a concept in political ecology and environmental policy that advocates sustainability and sustainable development as the supreme consideration for managing all human activities—political, social and economic.
Environmental, Social and Corporate Governance refers to the three central factors in measuring the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment in a company or business.
Benefit Corporation is a type of for-profit corporate entity that also has a positive impact on society, workers, the community and the environment. Benefit corporations differ from traditional C corporations in purpose, accountability, and transparency.
International Institute for Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable Development U.N.
U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
The Higher Education Sustainability Initiative (HESI)
Providing higher education institutions with a unique interface between education, science, and policy making.
Sustainability Consultancy focused on climate change.
Putting Nature and Heart in Sustainable Cities
Association of University Leaders for a Sustainable Future
Conscious World Summit
Occupy Consciousness
Housing Types (ideas)
International Sustainable World Engineering
Energy and Environment Project Olympiad (I-SWEEEP)
The Solutions Project
Renewable Energy Plans
Energy (electricity and power)
Water - Farming
Sustainable Media
Sustainable Life Media
Terrapass
Clean Development Mechanism provides for emissions reduction projects which generate Certified Emission Reduction units (CERs) which may be traded in emissions trading scheme.
Renewable Resource is a natural resource which replenishes to overcome resource depletion caused by usage and consumption, either through biological reproduction or other naturally recurring processes in a finite amount of time in a human time scale. Renewable resources are a part of Earth's natural environment and the largest components of its ecosphere. A positive life cycle assessment is a key indicator of a resource's sustainability.
Sustainable Calculators
 Footprint
Actions
Footprint
ActionsCalculator
My Footprint
Climate Path
Carbon Calculator
Carbon Calculator
Calculator Bioregional
Ecological Footprint Calculator
Sustainable Food Calculator
Internal Subject Pages - Eco-Initiative Ideas - Sustainable Landscaping - Grass - Edible Landscapes - Eco-Friendly Tools - Green Innovation Ideas - Self-Manage - City Development and Management - Environment - Low Impact Living - Environmentally Friendly Living - Biodegradable Products - Toilets that are Earth Friendly.
Sustainable Farming
 Sustainable Agriculture is Farming in sustainable
ways based on an understanding of ecosystem services, the study of
relationships between organisms and their
environment. It has been defined
as "an integrated system of plant and animal production practices having a
site-specific application that will last over the long term", for example:
Satisfy human food and fiber needs, Enhance environmental quality and the
natural resource base upon which the agricultural economy depends, Make
the most efficient use of non-renewable resources and on-farm resources
and integrate, where appropriate, natural biological cycles and controls,
Sustain the economic viability of farm operations, Enhance the quality of
life for farmers and society as a whole.
Sustainable Agriculture is Farming in sustainable
ways based on an understanding of ecosystem services, the study of
relationships between organisms and their
environment. It has been defined
as "an integrated system of plant and animal production practices having a
site-specific application that will last over the long term", for example:
Satisfy human food and fiber needs, Enhance environmental quality and the
natural resource base upon which the agricultural economy depends, Make
the most efficient use of non-renewable resources and on-farm resources
and integrate, where appropriate, natural biological cycles and controls,
Sustain the economic viability of farm operations, Enhance the quality of
life for farmers and society as a whole.Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable Food Alliance
Sustainability for Food and Agriculture
Nat. Sustainable Agriculture
Permaculture
Holistic Agriculture Management is a systems thinking approach to managing resources that was originally developed by Allan Savory for reversing desertification. Trees.
Dry Land Farming
Holistic Management
Sustainable Education
Sustainability - Water
Sustainable Conservation
Environmentally Friendly Farming Practices used by nearly one third of world's farms while continuing to be Productive.
Closed System Farming or Closed Loop Agriculture is Farming Practice that recycles all nutrients and organic matter material back to the soil that it grew in. This forms part of an agricultural practice that preserves the nutrient and carbon levels within the soil and allows farming to be carried out on a sustainable basis. A farming system is defined as a population of individual farm systems that have broadly similar resource bases, enterprise patterns, household livelihoods and constraints, and for which similar development strategies and interventions would be appropriate.
Green Revolution refers to a set of research and development of technology transfer initiatives occurring between the 1930s and the late 1960s.
