BK101
Knowledge Base
Human Reproduction - Child Birth
Pre-Natal Care - Giving Birth - Feeding - Child Development - Sleep Training - Crying
Toxins (poisons)
 Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy,
Childbirth, and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics
is combined with gynaecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and
gynaecology (OB/GYN).
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy,
Childbirth, and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics
is combined with gynaecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and
gynaecology (OB/GYN). Gynaecology is the medical practice dealing with the health of the female reproductive systems (vagina, uterus, and ovaries) and the breasts.
Procreation is the sexual activity of conceiving and bearing offspring.
Conception is the act of becoming pregnant by the fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon. The creation of something in the mind or an abstract or general idea inferred or derived from specific instances. The event that occurred at the beginning of something.
Human Reproduction is any form of sexual reproduction resulting in human fertilization, typically involving sexual intercourse between a man and a woman. During sexual intercourse, the interaction between the male and female reproductive systems results in fertilization of the woman's ovum by the man's sperm.
Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parents". Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual and Sexual. Seeds - Self-Assembly.
Reproductive System is a system of sex organs within an organism which work together for the purpose of sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring. Drug Dangers.
Sexual Reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction.
Chromosome (DNA)
Reproductive Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity, reproductive health, or sexual health/hygiene, addresses the reproductive processes, functions and system at all stages of life. Reproductive health implies that people are able to have a responsible, satisfying and safer sex life and that they have the capability to reproduce and the freedom to decide if, when and how often to do so. One interpretation of this implies that men and women ought to be informed of and to have access to safe, effective, affordable and acceptable methods of birth control; also access to appropriate health care services of sexual, reproductive medicine and implementation of health education programs to stress the importance of women to go safely through pregnancy and childbirth could provide couples with the best chance of having a healthy infant. Individuals do face inequalities in reproductive health services. Inequalities vary based on socioeconomic status, education level, age, ethnicity, religion, and resources available in their environment. It is possible for example, that low income individuals lack the resources for appropriate health services and the knowledge to know what is appropriate for maintaining reproductive health.
Proactive community case management and child survival in periurban Mali. Imagine a world in which pregnant women and little kids get regular home visits from a health worker, and free health care. The leading causes of maternal, newborn and child death are curable.
Generation is the act of producing an offspring. In kinship terminology, it is a structural term designating the parent-child relationship. It is also known as biogenesis, reproduction, or procreation in the biological sciences.
Biological Imperative - Social Influences
Family Planning is the practice of controlling the number of children in a family and the intervals between their births, particularly by means of artificial contraception or voluntary sterilization. Because "family" is included in the concept's name, consideration of a couple's desire to bear children, in the context of a family unit, is often considered primarily. Contemporary notions of family planning, however, tend to place a woman and her childbearing decisions at the center of the discussion, as notions of women's empowerment and reproductive autonomy have gained traction in many parts of the world. Family planning may involve consideration of the number of children a woman wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, as well as the age at which she wishes to have them. These matters are obviously influenced by external factors such as marital situation, career considerations, financial position, any disabilities that may affect their ability to have children and raise them, besides many other considerations. If sexually active, family planning may involve the use of contraception and other techniques to control the timing of reproduction. Other techniques commonly used include sexuality education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and management, and infertility management. Family planning is sometimes used as a synonym or euphemism for access to and the use of contraception. However, it often involves methods and practices in addition to contraception. Additionally, there are many who might wish to use contraception but are not, necessarily, planning a family (e.g., unmarried adolescents, young married couples delaying childbearing while building a career); family planning has become a catch-all phrase for much of the work undertaken in this realm. It is most usually applied to a female-male couple who wish to limit the number of children they have and/or to control the timing of pregnancy (also known as spacing children). Family planning may encompass sterilization, as well as abortion. Family planning services are defined as "educational, comprehensive medical or social activities which enable individuals, including minors, to determine freely the number and spacing of their children and to select the means by which this may be achieved".
Global birth season study links environment with disease risk. In utero environmental exposures may explain why birth month correlates with some diseases. Studies have shown that babies born in winter tend to have a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes at some point, while fall babies have a greater lifetime risk of depression. Data scientists have found that a woman's exposure to certain seasonal or environmental factors during pregnancy may affect her offspring's lifetime disease risk.
Child Development - Brain Health
Prenatal Diagnosis are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting anatomic and physiologic problems with the zygote, embryo, or fetus as early as possible, either before gestation even starts (as in preimplantation genetic diagnosis) or as early in gestation as practicable. They use medical tests to detect problems such as neural tube defects, chromosome abnormalities, and gene mutations that would lead to genetic disorders and birth defects, such as spina bifida, cleft palate, Tay–Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and fragile X syndrome. The screening focuses on finding problems among a large population with affordable and noninvasive methods, whereas the diagnosis focuses on pursuing additional detailed information once a particular problem has been found, and can sometimes be more invasive. Screening can also be used for prenatal sex discernment. Common testing procedures include amniocentesis, ultrasonography including nuchal translucency ultrasound, serum biomarker testing, or genetic screening. In some cases, the tests are administered to determine if the fetus will be aborted, though physicians and patients also find it useful to diagnose high-risk pregnancies early so that delivery can be scheduled in a tertiary care hospital where the baby can receive appropriate care.
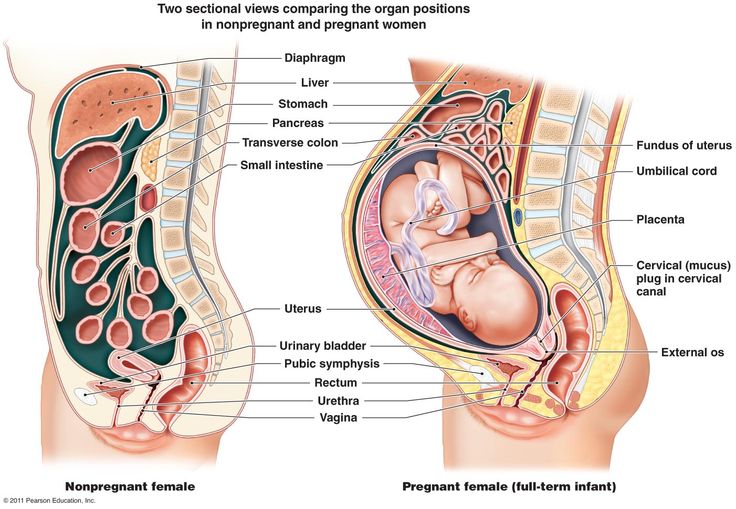
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops inside a woman. Birth.
Womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals, including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, (uterine tubes) depending on the species. It is within the uterus that the fetus develops during gestation, usually developing completely in placental mammals such as humans and partially in marsupials such as kangaroos and opossums. Female Body.
Hysterosalpingography is a radiologic procedure to investigate the shape of the uterine cavity and the shape and patency of the fallopian tubes. It injects a radio-opaque material into the cervical canal and usually fluoroscopy with image intensification. A normal result shows the filling of the uterine cavity and the bilateral filling of the fallopian tube with the injection material. To demonstrate tubal rupture, spillage of the material into the peritoneal cavity needs to be observed
Prenatal Stress Changes Brain Connectivity In-Utero, meaning "in the womb". Child Development Effects.
Embryo
Embryo is an early stage of development of a multicellular diploid eukaryotic organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, an embryo develops from a zygote, the single cell resulting from the fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The zygote possesses half the DNA of each of its two parents. In plants, animals, and some protists, the zygote will begin to divide by mitosis to produce a multicellular organism. The result of this process is an embryo. In humans, a pregnancy is generally considered to be in the embryonic stage of development between the fifth and the eleventh weeks after fertilization, and is expressed as a fetus from the twelfth week.
Ovum is a mature female reproductive cell which can divide to give rise to an embryo usually only after fertilization by a male cell.
Female Gametes are also called eggs or ova. They are created during the cellular reproduction process known as meiosis. The resulting gamete cell is a haploid cell. When the two haploid cells, the egg and sperm, fuse together during fertilization, the result is a diploid cell called a zygote.
Gamete is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization (conception) in organisms that sexually reproduce. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum (or egg)—and a male produces the smaller tadpole-like type—called a sperm. In short a gamete is an egg (female gamete) or a sperm (male gamete). This is an example of anisogamy or heterogamy, the condition in which females and males produce gametes of different sizes (this is the case in humans; the human ovum has approximately 100,000 times the volume of a single human sperm cell). In contrast, isogamy is the state of gametes from both sexes being the same size and shape, and given arbitrary designators for mating type. The name gamete was introduced by the Austrian biologist Gregor Mendel. Gametes carry half the genetic information of an individual, one ploidy of each type, and are created through meiosis. Oogenesis is the process of female gamete formation in animals. This process involves meiosis (including meiotic recombination) occurring in the diploid primary oocyte to produce the haploid ovum (gamete). Spermatogenesis is the process of male gamete formation in animals. This process also involves meiosis (including meiotic recombination) occurring in the diploid primary spermatocyte to produce the haploid spermatozoon (gamete).
Oogenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further development when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated in the embryonic stage.
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo forms and develops. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the egg cell (ovum) by a sperm cell, (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum is referred to as a zygote, a single diploid cell. The zygote undergoes mitotic divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage) and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo. Although embryogenesis occurs in both animal and plant development, this article addresses the common features among different animals, with some emphasis on the embryonic development of vertebrates and mammals.
Embryonic Development is the process by which the embryo forms and develops. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages.
Fetal Development is the process in which a human embryo and later fetus (or foetus) develops during pregnancy, from fertilization until birth. Often, the terms fetal development, or embryology are used in a similar sense.
How Tissues and Organs are Sculpted during Embryogenesis. Cells coordinate by exchanging biochemical signals, but they also hold to and push on each other to build the body structures we need to live, such as the eyes, lungs and heart. And, as it turns out, sculpting the embryo is not far from glass molding or 3D printing. A fluid-to-solid jamming transition underlies vertebrate body axis elongation. Cell collectives switch from fluid to solid states in a controlled manner to build the vertebrate embryo, in a way similar to how we mold glass into vases or 3D print our favorite items. Or, if you like, we 3D print ourselves, from the inside.
Egg Cell or ovum, is the female reproductive cell (gamete) in oogamous organisms. The egg cell is typically not capable of active movement, and it is much larger (visible to the naked eye) than the motile sperm cells. When egg and sperm fuse, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism. Diploid Cells have two homologous copies of each chromosome, usually one from the mother and one from the father. All or nearly all mammals are diploid organisms.
Placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, thermo-regulation, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply; to fight against internal infection; and to produce hormones which support pregnancy. The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to growing fetuses and removes waste products from the fetus's blood. The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus, and the fetus's umbilical cord develops from the placenta. These organs connect the mother and the fetus.
Placenta defects a factor in prenatal deaths. Almost 70 percent of 103 genes linked to prenatal death affect the placenta.
Pre-Natal Development - Prenatal Development
Prenatal Care is a type of preventive healthcare with the goal of providing regular check-ups that allow doctors or midwives to treat and prevent potential health problems throughout the course of the pregnancy while promoting healthy lifestyles that benefit both mother and child, also known as antenatal care. During check-ups, pregnant women receive medical information over maternal physiological changes in pregnancy, biological changes, and prenatal nutrition including prenatal vitamins. Recommendations on management and healthy lifestyle changes are also made during regular check-ups. The availability of routine prenatal care, including prenatal screening and diagnosis, has played a part in reducing the frequency of maternal death, miscarriages, birth defects, low birth weight, neonatal infections and other preventable health problems.
Antenatal Care is the care you receive from healthcare professionals during your pregnancy. This care can be provided by a team that can include a doctor, a midwife, and usually with a doctor who specializes in pregnancy and birth (an obstetrician).
Antenatal Education Programs for Childbirth or Parenthood
Rethinking Childbirth Education could save $97 Million P.A..
Exercises for Pregnant Women
Complications of Pregnancy are health problems that are caused by pregnancy. In the immediate postpartum period, 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem. Long term health problems (persisting after 6 months postpartum) are reported by 31% of women. Severe complications of pregnancy are present in 1.6% of mothers in the US and in 1.5% of mothers in Canada. The relationship between age and complications of pregnancy are now being researched with greater impetus.
