BK101
Knowledge Base
Meditation - Relaxation - Breathing - Hypnosis - Natural Therapy's
Meditation is a practice where an individual trains the mind or induces a mode of consciousness, either to realize some benefit, or for the mind to simply acknowledge its content without becoming identified with that content, or as an end in itself. Disclaimer.
Breathing - Vibrations - Energy - Sound - Silence - Hypnosis - Yoga - Transformation
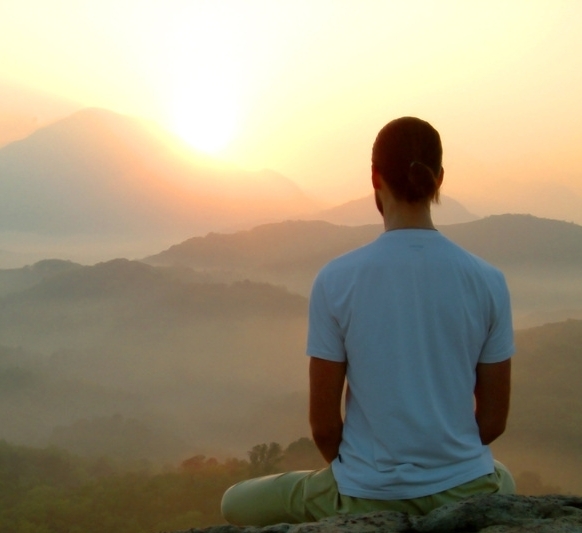 Every
now and then you have to take a break
because our physical health and
mental health depends on it. And
meditation is a convenient way to relax, reconnect,
balance and reenergize our well
being. Our lives can easily become disconnected from
reality. So we need to
unplug and step back once in a
while in order to reassess our
baseline.
And sometimes we need to reboot and
start over fresh.
Every
now and then you have to take a break
because our physical health and
mental health depends on it. And
meditation is a convenient way to relax, reconnect,
balance and reenergize our well
being. Our lives can easily become disconnected from
reality. So we need to
unplug and step back once in a
while in order to reassess our
baseline.
And sometimes we need to reboot and
start over fresh. Deep Meditation - 2 Minute Meditation
Guided Meditation For Centering Yourself (youtube)
Harmonic Convergence is the name given to one of the world's first globally synchronized meditation events, which occurred on August 16–17, 1987. This event also closely coincided with an exceptional alignment of planets in the Solar System.
Meditation Practitioners - Spiritual Teachers
Vibrations - Hz - Sounds - The Force - Aroma Therapy - Imagery - Colors
Mindfulness - Stop and Think
Mindfulness is the psychological process of bringing one's attention to the internal and external experiences occurring in the present moment, which can be developed through the practice of meditation and other training.
Conscious Living - Awareness - Stop and Smell the Roses
Mindfulness Resources - Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction Training - Awareness for Kids - Mindfulness Training - Mindfulness Programs - Reducing distress in mothers of children with autism and other disabilities: a randomized trial.
Free the Mind (documentary)
Mindful - Wild Mind - Body Scan
Mind Wandering (silence)
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction is a program that incorporates mindfulness to assist people with pain and a range of conditions and life issues that were initially difficult to treat in a hospital setting.
Breathing - The Cycle of Air coming In and Air going Out
Breathing is the process that moves air in and out of the lungs, inhalation and exhalation, drawing air into, and expelling air out of, the lungs; the process of taking in oxygen from inhaled air and releasing carbon dioxide by exhalation. Passing or able to pass air in and out of the lungs normally; sometimes used in combination. Air Pressure - Focused Breathing.
 Respiration is a
single complete act of breathing in and out, the
metabolic processes whereby certain
organisms obtain energy from organic
molecules; processes
that take place in the cells and
tissues during which energy is
released and carbon dioxide is produced and absorbed by the blood to be
transported to the lungs.
Respirator - Choking -
Not Breathing.
Respiration is a
single complete act of breathing in and out, the
metabolic processes whereby certain
organisms obtain energy from organic
molecules; processes
that take place in the cells and
tissues during which energy is
released and carbon dioxide is produced and absorbed by the blood to be
transported to the lungs.
Respirator - Choking -
Not Breathing.Breathing Meditation | UCLA Mindful Awareness Research Center (youtube) - Yoga
Vase Breathing Kundalini Exercise (youtube)
Breathing During Exercising or Singing
Breathing Tips to Improve Learning
Breathing through the Nose forces us to slow down until proper breath is trained; therefore, proper nose breathing reduces hypertension and stress. It also helps prevent us from overexerting ourselves during a workout. Our nostrils and sinuses filter and warm/cool air as it enters our bodies. Mouth breathing bypasses the nasal mucosa and makes regular breathing difficult, which can lead to snoring, breath irregularities and sleep apnea. Clearing Your Chest with Breathing Exercises (youtube).
Static Apnea is a discipline in which a person holds their breath (apnea) underwater for as long as possible, and need not swim any distance. Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, defined as a heart rate of under 60 beats per minute or BPM in adults.
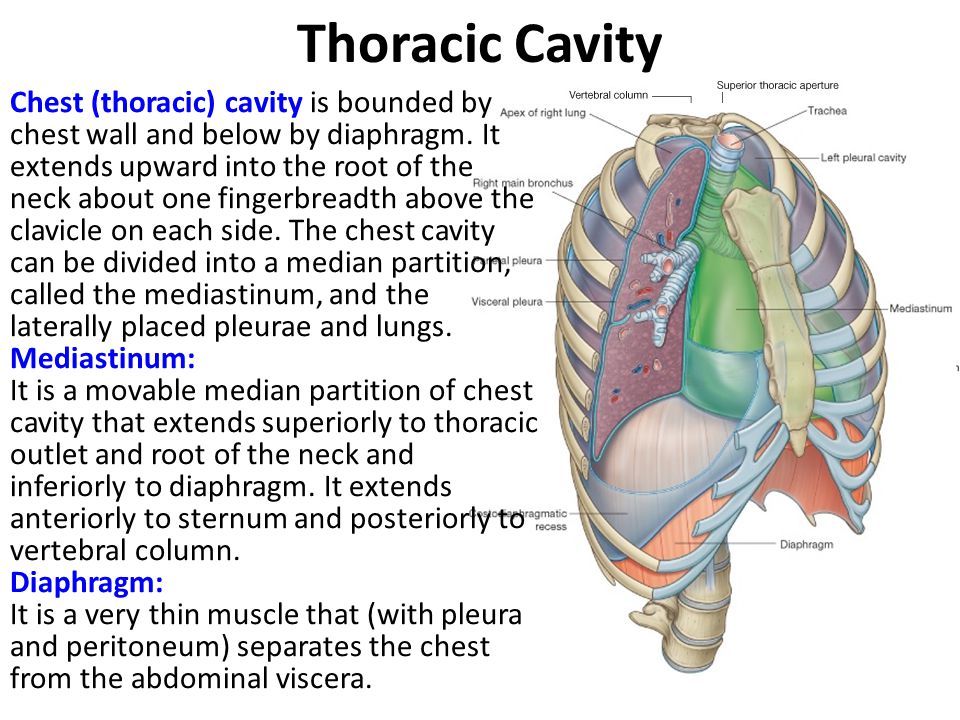 Diaphragmatic
Deep Breathing or Belly
Breathing is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm,
which is a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and
abdominal cavity. Air enters the lungs and the belly expands during this
type of breathing. This deep breathing is marked by
expansion of the abdomen rather than the
chest when breathing.
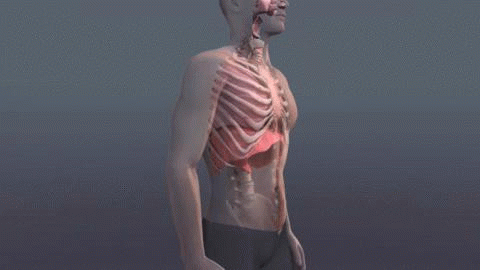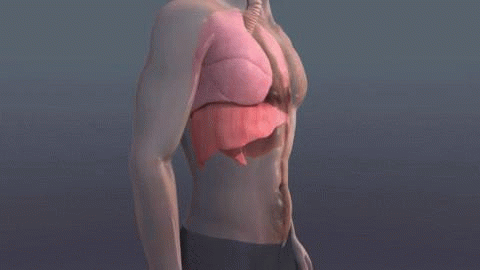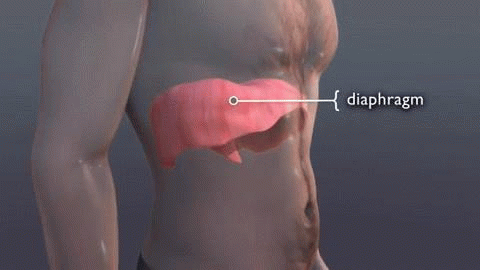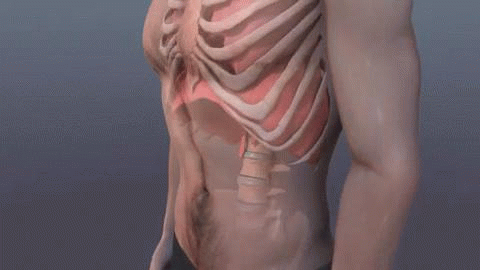
Diaphragmatic
Deep Breathing or Belly
Breathing is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm,
which is a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and
abdominal cavity. Air enters the lungs and the belly expands during this
type of breathing. This deep breathing is marked by
expansion of the abdomen rather than the
chest when breathing. Diaphragm is a muscular partition separating the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity that contains the heart and lungs. The diaphragm performs an important function in respiration. As the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases and air is drawn into the lungs. The thoracic diaphragm is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. Abdominal (belly) Breathing (youtube) - Gas Buildup.
Ujjayi Breath is a diaphragmatic breath, which first fills the lower belly (activating the first and second chakras), rises to the lower rib cage (the third and fourth chakras), and finally moves into the upper chest and throat. The technique is very similar to the three-part Tu-Na breathing found in Taoist Qigong practice. Inhalation and exhalation are both done through the nose. The "ocean sound" is created by moving the glottis as air passes in and out. As the throat passage is narrowed so, too, is the airway, the passage of air through which creates a "rushing" sound. The length and speed of the breath is controlled by the diaphragm, the strengthening of which is, in part, the purpose of ujjayi. The inhalations and exhalations are equal in duration, and are controlled in a manner that causes no distress to the practitioner.
Wim Hof Method: The Power Breath #173 (youtube) - 30 breaths, and then on the last breath completely exhale and don't breathe for 15-30 seconds, then inhale and hold for 15-30 seconds. Comfortable Meditation Position where you can expand your lungs freely without any constrictions (empty stomach preferred). Close Eyes, imagine blowing up a balloon and inhale fully in through the nose and exhale through the mouth in short powerful burst, use midriff or Abdomen or Belly fully. (30 times). Should feel light head or tingling sensations. On the last breath fill the lungs to maximum without force, then let the air out and hold for as long as you can until you experience the gasp reflex. Then inhale to full capacity and then hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 3 more times. Enjoy the moment. CO2 Reduction.
Shallow Breathing is thoracic breathing, or chest breathing is the drawing of minimal breath into the lungs, usually by drawing air into the chest area using the intercostal muscles rather than throughout the lungs via the diaphragm. Shallow breathing can result in or be symptomatic of rapid breathing and hypoventilation. Most people who breathe shallowly do it throughout the day and are almost always unaware of the condition. In upper lobar breathing, clavicular breathing, or clavicle breathing air is drawn predominantly into the chest by the raising of the shoulders and collarbone (clavicles), and simultaneous contracting of the abdomen during inhalation. Maximum amount of air can be drawn this way only for short periods of time, since it requires a lot of effort. When used for prolonged time, this is the most superficial mode of shallow breathing. Thoracic relates to the chest or thorax, which is the part of the human torso between the neck and the diaphragm.
Six-Second Breath - Throat Breathing (youtube)
Glottis is defined as the opening between the vocal folds.
Relax the Abdominal Muscles and Inhale for 3 Seconds, breathing through the nose to “disinfect, filter, condition and moisturize the air before it reaches the lungs, expanding completely around the waistline. Pause momentarily and exhale through the nose or mouth for three seconds, gently contracting the abdomen to help expel the air. Bhastrika Pranayama: The Bellows Breath (youtube).
Pursed Lip Breathing Exercise is breathing in through your nose for 3 seconds and then breathing out through your mouth with pursed lips for 6 seconds. This reduces the number of breaths that you take and keeps your airways open longer. More air is able to flow in and out of your lungs. Pursed lips is like when you're whistling.
Inhale vigorously through the nose while raising the arms above the head, fingers extended, and then forcibly exhales through the nose while pulling the elbows down alongside the ribs with fingers closing gently. Natural Awakenings.
4-2-10 Breathing: Inhale through the nose for four seconds, hold for two, and then slowly release the breath for up to 10 seconds.
4-7-8 Breath - Video
Box Breathing is a technique used in taking slow, deep breaths. This can heighten performance and concentration while also being a powerful stress reliever. Step 1: Sitting upright, slowly exhale, getting all the oxygen out of your lungs. Focus on this intention and be conscious of what you’re doing. Step 2: Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose to the count of four. In this step, count to four very slowly in your head. Feel the air fill your lungs, one section at a time, until your lungs are completely full and the air moves into your abdomen. Step 3: Hold your breath for another slow count of four. Step 4: Exhale through your mouth for the same slow count of four, expelling the air from your lungs and abdomen. Be conscious of the feeling of the air leaving your lungs. Step 5: Hold your breath for the same slow count of four before repeating this process.
Sleeping Knowledge - Routines - Yoga Breathing
Sama Vritti Breathing (youtube)
Gigong Target Deep, Slow Breathing is a holistic system of coordinated body posture and movement, breathing, and meditation used for health, spirituality, and martial arts training.
Shining Skull Breath (youtube)
Breathwork is the conscious control of breathing that is meant to influence a person's mental, emotional and/or physical state, with a claimed therapeutic effect. Breathwork has no proven positive health impact other than promoting relaxation and can cause distress if not done correctly under guidance.
Rebirthing Breathwork is claimed to be capable of releasing suppressed traumatic childhood memories.
Vivation claims to improve wellbeing through the use of circular breathing.
Holotropic Breathwork is a practice that uses breathing and other elements to putatively allow access to non-ordinary states of consciousness. Other types include Integrative Breathwork, Transformational Breathwork, Shamanic Breathwork, Conscious Connected Breathing, Radiance Breathwork, Zen Yoga Breathwork and many others. Concerns about the risk that the hyperventilation technique could cause seizure or lead to psychosis in vulnerable people caused the Findhorn Foundation to suspend its breathwork programme.
Kapalabhati Hatha Yoga the yogic system of body cleansing techniques intended mainly for cleaning the cranial sinuses but has many other effects including curing anemia.
Freediving Breathe Up Techniques (youtube)
Breathing Exercises - Somatic Breath Therapy - Pranic Breathing
Somatic Psychology is a form of alternative medicine that focuses on somatic experience, and the embodied self, including therapeutic and holistic approaches to body.
Somatics is a field within bodywork and movement studies which emphasizes internal physical perception and experience. Breath.
Hyperventilation occurs when the rate and quantity of alveolar ventilation of carbon dioxide exceeds the body's production of carbon dioxide. When alveolar ventilation is excessive, more carbon dioxide will be removed from the blood stream than the body can produce. This causes the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood stream to fall and produces a state known as hypocapnia, which is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood. The body normally attempts to compensate for this metabolically. If excess ventilation cannot be compensated metabolically, it will lead to a rise in blood pH. This rise in blood pH is known as respiratory alkalosis. When hyperventilation leads to respiratory alkalosis, it may cause a number of physical symptoms: dizziness, tingling in the lips, hands or feet, headache, weakness, fainting and seizures. In extreme cases it can cause carpopedal spasms (flapping and contraction of the hands and feet). Over-Breathing.
Bohr Effect is when hemoglobin's oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide. Since carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid, an increase in CO2 results in a decrease in blood pH, resulting in hemoglobin proteins releasing their load of oxygen. Conversely, a decrease in carbon dioxide provokes an increase in pH, which results in hemoglobin picking up more oxygen. Oxygen-Hemoglobin Dissociation Curve (wiki)
Rebreather - Gases - Air (knowledge)
Learning can improve by Breathing
Merkaba Meditation (youtube)
Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. It is one of six civilizations to arise independently.
Spirit of Maat Egyptian Orgasm - 12 Biogeometry
Ankh is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic ideograph with the meaning "Life". Ankh and other Energy Devices (youtube) - Secret of the Ankh.
Breathing Secrets - Ten Keys
Inner Harmony - Modern Mystery School
Buteyko Breathing Method. Nasal breathing: The Buteyko method emphasizes the importance of nasal breathing, which protects the airways by humidifying, warming, and cleaning the air entering the lungs. A majority of asthmatics have problems sleeping at night, and this is thought by Buteyko practitioners to be linked with poor posture or unconscious mouth-breathing. By keeping the nose clear and encouraging nasal breathing during the day, night-time symptoms can also improve. Strictly nasal breathing during physical exercise is another key element of the Buteyko method. Reduced breathing exercises: The core Buteyko exercises involve breath control; consciously reducing either breathing rate or breathing volume. Many teachers refer to Buteyko as 'breathing retraining' and compare the method to learning to ride a bicycle. Once time has been spent practicing, the techniques become instinctive and the exercises are gradually phased out as the condition improves. Buteyko uses a measurement called the Control Pause (CP), the amount of time between breaths that an individual can comfortably hold breath. According to Buteyko teachers, people with asthma who regularly practice Buteyko breathing will notice an increase in CP and decrease in pulse rate that corresponds to decreased asthma symptoms. Relaxation: Dealing with asthma attacks is an important factor of Buteyko practice. The first feeling of an asthma attack is unsettling and can result in a short period of rapid breathing. By controlling this initial over-breathing phase, asthmatics can prevent a "vicious circle of over-breathing" from developing and spiraling into an asthma attack. This theory asserts that asthma attacks may be averted simply by breathing less.