Ecology and Society
Syngenta Foundation
Sustainable Fare Food Service
Sustainable Table
Farm to Table Restaurants
Biodynamic Agriculture is a form of alternative agriculture very similar to organic farming, but which includes various esoteric concepts drawn from the ideas of Rudolf Steiner (1861–1925).
Biodynamics Non-Chemical Agricultural
Organic Pesticides
Global Agricultural Research Partnership
Climate Smart Village
Climate Smart Agricultural Practices
Land Institute Sustainable Agriculture
Quivira Coalition
Purdue Agriculture
MSU Metro Food
Minnesota Project
Carbon Ranching
American Farmers Network
Conservation Easement is a power invested in a qualified private land conservation organization (often called a "land trust") or government (municipal, county, state or federal) to constrain, as to a specified land area, the exercise of rights otherwise held by a landowner so as to achieve certain conservation purposes. It is an interest in real property established by agreement between a landowner and land trust or unit of government. The conservation easement "runs with the land," meaning it is applicable to both present and future owners of the land. As with other real property interests, the grant of conservation easement is recorded in the local land records; the grant becomes a part of the chain of title for the property.
GADCO integrated agri-food company focused on sustainable triple bottom-line returns in Africa.
Arcadia Center for Sustainable Food and Agriculture
Sustainably Agriculture could unlock 14 major business opportunities worth $2.3 trillion annually by 2030
Hjertefølgerne - The Heart Followers Video of a House built inside a Glass Dome in the Arctic climate.
No Waste Farming - Food Security - Food Waste
Subsistence - Organic
Sustainable Food Film is a vital investigation of the economic and environmental instability of America’s food system, from the agricultural issues we face — soil loss, water depletion, climate change, pesticide use — to the community of leaders who are determined to fix it. Sustainable is a film about the land, the people who work it and what must be done to sustain it for future generations. The narrative of the film focuses on Marty Travis from The Spence Farm, a seventh-generation farmer in central Illinois who watched his land and community fall victim to the pressures of big agribusiness. Determined to create a proud legacy for his son, Marty transforms his profitless wasteland and pioneers the sustainable food movement in Chicago. Sustainable travels the country seeking leadership and wisdom from some of the most forward thinking farmers like Bill Niman, Klaas Martens and John Kempf – heroes who challenge the ethical decisions behind industrial agriculture. It is a story of hope and transformation, about passion for the land and a promise that it can be restored to once again sustain us.
Sustainable Landscaping
 Sustainable Landscape Architecture is a category of sustainable design
concerned with the planning and design of
outdoor space. This can include
ecological, politically correct, social and economic aspects of
sustainability. For example, the design of a sustainable urban drainage
system can: improve habitats for
fauna and flora; improve recreational
facilities, because people love to be beside water; save money, because
building culverts is expensive and floods cause severe financial harm. The
design of a green roof or a roof garden can also contribute to the
sustainability of a landscape architecture project. The roof will help
manage surface water, provide for
wildlife and provide for recreation.
Sustainability appears to be a new addition to the traditional Vitruvian
objectives of the design process: a structure must be solid, useful, and
beautiful (firmitas, utilitas, venustas). But it can be seen as an aspect
of both solidity and usefulness: an outdoor space is likely to last longer
and give more usefulness to its owners if it requires low inputs of
energy, water, fertiliser etc., and if it produces fewer outputs of
noise,
pollution, surface water runoff etc.
Sustainable Landscape Architecture is a category of sustainable design
concerned with the planning and design of
outdoor space. This can include
ecological, politically correct, social and economic aspects of
sustainability. For example, the design of a sustainable urban drainage
system can: improve habitats for
fauna and flora; improve recreational
facilities, because people love to be beside water; save money, because
building culverts is expensive and floods cause severe financial harm. The
design of a green roof or a roof garden can also contribute to the
sustainability of a landscape architecture project. The roof will help
manage surface water, provide for
wildlife and provide for recreation.
Sustainability appears to be a new addition to the traditional Vitruvian
objectives of the design process: a structure must be solid, useful, and
beautiful (firmitas, utilitas, venustas). But it can be seen as an aspect
of both solidity and usefulness: an outdoor space is likely to last longer
and give more usefulness to its owners if it requires low inputs of
energy, water, fertiliser etc., and if it produces fewer outputs of
noise,
pollution, surface water runoff etc.Landscaping is a garden laid out for esthetic effect. To embellish with plants.