Symptoms and Discomforts of Pregnancy are those presentations and conditions that result from pregnancy but do not significantly interfere with activities of daily living or pose any significant threat to the health of the mother or baby, in contrast to pregnancy complications.
Morning Sickness is a symptom of pregnancy that involves nausea or vomiting. Despite the name, nausea or vomiting can occur at any time during the day. Typically these symptoms occur between the 4th and 16th week of pregnancy. About 10% of women still have symptoms after the 20th week of pregnancy. A severe form of the condition is known as hyperemesis gravidarum and results in weight loss.
Hyperemesis Gravidarum is a pregnancy complication that is characterized by severe nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and possibly dehydration. Signs and symptoms may also include vomiting several times a day and feeling faint. Hypremesis geavidarum is considered more severe than morning sickness. Often symptoms get better after the 20th week of pregnancy but may last the entire pregnancy duration.
Postpartum-Depression. Your body and mind go through many changes during and after pregnancy. If you feel empty, emotionless, or sad all or most of the time for longer than 2 weeks during or after pregnancy, reach out for help. If you feel like you don’t love or care for your baby, you might have postpartum depression. Treatment for depression, such as therapy or medicine, works and will help you and your baby be as healthy as possible in the future.
Postpartum Psychosis is a rare illness, compared to the rates of postpartum depression or anxiety. It occurs in approximately 1 to 2 out of every 1,000 deliveries, or approximately .1 -.2% of births. The onset is usually sudden, most often within the first 2 weeks postpartum. Symptoms of postpartum psychosis can include: Delusions or strange beliefs. Hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there). Feeling very irritated. Hyperactivity. Decreased need for or inability to sleep. Paranoia and suspiciousness. Rapid mood swings. Difficulty communicating at times.
Reproductive Health and Rights in U.S. Under Assault
What to Expect
Universal Access to Family Planning Information, Education, and Services
Reproductive Technology (women who need help getting pregnant)
Premature Births - Populations
Many Babies are Born around 8:00 A.M. Info-Graph - Info-Graph - Info-Graph.
The Urge to Have a Baby
Biological Imperative are the needs of living organisms required to perpetuate their existence to survive. What's the difference between Biological Imperative and the urge to have a baby?
We have all been given these sexual urges and animal instincts to procreate, because that is something that animals need to do in order for the species to survive by reproduction. Other animal species on our planet also share these same types of instincts, so it's not unusual. If these instincts were not given to us we would not reproduce as much and we would most likely go extinct. But luckily humans also have another very influential drive called pleasure, which also helps to encourage reproduction. But even if we control our instincts, Humans can also be more aware of their surroundings so they don't even need instincts or pleasure in order to reproduce because they feel it is simply a need. So now that some humans are becoming more educated and more aware of of their choices and options, some people are now making better choices and also have a much better understanding of self-control. So does this mean that our species will go extinct because people are now making better choices and better decisions? No. Because fully educated people will be totally aware that their species needs to reproduce in order to survive, so people will always be having babies, maybe just not as much, or at the least, not more then the planet can sustain.
Too many women believe that if they have a child their world will be better. It's not the child that will make a mothers life better, it's the mother who has to make her own life better. Don't put the responsibility on the child to make your life better, it's not fair, and it's also not a very good plan. It's the Mothers who are responsible for making their own lives better, not their children. Learn how to make life better, then share that knowledge with your children. Then you will all share a good life together.
More than 200 million women worldwide want contraceptives, but don't have access to them, according to an editorial published in the British medical journal, Lancet. That results in 76 million unintended pregnancies every year.
Unsafe Abortions Kill 70,000 Annually.
How Many People Can Live on Earth Sustainably?
AAn 18th-century Russian woman holds the world record for having birthed the most children: 69, which she had over the course of 27 pregnancies that included sixteen pairs of twins, seven sets of triplets, and four sets of quadruplets. But she's outdone by the male record-holder for most kids, a Moroccan emperor who, according to the Guinness Book of World Records, sired "at least 342 daughters and 525 sons, and by 1721, he was reputed to have 700 male descendants."
Reproductive Assistance - Help Getting Pregnant
Reproductive Medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with prevention, diagnosis and management of reproductive problems; goals include improving or maintaining reproductive health and allowing people to have children at a time of their choosing. It is founded on knowledge of reproductive anatomy, physiology, and endocrinology, and incorporates relevant aspects of molecular biology, biochemistry and pathology.
ASRM
Fertility is the natural capability to produce offspring. As a measure, fertility rate is the number of offspring born per mating pair, individual or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction (influenced by gamete production, fertilization and carrying a pregnancy to term). A lack of fertility is infertility while a lack of fecundity would be called sterility. Human fertility depends on factors of nutrition, sexual behavior, consanguinity, culture, instinct, endocrinology, timing, economics, way of life, and emotions.
Assisted Reproductive Technology is the technology used to achieve pregnancy in procedures such as fertility medication, in vitro fertilization and surrogacy. It is reproductive technology used primarily for infertility treatments, and is also known as fertility treatment. It mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility, and may also include intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and cryopreservation. Some forms of ART are also used with regard to fertile couples for genetic reasons (preimplantation genetic diagnosis). ART is also used for couples who are discordant for certain communicable diseases; for example, HIV to reduce the risk of infection when a pregnancy is desired.
Embryo Donation is a form of third party reproduction. It is defined as the giving—generally without compensation—of embryos remaining after one couple's in vitro fertilisation to either another person or couple for implantation or to research. Where it is given for the purpose of implantation, the donation is followed by the placement of those embryos into the recipient woman's uterus to facilitate pregnancy and childbirth in the recipient. The resulting child is considered the child of the woman who carries it and gives birth, and not the child of the donor. This is the same principle as is followed in egg donation or sperm donation. Most often, the embryos are donated after the woman for whom they were originally created has successfully carried one or more pregnancies to term.
Artificial insemination is the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female's uterus or cervix for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse. It is a fertility treatment for humans, and is common practice in animal breeding, including dairy cattle (see Frozen bovine semen) and pigs.
In Vitro Fertilization is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) commonly referred to as IVF. IVF is the process of fertilization by extracting eggs, retrieving a sperm sample, and then manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory dish. The embryo(s) is then transferred to the uterus.
Third Party Reproduction is any human reproduction in which DNA or gestation is provided by a third party or donor other than the one or two parents who will raise the resulting child. This goes beyond the traditional father–mother model, and the third party's involvement is limited to the reproductive process and does not extend into the raising of the child. Third-party reproduction is used by couples unable to reproduce where they would otherwise be unable to do so, by same-sex couples, and by men and women without a partner. Where donor gametes are provided by a donor, the donor will be a biological parent of the resulting child, but in third party reproduction, he or she will not be the caring parent. One can distinguish several categories, some of which may be combined: Sperm donation. A donor provides sperm in order to father a child for a third-party female. Egg donation. A donor provides ova to a woman or couple in order for the egg to be fertilized and implanted in the recipient woman. Spindle transfer. A third party's mitochondrial DNA is transferred to the future mother's ovum. This is used to prevent mitochondrial disease. Embryo donation with embryos which were originally created for a genetic mother's assisted pregnancy. Once the genetic mother has completed her own treatment, she may donate unused embryos for use by a third party. or where embryos are specifically created for donation using donor eggs and donor sperm. Embryo adoption. Embryos created during a donor's assisted pregnancy are adopted to be implanted in a third party recipient. Surrogacy. An embryo is gestated in a third party's uterus (traditional surrogacy) or a woman is inseminated in order to gestate a child for a third party (straight surrogacy). Pregnancy is typically initiated by artificial insemination in the case of sperm donation and by embryo transfer after in vitro fertilisation (IVF) in the case of egg donation, embryo donation, and surrogacy. Thus a child can have a genetic and social (non-genetic, non-biological) father, and a genetic, gestational, and social (non-biological) mother, and any combinations thereof. Theoretically a child thus could have 5 parents. A donor treatment is where gametes, i.e. sperm, ova or embryos are provided, or 'donated' by a third party for the purpose of third-party reproduction.
Pregnancy Problems and Risks
Abdominal Pregnancy can be regarded as a form of an ectopic pregnancy where the embryo or fetus is growing and developing outside the womb in the abdomen, but not in the Fallopian tube, ovary or broad ligament.
The 46 Year Pregnancy - My Shocking Story (youtube)
Lithopedion or stone baby, is a rare phenomenon which occurs most commonly when a fetus dies during an abdominal pregnancy, is too large to be reabsorbed by the body, and calcifies on the outside as part of a maternal foreign body reaction, shielding the mother's body from the dead tissue of the fetus and preventing infection.
Teenage Pregnancy is pregnancy in females under the age of 20.[2] A female can become pregnant from sexual intercourse after she has begun to ovulate, which can be before her first menstrual period (menarche) but usually occurs after the onset of her periods. In well-nourished females, menarche usually takes place around the age of 12 or 13.
State Health Facts - Teen Birth Facts
Child Abandonment is the practice of relinquishing interests and claims over one's offspring in an extralegal way with the intent of never again resuming or reasserting guardianship over them. Causes include many social and cultural factors as well as mental illness. An abandoned child is called a foundling (as opposed to a runaway or an orphan). Baby dumping refers to parents abandoning or discarding a child younger than 12 months in a public or private place with the intent of ending their guardianship over them. It is also known as rehoming in cases of failed adoptions.
Infanticide is the intentional killing of infants. Parental infanticide researchers have found that mothers are far more likely than fathers to be the perpetrator for neonaticide and slightly more likely to commit infanticide in general. In many past societies, certain forms of infanticide were considered permissible. In India female infanticide is more common than the killing of male offspring, due to sex-selective infanticide. In China for example, the sex gap between males and females aged 0–19 years old was estimated to be 25 million in 2010 by the United Nations Population Fund. In English law infanticide is established as a distinct offence by the Infanticide Acts. Defined as the killing of a child under 12 months of age by their mother, the effect of the Acts are to establish a partial defence to charges of murder.
Abortion - Adoption
Surrogacy is a method or agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person or persons, who will become the newborn child's parent(s) after birth. Intended parents may seek a surrogacy arrangement when pregnancy is medically impossible, pregnancy risks present an unacceptable danger to the mother's health, or a man or male couple wish to have a child. Monetary compensation may or may not be involved in these arrangements. If the surrogate receives money for the surrogacy the arrangement is considered commercial surrogacy; if she receives no compensation beyond reimbursement of medical and other reasonable expenses it is referred to as altruistic. The legality and costs of surrogacy vary widely between jurisdictions, sometimes resulting in interstate or international surrogacy arrangements. There are laws in some countries which restrict and regulate surrogacy and the consequences of surrogacy. Some couples or individuals wanting a child in this manner but who live in a jurisdiction which does not permit surrogacy may travel to another jurisdiction which permits it. (See surrogacy laws by country and fertility tourism).
Population Growth
Though the teen birth rate has decreased, in 2010, teens in the US between the ages of 15 and 19, had a birth rate of 37.9 per 1,000 women. Russia was 30.2 per 1,000, Britain has 25 per 1,000 and Switzerland has 4.3 births per 1,000 teen women.
Birth Rates for Teens (PDF)
The United States Department of Agriculture today that if you had a child in 2012, it'll cost you $241,080 to raise him or her for next 17 years, and If you adjust it for inflation, that number soars to $301,970. (why is this an ignorant statement?)
Everyone should understand the requirements that a person needs in order to Adopt a Child or to be a Foster Parent or Surrogate. These requirements will give you a little insight on what it takes to be a parent and to start a family. It doesn't cover everything but it makes you aware of how much you should know. Even if you were a women wanting to donate her eggs, you would still need to have certain requirements in order to be a donor. The same goes for a man, if a man wants to donate his sperm to a sperm bank he would have to have certain requirements before he is even excepted. So it makes you wonder, what requirements do you need to start life, and what requirements do you need to be responsible for a child's care? Should you get a DNA Test?