When changes in heart rate are analyzed formally, as in a Differential Fourier Transform (DFT) by frequency, the predominant frequency ranges of heart rate variability can identified by their higher amplitudes. Three such relatively high amplitude frequency ranges have been proven to be sensitive indicators of autonomic nervous system regulation and associated changes in emotion, alertness, attention, and stress. These are the Very Low Frequency (VLF, 0.0033 to 0.04 Hz), Low Frequency (LF, 0.04 to 0.15 Hz), and High frequency (HF, 0.15 to 0.4 Hz, RSA, or breathing heart wave) ranges. Monitoring and recording HRV in these frequency bands has proven useful in tracking and evaluating autonomic nervous system function.
To circulate the Vital Breath: Breathe deeply, then it will collect. When it is collected, it will expand. When it expands, it will descend. When it descends, it will become stable. When it is stable, it will be regular. When it is regular, it will sprout. When it sprouts, it will grow. When it grows, it will recede. When it recedes, it will become heavenly. The dynamism of Heaven is revealed in the ascending; The dynamism of Earth is revealed in the descending. Follow this and you will live; oppose it and you will die. (tr. Roth 1997:298).
Inhale through your Nose and Exhale through your Mouth. Breathing is a way that can provide a powerful medical benefit that can help the body fight viral infections. The reason is that your nasal cavities produce the molecule nitric oxide, which chemists abbreviate NO, that increases blood flow through the lungs and boosts oxygen levels in the blood. Breathing in through the nose delivers NO directly into the lungs. The higher oxygen saturation of the blood can make one feel more refreshed and provides greater endurance. Nitric oxide is a widespread signaling molecule that triggers many different physiological effects. It is also used clinically as a gas to selectively dilate the pulmonary arteries in newborns with pulmonary hypertension. Unlike most signaling molecules, NO is a gas in its natural state. NO is produced continuously by the 1 trillion cells that form the inner lining, or endothelium, of the 100,000 miles of arteries and veins in our bodies, especially the lungs. Endothelium-derived NO acts to relax the smooth muscle of the arteries to prevent high blood pressure and to promote blood flow to all organs. Another vital role of NO is to prevent blood clots in normal arteries. In addition to relaxing vascular smooth muscle, NO also relaxes smooth muscle in the airways – trachea and bronchioles – making it easier to breathe. Another type of NO-mediated smooth muscle relaxation occurs in the erectile tissue (corpus cavernosum), which results in penile erection. In fact, NO is the principal mediator of penile erection and sexual arousal. This discovery led to the development and marketing of sildenafil, trade name Viagra, which works by enhancing the action of NO. Other types of cells in the body, including circulating white blood cells and tissue macrophages, produce nitric oxide for antimicrobial purposes. The NO in these cells reacts with other molecules, also produced by the same cells, to form antimicrobial agents to destroy invading microorganisms including bacteria, parasites and viruses. As you can see, NO is quite an amazing molecule. Since NO is a gas, it can be administered with the aid of specialized devices as a therapy to patients by inhalation. Inhaled NO is used to treat infants born with persistent pulmonary hypertension, a condition in which constricted pulmonary arteries limit blood flow and oxygen harvesting. Inhaled NO dilates the constricted pulmonary arteries and increases blood flow in the lungs. As a result, the red blood cell hemoglobin can extract more lifesaving oxygen and move it into the general circulation. Inhaled NO has literally turned blue babies pink and allowed them to be cured and to go home with mom and dad. Before the advent of inhaled NO, most of these babies died.
Nitric Oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical, i.e., it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (·N=O or ·NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a historic class that drew researches which spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. Nitric oxide should not be confused with nitrous oxide (N2O), an anesthetic, or with nitrogen dioxide (NO2), a brown gas and major air pollutant.
Nitrous Oxide commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidizer similar to molecular oxygen. It is soluble in water. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain reducing effects. inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the safest and most effective medicines needed in a health system. Nitrous oxide occurs in small amounts in the atmosphere, but has been found to be a major scavenger of stratospheric ozone, with an impact comparable to that of CFCs. It is estimated that 30% of the N2O in the atmosphere is the result of human activity, chiefly agriculture and industry. Being the third most important long-lived greenhouse gas, nitrous oxide substantially contributes to global warming.
Related Subject Pages - Sympathetic Nervous System - Parasympathetic Nervous System - Neuroscience - Brain - Plasticity - Lucid Dreaming - Sleeping - Remembering - Time Management - Physical Education - Worrying - Stress - Self-Control - Will Power - HOS (Human Operating System).
Brain Waves - Neural Oscillations - Good Vibrations
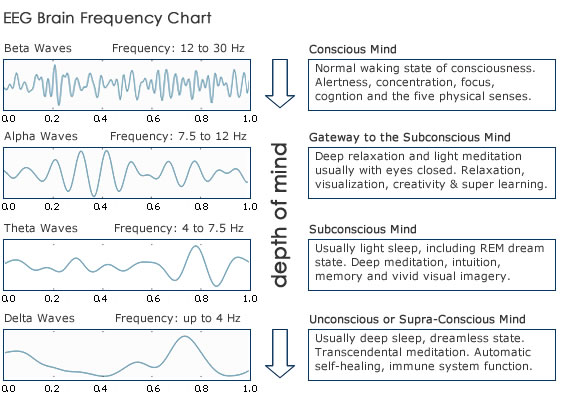 Brainwave Entrainment
refers to the capacity of the brain to naturally
synchronize its brainwave
frequencies with the
rhythm of periodic
external stimuli, most commonly
auditory, visual, or tactile. Brainwave entrainment technologies are
used to induce various brain states, such as relaxation or sleep, by
creating stimuli that occur at regular,
periodic intervals to mimic
electrical cycles of the
brain during the desired states, thereby
"training" the brain to consciously alter states. Recurrent acoustic
frequencies, flickering lights, or tactile vibrations are the most common
examples of stimuli applied to generate different
sensory responses.
Brainwave Entrainment
refers to the capacity of the brain to naturally
synchronize its brainwave
frequencies with the
rhythm of periodic
external stimuli, most commonly
auditory, visual, or tactile. Brainwave entrainment technologies are
used to induce various brain states, such as relaxation or sleep, by
creating stimuli that occur at regular,
periodic intervals to mimic
electrical cycles of the
brain during the desired states, thereby
"training" the brain to consciously alter states. Recurrent acoustic
frequencies, flickering lights, or tactile vibrations are the most common
examples of stimuli applied to generate different
sensory responses.
Instrument Tuning - Brain Plasticity - Neuro-Feedback - Sound Waves.
Neural Oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity. Speed Reading.
Sensorimotor Rhythm is a brain wave. It is an oscillatory idle rhythm of synchronized electric brain activity. It appears in spindles in recordings of EEG, MEG, and ECoG over the sensorimotor cortex. For most individuals, the frequency of the SMR is in the range of 13 to 15 Hz.
Are we on the Same Wave Length?
Mind Machine uses pulsing rhythmic sound, flashing light, electrical or magnetic fields, or a combination of these, to alter the frequency of the user's brainwaves. Mind machines can induce deep states of relaxation, concentration, and in some cases altered states of consciousness, which have been compared to those obtained from meditation and shamanic exploration. Photic mind machines work with flickering lights embedded in sunglasses. The process applied by some of these machines is said to induce brainwave synchronisation or entrainment.
Binaural Beats is an auditory illusion perceived when two different pure-tone sine waves, both with frequencies lower than 1500 Hz, with less than a 40 Hz difference between them, are presented to a listener dichotically (one through each ear). For example, if a 530 Hz pure tone is presented to a subject's right ear, while a 520 Hz pure tone is presented to the subject's left ear, the listener will perceive the auditory illusion of a third tone, in addition to the two pure-tones presented to each ear. The third sound is called a binaural beat, and in this example would have a perceived pitch correlating to a frequency of 10 Hz, that being the difference between the 530 Hz and 520 Hz pure tones presented to each ear.
Delta Wave is a high amplitude brain wave with a frequency of oscillation between 0.5 - 4 hertz. Delta waves, like other brain waves, are recorded with an electroencephalogram (EEG) and are usually associated with the deep stage 3 of NREM sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), and aid in characterizing the depth of sleep. 40-Hz Coherent Magnetic Activity - Fronto-Occipital Phase.
 Theta
Wave is a neural oscillatory pattern in electroencephalography (EEG)
signals (4 – 7 Hz), recorded either from
inside the brain or from electrodes glued to the scalp. Two types of theta
rhythm have been described. The "hippocampal theta rhythm" is a strong
oscillation that can be observed in the
hippocampus and other brain
structures in numerous species of mammals including rodents, rabbits,
dogs, cats, bats, and marsupials. "Cortical theta rhythms" are
low-frequency components of scalp EEG, usually recorded from humans. Theta
rhythms can be quantified using Quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG)
using freely available toolboxes, such as, EEGLAB or the
Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT).
Theta Binaural Beat 7hz
(youtube). A baby's brain, in utero and after birth,
operates primarily in theta and delta waves. These are the low, slow
waves. Children remain heavily in theta and delta until they are seven
years old. Only then do children begin to think remotely 'like an adult,'
with more alpha and beta processing brain waves.
Subconscious.
Theta
Wave is a neural oscillatory pattern in electroencephalography (EEG)
signals (4 – 7 Hz), recorded either from
inside the brain or from electrodes glued to the scalp. Two types of theta
rhythm have been described. The "hippocampal theta rhythm" is a strong
oscillation that can be observed in the
hippocampus and other brain
structures in numerous species of mammals including rodents, rabbits,
dogs, cats, bats, and marsupials. "Cortical theta rhythms" are
low-frequency components of scalp EEG, usually recorded from humans. Theta
rhythms can be quantified using Quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG)
using freely available toolboxes, such as, EEGLAB or the
Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT).
Theta Binaural Beat 7hz
(youtube). A baby's brain, in utero and after birth,
operates primarily in theta and delta waves. These are the low, slow
waves. Children remain heavily in theta and delta until they are seven
years old. Only then do children begin to think remotely 'like an adult,'
with more alpha and beta processing brain waves.
Subconscious. Alpha Wave are
neural oscillations in the frequency range of 7.5 – 12.5 Hz arising from
synchronous and coherent (in phase or constructive) electrical activity of
thalamic pacemaker cells in humans. They are also called Berger's wave in
memory of the founder of EEG. Alpha waves are one type of brain waves
detected either by electroencephalography (EEG) or magnetoencephalography
(MEG) and predominantly originate from the occipital lobe during wakeful
relaxation with closed eyes. Alpha waves are reduced with open eyes,
drowsiness and sleep. Historically, they were thought to represent the
activity of the visual cortex in an idle state. More recent papers have
argued that they inhibit areas of the cortex not in use, or alternatively
that they play an active role in network coordination and communication.
Occipital alpha waves during periods of eyes closed are the strongest EEG
brain signals.
Alpha Binaural Beat 12hz
(youtube)
- Earths Vibration is 7.83 Hz.
Alpha Wave are
neural oscillations in the frequency range of 7.5 – 12.5 Hz arising from
synchronous and coherent (in phase or constructive) electrical activity of
thalamic pacemaker cells in humans. They are also called Berger's wave in
memory of the founder of EEG. Alpha waves are one type of brain waves
detected either by electroencephalography (EEG) or magnetoencephalography
(MEG) and predominantly originate from the occipital lobe during wakeful
relaxation with closed eyes. Alpha waves are reduced with open eyes,
drowsiness and sleep. Historically, they were thought to represent the
activity of the visual cortex in an idle state. More recent papers have
argued that they inhibit areas of the cortex not in use, or alternatively
that they play an active role in network coordination and communication.
Occipital alpha waves during periods of eyes closed are the strongest EEG
brain signals.
Alpha Binaural Beat 12hz
(youtube)
- Earths Vibration is 7.83 Hz. Beta
Wave or beta rhythm, is the term used to designate the frequency range
of human brain activity between 12.5 and 30 Hz
(12.5 to 30 transitions or cycles per second). Beta waves can be split
into three sections: Low Beta Waves (12.5–16 Hz, "Beta 1 power"); Beta
Waves (16.5–20 Hz, "Beta 2 power"); and High Beta Waves (20.5–28 Hz, "Beta
3 power"). Beta states are the states associated with normal
waking
consciousness.
Beta Binaural Beat 20hz (youtube).
Radio Waves.
Beta
Wave or beta rhythm, is the term used to designate the frequency range
of human brain activity between 12.5 and 30 Hz
(12.5 to 30 transitions or cycles per second). Beta waves can be split
into three sections: Low Beta Waves (12.5–16 Hz, "Beta 1 power"); Beta
Waves (16.5–20 Hz, "Beta 2 power"); and High Beta Waves (20.5–28 Hz, "Beta
3 power"). Beta states are the states associated with normal
waking
consciousness.
Beta Binaural Beat 20hz (youtube).
Radio Waves.Sensorimotor Rhythm is a brain wave. It is an oscillatory idle rhythm of synchronized electric brain activity. It appears in spindles in recordings of EEG, MEG, and ECoG over the sensorimotor cortex. For most individuals, the frequency of the SMR is in the range of 13 to 15 Hz.
 Gamma Wave is a pattern of neural oscillation in
humans with a frequency between 25 and 140 Hz, though 40 Hz
or 62-78 MHz is typical. Gamma
rhythms are correlated with large scale brain network activity and
cognitive phenomena such as working memory, attention,
and perceptual grouping, and can be increased
in amplitude via meditation or neurostimulation. Altered gamma activity
has been observed in many mood and cognitive disorders.
Gamma Wave is a pattern of neural oscillation in
humans with a frequency between 25 and 140 Hz, though 40 Hz
or 62-78 MHz is typical. Gamma
rhythms are correlated with large scale brain network activity and
cognitive phenomena such as working memory, attention,
and perceptual grouping, and can be increased
in amplitude via meditation or neurostimulation. Altered gamma activity
has been observed in many mood and cognitive disorders.
Resonance is a phenomenon in which a vibrating system or external force drives another system to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are known as the system's resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies. At resonant frequencies, small periodic driving forces have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations, due to the storage of vibrational energy.
Schumann Resonances are a set of spectrum peaks in the extremely low frequency (ELF) portion of the Earth's electromagnetic field spectrum. Schumann resonances are global electromagnetic resonances, generated and excited by lightning discharges in the cavity formed by the Earth's surface and the ionosphere.
Schumann Resonance 7.83 HZ (youtube)
7.83 Hz-Grounding with Isochronic Tones (youtube)
Micro-Currents Pulsed Magnetic Fields
Physics - Aura - Tuner
Delta Binaural Beat Hz (youtube)
Love Signal 528 Hz (youtube)
528 Hz | Miracle Tone (youtube)
528Hz | Miracle Tone | 8 Hours (youtube)
Solfeggio Frequencies
528 Hz – Transformation (DNA Repair)
Healing Sounds (youtube)
Slow, steady waves keep brain humming. Researchers have found that very slow waves are directly linked to state of consciousness and may be involved in coordinating activity across distant brain regions.
Sound - Rhythm - Tingling Feeling or Whole Body Vibration from an Emotional Memory or Experience.
Brain Wave Device Enhances Memory Function. The entrainment of theta brain waves enhances theta wave activity, but also boosts memory performance.
Q Factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, and characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency. Higher Q indicates a lower rate of energy loss relative to the stored energy of the resonator; the oscillations die out more slowly. A pendulum suspended from a high-quality bearing, oscillating in air, has a high Q, while a pendulum immersed in oil has a low one. Resonators with high quality factors have low damping so that they ring or vibrate longer.
Brain Tuner (youtube)
Deep Brain Stimulation is a neurosurgical procedure introduced in 1987, involving the implantation of a medical device called a neurostimulator (sometimes referred to as a 'brain pacemaker'), which sends electrical impulses, through implanted electrodes, to specific targets in the brain (brain nuclei) for the treatment of movement and neuropsychiatric disorders. DBS in select brain regions has provided therapeutic benefits for otherwise-treatment-resistant disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, dystonia, chronic pain, major depression and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). Despite the long history of DBS, its underlying principles and mechanisms are still not clear. DBS directly changes brain activity in a controlled manner, its effects are reversible (unlike those of lesioning techniques), and it is one of only a few neurosurgical methods that allow blinded studies
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart transmits signals generated usually by the sinoatrial node to cause contraction of the heart muscle. The pacemaking signal generated in the sinoatrial node travels through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node, along the Bundle of His and through bundle branches to cause contraction of the heart muscle. This signal stimulates contraction first of the right and left atrium, and then the right and left ventricles. This process allows blood to be pumped throughout the body. The conduction system consists of specialized heart muscle cells, and is situated within the myocardium. There is a skeleton of fibrous tissue that surrounds the conduction system which can be seen on an ECG. Dysfunction of the conduction system can cause irregular, fast, or slow heart rhythms.