Landscape is an expanse of scenery that can be seen in a single view. A garden embellish with plants.
Garden is a yard or lawn adjoining a house or a plot of ground where plants are cultivated, like flowers, vegetables, fruits or herbs.
Landscape Planning is defined as an activity concerned with reconciling competing land uses while protecting natural processes and significant cultural and natural resources. Trees - Habitat - Fire-Safe Landscaping.
Permaculture - Low Maintenance, Less Water, Less Chemicals, Less Waste, Less Risk, More Beneficial, More Productive, Longer Life.
Landscape Architecture is the design of outdoor areas, landmarks, and structures to achieve environmental, social-behavioural, or aesthetic outcomes. It involves the systematic investigation of existing social, ecological, and soil conditions and processes in the landscape, and the design of interventions that will produce the desired outcome. The scope of the profession includes landscape design; site planning; storm water management; environmental restoration; parks and recreation planning; visual resource management; green infrastructure planning and provision; and private estate and residence landscape master planning and design; all at varying scales of design, planning and management. A practitioner in the profession of landscape architecture is called a landscape architect.
Body Image Mistakes - It's not always greener on the other side.
Landscape Ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. As a highly interdisciplinary field in systems science, landscape ecology integrates biophysical and analytical approaches with humanistic and holistic perspectives across the natural sciences and social sciences. Landscapes are spatially heterogeneous geographic areas characterized by diverse interacting patches or ecosystems, ranging from relatively natural terrestrial and aquatic systems such as forests, grasslands, and lakes to human-dominated environments including agricultural and urban settings. The most salient characteristics of landscape ecology are its emphasis on the relationship among pattern, process and scale, and its focus on broad-scale ecological and environmental issues. These necessitate the coupling between biophysical and socioeconomic sciences. Key research topics in landscape ecology include ecological flows in landscape mosaics, land use and land cover change, scaling, relating landscape pattern analysis with ecological processes, and landscape conservation and sustainability. Adaptive and Resilient Urban Habitats.
Sustainable Landscaping encompasses a variety of practices that have developed in response to environmental issues. These practices are used in every phase of landscaping, including design, construction, implementation and management of residential and commercial landscapes. Sustainable Landscape.
Sustainable Gardening includes the more specific sustainable landscapes, sustainable landscape design, sustainable landscaping, sustainable landscape architecture, resulting in sustainable sites. It comprises a disparate group of horticultural interests that can share the aims and objectives associated with the international post-1980s sustainable development and sustainability programs developed to address the fact that humans are now using natural biophysical resources faster than they can be replenished by nature. Included within this compass are those home gardeners, and members of the landscape and nursery industries, and municipal authorities, that integrate environmental, social, and economic factors to create a more sustainable future. Organic gardening and the use of native plants are integral to sustainable gardening.
Sustainable Planting is an approach to planting design and landscaping-gardening that balances the need for resource conservation with the needs of farmers pursuing their livelihood. The demand on resources, specifically land/crops, is constantly increasing due to the long human lifespan. It is a form of sustainable agriculture and, “it considers long-term as well as short-term economics because sustainability is readily defined as forever, that is, agricultural environments that are designed to promote endless regeneration”. The idea of sustainable planting can be dated back millennia, when the ancient Greeks and Chinese practised organic farming, the oldest method of farming. Later this practice was largely replaced by inorganic farming. In 1907 Franklin H. King in his book ``Farmers of Forty Centuries`` discussed the advantages of sustainable agriculture, and warned that sustainable practices would be vital to farming in the future.
Climate-Friendly Gardening is gardening in ways which reduce emissions of greenhouse gases from gardens and encourage the absorption of carbon dioxide by soils and plants in order to aid the reduction of global warming. To be a climate-friendly gardener means considering both what happens in a garden and the materials brought into it and the impact they have on land use and climate. It can also include garden features or activities in the garden that help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions elsewhere.
Landscape Epidemiology is used to analyze both risk patterns and environmental risk factors.
Agroecology is the study of ecological processes applied to agricultural production systems.
Landscape Archaeology is the study of the ways in which people in the past constructed and used the environment around them. Landscape archaeology is inherently multidisciplinary in its approach to the study of culture, and is used by pre-historical, classic, and historic archaeologists. The key feature that distinguishes landscape archaeology from other archaeological approaches to sites is that there is an explicit emphasis on the sites' relationships between material culture, human alteration of land/cultural modifications to landscape, and the natural environment. The study of landscape archaeology (also sometimes referred to as the archaeology of the cultural landscape) has evolved to include how landscapes were used to create and reinforce social inequality and to announce one's social status to the community at large.