The world's single greatest killer of pregnant women is Malaria.
Mosquito Net offers protection against mosquitos, flies, and other insects, and thus against the diseases they may carry. Examples include malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, zika virus and various forms of encephalitis, including the West Nile virus. To be effective the mesh of a mosquito net must be fine enough to exclude such insects without reducing visibility or air flow to unacceptable levels. It is possible to increase the effectiveness of a mosquito net greatly by treating it with an appropriate insecticide or mosquito repellant. Research has shown mosquito nets to be an extremely effective method of malaria prevention, averting approximately 451 million cases of malaria over the period 2000–2015.
Private Sleeping Area
Freedom of Choice Act was a bill in the 110th United States Congress which "declares that it is the policy of the United States that every woman has the fundamental right to choose to bear a child; terminate a pregnancy prior to fetal viability; or terminate a pregnancy after viability when necessary to protect her life or her health." It prohibits a federal, state, or local governmental entity from denying or interfering with a woman's right to exercise such choices; or discriminating against the exercise of those rights in the regulation or provision of benefits, facilities, services, or information. Provides that such prohibition shall apply retroactively. It also authorizes an individual aggrieved by a violation of this Act to obtain appropriate relief, including relief against a governmental entity, in a civil action." Earlier versions of the bill were introduced in 1989 and 1993.
Parental DNA Testing (heredity)
Marriage License - Wedding Info - Dowry
Family and Medical Leave Act is a United States labor law requiring covered employers to provide employees with job-protected and unpaid leave for qualified medical and family reasons. These include pregnancy, adoption, foster care placement of a child, personal or family illness, or family military leave. The FMLA is administered by the Wage and Hour Division of the United States Department of Labor.
Why are Blood Tests mandatory before you get married?
Of the 27 industrialized countries studied by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the U.S. had 25.8 percent of children being raised by a Single Parent, compared with an average of 14.9 percent across the other countries.
Child Info - 101 East : China: Unnatural Selection (youtube)
Legitimacy is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, illegitimacy (or bastardy) has been the status of a child born outside marriage, such a child being known as a bastard, or love child, when such a distinction has been made from other children.
Single Parent is a parent that parents alone without the other parent's support, meaning this particular parent is the only parent to the child, responsible for all financial, material, and emotional needs. It means there is an absence of the other parent as opposed to a co-parent, meaning that the parent is not the only parent regardless of whether or not they are a couple. Of course, this definition is loosely true. There is no true definition of what "single parent" means and is more based on opinions. Sometimes, one finds themselves in a single-parent family structure that has arisen due to death of the partner, intentional artificial insemination, or unplanned pregnancy.
Mommy Pregnancy Exercises
Pregnancy Exercise Guidelines - Pregnancy Exercises
Exercise During Pregnancy - Pregnancy Exercise
Exercise Tips
Diastasis Recti is a gap of roughly 2.7 cm or greater between the two sides of the rectus abdominis muscle.
Exercises: The following exercises are often recommended to help build abdominal strength, which may or may not help reduce the size of diastasis recti.
Core contraction – In a seated position, place both hands on abdominal muscles. Take small controlled breaths. Slowly contract the abdominal muscles, pulling them straight back towards the spine. Hold the contraction for 30 seconds, while maintaining the controlled breathing. Complete 10 repetitions.
Seated squeeze - Again in a seated position, place one hand above the belly button, and the other below the belly button. With controlled breaths, with a mid-way starting point, pull the abdominals back toward the spine, hold for 2 seconds and return to the mid-way point. Complete 100 repetitions.
Head lift – In a lying down position, knees bent at 90° angle, feet flat, slowly lift the head, chin toward your chest, (concentrate on isolation of the abdominals to prevent hip-flexors from being engaged), slowly contract abdominals toward floor, hold for two seconds, lower head to starting position for 2 seconds. Complete 10 repetitions. Upright push-up – A stand-up push-up against the wall, with feet together arms-length away from wall, place hands flat against the wall, contract abdominal muscles toward spine, lean body towards wall, with elbows bent downward close to body, pull abdominal muscles in further, with controlled breathing. Release muscles as you push back to starting position. Complete 20 repetitions.
Squat against the wall – Also known as a seated squat, stand with back against the wall, feet out in front of body, slowly lower body to a seated position so knees are bent at a 90° angle, contracting abs toward spine as you raise body back to standing position. Optionally, this exercise can also be done using an exercise ball placed against the wall and the lower back. Complete 20 repetitions.
Squat with squeeze – A variation to the "squat against the wall" is to place a small resistance ball between the knees, and squeeze the ball while lowering the body to the seated position. Complete 20 repetitions.
Avoid Crossover crunches or bicycle crunches because they splay your abs apart in so many ways.
It is also noted that incorrect exercises, including crunches, can increase the distasis recti separation. All corrective exercises should be in the form of pulling in of the abdominal muscles rather than a pushing of them outwards. Consultation of a professional physiotherapist is recommended for correct exercise routines. In addition to the above exercises, the Touro College study concluded the "quadruped" position yielded the most effective results. A quadruped position is defined as "a human whose body weight is supported by both arms as well as both legs". In this position, the subject would start with a flat back, then slowly tilt the head down, and arch the back, contracting the abdominal muscles towards the spine, holding this position for 5 seconds, then releasing back to starting position. Complete two sets of 10 repetitions.
Toxins - Exposures
Poisons that Parents and Children should Avoid - Prenatal Exposures
 Environmental Toxicants and
Fetal Development is the impact
of different toxic substances from the environment on the development of
the fetus. This article deals with potential adverse effects of
environmental toxicants on the prenatal development of both the embryo or
fetus, as well as pregnancy complications. The human embryo or fetus is
relatively susceptible to impact from adverse conditions within the
mother's environment. Substandard fetal conditions often cause various
degrees of developmental delays, both physical and
mental, for the growing
baby. Although some variables do occur as a result of genetic conditions
pertaining to the father, a great many are directly brought about from
environmental toxins that the mother is exposed to. Various toxins pose a
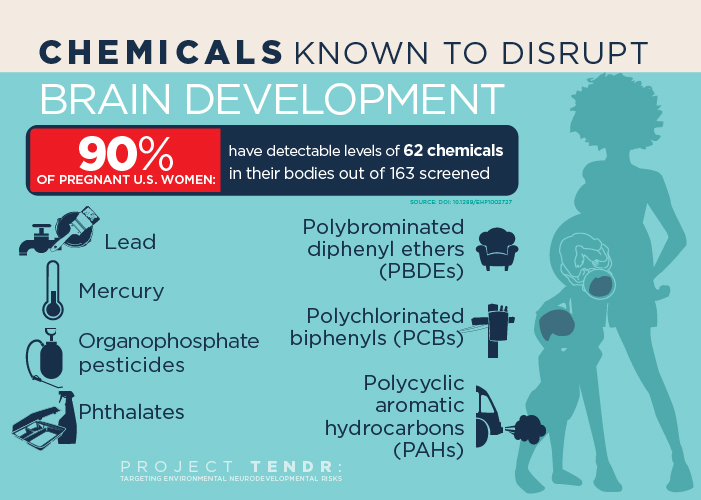
significant hazard to fetuses during development. A 2011 study found that
virtually all US pregnant women carry multiple chemicals, including some
banned since the 1970s, in their bodies. Researchers detected
polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides,
perfluorinated
compounds, phenols, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, phthalates, polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons, perchlorate PBDEs, compounds used as flame
retardants, and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), a pesticide banned
in the United States in 1972, in the bodies of 99 to 100 percent of the
pregnant women they tested. Bisphenol A (BPA) was identified in 96 percent
of the women surveyed. Several of the chemicals were at the same
concentrations that have been associated with negative effects in children
from other studies and it is thought that exposure to multiple chemicals
can have a greater impact than exposure to only one substance.
Toxic metals in baby food more widespread than thought, new study shows.
Environmental Toxicants and
Fetal Development is the impact
of different toxic substances from the environment on the development of
the fetus. This article deals with potential adverse effects of
environmental toxicants on the prenatal development of both the embryo or
fetus, as well as pregnancy complications. The human embryo or fetus is
relatively susceptible to impact from adverse conditions within the
mother's environment. Substandard fetal conditions often cause various
degrees of developmental delays, both physical and
mental, for the growing
baby. Although some variables do occur as a result of genetic conditions
pertaining to the father, a great many are directly brought about from
environmental toxins that the mother is exposed to. Various toxins pose a
significant hazard to fetuses during development. A 2011 study found that
virtually all US pregnant women carry multiple chemicals, including some
banned since the 1970s, in their bodies. Researchers detected
polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides,
perfluorinated
compounds, phenols, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, phthalates, polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons, perchlorate PBDEs, compounds used as flame
retardants, and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), a pesticide banned
in the United States in 1972, in the bodies of 99 to 100 percent of the
pregnant women they tested. Bisphenol A (BPA) was identified in 96 percent
of the women surveyed. Several of the chemicals were at the same
concentrations that have been associated with negative effects in children
from other studies and it is thought that exposure to multiple chemicals
can have a greater impact than exposure to only one substance.
Toxic metals in baby food more widespread than thought, new study shows.Body Burden - Food Additives - Vaccine Ingredients - Sperm Count
Household chemical use linked to child language delays. Young children from low-income homes whose mothers reported frequent use of toxic chemicals such as household cleaners were more likely to show delays in language development by age 2, a new study found.
Environmental toxins impair immune system over multiple generations. New research shows that maternal exposure to a common and ubiquitous form of industrial pollution can harm the immune system of offspring and that this injury is passed along to subsequent generations, weakening the body's defenses against infections such as the influenza virus.
Exposure to Specific Toxins and Nutrients During Late Pregnancy and Early Life Correlated With Autism Risk.
You can't say a Product is Safe. You can only say that the product is safe as far as the manufacturer knows, which means that the safety of the product is based on a few particular testing methods that give the perception that the product is safe. But it can not guarantee that the product is safe for everyone since everyone is a little different. So the product may cause bad reactions in some people because of a particular scenario that came from different reasons, reasons that were not tested for.
Heavy Metals in Foods - Water - Fluoride - Toxic Hotspots
Potentially harmful chemicals found in plastic toys. New research suggests that more than 100 chemicals found in plastic toy materials may pose possible health risks to children. The study provides findings that may lead to stricter international regulations. Out of 419 chemicals found in hard, soft and foam plastic materials used in children toys, we identified 126 substances that can potentially harm children's health either via cancer or non-cancer effects, including 31 plasticizers, 18 flame retardants, and 8 fragrances. Being harmful in our study means that for these chemicals, estimated exposure doses exceed regulatory Reference Doses (RfD) or cancer risks exceed regulatory risk thresholds. These substances should be prioritized for phase-out in toy materials and replaced with safer and more sustainable alternatives.
Exposome measures the influence of environmental exposures which encompasses the totality of human environmental (i.e. non-genetic) exposures from conception onwards, complementing the genome.. In molecular epidemiology the body's response with its endogenous metabolic processes which alter the processing of chemicals, which include, a general external environment including the urban environment, education, climate factors, social capital, stress, a specific external environment with specific contaminants, radiation, infections, lifestyle factors (e.g. tobacco, alcohol), diet, physical activity, etc.. An internal environment to include internal biological factors such as metabolic factors, hormones, gut microflora, inflammation, oxidative stress.
Hormesis is any process in a cell or organism that exhibits a biphasic response to exposure to increasing amounts of a substance or condition. Within the hormetic zone, there is generally a favorable biological response to low exposures to toxins and other stressors. Hormesis comes from Greek hórmesis "rapid motion, eagerness", itself from ancient Greek hormáein "to set in motion, impel, urge on". Hormetics is the term proposed for the study and science of hormesis. In toxicology, hormesis is a dose response phenomenon characterized by a low dose stimulation, high dose inhibition, resulting in either a J-shaped or an inverted U-shaped dose response. Such environmental factors that would seem to produce positive responses have also been termed "eustress". The hormesis model of dose response is vigorously debated. The notion that hormesis is important for chemical risk regulations is not widely accepted. The biochemical mechanisms by which hormesis works remain under laboratory research and are not well understood.