Sinoatrial Node is a group of cells located in the wall of the right atrium of the heart. These cells have the ability to spontaneously produce an electrical impulse action potential that travels through the heart via the electrical conduction system causing it to contract. In a healthy heart, the SAN continuously produces action potential, setting the rhythm of the heart and so is known as the hearts natural pacemaker. The rate of action potential production (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by nerves that supply it.
The Beach Boys - Good Vibrations (youtube)
Bad Vibrations (microwaves from cellphones)
Frisson is a sensation somewhat like shivering, usually caused by stimuli other than cold. It is typically expressed as an overwhelming emotional response combined with piloerection (goosebumps). Stimuli that produce a response are specific to the individual. Frisson is of short duration, usually no more than 4–5 seconds, usually pleasurable. Typical stimuli include loud passages of music and passages that violate some level of musical expectation. It has been shown that during frisson, the skin of the lower back flexes, and shivers rise upward and inward from the shoulders, up the neck, and may extend to the cheeks and scalp. The face may become flush, hair follicles experience piloerection. This frequently occurs in a series of 'waves' moving up the back in rapid succession. The frissoner usually feels the experience as involuntary. It has been shown that some experiencing musical frisson report reduced excitement when under administration of naloxone (an opioid receptor antagonist), suggesting musical frisson gives rise to endogenous opioid peptides similar to other pleasurable experiences. Frisson may be enhanced by the amplitude of the music and the temperature of the environment. Cool listening rooms and movie theaters may enhance the experience.
Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (softly spoken words and sounds)
Centerpointe - Brainwave Research
Muse Brain-Sensing Headband - Elixa Brain Tuner.
Everything moves at different speeds and at different wavelengths and at different timescales. That's everything we can sense, and everything that we know, so far.
Morphic Resonance is a paranormal influence by which a pattern of events or behavior can facilitate subsequent occurrences of similar patterns.
Voice Frequency - Words that Resonate
Human Voice Frequency is one of the frequencies, within part of the audio range, that is used for the transmission of speech. In telephony, the usable voice frequency band ranges from approximately 300 Hz to 3400 Hz. It is for this reason that the ultra low frequency band of the electromagnetic spectrum between 300 and 3000 Hz is also referred to as voice frequency, being the electromagnetic energy that represents acoustic energy at baseband. The bandwidth allocated for a single voice-frequency transmission channel is usually 4 kHz, including guard bands, allowing a sampling rate of 8 kHz to be used as the basis of the pulse code modulation system used for the digital PSTN. Per the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, the sampling frequency (8 kHz) must be at least twice the highest component of the voice frequency via appropriate filtering prior to sampling at discrete times (4 kHz) for effective reconstruction of the voice signal.
Human Voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal folds for talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, etc. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering. Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx, and the articulators. The lung (the pump) must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds (this air pressure is the fuel of the voice). The vocal folds (vocal cords) are a vibrating valve that chops up the airflow from the lungs into audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to ‘fine-tune’ pitch and tone. The articulators (the parts of the vocal tract above the larynx consisting of tongue, palate, cheek, lips, etc.) articulate and filter the sound emanating from the larynx and to some degree can interact with the laryngeal airflow to strengthen it or weaken it as a sound source. The vocal folds, in combination with the articulators, are capable of producing highly intricate arrays of sound. The tone of voice may be modulated to suggest emotions such as anger, surprise, or happiness. Singers use the human voice as an instrument for creating music.
Polyphonic Singing - Mantras - The Power of Words
 Om
Mantra Chanting Soothing Voice (youtube)
Om
Mantra Chanting Soothing Voice (youtube)OM-AUM Mantra Chant (youtube)
Om is a sacred sound and a spiritual icon in Hindu religion. It is also a mantra in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. Om is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. The symbol has a spiritual meaning in all Indian dharmas, but the meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions.
Radionics is an alternative medicine that claims disease can be diagnosed and treated with a kind of energy similar to radio waves. The concept behind radionics originated in the early 1900s with Albert Abrams (1864–1924), who became a millionaire by leasing radionic machines which he designed himself.
Biosonics Sounds Healing - Words the Imitate Sounds
Resonance (HZ) - Waves - Message (meridians) - Human Touch
Acoustic Resonance is a phenomenon that consists of a given acoustic system amplifying a sound whose frequency matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration (its resonance frequencies). The term "acoustic resonance" is sometimes used to narrow mechanical resonance to the frequency range of human hearing, but since acoustics is defined in general terms concerning vibrational waves in matter acoustic resonance can occur at frequencies outside the range of human hearing. An acoustically resonant object usually has more than one resonance frequency, especially at harmonics of the strongest resonance. It will easily vibrate at those frequencies, and vibrate less strongly at other frequencies. It will "pick out" its resonance frequency from a complex excitation, such as an impulse or a wideband noise excitation. In effect, it is filtering out all frequencies other than its resonance. Acoustic resonance is an important consideration for instrument builders, as most acoustic instruments use resonators, such as the strings and body of a violin, the length of tube in a flute, and the shape of a drum membrane. Acoustic resonance is also important for hearing. For example, resonance of a stiff structural element, called the basilar membrane within the cochlea of the inner ear allows hair cells on the membrane to detect sound. (For mammals the membrane has tapering resonances across its length so that high frequencies are concentrated on one end and low frequencies on the other.) Like mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance can result in catastrophic failure of the vibrator. The classic example of this is breaking a wine glass with sound at the precise resonant frequency of the glass; although this is difficult in practice.
Sounds Create Shapes
Cymatics is when shapes and patterns are created from sound wave vibrations, usually using the surface of a plate, diaphragm or membrane. Regions of maximum and minimum displacement are made visible in a thin coating of particles, paste or liquid. Different patterns emerge in the excitatory medium depending on the geometry of the plate and the driving frequency.
Cymatics (youtube) - Chromatic Scale - Sonar - Synesthesia - Noise
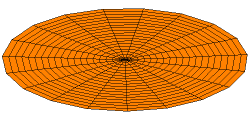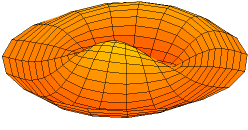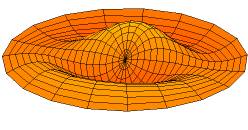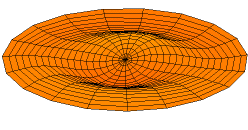 Normal
Mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all
parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a
fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes
place at the fixed frequencies. These fixed frequencies of the normal
modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant
frequencies. A physical object, such as a building, bridge or molecule,
has a set of normal modes and their natural frequencies that depend on its
structure, materials and boundary conditions. The most general motion of a
system is a superposition of its normal modes. The modes are normal in the
sense that they can move independently, that is to say that an excitation
of one mode will never cause motion of a different mode. In mathematical
terms, normal modes are orthogonal to each other.
Symmetry.
Normal
Mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all
parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a
fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes
place at the fixed frequencies. These fixed frequencies of the normal
modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant
frequencies. A physical object, such as a building, bridge or molecule,
has a set of normal modes and their natural frequencies that depend on its
structure, materials and boundary conditions. The most general motion of a
system is a superposition of its normal modes. The modes are normal in the
sense that they can move independently, that is to say that an excitation
of one mode will never cause motion of a different mode. In mathematical
terms, normal modes are orthogonal to each other.
Symmetry.
Numbers make Shapes - Sound in Outer Space
Magnetic Machine (video)
Sisyphus
512 Hz Tuning Fork in Water at 2560 fps (youtube)
Synaptic and Cellular Resonance
Oscillations Synapses Resonance
Seeing Sound with Light: Strobes and Resonance (youtube)
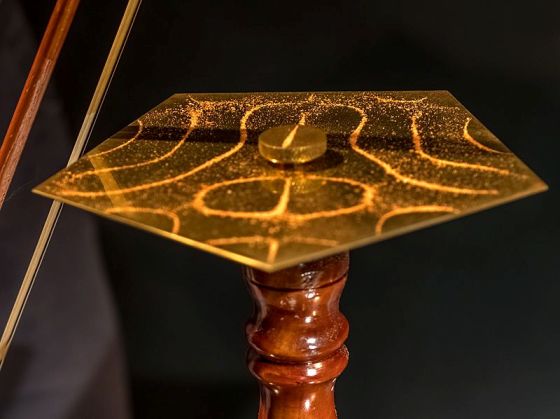 Ernst Chladni
did esearch on vibrating plates and the calculation of the speed of sound
for different gases. One of Chladni's best-known achievements was
inventing a technique to show the various modes of vibration on a rigid
surface, known as Chladni figures due to
the various shapes or patterns created by various modes. When resonating,
a plate or membrane is divided into regions that vibrate in opposite
directions, bounded by lines where no vibration occurs (nodal lines).
Chladni repeated the pioneering experiments of Robert Hooke who, on July
8, 1680, had observed the nodal patterns associated with the vibrations of
glass plates. Hooke ran a violin bow along the edge of a plate covered
with flour and saw the nodal patterns emerge. Chladni's technique, first
published in 1787 in his book Entdeckungen über die Theorie des Klanges
("Discoveries in the Theory of Sound"), consisted of drawing a bow over a
piece of metal whose surface was lightly covered with sand. The plate was
bowed until it reached resonance, when the vibration causes the sand to
move and concentrate along the nodal lines where the surface is still,
outlining the nodal lines. The patterns formed by these lines are what are
now called Chladni figures. Similar nodal patterns can also be found by
assembling microscale materials on Faraday waves.
Demonstrating
Resonance with Chladni Figures - Saint Andrews Cross - Christmas Lectures
with Charles Taylor (youtube).
Ernst Chladni
did esearch on vibrating plates and the calculation of the speed of sound
for different gases. One of Chladni's best-known achievements was
inventing a technique to show the various modes of vibration on a rigid
surface, known as Chladni figures due to
the various shapes or patterns created by various modes. When resonating,
a plate or membrane is divided into regions that vibrate in opposite
directions, bounded by lines where no vibration occurs (nodal lines).
Chladni repeated the pioneering experiments of Robert Hooke who, on July
8, 1680, had observed the nodal patterns associated with the vibrations of
glass plates. Hooke ran a violin bow along the edge of a plate covered
with flour and saw the nodal patterns emerge. Chladni's technique, first
published in 1787 in his book Entdeckungen über die Theorie des Klanges
("Discoveries in the Theory of Sound"), consisted of drawing a bow over a
piece of metal whose surface was lightly covered with sand. The plate was
bowed until it reached resonance, when the vibration causes the sand to
move and concentrate along the nodal lines where the surface is still,
outlining the nodal lines. The patterns formed by these lines are what are
now called Chladni figures. Similar nodal patterns can also be found by
assembling microscale materials on Faraday waves.
Demonstrating
Resonance with Chladni Figures - Saint Andrews Cross - Christmas Lectures
with Charles Taylor (youtube).Amazing Resonance Experiment over 1000hz (youtube) - Vibrate Metal plate using a Tone Generator. A Tone Generator can play four different waveforms: Sine, Square, Sawtooth and Triangle.
Standing Wave is a wave which oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the opposite direction to the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium as a result of interference between two waves traveling in opposite directions. The most common cause of standing waves is the phenomenon of resonance, in which standing waves occur inside a resonator due to interference between waves reflected back and forth at the resonator's resonant frequency. For waves of equal amplitude traveling in opposing directions, there is on average no net propagation of energy.
Node in physics is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude. For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. By changing the position of the end node through frets, the guitarist changes the effective length of the vibrating string and thereby the note played. The opposite of a node is an anti-node, a point where the amplitude of the standing wave is at maximum. These occur midway between the nodes.
Resonance describes the phenomena of amplification that occurs when the frequency of a periodically applied force is in harmonic proportion to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamical system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and resonance of quantum wave functions. Resonant systems can be used to generate vibrations of a specific frequency (e.g., musical instruments), or pick out specific frequencies from a complex vibration containing many frequencies (e.g., filters). The term resonance (from Latin resonantia, 'echo', from resonare, 'resound') originated from the field of acoustics, particularly the sympathetic resonance observed in musical instruments, e.g., when one string starts to vibrate and produce sound after a different one is struck. Another example, electrical resonance, occurs in a circuit with capacitors and inductors because the collapsing magnetic field of the inductor generates an electric current in its windings that charges the capacitor, and then the discharging capacitor provides an electric current that builds the magnetic field in the inductor. Once the circuit is charged, the oscillation is self-sustaining, and there is no external periodic driving action. This is analogous to a mechanical pendulum, where mechanical energy is converted back and forth between kinetic and potential, and both systems are forms of simple harmonic oscillators.
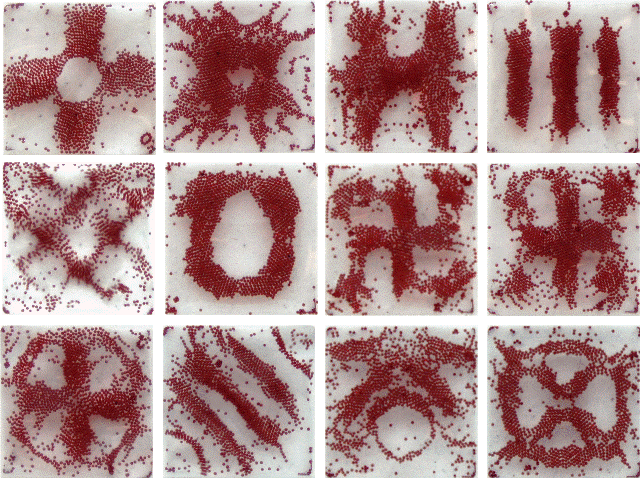 Faraday Wave are nonlinear standing waves that appear on liquids
enclosed by a vibrating receptacle. When the vibration frequency exceeds a
critical value, the flat hydrostatic surface becomes unstable. This is
known as the Faraday instability.
Faraday Wave are nonlinear standing waves that appear on liquids
enclosed by a vibrating receptacle. When the vibration frequency exceeds a
critical value, the flat hydrostatic surface becomes unstable. This is
known as the Faraday instability.Tonoscope is a device that makes sound visible by displaying vibrations. Oscilloscope.
Tuning Fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs (tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it against a surface or with an object, and emits a pure musical tone once the high overtones fade out. The pitch that a particular tuning fork generates depends on the length and mass of the two prongs. It is frequently used as a standard of pitch to tune musical instruments.
Biofield Tuning - 432 HZ - Hearing Test.
Tuning Fork Frequencies (youtube)
Top 10 Demonstrations with Tuning Forks (youtube)
Sound Healing with Ohm Tuning Forks - www.soundhealingtools.com (youtube)
Natural Frequency is the frequency at which a system tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving or damping force. The motion pattern of a system oscillating at its natural frequency is called the normal mode (if all parts of the system move sinusoidally with that same frequency). If the oscillating system is driven by an external force at the frequency at which the amplitude of its motion is greatest (close to a natural frequency of the system), this frequency is called resonant frequency. (also known as eigenfrequency).
Bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell (jingle bell). Bells are usually cast from bell metal (a type of bronze) for its resonant properties, but can also be made from other hard materials; this depends on the function. Some small bells such as ornamental bells or cowbells can be made from cast or pressed metal, glass or ceramic, but large bells such as a church, clock and tower bells are normally cast from bell metal. Bells intended to be heard over a wide area can range from a single bell hung in a turret or bell-gable, to a musical ensemble such as an English ring of bells, a carillon or a Russian zvon which are tuned to a common scale and installed in a bell tower. Many public or institutional buildings house bells, most commonly as clock bells to sound the hours and quarters. Historically, bells have been associated with religious rites, and are still used to call communities together for religious services. Later, bells were made to commemorate important events or people and have been associated with the concepts of peace and freedom. The study of bells is called campanology. Mindfulness Bells (amazon)
Standing Bell is an inverted bell, supported from below with the rim uppermost. Such bells are normally bowl-shaped, and exist in a wide range of sizes, from a few centimetres to a metre in diameter. They are often played by striking, but some—known as singing bowls—may also be played by rotating a mallet around the outside rim to produce a sustained musical note. Struck bowls are used in some Buddhist religious practices to accompany periods of meditation and chanting. Struck and singing bowls are widely used for music making, meditation and relaxation, as well for personal spirituality. They have become popular with music therapists, sound healers and yoga practitioners. Standing bells originated in China. An early form called nao took the shape of a stemmed goblet, mounted with rim uppermost, and struck on the outside with a mallet. The manufacture and use of bowls specifically for 'singing' is believed to be a modern phenomenon. Bowls that were capable of singing began to be imported to the West from around the early 1970s. Since then they have become a popular instrument in the US-originating new-age genre often marketed as 'Tibetan music'.
Tubular Bells are musical instruments in the percussion family. Their sound resembles that of church bells, carillon, or a bell tower; the original tubular bells were made to duplicate the sound of church bells within an ensemble. Each bell is a metal tube, 30–38 mm (1 1⁄4–1 1⁄2 in) in diameter, tuned by altering its length. Its standard range is C4–F5, though many professional instruments reach G5. Tubular bells are often replaced by studio chimes, which are a smaller and usually less expensive instrument. Studio chimes are similar in appearance to tubular bells, but each bell has a smaller diameter than the corresponding bell on tubular bells.
Wind Chime are a type of percussion instrument constructed from suspended tubes, rods, bells or other objects that are often made of metal or wood. The tubes or rods are suspended along with some type of weight or surface which the tubes or rods can strike when they or another wind-catching surface are blown by the natural movement of air outside. They are usually hung outside of a building or residence as a visual and aural garden ornament. Since the percussion instruments are struck according to the random effects of the wind blowing the chimes, wind chimes have been considered an example of chance-based music. The tubes or rods may sound either indistinct pitches, or fairly distinct pitches. Wind chimes that sound fairly distinct pitches can, through the chance movement of air, create simple melodies or broken chords.