Integrated Landscape Management is a way of managing a landscape that brings together multiple stakeholders, who collaborate to integrate policy and practice for their different land use objectives, with the purpose of achieving sustainable landscapes.
Low Maintenance Landscaping using Slow Growing Grass saves water, energy, time and resources.
Short Grass Seed (less mowing) - Draught Tolerant Grass
You can also Rent Goats to Mow your Lawn. - Goat Finder
Of course nothing better then a Fiskars 6208 17-Inch Staysharp Push Reel Lawn Mower
Push Mowers
You can also use Electric Cordless Rechargeable Lawn Mowers if your energy supplier offers renewable clean energy.
LA lawns lose lots of Water: 70 Billion Gallons a Year. In summer 2010, Los Angeles was losing about 100 gallons of water per person per day to the atmosphere through the evaporation and plant uptake of lawns and trees. Lawns accounted for 70 percent of the water loss, while trees accounted for 30 percent.
Also add an indoor Water Meter so that people are aware of their Water Use too.
Water Use Knowledge
Modern Home in Mexican Plateau Revives Ancient Water Harvest (youtube) - In the slope of Tepozteco mountain, Meztitla (Náhuatl for “place near the moon”), Casa Meztitla is in a never ending relationship with nature, harvesting/filtering water the way it was done in Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Surrounded by subtropical rainforest that remains untouched, its inhabitants believe that what the land gives should be returned to the property. In an area with no public water supply and a rainy season that lasts only from July through September/October, the home uses only the water it can capture and reuse from the property. Water flows through an intricate system of filtration. Two main (or three including the pool) water reservoirs exist: the potable water reservoir covered by the grass patio, and the open-air reservoir (using aquatic plants, fish and a pump) for irrigation which resembles “cenotes”, open air water sources sacred to Mayans. The water system relies on gravity and can store 30,000 liters; it provides enough water for the house all year round. Conceptually, this storm water management captures every drop of rain that touches the property (3800 square meters), uses it in different ways, and does not let a drop out. The result is abundant water and land that is constantly irrigated in a region with seasonal droughts. EDAA - Architects - Luis Arturo García.
Low Impact Development (LID)
Low-impact Development describes planning and engineering design approach to managing storm water runoff.
Waste - Low Impact Development
Over Development Dangers
Dry Land Farming
Organic Lawn Fertilizer
Organic Land Care
Organic Lawncare 101 - PDF
Safe Lawns
Natura Lawn
Pesticides
Environmentally Friendly Lawn Care Services
Clean Air Lawn Care
Low-Maintenance Landscaping
Landscapes - ideas
Low Maintenance Plants
Green Landscaping
Eco-Landscaping
Ecology Landscape
Ecological Landscape Alliance
Land Care Network
American Nursery & Landscape Association
American Society of Landscape Architects
Northwest Nature-Scapes runs his business from a three-wheeled electric bicycle. Battery backpack becomes the power source for his power tools, electric mower and hedge trimmer.
Organic Food - Organic Farming - Composting - Soil Testing
Biodiesel Lawn Mowers. There are 89 million gas lawnmowers and related equipment in the U.S.. Each weekend 54 million people mow their lawns Burning 800 Million Gallons of Gasoline a year and Spilling 17 million gallons a gas a year. Operating a lawn mower one hour could create the same pollution levels as driving a new car 340 miles. A single gasoline lawn mower could create more pollution than 73 new cars.
Hugr Systems - Toro Biodiesel
Biodiesel Fuels - Fuel Vaporizers
Lawnmower is a machine utilizing one or more revolving blades to cut a grass surface to an even height.
Weather Monitoring
Western Land Owners Improving the ecological health and economic prosperity of working lands in the American West. The Western Landowners Alliance advances policies and practices that sustain working lands, connected landscapes, and native species.
"Life is naturally sustainable in many ways because it has to be. But if you're living an unsustainable life filled with waste and abuse, then you are an ignorant scumbag criminal who is a threat to life. So what's your excuse moron? And why would you want to be an as*hole to every person and every living thing on Earth?"