We are Bombarded by thousands of Diverse Species and Chemicals.
Envirome the total set of environmental factors, both present and past, that affect the state, and in particular the disease state, of an organism, which includes all of the environmental conditions required for successful biological life that affect human health. While there can be both positive and negative effects of the envirome on the organism, negative effects are often emphasized in discussing disease.
Environmental Epidemiology is a branch of epidemiology concerned with the discovery of the environmental exposures that contribute to or protect against injuries, illnesses, developmental conditions, disabilities, and deaths; and identification of public health and health care actions to manage the risks associated with harmful exposures. Environmental epidemiology studies external factors that affect the incidence, prevalence, and geographic range of health conditions. These factors may be naturally occurring or may be introduced into environments where people live, work, and play. Environmental exposures are involuntary and thus generally exclude occupational exposures (covered by occupational epidemiology) and voluntary exposures such as active smoking, medications, and diet.
Environmental Health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment affecting human health.
Environmental Medicine is studying the interactions between environment and human health, and the role of the environment in causing or mediating disease.
Occupational Epidemiology is a subdiscipline of epidemiology that focuses on investigations of workers and the workplace. Occupational epidemiologic studies examine health outcomes among workers, and their potential association with conditions in the workplace including noise, chemicals, heat, or radiation, or work organization such as schedules.
Exposure Science is the study of an organism's (usually human) contact with chemical, physical, or biological agents occurring in their environments, and advances knowledge of the mechanisms and dynamics of events either causing or preventing adverse health outcomes.
Toxicology is concerned with the study of the adverse effects of chemicals on living organisms. Toxicology is a branch of biology, chemistry, and medicine (homeopathic or pharmacology).
Dosage Limits - Radioactive Dose
Contaminant is to make something dangerous or toxic by introducing impurities or foreign matter. To make something impure by exposure to or addition of a poisonous or polluting substance.
Contamination is the presence of an unwanted constituent, contaminant or impurity in a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc. Contaminants are biological, chemical, physical or radiological substance. Contamination is the action or state of making or being made impure by polluting or poisoning.
Poison is a substance that is capable of causing the illness or death of a living organism when introduced or absorbed. Poisons are harmful substances that cause disturbances in organisms, particularly corrosive substances, carcinogens, mutagens, teratogens and harmful pollutants. Usually by chemical reaction or other activity on the molecular scale, when an organism absorbs a sufficient quantity and increases the dangers of chemicals.
Chemical Warfare (pesticides) - Cancer - Fluoride
Poisons in our Bodies (NY Times)
 Toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or
organisms.
Toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or
organisms.
Toxicant is any toxic substances made by humans or introduced into the environment by human activity. Toxicants are poisonous. Toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell (cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). By extension, the word may be metaphorically used to describe toxic effects on larger and more complex groups, such as the family unit or society at large. Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage. Pollution.
Toxic Hotspot are locations where emissions from specific sources such as water or Air Pollution may expose local populations to elevated health risks, such as cancer. These emissions contribute to cumulative health risks of emissions from other sources nearby. Urban, highly populated areas around
pollutant emitters such as old factories and waste storage sites are often toxic hotspots. Radiation.
Allergies - Additives - Food Safety
A host of common Chemicals Endanger Child Brain Development.
A Strategy for Comparing the Contributions of Environmental Chemicals and Other Risk Factors to Neurodevelopment of Children.
Prenatal Environmental Exposures.
Prenatal Exposures: A continuum of vulnerability to environmental toxicants.
Toxic Matters
Call Action to Protect Children from Toxins
Targeting Environmental Neuro-Developmental Risks - TENDR
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)
Consumer Protection
Environmental illness
P65 Warnings
A New Study has Found a Connection between Common Household Chemicals and Birth Defects. Known as quaternary ammonium compounds or "quats," the chemicals are often used as disinfectants and preservatives in household and personal products such as cleaners, laundry detergent, fabric softener, shampoo and conditioner, and eye drops. The research demonstrated a link between quats and neural tube birth defects in both mice and rats.
National Toxicology Program
Dioxins and Dioxin-Like Compounds are compounds that are highly toxic environmental persistent organic pollutants (POPs). They are mostly by-products of various industrial processes - or, in case of dioxin-like PCBs and PBBs, part of intentionally produced mixtures. They include: Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins. PCDDs are derivatives of dibenzo-p-dioxin. There are 75 PCDD congeners, differing in the number and location of chlorine atoms, and seven of them are especially toxic, the most dangerous being 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD). Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), or furans. PCDFs are derivatives of dibenzofuran. There are 135 isomers, ten have dioxin-like properties. Polychlorinated/polybrominated biphenyls (PCBs/PBBs), derived from biphenyl, of which twelve are "dioxin-like". Under certain conditions PCBs may form dibenzofurans/dioxins through partial oxidation. Finally, dioxin may refer to 1,4-Dioxin proper, the basic chemical unit of the more complex dioxins. This simple compound is not persistent and has no PCDD-like toxicity.
Perfluorooctanoic Acid also known as C8, is a synthetic perfluorinated carboxylic acid and fluorosurfactant. One industrial application is as a surfactant in the emulsion polymerization of fluoropolymers. It has been used in the manufacture of such prominent consumer goods as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE; Teflon and similar products). PFOA has been manufactured since the 1940s in industrial quantities. It is also formed by the degradation of precursors such as some fluorotelomers. PFOA has been detected in the blood of more than 98% of the general US population in the low and sub-parts per billion (ppb) range, and levels are higher in chemical plant employees and surrounding subpopulations. PFOA has been detected in industrial waste, stain-resistant carpets, carpet-cleaning liquids, house dust, microwave popcorn bags, water, food, some cookware -Teflon and PTFE products. As a result of a class-action lawsuit and community settlement with DuPont. The studies concluded that there was probably an association between PFOA exposure and six health outcomes: kidney cancer, testicular cancer, ulcerative colitis, thyroid disease, hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), and pregnancy-induced hypertension. 3M. PFOA and PFOS are extremely persistent in the environment and Resistant to Typical Environmental Degradation Processes. [They] are widely distributed across the higher trophic levels and are found in soil, air and groundwater at sites across the United States. The toxicity, mobility and bioaccumulation potential of PFOS and PFOA pose potential adverse effects for the environment and human health. GenX was released by DuPont into the Cape Fear River which feeds the Wilmington, NC water supply for decades resulting in controversy over its potential health effects. On November 2, 2017, a federal lawsuit was filed by the Brunswick County Government alleging that DuPont failed to disclose research regarding potential risks from the chemical.
DuPont vs. the World: Chemical Giant Covered Up Health Risks of Teflon Contamination Across Globe (youtube)
How DuPont Poisoned the Ohio River Valley for Over 50 Years (youtube)
The Devil We Know
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency says it will begin the process this year of setting limits on two man-made chemicals that are linked to cancer and other illnesses, and are found widely in drinking water and soil.
Toxic Fluorinated Chemicals in Tap Water and at Industrial or Military Sites.
Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid is an anthropogenic fluorosurfactant and global pollutant. PFOS was the key ingredient in Scotchgard, a fabric protector made by 3M, and numerous stain repellents. It was added to Annex B of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in May 2009. PFOS can be synthesized in industrial production or result from the degradation of precursors. PFOS levels that have been detected in wildlife are considered high enough to affect health parameters, and recently higher serum levels of PFOS were found to be associated with increased risk of chronic kidney disease in the general US population. "This association was independent of confounders such as age, sex, race/ethnicity, body mass index, diabetes, hypertension, and serum cholesterol level."
Forever Chemicals are a class of about 5,000 fluorinated compounds that don't naturally break down and there is no known way to destroy them. Half-Life.
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals that includes PFOA, PFOS, GenX, and many other chemicals. PFAS Water Contamination - How Military Pollution Could Cause The Next Water Crisis (youtube).
Aqueous Film Forming Foam or Firefighting Foam is a foam used for fire suppression. AFFF role is to cool the fire and to coat the fuel, preventing its contact with oxygen, resulting in suppression of the combustion. Studies have shown that PFOS is a persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic pollutant.
Previously Blocked Federal Study Raises Alarm About Chemicals Like C8.
Phytotoxin describes toxic chemicals produced by plants which function as defensive agents against their predators. Most examples pertaining to this definition of phytotoxin are members of various classes of secondary metabolites, including alkaloids, terpenes, and especially phenolics, though not all such compounds are toxic or serve defensive purposes. Phytotoxins may also be toxic to humans. The term is also sometimes used to describe substances (known as phytotoxic substances) that are inhibitory to the growth of or poisonous to plants. Phytotoxic substances may result from human activity, as with herbicides, or they may be produced by plants, by microorganisms, or by naturally occurring chemical reactions. A good soil will protect plants from toxic concentrations of such substances by ventilating gases, decomposing or adsorbing organic toxins, or suppressing toxin-producing organisms.
Snowflake, Arizona: where the residents are allergic to multiple chemical sensitivities and environmental illness. (youtube)
Multiple Chemical Sensitivity (MCS)
Exposure to chemical Bisphenol A (BPA) found in Plastics 'hard to avoid' in everyday life.
di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), a plasticiser which disrupts the body’s hormone system. It is found in a wide array of industrial and consumer products, including cosmetics, plastic toys, medical devices and PVC piping and tubing.
Study Finds Dangerous Chemicals in Consumer Products
Outgassing is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation which are phase transitions of a substance into a gas, as well as desorption, seepage from cracks or internal volumes and gaseous products of slow chemical reactions. Boiling is generally thought of as a separate phenomenon from outgassing because it consists of a phase transition of a liquid into a vapor made of the same substance. (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality).
Volatile Organic Compound are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room temperature. Their high vapor pressure results from a low boiling point, which causes large numbers of molecules to evaporate or sublimate from the liquid or solid form of the compound and enter the surrounding air, a trait known as volatility. For example, formaldehyde, which evaporates from paint, has a boiling point of only –19 °C (–2 °F). (also known as VOC's).
Volatile is something that evaporates readily at normal temperatures and pressures, which can make something vary often or change rapidly, widely and unpredictably from its original state.
Volatility in chemistry is quantified by the tendency of a substance to vaporize.
Fire Retardants - Bromine (wiki)
NYC Toddlers Exposed to Potentially Harmful Flame-Retardants
Flame Retardant Chemicals may affect Social Behavior in young Children
Center for Environmental Research and Children's Health
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)
Tyrone Hayes Penelope Jagessar Chaffer: The Toxic Baby (video)
Atrazine Dangers
Atrazine is an herbicide of the triazine class.
Food Safety
Lead Poisoning is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, inability to have children, and tingling in the hands and feet. It causes almost 10% of intellectual disability of otherwise unknown cause and can result in behavioral problems. Some of the effects are permanent. In severe cases anemia, seizures, coma, or death may occur.
Little Things Matter: The Impact of Toxins on the Developing Brain (youtube)
Epigenetics studies stable heritable traits (or "phenotypes") that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence.
Vaccines
Toxic Chemicals in Products
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (wiki)
Persistent Organic Pollutant are organic compounds that are resistant to environmental degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. Because of their persistence, POPs bioaccumulate with potential significant impacts on human health and the environment. The effect of POPs on human and environmental health was discussed, with intention to eliminate or severely restrict their production, by the international community at the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001.
Persistent Organic Pollutants Global Response
Safe Markets
Makeup and Cosmetics
Eco-Friendly Products
List of Extremely Hazardous Substances (wiki)
Hazardous 100 List (PDF)
Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)
Poisoned Legacy
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas and pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (P2H4). With traces of P2H4 present, PH3 is spontaneously flammable in air, burning with a luminous flame. Phosphines are also a group of organophosphorus compounds with the formula R3P (R = organic derivative). Organophosphines are important in catalysts where they complex to various metal ions; complexes derived from a chiral phosphine can catalyze reactions to give chiral, enantioenriched products.