Schlieren are optical inhomogeneities in transparent material not necessarily visible to the human eye. Schlieren physics developed out of the need to produce high-quality lenses devoid of these inhomogeneities. These inhomogeneities are localized differences in optical path length that cause light deviation. This light deviation can produce localized brightening, darkening, or even color changes in an image, depending on which way the ray deviates. 761 mph is the speed of sound.
Sound Waves direct particles to self-assemble, self-heal. - Berkeley National Laboratory
Difference between Sound Waves and Electromagnetic Waves
Electricity - Brain - EMF - Human Energy
147Hz Sublimation (youtube) - What is ASMR? BINAURAL triggers (youtube)
Binaural Recording is a method of recording sound that uses two microphones, arranged with the intent to create a 3-D stereo sound sensation for the listener of actually being in the room with the performers or instruments. This effect is often created using a technique known as "dummy head recording", wherein a mannequin head is outfitted with a microphone in each ear. Binaural recording is intended for replay using headphones and will not translate properly over stereo speakers. This idea of a three dimensional or "internal" form of sound has also translated into useful advancement of technology in many things such as stethoscopes creating "in-head" acoustics and IMAX movies being able to create a three dimensional acoustic experience.
Psychoacoustics is the scientific study of sound perception and audiology. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological and physiological responses associated with sound (including noise, speech and music). It can be further categorized as a branch of psychophysics. Psychoacoustics received its name from a field within psychology—i.e., recognition science—which deals with all kinds of human perceptions. It is an interdisciplinary field of many areas, including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science.
Sounds that Help you Sleep
Brain Waves Measuring (EEG) - Bio Mat
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is no different from 'normal' (audible) sound in its physical properties, except in that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and to accelerate chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. Scientists are also studying ultrasound using graphene diaphragms as a method of communication. Ultrasonic is having frequencies above those of audible sound.
The process of signal transduction uses specific frequencies traveling into the cells, through each cell, specific frequencies travel efficiently through the central nervous system without the disbursement of the energy of the sound waves, which is an opposite effect compared to white noise, as documented in the 2015 NCBI published report, Journal ListFront Psycholv.6; 2015PMC4630540. Receptors of cells receive environmental influences from chemical, heat, light and sound influences. A simple visual example of how frequencies travel efficiently (or not) through the central nervous system can be observed from cymatics. The white noise has disburses its energy without direction, while other specific frequencies will move matter into a geometric pattern, traveling with least friction of the cytoplasm of the cellular walls.
Frequency Following Response is an evoked potential generated by periodic or nearly-periodic auditory stimuli. Part of the auditory brainstem response (ABR), the FFR reflects sustained neural activity integrated over a population of neural elements: "the brainstem response...can be divided into transient and sustained portions, namely the onset response and the frequency-following response (FFR)". It is often phase-locked to the individual cycles of the stimulus waveform and/or the envelope of the periodic stimuli. It has not been well studied with respect to its clinical utility, although it can be used as part of a test battery for helping to diagnose auditory neuropathy. This may be in conjunction with, or as a replacement for, otoacoustic emissions.
Evoked Potential is an electrical potential recorded from the nervous system of a human or other animal following presentation of a stimulus, as distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), or other electrophysiologic recording method. Such potentials are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring. Evoked potential amplitudes tend to be low, ranging from less than a microvolt to several microvolts, compared to tens of microvolts for EEG, millivolts for EMG, and often close to 20 millivolts for ECG. To resolve these low-amplitude potentials against the background of ongoing EEG, ECG, EMG, and other biological signals and ambient noise, signal averaging is usually required. The signal is time-locked to the stimulus and most of the noise occurs randomly, allowing the noise to be averaged out with averaging of repeated responses. Signals can be recorded from cerebral cortex, brain stem, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Usually the term "evoked potential" is reserved for responses involving either recording from, or stimulation of, central nervous system structures. Thus evoked compound motor action potentials (CMAP) or sensory nerve action potentials (SNAP) as used in nerve conduction studies (NCS) are generally not thought of as evoked potentials, though they do meet the above definition.
Drawing with Sound (Oscilloscope Music) - Smarter Every Day 224 (youtube)
Oscilloscope Music - Pictures from Sound (youtube)
Water has Memory
Auditory Brainstem Response is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated.
Music - Pleasing Sounds and Rhythms can be Therapeutic
Drum Circle is any group of people playing (usually) hand-drums and percussion in a circle. They are distinct from a drumming group or troupe in that the drum circle is an end in itself rather than preparation for a performance. They can range in size from a handful of players to circles with thousands of participants. Drum circles are related to other community-based music gatherings such as flute circles or vocal improvisation groups.
Sound Waves - Electronic Music - Music Therapy - Sound Healer - Sound Healers Association - Sound Listening
Music to Help Learning - Hearing Impaired
Electronic Awakening - Moontribe - You are Listening - Sailing: Christopher Cross (youtube)
Radionics is an alternative medicine that claims disease can be diagnosed and treated with a kind of energy similar to radio waves.
Grounded - Earthing
Earthing is having your body in contact with earth or the ground. Earthing is the process of absorbing free flowing electrons from it's surface through the soles of your feet while barefoot and not wearing any shoes. Being grounded. Health Benefits from being Outdoors - Play Grounds.
Earthing System or grounding system connects specific parts of that installation with the Earth's conductive surface for safety and functional purposes. The point of reference is the Earth's conductive surface, or on ships, the surface of the sea. The choice of earthing system can affect the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of the installation. Regulations for earthing systems vary considerably among countries and among different parts of electrical systems, though many follow the recommendations of the International Electrotechnical Commission which are described below. This article only concerns grounding for electrical power. Examples of other earthing systems are listed below with links to articles: To protect a structure from lightning strike, directing the lightning through the earthing system and into the ground rod rather than passing through the structure. As part of a single-wire earth return power and signal lines, such as were used for low wattage power delivery and for telegraph lines. In radio, as a ground plane for large monopole antenna. As ancillary voltage balance for other kinds of radio antennas, such as dipoles. As the feed-point of a ground dipole antenna for VLF and ELF radio.
Ground in electricity is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage when electrical insulation fails. In electrical power distribution systems, a protective ground conductor is an essential part of the safety Earthing system. Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return). For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a "ground" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard. The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a "ground" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite "common" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the "ground plane" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.
Valence Electron (atoms) - Electromagnetic Pulse - Science of Being - Star Exercise - The Star Exercise (youtube)
Electrobiology is the study of the production and use of electricity by biological organisms.
Electrophysiology is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring.
Light Therapy - Color Psychology
Light Therapy or phototherapy, classically referred to as heliotherapy — consists of exposure to daylight or to specific wavelengths of light using polychromatic or two or more colors of polarised light, lasers, light-emitting diodes, fluorescent lamps, dichroic lamps or very bright, full-spectrum light. The light is administered for a prescribed amount of time and, in some cases, at a specific time of day. One common use of the term is associated with the treatment of skin disorders, chiefly psoriasis, acne vulgaris, eczema and neonatal jaundice. Light therapy which strikes the retina of the eyes is used to treat diabetic retinopathy and also circadian rhythm disorders such as delayed sleep phase disorder and can also be used to treat seasonal affective disorder, with some support for its use also with non-seasonal psychiatric disorders.
Ayo Light Based Energy Boosting Wearable
Light (spectrum knowledge) - LED's - Photonics (optogenetics)
Dark Therapy (sleeping) - Hearing Light - Synesthesia
Photobiology is the scientific study of the interactions of light (technically, non-ionizing radiation) and living organisms. The field includes the study of photophysics, photochemistry, photosynthesis, photomorphogenesis, visual processing, circadian rhythms, photomovement, bioluminescence, and ultraviolet radiation effects. The division between ionizing radiation and nonionizing radiation is typically considered to be 10 eV, the energy required to ionize an oxygen atom.
Color Vision is the ability of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths (or frequencies) of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit. Colors can be measured and quantified in various ways; indeed, a person's perception of colors is a subjective process whereby the brain responds to the stimuli that are produced when incoming light reacts with the several types of cone cells in the eye. In essence, different people see the same illuminated object or light source in different ways.
Color Psychology is the study of hues as a determinant of human behavior. Color influences perceptions that are not obvious, such as the taste of food. Colours can also enhance the effectiveness of placebos. For example, red or orange pills are generally used as stimulants. Colour can indeed influence a person; however, it is important to remember that these effects differ between people. Factors such as gender, age, and culture can influence how an individual perceives color. For example, males reported that red colored outfits made women seem more attractive, while women answered that the color of a male's outfit did not affect his attractiveness.
Individuals exposed to blue wavelength lights experienced faster reaction times.
Violet is located between blue and purple, has the highest frequency and the highest energy level. Valence Electrons.
Color Therapy (youtube) - Therapy Color
Chromotherapy, sometimes called color therapy, colorology or cromatherapy, is an alternative medicine method, which is considered pseudoscience. Chromotherapists claim to be able to use light in the form of color to balance "energy" lacking from a person's body, whether it be on physical, emotional, spiritual, or mental levels. Research has shown it is ineffective. Color therapy is distinct from other types of light therapy, such as neonatal jaundice treatment and blood irradiation therapy which is a scientifically accepted medical treatment for a number of conditions, and from photobiology, the scientific study of the effects of light on living organisms.
Spectral Sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal. In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics of the photopigments in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye. It is known that the rod cells are more suited to scotopic vision and cone cells to photopic vision, and that they differ in their sensitivity to different wavelengths of light. It has been established that the maximum spectral sensitivity of the human eye under daylight conditions is at a wavelength of 555 nm, while at night the peak shifts to 507 nm.
Gaze means "to look steadily, intently, and with fixed attention.
Sungazing is the act of looking directly into the Sun. It is sometimes done as part of a spiritual or religious practice. However, the human eye is very sensitive, and prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can lead to solar retinopathy, pterygium, cataracts, and even blindness. Studies have shown that even when viewing a solar eclipse the eye can still be exposed to harmful levels of ultraviolet radiation.
Imagery - Visualization
Guided Imagery is a mind-body intervention by which a trained practitioner or teacher helps a participant or patient to evoke and generate mental images that simulate or re-create the sensory perception of sights, sounds, tastes, smells, movements, and images associated with touch, such as texture, temperature, and pressure, as well as imaginative or mental content that the participant or patient experiences as defying conventional sensory categories, and that may precipitate strong emotions or feelings in the absence of the stimuli to which correlating sensory receptors are receptive. The practitioner or teacher may facilitate this process in person to an individual or a group. Alternatively, the participant or patient may follow guidance provided by a sound recording, video, or audiovisual media comprising spoken instruction that may be accompanied by music or sound.
Guided Imagery - Guided Imagery - Dreams - Health Journeys
Creative Visualization is the cognitive process of purposefully generating visual mental imagery, with eyes open or closed, simulating or recreating visual perception, in order to maintain, inspect, and transform those images, consequently modifying their associated emotions or feelings, with intent to experience a subsequent beneficial physiological, psychological, or social effect, such as expediting the healing of wounds to the body, minimizing physical pain, alleviating psychological pain including anxiety, sadness, and low mood, improving self-esteem or self-confidence, and enhancing the capacity to cope when interacting with others. Mind Maps.
Eidetic Imagery is a type of vivid mental image, not necessarily derived from an actual external event or memory. A material picture in the mind which can be scanned by the person as he would scan a real current event in his environment, a normal subjective visual image experienced with noticeable vividness whether evoked by an actual external object or not. The eidetic image is not dependent on any prior experience, condition, state, or event. The eidetic image is “seen” within the mind or literally seen externally. In seeing an eidetic image, definite somatic events as well as a feeling of meaning are also present. A exceptionally vivid memory image that occurs immediately after the perception.
Visual System (seeing) - Pineal Gland (third eye)
Relax into Healing - Scripts
Healing Health C,A.R.E. TV - Music
Teleportation is the theoretical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. It is a common subject in science fiction literature, film, video games, and television. Telepathy.
Dimethyltryptamine - DMT - Ayahuasca
Teachers - Mind Masters
Yoga - Counseling - Therapy
Cozy Rain (youtube channel) - Mixing real and fantasy atmospheric environments, which produce good vibrations and sensations to calm your mind, help your creativity and help you sleep.
Interpersonal intelligence - Solitude Skills
Reality - Mind Your Reality
Auditory Imagery is a form of mental imagery that is used to organize and analyze sounds when there is no external auditory stimulus present. This form of imagery is broken up into a couple of auditory modalities such as verbal imagery or musical imagery. This modality of mental imagery differs from other sensory images such as motor imagery or visual imagery. The vividness and detail of auditory imagery can vary from person-to-person depending on their background and condition of their brain. Through all of the research developed to understand auditory imagery behavioral neuroscientists have found that the auditory images developed in subjects' minds are generated in real time and consist of fairly precise information about quantifiable auditory properties as well as melodic and harmonic relationships. These studies have been able to recently gain confirmation and recognition due to the arrival of Positron emission tomography and fMRI scans that can confirm a physiological and psychological correlation.
Smell - Aroma Therapy
Aromatherapy uses plant materials and aromatic plant oils, including essential oils, and other aroma compounds for improving psychological or physical well-being. It can be offered as a complementary therapy or, more controversially, as a form of alternative medicine. Complementary therapy can be offered alongside standard treatment, with alternative medicine offered instead of conventional, evidence-based treatments. Aromatherapists, who specialize in the practice of aromatherapy, utilize blends of therapeutic essential oils that can be issued through topical application, massage, inhalation or water immersion to stimulate a desired response. There is no good medical evidence that aromatherapy can either prevent or cure any disease, but it might help improve general well-being. Aromatherapy - Synesthesia.
The Scent of a Romantic Partner can help lower Stress Levels
Essential Oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetherolea, or simply as the oil of the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove. An oil is "essential" in the sense that it contains the "essence of" the plant's fragrance—the characteristic fragrance of the plant from which it is derived. The term essential used here does not mean indispensable as with the terms essential amino acid or essential fatty acid which are so called since they are nutritionally required by a given living organism. Essential oils are generally extracted by distillation, often by using steam. Other processes include expression, solvent extraction, absolute oil extraction, resin tapping, and cold pressing. They are used in perfumes, cosmetics, soaps and other products, for flavoring food and drink, and for adding scents to incense and household cleaning products.
Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds, fixatives and solvents, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable or pleasant scent. It is usually in liquid form and used to give a pleasant scent to a person's body. Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin or coumarin, which allowed for the composition of perfumes with smells previously unattainable solely from natural aromatics alone. Scented Products.
Fragrant is something that is pleasant-smelling. Sense of Smell.
Aroma is a distinctive odor that is pleasant to smell. Aroma Compound is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For a chemical compound to have a smell or odor it must be sufficiently volatile to be transported to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose.
Scent is a distinctive odor that is pleasant to smell.
Olfactory System - Olfaction - Scents and Smells - Hormones
Lavender can help you relax.
Pine can help you feel less stress.
Fresh-cut grass can elevate your mood.
Vanilla can elevate your mood.
Jasmine may ease depression.
Cinnamon can sharpen your mind.
Peppermint may boost concentration.
Citrus can help you feel more energized.
Pumpkin can serve as an aphrodisiac.
Apples may mitigate a migraine.
Olive oil can satisfy your appetite.
Wholesale Lotions
Incense is aromatic biotic material which releases fragrant smoke when burned. The term refers to the material itself, rather than to the aroma that it produces. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, and in therapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insectifuge.
Scent From Heaven (youtube)
Aromas of Rosemary and Lavender essential oils differentially affect cognition and mood in healthy adults.
Burn Bay Leaves in the House and See What Would Happen in just 10 Minutes! (youtube)
Rosemary Aroma can Aid Children’s Working Memory
Moodo fragrance dispenser in a box that enables you to mix and match fragrances.
Related Subjects - Synesthesia - Senses - Message - Acupressure - Meridian Tapping.
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a state of human consciousness involving focused attention and reduced peripheral awareness and an enhanced capacity for response to suggestion. The term may also refer to an art, skill, or act of inducing hypnosis.
Self-Hypnosis is a form, process or result of hypnosis which is self-induced, and normally makes use of self-suggestion. Self-hypnosis can make a person more yielding than normal. Sleep Learning - Rote Learning.
Hypnotized is when a person has a reduced peripheral awareness and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion. Having your attention fixated as though by a magic spell. To capture the whole attention of someone, like a mind controlled brainwashing.
Trance is a state of mind in which consciousness is fragile and voluntary action is poor or missing; a state resembling deep sleep.
Self-Hypnosis - Perform Self-Hypnosis - Make Your Own Self Hypnosis CD
Truth About Hypnosis - Hypnagogic (half asleep)
Hypnotic Language - Hypnotic Language Patterns that Work? - Covert Hypnosis - Kevin Hogan (youtube)
Subliminal Stimuli - Implicit Learning - Sub-Conscious
Language Patterns Embedded - Embedded Words
Synesthesia induced with Hypnosis. Hypnosis can alter the way certain individuals information process information in their brain. hypnosis to induce a functional analogue of synaesthesia. The discovery can open a window into the previously unexplored domains of cognitive neuroscience. Brain Plasticity.
Hypnotic Suggestion
Autosuggestion is a form of self-induced suggestion in which individuals guide their own thoughts, feelings, or behavior. The technique is often used in self-hypnosis and a psychological technique related to the placebo effect.