Aluminium Phosphide is a highly toxic inorganic compound with the chemical formula AlP used as a wide band gap semiconductor and a fumigant. This colorless solid is generally sold as a grey-green-yellow powder due to the presence of impurities arising from hydrolysis and oxidation.
What is Natural?
More than 80,000 Chemicals available in the U.S. have never been fully tested for their toxic effects on our health and environment.
Risk of autism with intellectual disability linked with maternal immune dysfunction during pregnancy.
Dibutyl Phthalate (DnBP) and Diisobutyl Phthalate (DiBP) are found in a wide range of products including vinyl upholstery, shower curtains, plastic food containers, raincoats, dryer sheets, lipstick, hairspray, nail polish, certain soaps and chemical air fresheners. The chemicals provide flexibility and durability to products. But they can be absorbed into a person's body, and exposure in-utero was linked in the study to lower IQs later in a child's life.
Brain Development - Hormones
$72 million of damages to the family of a woman whose death from ovarian cancer was linked to her use of the company's talc-based Baby Powder and Shower to Shower for several decades.
Chemicals and Pollutants Detected in Human Umbilical Cord Blood.
Body Burden Test Analysis and Bio-monitoring.
Do Babies Need Detox? Alarming Levels of Chemicals Found in Infant Brains.
Hazardous PFCs in Remote Locations around the Globe (PDF)
1. BPA. This synthetic hormone has been linked to various forms of cancer, as well as reproductive problems and heart disease. How to Avoid It: Many canned goods use BPA in their lining, but the chemical is also found in up to 40% of store receipts, and some hard plastic containers. Forgo taking sales receipts whenever possible and avoid plastics that are marked with "PC" or recycling label #7. BPA levels in humans dramatically underestimated. Researchers have developed a more accurate method of measuring bisphenol A (BPA) levels in humans and found that exposure to the endocrine-disrupting chemical is far higher than previously assumed. The study provides the first evidence that the measurements relied upon by regulatory agencies, including the US Food and Drug Administration, are flawed, underestimating exposure levels by as much as 44 times. Learn Chemistry.
2. Dioxin. This carcinogen can build up in the body and the food chain, and can adversely affect the immune and reproductive systems of those who are exposed to it. How to Avoid It: Industrial processes release dioxin, meaning that the American food supply is already widely contaminated. But it helps to cut down on exposure by eating fewer animal products, especially meat, fish, milk, eggs and butter.
3. Atrazine. An herbicide frequently used on corn crops, Atrazine is also a common drinking water contaminant that's been linked to breast tumors and prostate cancer. How to Avoid It: Buy organic produce and purchase a drinking water filter that's certified to remove Atrazine. You can find a list of EWG-approved filters on their website.
4. Phthalates. Phthalates can encourage the death of testicular cells in men and are linked to hormonal changes, birth defects related to the male reproductive system and thyroid abnormalities. How to Avoid It: Avoid plastic food containers, children's toys and plastic wrap that's made from PVC. Phthalates are also found in some personal care items, sometimes listed generically as "fragrance", so check your labels. Sperm Count - Hormone Levels in Developing Babies in the Womb.
5. Perchlorate. This rocket fuel component can severely disrupt the proper thyroid function. How to Avoid It: Perchlorate is already widely found in produce and milk, so avoiding it altogether isn't necessarily possible. But using a reverse osmosis water filter can help reduce your intake.
6. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. PBDEs are flame retardants, and while some of them have been phased out of industrial use, their long chemical lives mean that people and wildlife across the world have already been exposed to them. How to Avoid Them: It's virtually impossible to avoid PBDE's entirely, but it helps to use a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter, which can cut down on toxic-laden house dust. Taking extra safety precautions when removing carpet is also recommended, as old padding underneath may contain PBDEs.
7. Lead. It's common to write off lead as something that's avoidable as long as you're not eating paint chips, but exposure to it can also come by way of breathing in the dust from old paint that's crumbling off your walls. This hormone disruptor has been linked to brain and kidney damage, nervous system problems and a host of other physical and psychological impairments. How to Avoid It: Keeping your home free from crumbling paint helps to avoid exposure, as does using a filter that prevents lead contaminants from making it into your drinking water.
8. Arsenic. This poison can cause skin, bladder and lung cancer, but it can also result in osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and suppression of the immune system. How to Avoid It: Use a water filter. (Are you sensing a trend yet?). Barium (wiki).
9. Mercury. This toxic metal gets into the air and oceans primarily through the burning of coal. Mercury can damage pancreatic cells as well as women's reproductive processes, and poses significant problems for pregnant women in particular. How to Avoid It: Some people are weary of eating seafood at all because of its association with mercury, but the EWG recommends that if you still want to eat sustainably-sourced varieties, your best bets are wild salmon and farmed trout.
10. Perfluorinated Chemicals. PFCs are so pervasive and resistant to biodegration, 99 percent of Americans carry traces of them in their bodies. The chemicals have been linked to health issues like kidney disease, thyroid disease and low birth weight in infants. How to Avoid Them: Avoid using nonstick cookware, and forgo furniture, clothing and carpet that comes with water-resistant coatings.
11. Organophosphate Pesticides. These pesticides were originally developed by Nazi Germany during World War II for use in chemical warfare. Using the same chemistry, we now spray them on our crops. Organophosphates are linked to impaired brain development, fertility and thyroid function. How to Avoid Them: Buy organic produce whenever possible and use the EWG guide to find out which nonorganic produce contains the least amount of pesticide residue.
12. Glycol Ethers. Glycol ethers are solvents found in paint, brake fluid and some cleaning products, and exposure to them has been linked to blood abnormalities, fertility impairments and increased asthma in children. How to Avoid Them: Keep away from cleaning products that carry ingredients like 2-butoxyethanol (EGBE) and methoxydiglycol (DEGME).
Titanium Dioxide. The ability of small intestine cells to absorb nutrients and act as a barrier to pathogens is "significantly decreased" after chronic exposure to nanoparticles of titanium dioxide, a common food additive found in everything from chewing gum to bread, according to research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) are used to make moisture-wicking and water-repellent equipment including jackets, pants, sleeping bags, boots, and tents.
Having too much caffeine during pregnancy may impair baby's liver development and increase the risk of liver disease in adulthood. The study findings indicate that consumption of caffeine equivalent to 2-3 cups of coffee may alter stress and growth hormone levels in a manner that can impair growth and development, and increase the risk of liver disease in adulthood. Junk Food.
Drug Addicted Pregnant Mothers - Birth Defects
Children Exposed to Drugs in the Womb - Drugs during Pregnancy
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) used for mild to moderate pain During Pregnancy linked to abnormal fetal neurodevelopment and Behavioral Problems in Childhood.
Research shows even small amounts of alcohol consumed during pregnancy can cause insulin-resistance, which increases the likelihood of diabetes, in male rat offspring.
Addictions (bad habits) - Opioid Crisis
Medications and Pregnancy - Taking Medicine during Pregnancy
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (wiki)
More than 21,000 infants born in the U.S. in 2012 experienced symptoms of opioid withdrawal. The care for each baby costs roughly $50,000 to treat.
Interactive: Explore what’s driving surging overdose deaths
Congenital Disorder (Birth Defects) (wiki) - Gastroschisis
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
Medication Dangers
Use of Medication in Pregnancy A 2011 study using U.S. data from 1976-2008 reported that most women (about 90%) take at least one medication during pregnancy and 70% take at least one prescription medication.
Medications during Pregnancy - Pharmaceutical Dangers
Mother to Baby evidence-based information to mothers, health care professionals, and the general public about medications and other exposures during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
Database contains information on drugs and other chemicals to which breastfeeding mothers may be exposed.
HIV Pregnancy Ethics women’s reproduction and HIV prevention, treatment, and management.
Birth - Having a Baby
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also known as parturition. BIRTH VLOG! *Raw & Real* Labour & Delivery Of Our First Baby! (youtube).
Childbirth also known as labor and delivery, is the ending of a pregnancy by one or more babies leaving a woman's uterus.
The first stage of labor is the longest and involves three phases: Early Labor Phase –The time of the onset of labor until the cervix is dilated to 3 cm. Active Labor Phase – Continues from 3 cm. until the cervix is dilated to 7 cm. Transition Phase – Continues from 7 cm. until the cervix is fully dilated to 10 cm. Pre-Labor consists of the early signs before labor starts. It is the body's preparation for real labor.
Midwifery is a health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period (including care of the newborn), besides sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many countries, midwifery is a medical profession (special for its independent and direct specialized education; should not be confused with a medical specialty, which depends on a previous general training). Midwifery is also known as obstetrics. A professional in midwifery is known as a midwife.
Doula also known as a birth companion and post-birth supporter, is a nonmedical person who assists a person before, during, and/or after childbirth, as well as her spouse and/or family, by providing physical assistance and emotional support. The provision of continuous support during labour is associated with improved maternal and fetal health and a variety of other benefits, including lower risk of induction and interventions and less need for pain relief. These benefits are particularly significant when continuous support is provided by someone who is not there as family/friend or as medical staff (i.e. a doula). Additionally, a doula is sometimes hired to work with families beyond the postpartum stages, providing continued physical and emotional support, for as long as needed (sometimes, this support can be ongoing for several years). Doula Education Program.
How Racism Harms Pregnant Women — and what can help: Miriam Zoila Pérez (video and interactive text)
Common Sense Child Birth - Jennie Joseph - Midwifery Team.
A Women Dies every 90 seconds from Complications of Pregnancy
300.000 Mothers die from complications from pregnancy and childbirth every year
Safe Motherhood
700 to 900 women will die in the U.S. from childbirth every year, most are preventable. and 50,000 will nearly die. Majority die after birth or after being discharged from the hospital. Near Miss’ Mothers: The Risk of Childbirth in America | NPR (youtube)
The United States is one of only eight countries in the world where decreases in child and adolescent mortality over a 27-year period haven't also been matched by reductions in maternal mortality. Additional findings include: More than half of the 6.64 million deaths in 2017 occurred in infants younger than 1 year, and of those, 47% occurred in the first week of life. There were a total of 50 countries where the probability of death by self-harm and interpersonal violence increased between 1990 and 2017. Every country in sub-Saharan Africa had either neonatal disorders, malaria, or HIV/AIDS as the leading cause of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), with either diarrhea or lower respiratory infections often ranked second. In 2017, the top 10 causes of years lived with disability (YLDs) globally were iron-deficiency anemia, vitamin A deficiency, headache, conduct disorder, neonatal disorders, anxiety disorder, skin diseases, lower back pain, congenital disorders, and depression. Rates of YLDs decreased only slightly between 1990 and 2017, and increased with age.
Birth in Nepal (youtube)
The Business of Being Born (youtube 1:27 min. 2008 Abby Epstein) Website
The Nine Months That Made You 2011 BBC Horizon (youtube)
Welcome to the World - Why Poverty?
A Simple Birth Kit for Mothers in the Developing World: Zubaida Bai (video and interactive text)
Black life at the intersection of birth and death: Mwende "FreeQuency" Katwiwa (video and interactive text)
Maternal Mortality has Doubled in the U.S.
Centering Healthcare Institute empowers patients, strengthens patient-provider relationships, and builds communities through these three main components. Both provider and patient are involved in the health assessment. Patients receive one-on-one time with their provider and learn to take some of their own assessments. This engages them in their own self-care or care of their child. Engaging activities and facilitated discussions help patients to be more informed, confident and empowered to make healthier choices for themselves, their children and their families. One person’s question is another one’s question. Patients quickly find comfort in knowing they are not alone. Participation in group care lessens the feelings of isolation and stress while building friendships, community and support systems.
Parental Leave by Country (Info-Graph)
Parental Leave
Maternity Leave in the U.S.
The US needs Paid Family Leave — for the sake of its future (video and text)
BD Odon Device
Maternity Package 2017
Maternal and Child Survival Program
Seed Global Health Education
Global Health Service Partnership (GHSP)
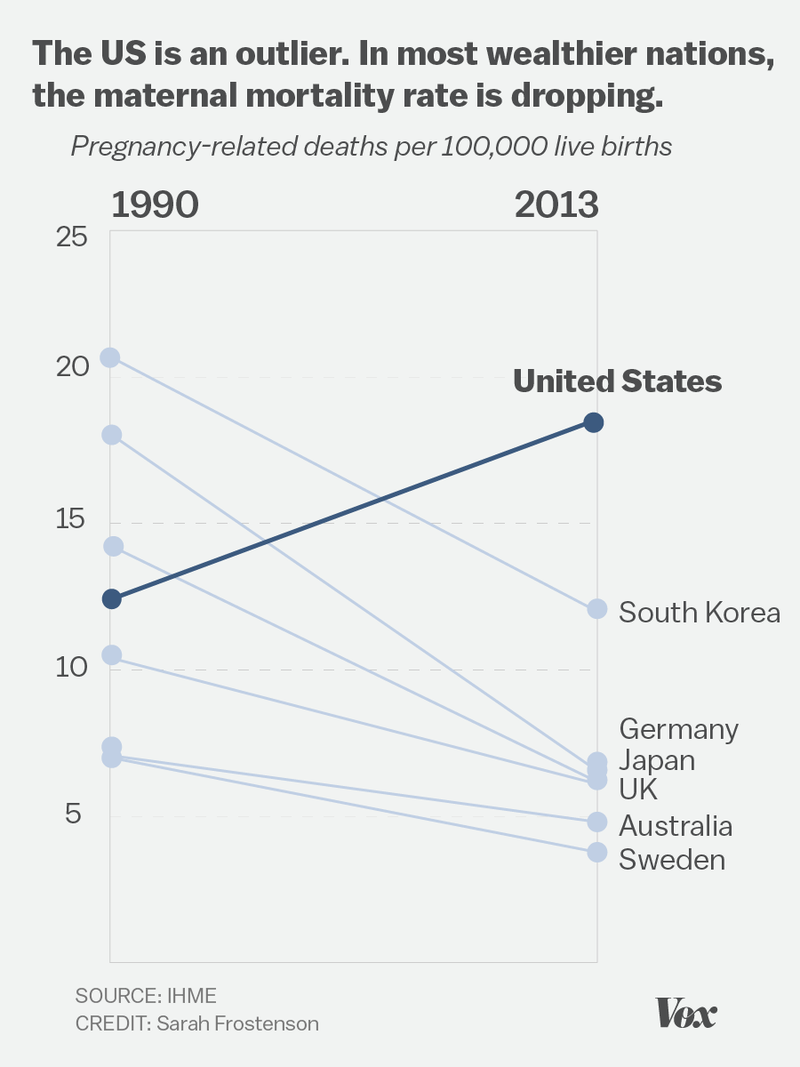 In 2013, 6.3 million children under the age
of 5 died from preventable and treatable conditions.
In 2013, 6.3 million children under the age
of 5 died from preventable and treatable conditions.Child Mortality - Mortality Rates (populations)
New diagnostic tools for dehydration severity in children Dehydration from diarrhea, either viral or from cholera, kills 700,000 children a year worldwide.
Maternal, Newborn; Child Health Data - Countdown to 2015 Countdown to 2015 tracks key global health data by country for the 75 highest-burden countries, compiling and analyzing global health statistics including coverage levels for interventions proven to reduce maternal mortality, newborn mortality, and child mortality. It fosters accountability, identifies knowledge gaps, and proposes actions to reach Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5 and improve maternal health and child health. - Global MNH.
Infant mortality rate rises in Gaza for first time in fifty years
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage which is an early pregnancy loss and live birth where the baby is born alive, even if it dies shortly after.
Pregnant Women can Lower the Risk of Stillbirth by Sleeping on their Side and NOT on their Back. SSleep Positions.
More than half of infants in the United States are still sleeping in unsafe conditions in cribs containing blankets, pillows and other loose bedding that has been shown to dramatically raise the risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, a new government study finds. More educated moms were less likely to use hazardous bedding materials, but use was still at 50 percent among those with a college education. Education Reform.
Every year about 100,000 women around the world die of blood loss soon after a baby is born. It's the biggest cause of maternal death worldwide.
Postpartum Bleeding is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood within the first 24 hours following childbirth. Signs and symptoms may initially include: an increased heart rate, feeling faint upon standing, and an increased breath rate. As more blood is lost the women may feel cold, their blood pressure may drop, and they may become restless or unconscious. The condition can occur up to six weeks following delivery.
Tranexamic Acid is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from major trauma, surgery, tooth removal, nose bleeds, and heavy menstruation. It is also used for hereditary angioedema. It is taken either by mouth or injection into a vein. Side effects are rare. Some include changes in color vision, blood clots and allergic reactions. Greater caution is recommended in people with kidney disease. Tranexamic appears to be safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Tranexamic acid is in the antifibrinolytic family of medications.
50,000 mothers die each year in India as a result of birth complications, versus 1,200 in the United States. In India nearly 300,000 babies die the day they are born — more than any other country in the world, accounting for nearly a third of all newborn deaths worldwide.
There's new evidence that delaying Umbilical Cord clamping and sniping by a minute can benefit babies, like having higher hemoglobin levels 24 to 48 hours after birth, having higher birth weights, and it also sends more iron from the placenta to your baby, which could avoid babies being iron-deficient three to six months after birth.
Lotus Birth is the practice of leaving the umbilical cord uncut after childbirth so that the baby is left attached to the placenta until the cord naturally separates at the umbilicus, usually a few days after birth. Lotus Birth.
Kangaroo Care
Episiotomy also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through.
Mothers ill-informed about the dangers they face after giving birth.. Postpartum nurses provide important physical and emotional care and recovery for both the new mom and the newborn baby following a delivery.
Nurses' Knowledge and Teaching of Possible Postpartum Complications. - The American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing.
An estimated 700 to 900 women die in the U.S. every year from pregnancy- and childbirth-related causes. Another 65,000 nearly die, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rates are highest among black mothers and women in rural areas. A recent CDC Foundation analysis of data from four states found that close to 60 percent of maternal deaths were preventable.
Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses.
Discharge Education on Maternal Morbidity and Mortality Provided by Nurses to Women in the Postpartum Period.
Improving Postpartum Discharge Education About Potential Complications.
Over 50% of maternal deaths occur in the postpartum period compared to 16.8% on the day of delivery. 18% of these maternal deaths occurred 1-6 days postpartum and 21% occurred 7-41 days postpartum. It is impossible to predict with any certainty which women will have a postpartum complication. All women need education on which signs and symptoms are emergencies and which require urgent care. RN's who provide discharge education are in a key role to educate women about the signs & symptoms of potential postpartum complications
Improving Postpartum Education About Warning Signs Of Maternal Morbidity and Mortality.
Learn These Post-Birth Warning Signs.
American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Probiotic Bacteria Could Protect Newborns From Deadly Infection.
Neonatal Sepsis - a major killer to be tackled in communities
A randomized synbiotic trial to prevent Sepsis among infants in rural India
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the death of tissue in the intestine. It occurs most often in premature or sick babies.
Fermented Fruits and Vegetables of Asia: A Potential Source of Probiotics.
Flattening The 'Mummy Tummy' With 1 Exercise, 10 Minutes A Day.
Diastasis Rehab - Dia Method
The Dia Method: 10 Minutes Flat Video Preview (youtube)
MuTu System - The Postpartum Exercise + Recovery Program
Diastasis Recti: 5 Exercises To Close the Gap for Postpartum Moms
Premature Births
Preterm Birth or premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age. These babies are known as preemies or premies. Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes or the leaking of fluid from the vagina. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and sight problems. These risks are greater the earlier a baby is born. The cause of preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, being pregnant with more than one baby, being either obese or underweight, a number of vaginal infections, tobacco smoking and psychological stress, among others. It is recommended that labor not be medically induced before 39 weeks unless required for other medical reasons. The same recommendation applies to cesarean section. Medical reasons for early delivery include preeclampsia. In those at risk, the hormone progesterone, if taken during pregnancy, may prevent preterm birth. Evidence does not support the usefulness of bed rest. It is estimated that at least 75% of preterm infants would survive with appropriate treatment, and the survival rate is highest among the infants born the latest. In women who might deliver between 24 and 37 weeks, corticosteroids improve outcomes. A number of medications, including nifedipine, may delay delivery so that a mother can be moved to where more medical care is available and the corticosteroids have a greater chance to work. Once the baby is born, care includes keeping the baby warm through skin to skin contact, supporting breastfeeding, treating infections and supporting breathing. Preterm birth is the most common cause of death among infants worldwide. About 15 million babies are preterm each year (5% to 18% of all deliveries). Approximately 0.5% of births are extremely early periviable births, and these account for most of the deaths. In many countries, rates of premature births have increased between the 1990s and 2010s. Complications from preterm births resulted in 0.81 million deaths in 2015 down from 1.57 million in 1990. The chance of survival at 22 weeks is about 6%, while at 23 weeks it is 26%, 24 weeks 55% and 25 weeks about 72%. The chances of survival without any long-term difficulties are lower.
2 Million Infants Born Before 32 weeks Each Year Worldwide. W.H.O.
The number of preterm births in the United States rose in 2015 for the first time in eight years. Preterm births cost us more than $26 billion a year or $51,600 per infant born preterm. Preterm births linked to air pollution in the United States totals over $4 billion a year. Exposures to high levels of air pollution increases toxic chemicals in the blood and can weaken the immune system, causing stress to the placenta and leading to preterm birth.
Premature Baby Development Concerns
Pelican Pulse Oximeter. Save Babies Worldwide from Pneumonia.
Low Cost Incubator
A unique womb-like environment designed by pediatric researchers could transform care for extremely premature babies, by mimicking the prenatal fluid-filled environment to give the tiniest newborns a precious few weeks to develop their lungs and other organs.
Artificial womb has been successfully used to incubate healthy baby lambs for a period of one week. (ex-vivo uterine environment (EVE) therapy).
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit is an intensive care unit specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as known as specialized nurseries or intensive care, has been around since the 1960s.
Kangaroo Care is a technique of newborn care where babies are kept skin-to-skin with a parent, typically their mother. It is most commonly used for low birth-weight preterm babies, who are more likely to suffer from hypothermia, while admitted to a neonatal unit to keep the baby warm and support early breastfeeding. Kangaroo Mother Care.
Even brief maternal deprivation early in life alters adult brain function and cognition. When a baby is taken from its mother for even a brief period early in life, this traumatic event significantly alters the future, adult function of the brain, according to a new animal model study.
Skin-to-Skin Contact affects Hormone Levels and may promote parental engagement for premature infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), skin-to-skin contact with parents influences levels of hormones related to mother-infant attachment (oxytocin) and stress (cortisol) -- and may increase parents' level of engagement with their infants.
Sproutling Baby Monitor
Neonatal Nursing is a subspecialty of nursing care for newborn infants up to 28 days after birth.
We have to keep softly talking to a baby when they are born, especially when they are born premature.
Listening to Language Boosts Infant Cognition
Child Development Mother's Milk May Help Prevent Blindness In Preemies (npr)
Retinopathy of Prematurity is a disease of the Eye affecting prematurely born babies generally having received intensive neonatal care, in which oxygen therapy is used on them due to the premature development of their lungs. It is thought to be caused by disorganized growth of retinal blood vessels which may result in scarring and retinal detachment. ROP can be mild and may resolve spontaneously, but it may lead to blindness in serious cases. As such, all preterm babies are at risk for ROP, and very low birth-weight is an additional risk factor. Both oxygen toxicity and relative hypoxia can contribute to the development of ROP.
Mtts Asia cost-effective solutions for newborns in need of intensive medical care.
American Pregnancy Association
Healthy Child
Cesarean Awareness
Child Birth Connection
Penn Researchers Develop Placenta-on-a-chip can fully model the transport of nutrients across the placental barrier.
causes of preterm birth and ways to prevent it.
Postpartum Depression is a type of mood disorder associated with childbirth, which can affect both sexes. Symptoms may include extreme sadness, low energy, anxiety, crying episodes, irritability, and changes in sleeping or eating patterns. Onset is typically between one week and one month following childbirth. PPD can also negatively affect the person's child.