Mantra - Programing - Social Influence - Propaganda - Subliminal - Brain Washing - Gullible
Suggestion is the psychological process by which one person guides the thoughts, feelings, or behavior of another. I Suggest educating yourself and learning the most valuable knowledge and information available.
Suggestibility is the quality of being inclined to accept and act on the suggestions of others. One may fill in gaps in certain memories with false information given by another when recalling a scenario or moment. Suggestibility uses cues to distort recollection: when the subject has been persistently told something about a past event, his or her memory of the event conforms to the repeated message. A person experiencing intense emotions tends to be more receptive to ideas and therefore more suggestible. Generally, suggestibility decreases as age increases. However, psychologists have found that individual levels of self-esteem and assertiveness can make some people more suggestible than others; this finding led to the concept of a spectrum of suggestibility.
Receptive is being open to arguments, ideas, or change. Ready or willing to receive something favorably.
Autogenic Training is a desensitation-relaxation technique that involves the daily practice of sessions that last around 15 minutes. During each session, the practitioner repeats a set of visualizations that induce a state of relaxation. Each session can be practiced in a position chosen amongst a set of recommended postures (for example, lying down, sitting meditation, sitting like a rag doll). The technique can be used to alleviate many stress-induced psychosomatic disorders. Addictions.
Hypnotherapy is a form of psychotherapy used to create subconscious change in a patient in the form of new responses, thoughts, attitudes, behaviours or feelings. It is undertaken with a subject in hypnosis. A person who is hypnotized displays certain unusual behavior characteristics and propensities, compared with a non-hypnotized subject, most notably heightened suggestibility and responsiveness. Recalling Old Memories.
Hypnotherapy (wikihow)
Overcoming Addictions with Hypnosis
Mind Zoom - Hypnosis 101
Obstructing the ‘inner eye’. Psychologists aim to develop brain theory of hypnosis.
Create Your own Subliminal Messages - -17 db or normal voice speaking Affirmations with Love Signal in background.
Make your own Subliminal Messages
Subliminal Message Learning
Whisper Therapy
Accelerated Learning
Mantras - Routines
Neuro-Linguistic Programming is a connection between neurological processes (neuro-), language (linguistic) and behavioral patterns learned through experience (programming), and that these can be changed to achieve specific goals in life.
NLP Hypnosis - Natural Language Processing
Methods of Neuro-Linguistic Programming are the specific techniques used to perform and teach neuro-linguistic programming, a pseudoscience which teaches that people are only able to directly perceive a small part of the world using their conscious awareness, and that this view of the world is filtered by experience, beliefs, values, assumptions, and biological sensory systems. NLP argues that people act and feel based on their perception of the world and how they feel about that world they subjectively experience. NLP teaches that language and behaviors (whether functional or dysfunctional) are highly structured, and that this structure can be 'modeled' or copied into a reproducible form. Using NLP a person can 'model' the more successful parts of their own behavior in order to reproduce it in areas where they are less successful or 'model' another person to affect belief and behavior changes to improve functioning. If someone excels in some activity, it can be learned how specifically they do it by observing certain important details of their behavior. NLP embodies several techniques, including hypnotic techniques, which proponents claim can affect changes in the way people think, learn and communicate. NLP is an eclectic field, often described as a 'toolbox' which has borrowed heavily from other fields in collating its presuppositions and techniques.
Neuro-Semantics is an attitude of apply to self. This focus leads to more congruency, more willingness to look at oneself, to use the processes with oneself, and to consciously aim to continually grow and improve. In turn, this leads to being more open and to honestly acknowledge the facets of NLP that we have found which do not work or are over-emphasized to the exclusion of something else. None of this is to say that one is right or better, but rather to point out differences, especially in terms of focus and direction. Neuro-Semantics Includes: Focus on References & Referencing. Non-Linear Thinking: Reflexivity. Systemic in its structure. Focus on Persons and Relationship and doing things to people and co-creating with others. Trained from Options meta-program. Applying the magic to self first. Emphasis on Connection, Authenticity. Ethical behavior and Win/Win Relationships. 1st Meta-Model 4 Meta-Domains: 1st MM 2nd MP 3rd Meta-States. 4th Meta-Modalities or the Cinematic features of the so-called “Sub-modalities”. Meta-Levels: Logical levels as Psycho-Logics, meta-levels, Multi-ordinality, Matrix. Logical levels as dynamic, fluid, layering. Mind as holistic and systemic. The Restoration of several “Why” Questions: Why of Intentionality, Why of Outcome. Meta means “emotion” sometimes more, sometimes less. Emotions seen as to be experienced, “bringing the kinesthetics back into NLP.” Sub-Modalities seen as meta-frames. Gestalting, moving up levels to create new Generalizations. Focus on Individual and on Community and on numerous social and cultural contexts. Generative or Transformative Change: moving up to the next level of development. The power and balance of the conscious mind. The focus in NLP, and this is the genius of NLP, is on representation. Recognizing that we think in terms of our sensory systems and uses what we see, hear, feel, smell and taste to re-present to ourselves within our minds gives us control knobs for “running our own brain.” We have a Movie Mind and this empowers us to take charge of what plays out in the theater of our mind. Oftentimes the simplest shifts or alternations in the cinematic features (“sub-modalities”) that we use to encode our understandings is sufficient to create powerfully Positive Transformations. The focus in Neuro-Semantics moves on from representation to references and referencing. First we bring in the world by taking a referent event and representing it. From there we transform the same event into frames of reference, and then frames of mind. This moves us up the levels as we classify or categories our learnings from the events. In this way we create layers of embedded frames that make up the Matrix of our Mind. And those layers emerge organically as the mind-body-emotion system grows. In moving up the levels, we do this primarily in language, hence the true place for the linguistic of NLP and the symbolic levels of Neuro-Semantics. NLP mostly and primarily involves Linear Thinking. We see this most prominently in the domain of eliciting and modeling of strategies. While there is a place for a meta response in the strategy model using T.O.T.E. format, it is a minor piece and de-emphasized in actual practice. NLP mostly talks about sending or swishing the brain somewhere, moving from present state to desired state, identifying desired outcomes and formatting them to be well-formed and then just future pacing the experience. All of that is linear in nature and structure. Neuro-Semantics focuses on and involves non-linear thinking precisely because it is driven by reflexivity. In Meta-States training we always begin with a warning that the kind of thinking required to understand meta-states is very different from the kind of thinking that governs NLP. At first, learning to think in non-linear ways can feel very disconcerting. Non-linear thinking means reckoning with going round and round in loops, spiraling up and down the levels of the mind, recognizing the numerous feedback and feed forward loops in a system, and recognizing that multiple processing will be occurring at any given moment.
Each and every day when you wake up to face the world, you wake up in a state—in a mind-body state. This state is a state of mind, a state of body, and a state of emotion. This is the most basic essence of our reality.
Analog Marking is a technique where one gives special identical emphasis to the words of an embedded command within a sentence, in order for the the unconscious mind of the receiver to interpret them as being related to each other. The emphasis can be a certain tone of voice, for instance.
Erotic Hypnosis is the practice of hypnosis for sexual purposes. Reducing inhibitions and increasing arousal is a notable goal of erotic hypnosis. The placement of trigger words in the subject's mind as post-hypnotic suggestion to produce actions and experiences on-demand is a common practice. Erotic hypnosis can also include suggestions intended to improve sexual health. This does not include hypnotherapy nor the therapeutic application of neurolinguistic programming and similar disciplines. Although often loosely referred to as "recreational hypnosis", recreational hypnosis is a broader subject, including practices like stage hypnosis and hypnosis for the enjoyment of the practice itself.
Self-Hypnosis is one of many methods used for learning. When self-hypnosis is used together with other learning methods it can be a very useful tool for communicating to our subconscious mind, so that we are more aware of our subconscious minds influence on our daily lives, but you still need a good amount of knowledge and information in order to fully understand your abilities as well as understand your vulnerabilities. (passive auditory stimulation).
Deep Meditation
 Mediation
starts with learning how to
discipline the mind. Meditation is the ability to
let go of everything and letting go of things that
you think you know
and
pretend to feel. Mediation is freeing the mind of
all
distractions and
letting your mind be
quite. Mediation starts out with your
mind wondering from
thought to thought until deep mediation becomes concentrated
and focused on a
spiritual reality where
time and space does not exist. A reality
that is calm and at peace. This is the moment and the point where your
mind becomes in tune with all the energy that surrounds
you, and you begin to see and feel with your mind, and these things
that you feel and perceive, are beyond explanation.
Mediation
starts with learning how to
discipline the mind. Meditation is the ability to
let go of everything and letting go of things that
you think you know
and
pretend to feel. Mediation is freeing the mind of
all
distractions and
letting your mind be
quite. Mediation starts out with your
mind wondering from
thought to thought until deep mediation becomes concentrated
and focused on a
spiritual reality where
time and space does not exist. A reality
that is calm and at peace. This is the moment and the point where your
mind becomes in tune with all the energy that surrounds
you, and you begin to see and feel with your mind, and these things
that you feel and perceive, are beyond explanation. Quite the mind and reduce worrying. Focus on just your breathing. Clear the mind of all thoughts. Use no words and pretend that words don't exist and words can no longer be thought of, there are no thoughts, only an experience of an internal existence, an existence that is perceived as neither here nor there or anywhere.
Samatha is tranquility of the mind, or mind-calmness that is said to be achieved by practicing single-pointed meditation or fixing your gaze on one steady object for a set period of time. This includes a variety of mind-calming techniques.
Buddhist Meditation - Teachers
Zen emphasizes rigorous self-control, meditation-practice, insight into Buddha-nature, and the personal expression of this insight in daily life, especially for the benefit of others. As such, it de-emphasizes mere knowledge of sutras and doctrine and favors direct understanding through zazen and interaction with an accomplished teacher.
Zen Guide - Mind over Matter - Breathing
Zen Meditation (youtube) - The Zen Mind (youtube)
Certain breathing exercises direct the body to perform a particular function that the body wouldn't do naturally on its own. So you are exercising your control over your body so that you can help maximize your bodies capabilities.
Maybe mediation is a method for accessing information that's in our DNA?
Zuowang is a classic Daoist meditation technique, described as a state of deep trance or intense absorption, during which no trace of ego-identity is felt and only the underlying cosmic current of the Dao is perceived as real. Sitting in oblivion and forgetting all things. to lose bodily awareness and remove all thoughts from consciousness. Just take the position of nonaction and all things unfold naturally. Let your body and limbs fall away, expel perception and intellect, leave relations and things behind in oblivion. Become mystically one with the immense and boundless, release your mind and free your spirit. Be silent and without an active spirit soul that interacts with the world. Cut off contacts, shut the doors. Fasting of the Heart empties the faculties, frees you from limitation and from preoccupation. Fasting of the heart begets unity and freedom.
 Meditation is a way to
connect to the
universe
and explore the
abilities of the human
mind. Don't just
clear the mind, open the mind and make peace with the mind.
Don't just turn off the mind, turn on the mind and let the mind go. Don't look
for something or expect something, just listen. Listen to the universe
without using words or thoughts. Don't try to focus or try
to stay in control, just be one with everything, and let things pass
through you and just travel through space is if there were no boundaries.
Start with body awareness. Are you relaxed and calm? Are you comfortable
and aligned? Are you
in a quiet place? Are you
ready? Now start your breathing exercises. Focusing
on deliberate breaths will start
the process of meditation. Meditation is practicing focus, focusing on
keeping your mind open, and not thinking about anything in particular, you
are focusing on
listening, and you are
filtering out the
noises of the physical world
because you're not listening with your ears, you are listening with the
mind, and you are not seeing with the eyes you are seeing with the mind.
You have a purpose, and one purpose of meditation is to listen. And you
can't listen when you're thinking about everyday things.
Distractions are
like noises, you need to filter out noises, even the noises produced in
your mind. You are an observer who is just witnessing. No analyzing or
interactions, just watching to see what happens. Unlike a
lucid dream where you might
want to interact with the dream and have some control in the dream, when
meditating, you're just an observer. You must let go and not be distracted by
your physical senses. And you must not use human
language when listening
or communicating with the universe, because the universe, or the inner and
outer worlds, has a language all its own.
Listen and
explore. But don't
try to understand the journey when you're in the process of meditating,
wait till after you're done meditating, and then try to explain your journey
and then learn what you can from your
experience.
Meditation is a way to
connect to the
universe
and explore the
abilities of the human
mind. Don't just
clear the mind, open the mind and make peace with the mind.
Don't just turn off the mind, turn on the mind and let the mind go. Don't look
for something or expect something, just listen. Listen to the universe
without using words or thoughts. Don't try to focus or try
to stay in control, just be one with everything, and let things pass
through you and just travel through space is if there were no boundaries.
Start with body awareness. Are you relaxed and calm? Are you comfortable
and aligned? Are you
in a quiet place? Are you
ready? Now start your breathing exercises. Focusing
on deliberate breaths will start
the process of meditation. Meditation is practicing focus, focusing on
keeping your mind open, and not thinking about anything in particular, you
are focusing on
listening, and you are
filtering out the
noises of the physical world
because you're not listening with your ears, you are listening with the
mind, and you are not seeing with the eyes you are seeing with the mind.
You have a purpose, and one purpose of meditation is to listen. And you
can't listen when you're thinking about everyday things.
Distractions are
like noises, you need to filter out noises, even the noises produced in
your mind. You are an observer who is just witnessing. No analyzing or
interactions, just watching to see what happens. Unlike a
lucid dream where you might
want to interact with the dream and have some control in the dream, when
meditating, you're just an observer. You must let go and not be distracted by
your physical senses. And you must not use human
language when listening
or communicating with the universe, because the universe, or the inner and
outer worlds, has a language all its own.
Listen and
explore. But don't
try to understand the journey when you're in the process of meditating,
wait till after you're done meditating, and then try to explain your journey
and then learn what you can from your
experience.
Disclaimer about Meditation
Meditation or Exercise alone will not solve all your problems. The most important activity is continually increasing your knowledge and understanding of yourself and the world around you, because this will always be the most important part of a strong mind and body. The ability to meditate and exercise are great tools to have when mastered. But having many tools is one thing, knowing how to use your tools effectively and efficiently is another. And it's not a good idea to always depend on the same tools working the same way that you think they will. Awareness is essential in order to be aware of the changes that life brings.
There are best practices, standards and ethics in most everything that we do. There are guidelines, but not necessarily boundaries. But if you do explore beyond known boundaries, you may be increasing the risks that might negate certain benefits. But taking risks are not always bad, as long as you learn from those experiences and share what you have learned. Not everyone will follow you and not everyone should. Everyone has their own destiny, and there's also a reason for everything.
When people mention the spiritual benefits of meditation, this will vary from person to person. The bottom line is, the mind benefits from exercise. But how much you benefit depends on how much you learn and how much you practice. Any benefit is better then no benefit at all. Awareness comes from knowledge and experience. So never get discouraged. Keep learning, keep practicing, keep living. Live, Learn, Love and Progress.
Meditation Resources - Meditation Techniques - How to Meditate - How to Meditate - Meditation is Easy - Meditation as a Blind Person.
2 Minute Meditation - Mini-Meditation
 Focus
all of your attention on your breath. You are not thinking of anything,
you're just focusing on your breathing, being only aware of breathing in,
and then, breathing out. Now relax every muscle in your face until there is no tension or
tightness anywhere in your face. Return to focusing on your breath. Make sure that your face and body feels totally relaxed. Keep focusing on
your breath. Think of nothing else except for breathing in, and breathing
out. Now look around and notice where you are.
Now close your eyes and notice the sounds around you. Allow
yourself to be there with the sounds.
Take one deep breath to settle yourself. Then follow your
breath, from the moment the air touches your nostrils as you
inhale, feeling it fill up your chest and belly, and as it
leaves your body as you exhale, noticing if the air feels warmer
or colder.
Repeat this for five deep breaths. Feel better?
Focus
all of your attention on your breath. You are not thinking of anything,
you're just focusing on your breathing, being only aware of breathing in,
and then, breathing out. Now relax every muscle in your face until there is no tension or
tightness anywhere in your face. Return to focusing on your breath. Make sure that your face and body feels totally relaxed. Keep focusing on
your breath. Think of nothing else except for breathing in, and breathing
out. Now look around and notice where you are.
Now close your eyes and notice the sounds around you. Allow
yourself to be there with the sounds.
Take one deep breath to settle yourself. Then follow your
breath, from the moment the air touches your nostrils as you
inhale, feeling it fill up your chest and belly, and as it
leaves your body as you exhale, noticing if the air feels warmer
or colder.
Repeat this for five deep breaths. Feel better?One Moment Meditation - Video - 2 Minute Rule
Micro-Meditation (inner peace in 30 seconds) - Micro-Meditation - Micromeditation
Take about a minute and a half to go through the list, relaxing every body part fully, and then clear your mind for ten seconds.
1:Relax the muscles in your face, including your tongue, jaw, and the muscles around your eyes.
2:Drop your shoulders as low as they’ll go. Then relax your upper and lower arm on one side, and then the other.
3:Breathe out, and relax your chest.
4:Relax your legs, first thighs and then calves.
5:Clear your mind and don't think, believe that there are no words.
The act of relaxing while focusing your thoughts, letting go of distractions, and allowing yourself to move into your creative flow.
Private Portable Space
Still Meditation: A traditional form of meditation using deep breathing; sitting still in a comfortable position with eyes closed; and clearing the mind of thought and/or focusing on a key thought, phrase, or word (mantra) to focus the energy. Benefits: Reduces stress, relaxes the mind and body, supports feelings of relief, calms "inner chatter," and expands awareness. Drawbacks: Requires time; a large amount of patience (even for 15 minutes!); and a quiet space without distraction -- usually not even music. Best option: Early mornings; before bedtime; during weekends, vacation, down time; or in times of great indecision or challenges.
Moving Meditation: The practice of getting centered by allowing thoughts to flow freely while moving the body -- perhaps walking, running, exercising, doing housework, etc. Benefits: Reduces stress, gives a physical/mental/spiritual outlet for energy to be released from the body, supports improved mood, stimulates creative thinking and problem solving. Drawbacks: Requires time, outdoor locations or larger spaces (if indoors), and may require equipment or supplies. Best option: In the morning immediately after rising, during the day (maybe during lunch), after work, weekends, or on days when ideas need to process. Also works best to help start out the day fresh or release stress at the end of the day to assist with relaxing at night.
Creative Meditation: Getting into the "create zone" by immersing yourself into creative flow--allowing new creative ideas to come to you by using techniques like brainstorming, freewriting, and possibility thinking. Benefits: Generates new ideas, allows for creative expression, taps creative intuition, and welcomes coincidence and creative collaboration. Drawbacks: Can be time-consuming, may hit creative roadblocks and stalemates, and may sometimes require input from others to be most effective. Doesn't work well if you're not in the creative mood. If using creative meditation with a group, you may need to all be in sync (commonly referred to as synergy) to be most effective. This may require larger blocks of time or minimal disruptions to stay in the creative flow. Best option: Best used when creating new ideas, solving a creative challenge, inventing a new product or service, or strengthening collaboration with others.
 Feng Fu (wind mansion). Hold a cube of ice for 20 minutes on the Feng Fu point.
At first you will begin to feel freezing, but after
thirty or forty seconds you will feel warmth. By doing
this every day you will begin to feel
euphoria. This is because the ice cube will cause for
endorphin to be released in your blood. It's
believed that there are also more benefits from using this technique.
Placebo.
Feng Fu (wind mansion). Hold a cube of ice for 20 minutes on the Feng Fu point.
At first you will begin to feel freezing, but after
thirty or forty seconds you will feel warmth. By doing
this every day you will begin to feel
euphoria. This is because the ice cube will cause for
endorphin to be released in your blood. It's
believed that there are also more benefits from using this technique.
Placebo.Apps for Meditation - Zen Wisdom (itunes) - Zen Space (itunes) - Breath Pranayama - Breathe 2 Relax - Serendipitor - Relaxing Sounds Of Nature Lite.
"I went looking for myself and I found someone else".
"Be still, and know that I am God. The kingdom of heaven is within you."
Can the mind become so focused that it can have the ability to activate hormones?
Pretend you are riding a bicycle, then pretend that you are watching yourself riding a bicycle. Perception.
Walking or riding your bike with no destination in mind, is totally different from doing these same activities as exercise or having a destination in mind. Not totally purposeless.
Take a Break - Rest - Relax - Peace of Mind - Free from Stress
Break is to lie down, recline, sit back, take it easy, unwind, wind down, breathe easy, calm down, catch one's breath, chill out, collect oneself, compose oneself, cool off, feel at home, hang loose, loosen up, make oneself at home, mellow out, put one's feet up, take five, take ten, stop work. This is not about being lazy, it's about having balance and awareness. Vacation.
Rest is the freedom from activity work or strain or responsibility. A feeling of refreshing tranquility and an absence of tension or worry. A pause for relaxation. Take a short break from one's activities in order to relax. Become less tense, rest, or take one's ease. Positivity - Mantras.
Relax is to become less tense by resting or by taking it easy. Slowing down. Time Management.
Relaxation the exponential return of a system to equilibrium after a disturbance. Parks.
Siesta is an afternoon rest or nap, especially one taken during the hottest hours of the day in a hot climate. A short nap taken in the early afternoon, often after the midday meal. Such a period of sleep is a common tradition in some countries, particularly those where the weather is warm. Lucid Dreaming - Positive Thinking.
You have to take that Break, even if you have to fantasize that you don't have a worry in the world, and that you are free to explore the world inward and outward. Just pretend that this is your job, believe that this is what you are supposed to be doing. This moment requires a new system of thinking, different parameters then the random and reoccurring thoughts of an every day busy life. You are going to put your daily life on hold. You are now in a closed private meeting with just yourself. Touching base with peace and tranquility. Letting life know that you are still here and that you appreciate the times alone together with just your spirit. The spirit of life and the earth. When Time is not of the Essence.
Clear Your Head means to take some time to think and relax in order to regain your composure so that you can think clearly and calmly about something important without any distractions and without any stress that arises from experiencing a difficult situation. (I took a walk for a while to clear my mind.)
Pause is temporary inactivity. Interrupt temporarily an activity before continuing. Cease an action temporarily.
Adjourn is to close at the end of a session. Break from a meeting or gathering.
Recess is a temporary pause from doing something, or the temporary inactivity or the suspension or work. Recess in school is a ten to thirty minute break where students are allowed to leave the school's interior to enter its adjacent outside park where they play on equipment such as slides and swings, play basketball, tetherball, study or talk. Many middle schools also offer a recess to provide students with a sufficient opportunity to consume quick snacks, communicate with their peers, visit the restroom, study, and various other activities.
Free Time is the amount of time that is available for personal activities or hobbies. The time that you have left after you have fulfilled your most important responsibilities.
Spare Time or Time Off is a period of time when you are not required to work, so that you may pursue other goals.
Pastime is an activity that someone does regularly for enjoyment rather than for work; a hobby.
Meantime is the time between one event, process, or period and another. The time during the time before something happens or before a specified period ends The new computers won't arrive until next week, but we can keep using the old ones in the meantime.
Stop and Smell the Roses means to take some time to enjoy life's beauty and splendor. To stop and take a moment to appreciate the finer things in life, especially when you have become overworked or overly stressed. Take a time out to relax from one's busy schedule. Don't hurry and Don't worry. Time flies and life is short, so don't forget to stop to smell the flowers. Be Mindful.
Non-Doing is to refrain from doing as the basis for allowing the body to function naturally, and for learning to act in such a way that we do not get in the way of this natural element in performance.
Non-Action does not mean doing nothing and keeping silent. Let everything be allowed to do what it naturally does, so that its nature will be satisfied. ~Chuang Tzu.
Wu wei is a concept literally meaning "inexertion", "inaction", or "effortless action".
Sitting too Long - Fatigue
Repose is freedom from activity, work, strain or responsibility. The absence of mental stress or anxiety. Lean in a comfortable resting position. Put in a horizontal position. Lie when dead.
Flâneur represents the ability to wander detached from society with no other purpose than to be an acute observer of society. A person of leisure, the idler, the urban explorer, the connoisseur of the street. From the French noun flâneur, which means "stroller", "lounger", "saunterer", or "loafer". Free to Roam.
Tranquility is a state of peace and quiet that is free from disturbances, trouble, stress or emotion. Tranquility is the quality or state of being calm, serene, and worry-free. Not agitated - Tranquility is Yours.
Comfort is a state of being relaxed and feeling no pain. A feeling of freedom from worry or disappointment. The act of consoling and giving relief from affliction. Lessen or alleviate pain and discomfort. Satisfaction or physical well-being provided by a person or thing. A freedom from financial difficulty that promotes a comfortable state.
Comfortable is experiencing physical well-being or relief from stress. Having peace of mind and mental ease.
Composed is free from agitation especially in times of stress. Not the same as Passive.
Calm is a peaceful and restful state that is free of noise and disturbance. Having self-control and steadiness of mind under stress. Not agitated.
Keep Calm and Carry On is a motivational poster produced by the British government in 1939 in preparation for World War II. The poster was intended to raise the morale of the British public, threatened with widely predicted mass air attacks on major cities. Calm Clinic.
Calmness is the mental state of peace of mind being free from agitation, excitement, or disturbance. It also refers being in a state of serenity, tranquility, or peace. Calmness can most easily occur for the average person during a state of relaxation, but it can also be found during much more alert and aware states. Some people find that focusing the mind on something external, or even internal, such as the breathing, can itself be very calming.
"Don't hold anything too tightly, just wish for it, want it, let it come from the intention of real truth for you and if it's supposed to be yours it will show up, and it won't show up until you stop holding it so tightly."
Chill Out is to calm down and go easy and be relaxed. Chill-out in reference to music is characterized by slow tempos and relaxed moods. Chill is being very relaxed or easygoing.
Easygoing is someone who is not demanding or controlling or burdensome or hurried. A relaxed person with a warm and friendly attitude with a flexible set of standards that is adaptable to most situations and moods. To go with the flow.
Off the Hook is when you are freed or relieved from an obligation, duty, burden, responsibility, or pressure. Off the hook can also mean when you leave the phone off the hook so that no one can call you, which is the same thing as turning off your smartphone or putting your smartphone in airplane mode so that you are not distracted or interrupted when someone calls.
Serenely is in a peacefully serene manner.
Surfeit is the state of being more than full.
Satiety is the state of being satisfactorily full and unable to take on more. The act of achieving full gratification.
Serenity is a disposition free from stress or emotion. The absence of mental stress or anxiety. Composed.
Wu Wei is a concept literally meaning "inexertion" or "inaction". Describing a state of un-conflicting personal Harmony, free-flowing spontaneity and savoir-faire, it generally also more properly denotes a state of spirit or mind, and in Confucianism accords with conventional morality. A state of perfect knowledge of the reality of the situation, perfect efficaciousness and the realization of a perfect economy of energy.
Tao is a Chinese word signifying "way", "path", "route", "road" or sometimes more loosely "doctrine", "principle" or "holistic beliefs". Tzu-jan is to follow the laws of nature.
Give yourself at least one guilt-free hour to relax per day.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation is a technique for learning to monitor and control the state of muscular tension. The technique involves learning to monitor tension in each specific muscle group in the body by deliberately inducing tension in each group. This tension is then released, with attention paid to the contrast between tension and relaxation. A modification of the technique is "biofeedback" in which one uses external measuring devices to indicate how successful one is in relaxing and then to use those techniques to relax without the help of external measuring devices.
Relaxation Exercise is any method, process, procedure, or activity that helps a person to relax; to attain a state of increased calmness; or otherwise reduce levels of pain, anxiety, stress or anger. Relaxation techniques are often employed as one element of a wider stress management program and can decrease muscle tension, lower the blood pressure and slow heart and breath rates, among other health benefits.
Relaxation Therapy - Relaxation Response Steps
Mental Workout - Mind and Life Institute - Delayed Gratification
Feeling Groovy - Paul Simon and Art Garfunkel (youtube) - Slow down, you move too fast. You got to make the morning last. Just kicking down the cobblestones. Looking for fun and feeling groovy.
My Mind Shift - Personal Development
Relaxing Piano Music (youtube) - Meditation Music, Relaxing Music, Soft Music, Relaxation Music - Relaxing Music for Learning - 4K Nature Videos with Relaxing Music (youtube).
Escapism is mental diversion by means of entertainment or recreation, as an "escape" or dissociation from the perceived unpleasant, boring, arduous, scary, or banal aspects of daily life. It can also be used as a term to define the actions people take to help relieve persisting feelings of depression or general sadness.
Unplug from Technology - Laughter - Humor
Workaholic is a person who works compulsively, and thus is not balanced between work and life. Works more and lives less.
The Relationships between Workaholism and Symptoms of Psychiatric Disorders.
32.7% of workaholics also met ADHD criteria, compared to 12.7% of non-workaholics.
25.6% of workaholics also met OCD criteria, compared to 8.7% of non-workaholics.
33.8% of workaholics also met anxiety criteria, compared to 11.9% of non-workaholics.
8.9% of workaholics also met depression criteria, compared to 2.6% of non-workaholics.
All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy (wiki) - THE SHINING (1980) - "All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy" [HD] (youtube)
Step Back, Pause, Take a Break, Take a Breather, Rest, Balance, Do Something Else, Ponder, Relax, Reexamine, Meditate, Pray, Think, Not Think, Contemplate, Dream, Fantasize, Question, Remember, Breath, Smell, Gaze, Listen, Feel.
"Doing nothing is doing something."
Sunday is a day of rest in most Western countries, as a part of the weekend.
Sabbath is a day set aside for rest and worship.
Leisure is time spent away or a break from every day activities and responsibilities. Freedom to choose a pastime or enjoyable activity. Time available for ease and relaxation.
Sabbatical is a rest from work, or a break, often lasting from two months to a year.
Air Traffic Controllers are required after every hour and a half or two hours of work to take a 15 to 30 minute break. And that means an unplugged disconnected break where they go for a walk or listen to music, they exercise, something to restore all of the burned up neurochemicals. Neurochemical are chemicals in the brain that allow brain cells to communicate with each other. A neurochemical is an organic molecule, such as serotonin, dopamine, or nerve growth factor, that participates in neural activity. Strength between brain cells helps the brain work more effectively and communication more effectively with other areas of the brain. Depression
Airplane Pilots have the “8 hour” rule, or , 8 hours from bottle to throttle, although many airlines have a more stringent 12 hour time limit. Most pilots do not know of the 0.04% FAR, which prohibits flying an aircraft with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.04% or higher.
Workers have the right to one uninterrupted 20 minute rest break during their working day, if they work more than 6 hours a day. This could be a tea or lunch break. The break doesn't have to be paid - it depends on their employment contract. Federal law does not require lunch or coffee breaks. However, when employers do offer short breaks, they usually last about 5 to 20 minutes.
Truckers Drivers who drive big trucks or 18 wheelers, have to take a 30-minute break after eight consecutive hours of driving. Truckers also have to have 10 continuous hours off, if a trucker starts driving at 6:00 a.m., they must not drive their truck after 8:00 p.m. that evening, which is 14 hours.
So it is not just the lack of sleep that can cause problems with judgment, awareness and reaction times, it's also anything that makes your brain impaired.
We spend too much time walking around unconscious and unaware. We need to spend more time being aware of ourselves, and the world around us. We need to exercise the ability of having awareness so that can we keep our minds strong, and, make ourselves more aware. And the best way to increase your awareness is to acquire new knowledge and to learn something new everyday. The human brain can store incredible amounts of information and knowledge. But if you are not learning and acquiring new knowledge, then you are weakening your abilities and your awareness, and at the same time, you are lowering your potential of accomplishing many different things that every human being is capable of doing. When you exercise and eat healthy, the body becomes stronger. When you learn and acquire new knowledge, your mind becomes stronger. And your mind will continue to become stronger and more effective as long as you keep learning. Any dream or goal that you have is possible, as long as you keep learning. When you stop learning, the possibilities will diminish. Keep Learning.
Blase is nonchalantly unconcerned. Uninterested because of frequent exposure or indulgence. Very sophisticated especially because of surfeit; versed in the ways of the world.
Nonchalantly is an unconcerned manner. Easy in mind; not worried. Not occupied or engaged with anything particular.
I don't like making a big deal of things. I don't like to overreact or jump to conclusions. I'm concerned, but not stressed or worried. I understand the importance of certain events and how meaningful some events are, I just don't want to make something any more significant than it needs to be. I take things seriously just enough to learn from them without being distracted by the experience or overwhelmed with emotions. I understand that the next biggest moment is still to come and it's just around the corner. And if I'm reminiscing about the past, I might not be ready for the future or be able to enjoy the moment. Time is all we have, spend it well, because before you know it, it's gone. Then what? Build a time machine? I ain't got time for that.
Sensory Deprivation - Isolation
Isolation Tank originally called a sensory deprivation tank (a.k.a. float tank, flotation tank or sensory attenuation tank) is a lightless, soundproof tank with high epsom salt (magnesium sulphate) content filled with salt water at skin temperature, in which individuals float. They were first used in 1954 to test the effects of sensory deprivation. Flotation is widely advertised on the internet as a form of alternative medicine with claims that it has beneficial health effect. Floatation Therapy.
Sensory Deprivation is the deliberate reduction or removal of stimuli from one or more of the senses. Simple devices such as blindfolds or hoods and earmuffs can cut off sight and hearing, while more complex devices can also cut off the sense of smell, touch, taste, thermoception (heat-sense), and 'gravity'. Sensory deprivation has been used in various alternative medicines and in psychological experiments (e.g. with an isolation tank). Short-term sessions of sensory deprivation are described as relaxing and conducive to meditation; however, extended or forced sensory deprivation can result in extreme anxiety, hallucinations, bizarre thoughts, and depression. A related phenomenon is perceptual deprivation, also called the ganzfeld effect. In this case a constant uniform stimulus is used instead of attempting to remove the stimuli; this leads to effects which have similarities to sensory deprivation. Dizziness.
Altered States (the movie)
Subliminal Phoenix - Star Pool - Space Travel - Biosphere 2
Sensory Adaptation is a change over time in the responsiveness of the sensory system to a constant stimulus. It is usually experienced as a change in the stimulus. For example, if one rests one's hand on a table, one immediately feels the table's surface on one's skin. Within a few seconds, however, one ceases to feel the table's surface. The sensory neurons stimulated by the table's surface respond immediately, but then respond less and less until they may not respond at all; this is an example of neural adaptation. Neural adaptation is also thought to happen at a more central level such as the cortex.
Infrared Sauna uses infrared heaters to emit infrared light experienced as radiant heat which is absorbed by the surface of the skin. Traditional saunas heat the body primarily by conduction and convection from the heated air and by radiation of the heated surfaces in the sauna room. Although saunas have been advertised to provide a wide range of health benefits, such as detoxification, there are no scientific evidence backing these claims.