Women, Infants and Children’s Program
Child Development - Parenting - Children's Health
Human Development is the process of growing to maturity. In biological terms, this entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being.
Breast Feeding
 Breastfeeding also known as nursing, is the feeding of babies and
young children with milk from a woman's breast. Health professionals
recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life
and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. During the first few
weeks of life babies may nurse roughly every two to three hours. The
duration of a feeding is usually ten to fifteen minutes on each breast.
Older children feed less often. Mothers may pump milk so that it can be
used later when breastfeeding is not possible. Breastfeeding has a number
of benefits to both mother and baby, which infant formula lacks.
Breastfeeding also known as nursing, is the feeding of babies and
young children with milk from a woman's breast. Health professionals
recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life
and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. During the first few
weeks of life babies may nurse roughly every two to three hours. The
duration of a feeding is usually ten to fifteen minutes on each breast.
Older children feed less often. Mothers may pump milk so that it can be
used later when breastfeeding is not possible. Breastfeeding has a number
of benefits to both mother and baby, which infant formula lacks. Malnutrition - Nutrition (food smart)
The Milky Way 2014 Documentary about Breast feeding (04/01/2014 | 1 hr. 33 min.)
What we don't know about mother's milk: Katie Hinde (video and interactive text)
Baby Friendly Hospital.
Breast Milk Sharing Bank.
Component of human breast milk enhances cognitive development in babies. Investigators show that early exposure to a carbohydrate found in breast milk, called 2'FL, positively influences neurodevelopment. Maternal factors, such as breast milk, have been shown to affect a baby's development, and previous animal studies have determined that a carbohydrate, the oligosaccharide 2'FL found in maternal milk, positively influences neurodevelopment.
Breastfeeding for the first 3 months was linked with a lower risk of respiratory allergies and asthma when children reached 6 years of age.
Golchi holds 2 beverages of different temperatures at once.
Breast Feeding Consultant or Lactation Consultant.
Only 15% of Babies in the U.S. are Breast Feed - Why Most Women “Can’t” Breastfeed
Feeding Baby (youtube)
What causes women to stop breastfeeding early? Potential sociodemographic, physical, mental, and social factors may cause breastfeeding mothers to stop breastfeeding before infants reach 6 months of age. Mothers who were young, had a low level of education, and returned to work within 12 weeks after giving birth were more likely to stop breastfeeding before 6 months. Those who gave birth by caesarean section and who had an inadequate milk supply also tended to stop breastfeeding early.
Boosting the milk of premature babies with healthy bacteria may have helped halve the number of serious gut problems and infections, according to new research.
New Born Nutrition - Pregnancy and Nutrition - Infant Nutrition
Natural Sugars in breastmilk linked to early childhood height and weight. Human milk oligosaccharides found in breast-milk may influence a child's growth from infancy through early childhood, according to a new study.
Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children - WIC
Infants who were started on solid foods at or before three months of age showed changes in the levels of gut bacteria and bacterial byproducts, called short-chain fatty acids, measured in their stool samples, according to a new study. Infants introduced early to solid foods show gut bacteria changes that may portend future health risks. Gut microbiome shifts may explain how early dietary factors bring later health risks.
Poor Nutrition Dangers
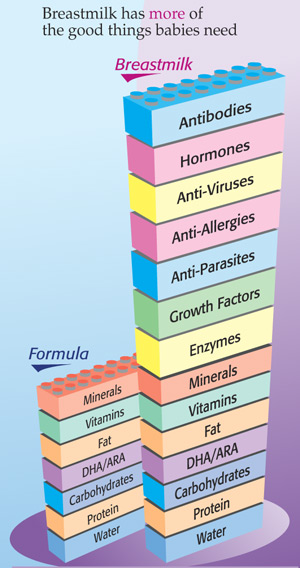 Stunting is the impaired growth and development that children experience
from poor nutrition, repeated infection, and inadequate psychosocial
stimulation. Children are defined as stunted if their height-for-age is
more than two standard deviations below the WHO Child Growth Standards median.
Stunting in early life -- particularly in the first 1000 days from
conception until the age of two - impaired growth has adverse functional
consequences on the child. Some of those consequences include poor
cognition and educational performance, low adult wages, lost productivity
and, when accompanied by excessive weight gain later in childhood, an
increased risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases in adult life.
Stunting is the impaired growth and development that children experience
from poor nutrition, repeated infection, and inadequate psychosocial
stimulation. Children are defined as stunted if their height-for-age is
more than two standard deviations below the WHO Child Growth Standards median.
Stunting in early life -- particularly in the first 1000 days from
conception until the age of two - impaired growth has adverse functional
consequences on the child. Some of those consequences include poor
cognition and educational performance, low adult wages, lost productivity
and, when accompanied by excessive weight gain later in childhood, an
increased risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases in adult life.
Food Security - Vitamin Deficiencies
Psychosocial stimulation, attachment, and feeding in early child development. A strong maternal-infant (or caregiver-infant) bond provided through psychosocial stimulation is essential for positive child development. The formation of this bond at the beginning of life is an essential step that sets the stage for cognitive, emotional, and social development later in life. Feeding and other care practices provide opportunities for psychosocial stimulation and help to establish a positive attachment between caregiver and child.
Stunted Growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of Malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, due to malnutrition during fetal development brought on by a malnourished mother.
Nutrition (food smart)
Formula is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepared for bottle-feeding or cup-feeding from powder (mixed with water) or liquid (with or without additional water). The U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) defines infant formula as "a food which purports to be or is represented for special dietary use solely as a food for infants by reason of its simulation of human milk or its suitability as a complete or partial substitute for human milk".
W.H.O International Code of Marketing of Breast-Milk Substitutes
Dangers of Baby Formula
14 Risks of Formula (PDF)
Benefits of Skin to Skin Contact between Mother and her Baby
Lactase Persistence is the continued activity of the enzyme lactase in adulthood. Since lactase's only function is the digestion of lactose in milk, in most mammal species, the activity of the enzyme is dramatically reduced after weaning. In some human populations, though, lactase persistence has recently evolved as an adaptation to the consumption of nonhuman milk and dairy products beyond infancy. The majority of people around the world remain lactase nonpersistent, and consequently are affected by varying degrees of lactose intolerance as adults. However, not all genetically lactase nonpersistent individuals are noticeably lactose intolerant, and not all lactose-intolerant individuals have the lactase nonpersistence genotype.
Prolactin is a protein that in humans is best known for its role in enabling mammals, usually females, to produce milk; Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation, and nursing. Prolactin is secreted in a pulsatile fashion in between these events. Prolactin also plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system, and pancreatic development.
Breast-Feeding Could Save 800,000 Lives a year. Researchers analyzed data from 28 studies, and their findings suggest that the lives of 823,000 children worldwide under the age of five could be saved annually, and about 20,000 breast cancer deaths could be prevented, if universal breastfeeding occurred. Research indicates that in high-income countries breastfeeding reduces the risk of sudden infant deaths by more than one-third. In low and middle-income countries breastfeeding can reduce about half of all diarrhea illnesses and a third of respiratory infections. The authors said it may also increase intelligence, and might protect against obesity and diabetes in later life. For nursing women, breastfeeding provided protection against breast cancer and it improved birth spacing, the authors wrote. It might also protect against ovarian cancer and type 2 diabetes.
Saving Lives at Birth
NIFT Infant Feeding Cup - NIFT Infant Feeding Cup
Breast milk has varied flavors whereas formula milk has a single flavor.
What mothers eat, even before we're born, affect the way we'll respond to those flavors when we later encounter them because they seem familiar. Babies are most open to trying new flavors between the ages of 4 and 7 months.
Mammary Gland is an exocrine gland in mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats). Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur.
Baby Colic is defined as episodes of crying for more than three hours a day, for more than three days a week, for three weeks in an otherwise healthy child. Often crying occurs in the evening. It typically does not result in long term problems. The crying can cause frustration for the parents, depression following delivery, excess visits to the doctor, and child abuse.
Pregnancy and Nutrition
Infant Antibiotic use linked to Adult Diseases
Excessive pregnancy weight gain may be associated with obesity in the offspring.
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, and also for sex determination, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and then the fetal DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities. The most common reason to have an "amnio" is to determine whether a baby has certain genetic disorders or a chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome. Amniocentesis (or another procedure, called chorionic villus sampling (CVS)) can diagnose these problems in the womb. Amniocentesis is performed when a woman is between 14 and 16 weeks gestation. Women who choose to have this test are primarily those at increased risk for genetic and chromosomal problems, in part because the test is invasive and carries a small risk of miscarriage. This process can be used for prenatal sex discernment and hence this procedure has legal restrictions in some countries.
Vitamin D levels during pregnancy linked with child IQ. A study showed that mothers' vitamin D levels during pregnancy were associated with their children's IQ, suggesting that higher vitamin D levels in pregnancy may lead to greater childhood IQ scores.
Neonatal Insulin Action Impairs Hypothalamic Neurocircuit Formation in Response to Maternal High-Fat Feeding.
Excess Folic Acid during pregnancy harms brain development of mice. Researchers found too much folic acid was just as detrimental as too little. Dosage.
Changing Diapers - Shit Happens
Diaper is a type of underwear that allows the wearer to defecate or urinate without the use of a Toilet, by absorbing or containing waste products to prevent soiling of outer clothing or the external environment. When diapers become soiled, they require changing, generally by a second person such as a parent or caregiver. Failure to change a diaper on a sufficiently regular basis can result in skin problems around the area covered by the diaper. Diapers are made of cloth or synthetic disposable materials. Cloth diapers are composed of layers of fabric such as cotton, hemp, bamboo, microfiber, or even plastic fibers such as PLA or PU, and can be washed and reused multiple times. Disposable diapers contain absorbent chemicals and are thrown away after use. Diapers are primarily worn by infants, toddlers who are not yet potty trained, and by children who experience bedwetting. They are also used by adults with incontinence, in certain circumstances where access to a toilet is unavailable or for psychological reasons. These can include those of advanced age, patients bed-bound in a hospital, individuals with certain types of physical or mental disability, diaper fetishists, and people working in extreme conditions, such as astronauts. It is not uncommon for people to wear diapers under dry suits.
Smart Diapers - The Engineering of a Disposable Diaper (youtube)
Changing Diapers: To change your baby, follow the steps below: Lay your baby on his back. Remove the soiled diaper. Lift your baby up gently so you can scoot the diaper out from under his bottom. Use wipes to clean your baby's diaper region. If the area is red or inflamed, soothe it with diaper ointment. How to Clean Baby during Diaper Change | Infant Care (youtube).
Toilet Training is the process of training someone, particularly a young child or infant, to use the toilet for urination and defecation. Little is known about toilet training in pre-modern societies, but attitudes toward training in recent history have fluctuated substantially, and may vary across cultures and according to demographics. Many the contemporary approaches to toilet training favor a behaviouralism- and cognitive psychology-based approach. Specific recommendations on techniques vary considerably, although a range of these are generally considered effective, and specific research on their comparative effectiveness is lacking. No single approach may be universally effective, either across learners or for the same learner across time, and trainers may need to adjust their techniques according to what is most effective in their situation. Training may begin shortly after birth in some cultures. However, in much of the developed world this occurs between the age of 18 months and two years, with the majority of children fully trained by age four, although many children may still experience occasional accidents. Certain behavioral or medical disorders may affect toilet training, and extend the time and effort necessary for successful completion. In certain circumstances, these will require professional intervention by a medical professional. However, this is rare and even for those children who face difficulties in training, the vast majority of children can be successfully trained. Children may face certain risks associated with training, such as slips or falling toilet seats, and toilet training may act in some circumstances as a trigger for abuse. Certain technologies have been developed for use in toilet training, some specialized and others commonly used. Hygiene - How to Potty Train Kids in Three Days | Parents (youtube).