Orgone described as an esoteric energy or hypothetical universal life force, originally proposed in the 1930s by Wilhelm Reich.
Silence
Silence is good for you, it helps the brain regenerate brain cells. Two hours of silence per day prompted cell development in the hippocampus region of the Brain. So take a few moments each day to be in total Silence, spend time in nature, take a break. Silence relieves stress and tension. It's good to get away from the sonic disruptions because it gives our brains Attention Center the opportunity to restore. Seek calming pleasures that contribute to peace of mind. Peace and quiet has great value.
Silence is Golden means that sometimes not saying nothing is often better than speaking too much or saying something inappropriate. Speech is silver, but silence is golden, unless you have to be a whistle blower.
Is Silence Golden? Effects of Auditory Stimuli and their absence on adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
Attention Restoration Theory asserts that people can concentrate better after spending time in nature, or even looking at scenes of nature. Natural environments abound with "soft fascinations" which a person can reflect upon in "effortless attention", such as clouds moving across the sky, leaves rustling in a breeze or water bubbling over rocks in a stream.
Default Mode Network is a network of interacting brain regions known to have activity highly correlated with each other and distinct from other networks in the brain. The default mode network is most commonly shown to be active when a person is not Focused on the outside world and the brain is at wakeful rest, such as during daydreaming and mind-wandering. But it is also active when the individual is thinking about others, thinking about themselves, remembering the past, and planning for the future. The network activates "by default" when a person is not involved in a task.
Mind Wandering is the experience of thoughts not remaining on a single topic for a long period of time, particularly when people are engaged in an attention-demanding task. Mind-wandering tends to occur during driving, reading and other activities where vigilance may be low. In these situations, people do not remember what happened in the surrounding environment because they are pre-occupied with their thoughts. This is known as the decoupling hypothesis. Studies using event-related potentials (ERPs) have quantified the extent that mind-wandering reduces the cortical processing of the external environment. When thoughts are unrelated to the task at hand, the brain processes both task relevant and unrelated sensory information in a less detailed manner.
Retreat is a place with peace and quiet and an area that has privacy where you can be alone and study.
Mindfulness - Listening - Focusing - Learning - White Noise
 The Quieter you become the more you can hear, Silence is Golden.
The Quieter you become the more you can hear, Silence is Golden.Silence is the lack of audible sound or the presence of sounds of very low intensity. By analogy, the word silence can also refer to any absence of communication or hearing, including in media other than speech and music. Silence is also used as total communication, in reference to nonverbal communication and spiritual connection. Silence also refers to no sounds uttered by anybody in a room or area. Silence is an important factor in many cultural spectacles, as in rituals. Could sound exist without silence?
Quiet is when a moment in time is free from noise or has the absence of sound or uproar. An untroubled state that is free from disturbances or a disposition that is free from stress or emotion. To be quiet is making very little sound or speaking in a softened tone or low voice.
Shush is to tell or signal someone to be silent by making a soft swishing or rustling sound.
Noise is sound that is an unpleasant auditory experience. Incomprehensibility resulting from irrelevant information or meaningless facts or remarks. Lacks musical quality.
 Noise Pollution s the disturbing or
excessive noise that may harm the
activity or balance of human or animal life.
Noise Pollution s the disturbing or
excessive noise that may harm the
activity or balance of human or animal life.Do Not Disturb indicates that somebody does not wish to be disturbed or bothered or distracted.
Disturb is to destroy or diminish the peace or tranquility of someone. Cause profound worry or make someone to feel uncomfortable or anxious.
"I love the sound you make when you shut up." Stay Calm
Health Effects From Noise are the health consequences of regular exposure, to consistent elevated sound levels. Elevated workplace or environmental noise can cause hearing impairment, Learning Impairments, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, annoyance, and sleep disturbance. Changes in the immune system and birth defects have been also attributed to noise exposure.
There are the times when Silence is Not an Option.
The Silence Game or Quiet Game is really just another way for kids to learn about mindfulness and meditation.
A Moment of Silence could also be a form of meditation, as well as Praying.
Vow of Silence is a religious or a spiritual practice taken in a monastic context, to maintain silence.
Centering Prayer is a popular method of meditation used by some Christians, placing a strong emphasis on interior silence.
The Gift of Silence - Nick Seaver - TEDxBeaconStreet (video)
Mantras - Stress Relief - Routines
Introvert - Solitary Confinement - Connect
Noise Dampening Tools and Technology
One Square Inch of Silence is very possibly the quietest place in the United States. It is an independent research project located in the Hoh Rain Forest of Olympic National Park, which is one of the most pristine, untouched, and ecologically diverse environments in the United States.
The Sounds of Silence (Simon & Garfunkel - youtube) - Disturbed - The Sound Of Silence (youtube).
Recording the Sounds of Extinction (youtube) - Bernie Krause has been recording wildlife sounds, or "soundscapes," for over forty years. He's amassed the largest archive in the world, and in doing so, can chart how wildlife sounds have changed over the course of climate change. Listen for yourself: the rising silence speaks volumes. Our Current Mass Extinction.
Guides - Spiritual Advisors - Teachers
 Dalai Lama
is a monk of the Gelug or Yellow Hat school of Tibetan Buddhism, the
newest of the schools of Tibetan Buddhism founded by Je Tsongkhapa. The
14th and current Dalai Lama is Tenzin Gyatso.
Dalai Lama
is a monk of the Gelug or Yellow Hat school of Tibetan Buddhism, the
newest of the schools of Tibetan Buddhism founded by Je Tsongkhapa. The
14th and current Dalai Lama is Tenzin Gyatso.Monk s a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decided to dedicate his life to serving all other living beings, or to be an ascetic who voluntarily chooses to leave mainstream society and live his or her life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many religions and in philosophy. Morality.
Guru is a teacher, guide, expert, or master of certain knowledge or field.
Yogi is a practitioner of yoga. In Vedic Sanskrit, yoga (from the root yuj) means "to add", "to join", "to unite", or "to attach".
Autobiography of a Yogi is an autobiography of Paramahansa Yogananda (January 5, 1893–March 7, 1952) first published in 1946. Yogananda was born Mukunda Lal Ghosh in Gorakhpur, India, into a Bengali family.
Kriya Yoga is described by its practitioners as the ancient Yoga system revived in modern times by Mahavatar Babaji through his disciple Lahiri Mahasaya, c. 1861. Kriya Yoga was brought to international awareness by Paramahansa Yogananda's book Autobiography of a Yogi and through Yogananda's introductions of the practice to the west from 1920. The Kriya Yogi mentally directs his life energy to revolve, upward and downward, around the six spinal centers (medullary, cervical, dorsal, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal plexuses) which correspond to the twelve astral signs of the zodiac, the symbolic Cosmic Man. One half-minute of revolution of energy around the sensitive spinal cord of man effects subtle progress in his evolution; that half-minute of Kriya equals one year of natural spiritual unfoldment. Offering inhaling breath into the outgoing breath, and offering the outgoing breath into the inhaling breath, the yogi neutralizes both these breaths; he thus releases the life force from the heart and brings it under his control.
Bodhisattva is the Sanskrit term for anyone who, motivated by great compassion, has generated bodhicitta, which is a spontaneous wish to attain buddhahood for the benefit of all sentient beings. Buddha.
Sadhu is a religious ascetic or holy person.
Sufism is a master of the way.
Swami is an ascetic or yogi who has been initiated into the religious monastic order, founded by some religious teacher. It is believed to be originally used for the ones who were initiated into to the Advaita Vedanta movement, started by Adi Shankara. The meaning of the Sanskrit root of the word "Swami" is "one who is one with his Self" ('Swa' stands for self) The usage of this word is not just for a yogi but also used for a religious guru, with or without disciples.
Sage is a mentor in spiritual and philosophical topics who is renowned for profound wisdom that comes with experience and continuous learning.
Coaching is a form of development in which a person called a coach supports a learner or client in achieving a specific personal or professional goal by providing training, advice and Guidance.
Counseling - Life Coaching - Teaching - Leadership
Spiritual Advisor is to help the development of the spiritual life of the members and to enable them to better understand the meaning of charity and its practical application toward those in need.
Spiritual Direction is the practice of being with people as they attempt to deepen their relationship with the divine, or to learn and grow in their own personal spirituality. The person seeking direction shares stories of his or her encounters of the divine, or how he or she is cultivating a life attuned to spiritual things. The director listens and asks questions to assist the directee in his or her process of reflection and spiritual growth. Spiritual direction advocates claim that it develops a deeper awareness with the spiritual aspect of being human, and that it is not psychotherapy, counseling, or financial planning.
Dhammapada is a collection of sayings of the Buddha in verse form and one of the most widely read and best known Buddhist scriptures.
5 Elements of Ayurveda - Ether is the first one of the great elements. This element is often referred to as “space” or “emptiness”. Because ether is empty space, it is known as the element that other fill. The ear and the mouth are associated with this element. However, all empty spaces in our body are connected with the ether element. Air represents oxygen, breath, motion, and lightness. This element is present in the respiratory system and nerves. It is also the second of the five elements since air has a close relationship with ether. Fire is the third of the great elements. It’s related to ether because it provides it with the space to burn. It’s also related to air because it provides the fire’s fuel. Fire is closely associated with the eyes and the body’s heat. Fire is also associated with thoughts, emotions, and obsessions. Water is the fourth great element. It’s associated with fire, ether, and air. Water is the protector of the body. The tongue is associated with water element. Water is expressed in the body in five distinct ways: saliva, stomach, the nerves, the joints, and the respiratory system. It’s also associated with blood. Earth is the last of all the elements because it evolves from the last four. It also contains these elements within it. This element is heavily associated with our sense of smell, bones, nails, and teeth.
Transformations - Transitions
Transform is to change or alter in form or to change the appearance or the nature of something or someone. To change the outward structure or the looks of something or change from one form or medium into another. Progress - Transduce - Energy.
Transformative is causing a marked change in someone or something. Activism - Re-Program - Reboot
Transformation is a qualitative change. Metamorphosis - Substitute - Change Habits - Personal Development
Reformation is forming again with improvements or removal of defects. Renewing and reconstituting. Rescuing from error and returning to a rightful course. Improvement in the existing form or condition of institutions or practices intended to make a striking change for the better in social or political or religious affairs.
Transition is the act of passing from one state or place to the next. Sustainable - Simplicity - Transference.
Transformative Learning the process of "perspective transformation" has three dimensions: psychological (changes in understanding of the self), convictional (revision of belief systems), and behavioral (changes in lifestyle). Transformative learning is the expansion of consciousness through the transformation of basic worldview and specific capacities of the self; transformative learning is facilitated through consciously directed processes such as appreciatively accessing and receiving the symbolic contents of the unconscious and critically analyzing underlying premises. A defining condition of being human is that we have to understand the meaning of our experience. For some, any uncritically assimilated explanation by an authority figure will suffice. But in contemporary societies we must learn to make our own interpretations rather than act on the purposes, beliefs, judgments, and feelings of others. Facilitating such understandings is the cardinal goal of adult education. Transformative learning develops autonomous thinking. Perspective transformation, leading to transformative learning, occurs infrequently. An important part of transformative learning is for individuals to change their frames of reference by critically reflecting on their assumptions and beliefs and consciously making and implementing plans that bring about new ways of defining their worlds. This process is fundamentally rational and analytical. Enlightenment (mysticism).
Transformative Change can Save Humans and Nature. Human impacts on life on Earth are unprecedented, requiring transformative action to address root economic, social and technological causes.
Transcend is to be or go beyond the range or limits of something abstract, typically a conceptual field or division.
Transcending is to be greater, superior or better in scope or size than some other standard. Upward Climb.
Transcendental is a characteristic of a system of philosophy emphasizing the intuitive and spiritual above the empirical and material.
Symmetry - Balance - Mantra - Life Force
Transcendental Meditation Technique is a specific form of mantra meditation developed by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi. It is often referred to as Transcendental Meditation, or simply TM. The meditation practice involves the use of a mantra and is practiced for 15–20 minutes twice per day while sitting with one's eyes closed. It is reported to be one of the most-widely practiced, and among the most widely researched meditation techniques, with over 340 peer-reviewed studies published.
Transcendence is a state of being or existence above and beyond the limits of material experience. The state of excelling or surpassing or going beyond usual limits. The quality of being which cannot be predicated on any actually existing thing insofar as it exists. Also means that God is completely outside of and beyond the world, as contrasted with the notion that God is manifested in the world.
Transcendental Meditation refers to a specific form of mantra meditation called the Transcendental Meditation technique.
Everything is in a constant state of transition. Even if your thoughts stay the same, the physical self is transitioning and the earth is transitioning. So you need to be able to adapt. It matters what you think. You can either slow down the transition or speed it up, but you can't stop it. You may change direction, but not the destination. You can zig-zag and go backwards momentarily, but eventually entropy will remind you of the inevitable. There is only so much you can do about that one thing, but there are still millions of other things that you can do in the mean time. So that's what we do, what else is there?
Higher Self describes an eternal, omnipotent, conscious, and intelligent being, who is one's real self or is part of an individual's metaphysical identity. The Higher Self is generally regarded as a form of being only to be recognized in a union with a divine source. Emergence of the Higher Self is a term associated with multiple belief systems.
Liminal is at a threshold or transitional stage. Metamorphosis.
Transition Assistance Program provides information and training to ensure service members transitioning from active-duty are prepared for their next step in life - whether pursuing additional education, finding a job in the public or private sector, or starting their own business. TAP is a cohesive, modular, outcome-based program that bolsters and standardizes the opportunities, services and training service members receive to better prepare post-military career goals. Life After Prison - Divorced.
Emergent is the process of coming into being or becoming prominent. Emergence.
Spiritual Enlightenment refers to the gathering of education and learning. When you seek a spiritual advisor, you are seeking education. Spiritual advisor is someone who can help you to be better in tune with your heart and your feelings.
Enlightenment (realization) - Spirituality
Self-Realization Fellowship is a worldwide spiritual organization founded by Paramahansa Yogananda in 1920 and legally incorporated as a non-profit religious organization in 1935, to serve as Yogananda’s instrument for the preservation and worldwide dissemination of his writings and teachings, including Kriya Yoga. Yogananda wrote in God Talks With Arjuna: The Bhagavad Gita that the science of Kriya Yoga was given to Manu, the original Adam, and through him to Janaka and other royal sages.
Soul - Out of Body Experience - Life Force
What would you do with a Heightened State Of Consciousness or a Higher State of Consciousness? What do you plan to accomplish? What is your purpose? What do you plan to Learn? If you don't have the necessary knowledge and information that's needed to describe your experience, then logically the first thing you should do is to learn as much as you can first. You can't progress without knowledge. So learning becomes the most important part of your journey.
First Evidence for Higher State of Consciousness Found
Maharishi Unified Field Peace Assembly Amherst Mass. 1979. The collective practice of the Maharishi Technology of the Unified Field by a group of approximately 2,500 individuals in the U.S.A. was found to result in a holistic improvement in the quality of life throughout the nation, as reflected by reductions in violent crime, motor vehicle fatalities, air transport fatal accidents, and fatalities from accidents, suicides and homicides, and by improvements in important national economic indicators.
Sensations are the building blocks of consciousness and Meditation are the building blocks of sub-consciousness.
Asceticism is a lifestyle characterized by abstinence from worldly pleasures, often for the purpose of pursuing spiritual goals.
Indian Aesthetics evolves an emphasis on inducing special spiritual or philosophical states in the viewer by representing them symbolically.
Chopra - Dosha - Success Consciousness
Shugenda enlightenment is equated with the attainment of oneness with the kami. - Shinto
Pingala is the traditional name of the author of the Chandaśāstra, the earliest known Sanskrit treatise on. Treatise is a systematic interpretation or an explanation of a specific topic. Prosody is a system of versification. Versification is a metrical adaptation of something.
Don't Trip Alone your First Time or Experiment by Yourself
When experimenting with mind altering drugs you should try to have professional or experienced guides to assist you. Be under the guidance of two health professionals who will create a positive framework for your journey. First have an interview or a few meetings to discuss to see if you are prepared and screened to see that you qualify so that you have the experience your hoping to have. It's important to have the right mindset, intentions, and to be in a good and safe environment that is comfortable. Your intentions may be to kick a chronic addiction, heal from a traumatic experience, or discover one’s purpose in life or come up with new ideas. During your drug experience and depending on your needs, the guides may help you navigate any negative feelings you might have and keep you calm if things get to intense or over whelming. Guides may ask you to control your breathing or to do some exercises, or some meditation, or some writing or even some singing or listening to music. Guides may also reassure you that you will return to a "normal" state of mind in time and Return to your Baseline. So just relax and let the substance run it's course. It's good to stay hydrated so always have water available. After your drug experience that day and for several days after, you will have some follow up meetings where they will to talk about what you thought about the experience and what things you may have learned. After a psychedelic journey is over, there is often an incredible wealth of information, emotions, ideas, and new perspectives to integrate.
Lucid Dreaming - Nutrition Consulting - Coming Down.
Shamanism is a practice that involves a practitioner reaching altered states of consciousness in order to perceive and interact with a spirit world and channel these transcendental energies into this world.