There is a time when an infant's attention moves from oral stimulation to anal stimulation (usually the bowels but occasionally the bladder), usually synchronous with learning to control their excretory functions—in other words, any form of child training and is not specifically linked to toilet training. Freud posited that children who experience conflicts, in which libido energy is under-indulged during this period of time, perhaps too-strongly chastised for toilet-training accidents, may develop "anal retentive" fixations or personality traits. These traits are associated with a child's efforts at excretory control: orderliness, stubbornness, and compulsions for control. Conversely, those who are overindulged during this period, may develop "anal-expulsive" personality types.
Sleep Training - Safe Sleeping Positions
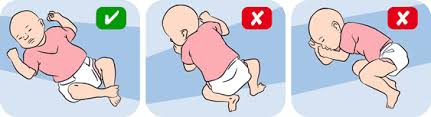 Babies should
sleep on their back with no items like toys or
pillows that could entangle or suffocate the baby.
Sleep Positions.
Babies should
sleep on their back with no items like toys or
pillows that could entangle or suffocate the baby.
Sleep Positions.For safety reasons, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends babies should sleep without any loose blankets, so at night it's best to choose an outfit that keeps your baby comfortable without extra layers. Avoid over-bundling your baby: most nights your infant can wear a onesie and a cotton swaddle, or cotton pajamas with feet. In the winter, heavier pajamas or an additional sleep sack (a sleeveless, wearable blanket) will work. Older children tend to kick off their covers at night, so you may want to dress your toddler or young child in an outfit that works without blankets as well. Choose pajama fabrics that are breathable and won't cause your child to sweat during the night. The same general principle of cool air for better sleep applies to children, so try to keep the room in the mid-60 degree range.
Sleep Training to help babies learn to fall asleep by themselves. Babies who feel secure are better able to handle separations, especially at night. Cuddling and Comforting your baby during the day can help him or her feel more secure. Other ways to help your baby learn to sleep include the following: Allow time for naps each day as needed for the age of the baby. Avoid stimulation and activity close to bedtime. Establish a bedtime routine, such as bath, reading books, and rocking. Play soft music while your baby is getting sleepy. Introduce a transitional object such as a small blanket or soft toy that your baby can take to bed, but not before your baby is old enough (able to roll and sit) to avoid the risk of suffocation. Tuck your baby into bed when he and she is drowsy, but before going to sleep. Comfort and reassure your baby when he or she is afraid. For night awakenings, comfort and reassure your baby by patting and soothing, but avoid taking your baby out of bed. If your baby cries, wait a few minutes, then return and reassure with patting and soothing. Then, say goodnight and leave (repeat as needed). Be consistent with the routine and your responses. Interventions.
How to train baby to sleep? Teaching Your Baby to Put themselves to Sleep. Wake your baby when you put her down to sleep. Begin to break the association between nursing/eating/sucking and sleep. Help your little one learn to fall asleep lying still (in your arms). Help your little one learn to fall asleep in his bed. Touch instead of holding, in her bed.
Behavioral treatment of bedtime problems and night waking's in infants and young children.
Improving infant sleep and maternal mental health: a cluster randomized trial.
What are the sleep needs of an infant?
Place your infant on his or her back for sleep or naps. This can decrease the risk for SIDS, aspiration, and choking. Never place your baby on his or her side or stomach for sleep or naps. If your baby is awake, allow your child time on his or her tummy as long as you are supervising, to decrease the chances that your child will develop a flat head. Share your room instead of your bed with your baby. Putting your baby in bed with you raises the risk for strangulation, suffocation, entrapment, and SIDS. Bed sharing is not recommended for twins or other higher multiples. Avoid overbundling, overdressing, or covering an infant's face or head. This will prevent him or her from getting overheated, reducing the risk for SIDS. Avoid using loose bedding or soft objects—bumper pads, pillows, comforters, blankets—in an infant's crib or bassinet to help prevent suffocation, strangulation, entrapment, or SIDS.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome is the sudden unexplained death of a child less than one year of age. Also known as cot death or crib death. SIDS is also known as cot death or crib death, is the sudden unexplained death of a child less than one year of age. Diagnosis requires that the death remains unexplained even after a thorough autopsy and detailed death scene investigation. SIDS usually occurs during sleep. Typically death occurs between the hours of 00:00 and 09:00. There is usually no evidence of struggle and no noise produced.
Sudden Unexplained Death in Childhood is the death of a child over the age of 12 months which remains unexplained after a thorough investigation and autopsy. There has not been enough research to identify risk factors, common characteristics, or prevention strategies for SUDC.
The Sudden Unexplained Death In Childhood (SUDC) Foundation.
Suffocation Prevention and Sleep Safety
Protecting Kids From Suffocation
Do Not Use Infant Sleep Positioners Due to the Risk of Suffocation
NeoNatalie is an inflatable simulator designed to teach basic neonatal resuscitation skills.
Parents shouldn't worry about their baby's inconsistent sleep patterns. New parents often expect their baby to start sleeping through the night around the time they reach six months of age. But according to a new study parents should view sleep consolidation as a process, instead of a milestone to be achieved at a specific age. researchers asked mothers to keep a sleep diary about their six-month-old infant for two weeks. On average, mothers reported that their infant slept 6 hours consecutively for about 5 nights out of a two-week period, and 8 consecutive hours for about 3 nights out of the same period. Half of the infants, however, never slept 8 hours consecutively. The researchers also found that some parental practices were related to variability in sleep patterns. For example, breastfeeding and co-sleeping were associated with more variability in sleep patterns night to night. While this finding is consistent with many studies, the researchers note that other factors could explain this occurrence. For instance, mothers who are breastfeeding and co-sleeping are more likely to observe their infant's night awakenings, even though these awakenings are not necessarily problematic or disturbing.
Crying - Cry it Out
Long continued or oft-repeated crying can produce so much cortisol that it can damage a baby's brain which reduces their capacity to learn. Don't jump in prematurely. Your baby might actually be asleep, or on the verge of falling back to sleep on his or her own. By intervening too soon, you can create infant sleep problems. Alarm Fatigue.
How often should a baby cry? On average, newborns cry for about two hours each day. Although the crying is spread out through the day, all that wailing adds up to more than you probably expected. Between birth and about 6 weeks of age, the amount of crying typically increases to almost three hours each day, no matter what you do!
Common Reasons Babies Cry: Sleepiness or fatigue, Wet or dirty diaper, Hunger, Overstimulation from noise or activity, Colic, acid reflux, or food allergies, Pain or illness, Gas, Hot or Cold, Stranger anxiety or fear.
Soothing a Crying Baby Tips: Hold your baby and gently move and rock back and forth or rock the baby in a Chair or Glider. Try to feed the Baby. Give the baby a Massage. Gently tap the babies back to release gas. Use a gentle touch and stroke the babies chest from the center outward and make small circles on their stomach, around their belly button. Encourage Sucking. Swaddle your Baby. Wear Baby in a Front-Pack Carrier. . Soothe the baby with White Noise. Sing a Song. Entertain. Wash Away the Tears. Keep Calm and Carry On.
Rocking Motions. For many infants, rocking, or using another kind of rhythmic movement, works as a natural sleep aid, since it reminds them of being inside their mother's body. While some babies have a strong preference for one particular type of movement, the truth is, there are many ways to soothe an infant. But be aware if a child's head banging and body rocking becomes more frequent. Though most children will grow out of this behavior by school age, you should always be aware of behaviors that can become problematic or turn into a rhythmic movement disorder. Exercise Jumping - Motion Sickness.
Rocking Chair is a type of chair with two curved bands or rockers attached to the bottom of the legs, connecting the legs on each side to each other. The rockers contact the floor at only two points, giving the occupant the ability to rock back and forth by shifting their weight or pushing lightly with their feet. Rocking chairs are most commonly made of wood. Some rocking chairs can fold.
How To Calm A Crying Baby - Dr. Robert Hamilton Demonstrates "The Hold" (Official) (youtube)
How to Calm a Crying Baby (youtube) - How To Calm a Crying Baby (youtube)
Colic is the term used to describe infants who cry excessively for no apparent reason during the first three months of life. Colic is one of the most distressing problems of infancy. It is distressing for the infant, the parents, and for the health care provider. Baby Colic is defined as episodes of crying for more than three hours a day, for more than three days a week, for three weeks in an otherwise healthy child. Often crying occurs in the evening. It typically does not result in long-term problems. The crying can result in frustration of the parents, depression following delivery, excess visits to the doctor, and child abuse.
A Baby Crying is almost like a fire alarm going off in your head. Letting your baby cry without ignoring your child’s basic means of communication. Your baby cries for a reason. Maybe they’re tired, hungry or cold. Maybe they’re frightened, poorly or anxious. Whatever the reason, their cries are often their only means of communicating with you. When a baby cries for a prolonged period of time, the body releases an increased amount of cortisol, the stress hormone. This stress hormone increases feelings of anxiety and can lower growth hormones which in turn can inhibit the development of nerve tissue in the brain- resulting in suppressed growth weakening of the immune system. Researchers have also found that babies who are regularly left to cry for long periods are likely to experience overactive adrenaline systems which can lead to aggressive and impulsive behavior. A baby crying might be a blessing. Be grateful you can hear the cries because it will be a lot more difficult to hear the cries when someone doesn't make a sound, meaning, when people get older, they sometimes stop crying even though they need help and even when they are in pain. So how will you know when someone needs you? How will you know if someone isn't suffering in silence? Sound Perception. Noise Masking - Wilhelm Scream.
Having a baby changes the structure of the brain so that regions that control empathy and anxiety have increased activity and that, along with hormonal changes, can make new moms react to a baby's cry with intense feelings of protectiveness and worry. The first trick to calming your baby is to recognize that you yourself are anything but calm. Take a moment to name how you are feeling (frustrated, angry, sad, rejected, etc.). Try taking deep, even breaths. People often breathe shallowly when stressed, so changing your breathing actually helps you feel calmer. Deep, even breathing sends the message to your nervous system that you are safe, which helps your body start to regulate. Breathe in through your nose and out through your mouth. Try counting to 10, or putting your hand on your stomach as you breathe to make sure you’re taking deep breaths. Babies first Words.
Separation Anxiety refers to excessive fear or worry about separation from home or an attachment figure. Separation anxiety is a normal stage in an infant's development, as it helps children understand relationships and master their environment. Separation anxiety differs from normal clinginess. Children with the disorder can't think about anything but the present fear of separation. They may have nightmares or regular physical complaints. They may be reluctant to go to school or other places. Separation Anxiety Disorder is an anxiety disorder in which an individual experiences excessive anxiety regarding separation from home and/or from people to whom the individual has a strong emotional attachment (e.g., a parent, caregiver, significant other or siblings). It is most common in infants and small children, typically between the ages of six to seven months to three years, although it may pathologically manifest itself in older children, adolescents and adults. Separation anxiety is a natural part of the developmental process. Unlike SAD (indicated by excessive anxiety), normal separation anxiety indicates healthy advancements in a child's cognitive maturation and should not be considered a developing behavioral problem. According to the American Psychiatric Association (APA), separation anxiety disorder is an excessive display of fear and distress when faced with situations of separation from the home and/or from a specific attachment figure. The anxiety that is expressed is categorized as being atypical of the expected developmental level and age. The severity of the symptoms ranges from anticipatory uneasiness to full-blown anxiety about separation. SAD may cause significant negative effects within areas of social and emotional functioning, family life, and physical health of the disordered individual. The duration of this problem must persist for at least four weeks and must present itself before a child is eighteen years of age to be diagnosed as SAD in children, but can now be diagnosed in adults with a duration typically lasting six months in adults as specified by the DSM-5. Non-medication based treatments are the first choice when treating individuals diagnosed with separation anxiety disorder. Counseling tends to be the best replacement for drug treatments. There are two different non-medication approaches to treat separation anxiety. The first is a psychoeducational intervention, often used in conjunction with other therapeutic treatments. This specifically involves educating the individual and their family so that they are knowledgeable about the disorder, as well as parent counseling and guiding teachers on how to help the child. The second is a psychotherapeutic intervention when prior attempts are not effective. Psychotherapeutic interventions are more structured and include behavioral, cognitive-behavioral, contingency, psychodynamic psychotherapy, and family therapy.