Terence McKenna was an American ethnobotanist, mystic, psychonaut, lecturer, author, and an advocate for the responsible use of naturally occurring psychedelic plants. He spoke and wrote about a variety of subjects, including psychedelic drugs, plant-based entheogens, shamanism, metaphysics, alchemy, language, philosophy, culture, technology, environmentalism, and the theoretical origins of human consciousness. He was called the "Timothy Leary of the '90s", "one of the leading authorities on the ontological foundations of shamanism", and the "intellectual voice of rave culture".
Rythmia is a resort in Costa Rica dedicated to relaxation and healing transformation. We utilize a range of programs, workshops, and natural support therapies.
Be Here Now is a 1971 book on spirituality, yoga and meditation by the Western-born yogi and spiritual teacher Ram Dass (born Richard Alpert). The title comes from a statement his guide, Bhagavan Das, made during Ram Dass's journeys in India. The cover features a mandala incorporating the title, a chair, radial lines, and the word "remember" repeated four times.
Philosophy - Enlightenment - Holistic Healing
How to be a Teacher - How to be a Leader
Turn On, Tune In, Drop Out - Turn On means go within to activate your neural and genetic equipment. Become sensitive to the many and various levels of consciousness and the specific triggers engaging them. Tune In means interact harmoniously with the world around you—externalize, materialize, express your new internal perspectives. Drop Out means self-reliance, a discovery of one's singularity, a commitment to mobility, choice, and change.
Show Me the Way: Peter Frampton (youtube)
Oxycise - Modern Mystery School - Mystery School
Vajrayana includes practices that make use of mantras, dharanis, mudras, mandalas and the visualization of deities and Buddhas. According to Vajrayāna scriptures, the term Vajrayāna refers to one of three vehicles or routes to enlightenment, the other two being the Śrāvakayāna (also known as the Hīnayāna) and Mahāyāna. Tantric Buddhism can be traced back to groups of wandering yogis called Mahasiddhas (great adepts). The mahasiddhas date to the medieval period in the Northern Indian Subcontinent (3–13 cen. CE), and used methods that were radically different than those used in Buddhist monasteries including living in forests and caves and practiced meditation in charnel grounds similar to those practiced by Shaiva Kapalika ascetics. These yogic circles came together in tantric feasts (ganachakra) often in sacred sites (pitha) and places (ksetra) which included dancing, singing, sex rites and the ingestion of taboo substances like alcohol, urine, meat, etc. It is interesting to note that at least two of the Mahasiddhas given in the Buddhist literature are actually names for Shaiva Nath saints (Gorakshanath and Matsyendranath) who practiced Hatha Yoga. Vajrayāna is usually translated as Diamond Vehicle or Thunderbolt Vehicle, referring to the Vajra, a mythical weapon which is also used as a ritual implement. Shugendo (wiki)
Doctor Strange is a 2016 American superhero film based on the Marvel Comics character of the same name. Strange goes to Kamar-Taj, where he is taken in by Mordo, a sorcerer under the Ancient One. The Ancient One demonstrates her power to Strange, revealing the astral plane and other dimensions such as the Mirror Dimension. She eventually agrees to train Strange, despite his arrogance. The imagery in this film looks like an Ayahuasca experience. Fasting.
Internal Energy - Life Force - Let the Force be with You
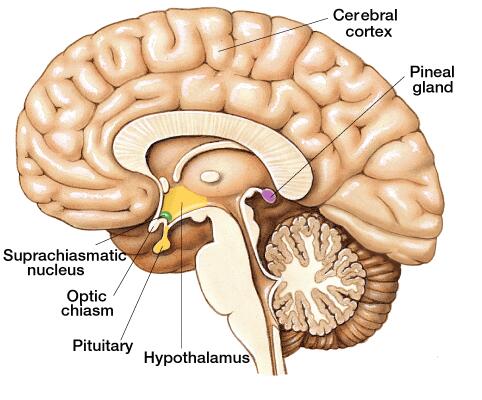 Third Eye, also called the
mind's eye, or inner eye,
is a mystical and esoteric concept referring to a speculative invisible
eye which provides perception beyond
ordinary sight. Kiss the third eye or gently touch it.
Remote Viewing.
Third Eye, also called the
mind's eye, or inner eye,
is a mystical and esoteric concept referring to a speculative invisible
eye which provides perception beyond
ordinary sight. Kiss the third eye or gently touch it.
Remote Viewing.Parietal Eye also known as a third eye or pineal eye, is a part of the epithalamus present in some animal species. The eye is photoreceptive and is associated with the pineal gland, regulating circadian rhythmicity and hormone production for thermoregulation. Energy from Food.
Pineal Gland is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. Fully developed in 49 days after conception. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, hence its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles. DMT is produced by the pineal gland, and so is VMAT2. Vesicular monoamine transporter 2 is an integral membrane protein that transports monoamines—particularly neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine—from cellular cytosol into synaptic vesicles. In nigrostriatal pathway and mesolimbic pathway dopamine-releasing neurons, VMAT2 function is also necessary for the vesicular release of the neurotransmitter GABA. "The God Gene". Imagery.
Pineal Gland Activation (youtube) - Create your own sound vibration Frequency.
PINEAL GLAND Activation Frequency 936Hz: BINAURAL BEATS Meditation Music Third Eye Opening (youutube)
Girl demonstrates Cool SuperPower (Third Eye) (youtube) -Nine-Year-Old Yogamaatha went to a "third eye awakening" course in India and is now demonstrating the unique ability to see with her third eye. With her eyes covered by three blindfolds, she claims to be able to read pieces of paper and play games as though her eyes were wide open.
Pineal Wave - Enteric Nervous System (brain)
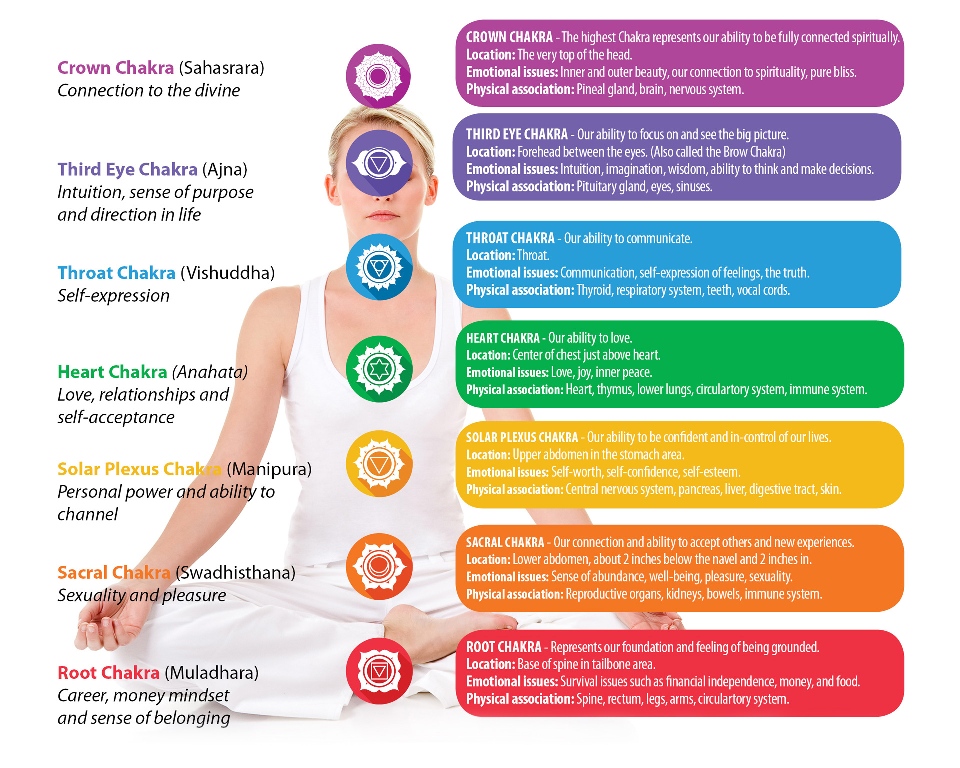
Chakra is thought to be an energy point or node in the subtle body. Soul Chakras are believed to be part of the subtle body, not the physical body, and as such, are the meeting points of the subtle (non-physical) energy channels called nadi. Nadi are believed to be channels in the subtle body through which the life force (prana) (non-physical) or vital energy (non-physical) moves. Green is the color of the Heart chakra, also known as Anahata. This chakra is located at the center of the chest area and is linked to this entire area, the heart, lungs, circulatory system, and cardiac plexus. The Heart Chakra bridges the gap between the physical and spiritual worlds. Opening the Heart chakra allows a person to love more, empathize, and feel compassion. Gemstones that will aid the Heart chakra include emerald, tourmaline, aventurine, malachite, rose quartz, and rhodonite. Activating the Flow of Positive Energy.
Meridians - Massage - Human EMF - Human Energy - Bio-Battery - Gut
Sri Yantra is a form of mystical diagram, known as a yantra, found in the Shri Vidya school of Hindu tantra. The diagram is formed by nine interlocking triangles that surround and radiate out from the central (bindu) point. The two dimensional Sri Chakra, when it is projected into three dimensions is called a Maha Meru. Mount Meru derives its name from this Meru like shape.
Prana is the Sanskrit word for life force or vital principle, is all cosmic energy, permeating the Universe on all levels. Prana is often referred to as the life force or life energy. It also includes energies present in inanimate objects. In the literature, prana is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements of the Universe. This life energy has been vividly invoked and described in the ancient Vedas and Upanishads.
Orenda is a supernatural force believed by the Iroquois Indians to be present, in varying degrees, in all objects or persons, and to be the spiritual force by which human accomplishment is attained or accounted for.
Kundalini refers to a form of primal energy (or shakti) located at the base of the spine.
Hara is a technical term for a specific area (physical/anatomical) or energy field (physiological/energetic) of the body. An alternative Japanese reading of the character is Hufu, the Chinese reading is Fu. should not be translated as "stomach" to avoid confusing it with the organ). (tanden).
 Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power,
and good health.
Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power,
and good health. Nadi in yoga is a term for the channels through which, in traditional Indian medicine and spiritual science, the energies of the physical body, the subtle body and the causal body are said to flow. Within this philosophical framework, the nadis are said to connect at special points of intensity called nadichakras. The Ida and Pingala nadis are often seen as referring to the two hemispheres of the brain. Pingala is the extroverted, solar nadi, and corresponds to left hemisphere. Ida is the introverted, lunar nadi, and refers to the right hemisphere of the brain. Ida nadi controls all the mental processes while Pingala nadi controls all the vital processes. Ida is associated with lunar energy. The word ida means "comfort" in Sanskrit. Ida has a moonlike nature and feminine energy with a cooling effect. It courses from the left testicle to the left nostril and corresponds to the Ganges river.
Pingala is associated with solar energy. The word pingala means "orange" or "tawny" in Sanskrit. Pingala has a sunlike nature and masculine energy. Its temperature is heating and courses from the right testicle to the right nostril. It corresponds to the river Yamuna.
Human Energy (aura) - Human Magnetic Field
Dantian, energy center. Dantian are the Qi Focus Flow Centers, important focal points for meditative and exercise techniques such as qigong, martial arts such as t'ai chi ch'uan, and in traditional Chinese medicine.
Qi is an active principle forming part of any living thing. Qi literally translates as "breath", "air", or "gas", and figuratively as "material energy", "life force", or "energy flow". Qi is the central underlying principle in traditional Chinese medicine and martial arts.
Energy in esotericism is the life force or élan vital or self-organization and spontaneous morphogenesis. An experience and phenomena that defy measurement and thus can be distinguished from the scientific form of energy.
Energy Medicine is the belief that healers can channel healing energy into a patient and effect positive results. This idea itself contains several methods: hands-on, hands-off, and distant (or absent) where the patient and healer are in different locations. Placebo.
Biofeedback - Eclectic Energies - One Mind One Energy - Self Mastery
Kundalini is a form of divine feminine energy (or shakti) believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the muladhara. It is an important concept in Shaiva Tantra, where it is believed to be a force or power associated with the divine feminine or the formless aspect of the Goddess. This energy in the body, when cultivated and awakened through tantric practice, is believed to lead to spiritual liberation.
Vitalism is the belief that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things". a Where vitalism explicitly invokes a vital principle, that element is often referred to as the "vital spark", "energy" or "élan vital", which some equate with the soul.
Akasha meaning of "open space, vacuity", which is the absence of matter, a region that is devoid of matter.
Vajrayana refers to one of three vehicles or routes to enlightenment, the other two being the Śrāvakayāna (also known as the Hīnayāna) and Mahāyāna. Bon is a Tibetan religion. Mahayana is Sanskrit for "Great Vehicle". Sanskrit is the primary sacred language of Hinduism and Mahāyāna Buddhism, a philosophical language in Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism.
Dharma signifies behaviours that are considered to be in accord with rta, the order that makes life and universe possible, and includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and ‘‘right way of living’’.
Etheric Plane represent the subtle part of the lower plane of existence. It represents the fourth [higher] subplane of the physical plane (a hyperplane), the lower three being the states of solid, liquid, and gaseous matter.
Neidan is an array of esoteric doctrines and physical, mental, and spiritual practices that Taoist initiates use to prolong life and create an immortal spiritual body that would survive after death.
Yogis Of Tibet (2002) (youtube) - Mantras Meditation Sanskrit
Purusha is a complex concept whose meaning evolved in Vedic and Upanishadic times. Depending on source and historical timeline, it means the cosmic man or Self, Consciousness, and Universal principle.
Reiki is a form of alternative medicine where Reiki practitioners use a technique called palm healing or hands-on healing through which a "universal energy" is allegedly transferred through the palms of the practitioner to the patient in order to encourage emotional or physical healing. Reiki.
Reiki Hand Positions for Self-Treatment (youtube)
The Fifth Element Life Mandala Match
Crystal Healing claims that stones and crystals have healing powers, although there is no scientific basis for this claim. In one method, the practitioner places crystals on different parts of the body, often corresponding to chakras; or else the practitioner places crystals around the body in an attempt to construct an energy grid, which is purported to surround the client with healing energy.
Age of Aquarius - Emotions - Sleeping
Ventricular System is a set of four interconnected cavities (ventricles or lumen) in the brain, Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced. The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Lateral Ventricles are the two largest cavities of the ventricular system of the human brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively. Each lateral ventricle resembles a C-shaped structure that begins at an inferior horn in the temporal lobe, travels through a body in the parietal lobe and frontal lobe, and ultimately terminates at the interventricular foramina where each lateral ventricle connects to the single, central third ventricle. Along the path, a posterior horn extends backward into the occipital lobe, and an anterior horn extends farther into the frontal lobe. Third Ventricle is one of four connected fluid-filled cavities comprising the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a median cleft in the diencephalon between the two thalami, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is in the midline, between the left and right lateral ventricles. Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Fourth Ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius) to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the pons or in the upper part of the medulla oblongata. CSF entering the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct can exit to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord through two lateral apertures and a single, midline median aperture.
Physical Training - Strong Body and Mind
Tai Chi or "Supreme Ultimate Boxing", is an Internal Chinese Martial Art 武术 practiced for both its defense training and its health benefits. Though originally conceived as a martial art, it is also typically practiced for a variety of other personal reasons: competitive wrestling in the format of pushing hands (tui shou), demonstration competitions, and achieving greater longevity. As a result, a multitude of training forms exist, both traditional and modern, which correspond to those aims with differing emphasis. Some training forms of t'ai chi ch'uan are especially known for being practiced with relatively slow movements.
Tai Chi - Tai Chi for Beginners (youtube)
Qigong is a holistic system of coordinated body movement and posture, breathing, and meditation used for health, spirituality, and martial arts training. With roots in Chinese medicine, philosophy, and martial arts, qigong is traditionally viewed as a practice to cultivate and balance qi (chi), translated as "life energy". Qigong practice typically involves moving meditation, coordinating slow-flowing movement, deep rhythmic breathing, and a calm meditative state of mind. People practice qigong throughout China and worldwide for recreation, exercise, relaxation, preventive medicine, self-healing, alternative medicine, meditation, self-cultivation, and training for martial arts. Because clinical research on qigong for its potential benefit in treating various diseases – such as hypertension, pain, and cancer – has been inconclusive due to poor quality, there remains no evidence that qigong has any therapeutic effect, as of 2016. Falun Dafa - Qigong.
Buddha was a monk (śramana), mendicant, and sage, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. He is believed to have lived and taught mostly in the northeastern part of ancient India sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE. Gautama taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and the severe asceticism found in the śramana movement common in his region. He later taught throughout other regions of eastern India such as Magadha and Kosala. Meditation.
Buddhism is the world's fourth-largest religion with over 520 million followers, or over 7% of the global population, known as Buddhists. An Indian religion, Buddhism encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and spiritual practices largely based on original teachings attributed to the Buddha and resulting interpreted philosophies. Buddhism originated in ancient India as a Sramana tradition sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE, spreading through much of Asia. Two major extant branches of Buddhism are generally recognized by scholars: Theravada (Pali: "The School of the Elders") and Mahayana (Sanskrit: "The Great Vehicle"). All Buddhist traditions share the goal of overcoming suffering and the cycle of death and rebirth, either by the attainment of Nirvana or through the path of Buddhahood. Buddhist schools vary in their interpretation of the path to liberation, the relative importance and canonicity assigned to the various Buddhist texts, and their specific teachings and practices. Widely observed practices include taking refuge in the Buddha, the Dharma and the Sangha, observance of moral precepts, monasticism, meditation, and the cultivation of the Paramitas (virtues). Schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism that have existed from ancient times up to the present. Buddha Wallpaper - Buddha Photos (images).
Buddhist Meditation refers to the meditative practices associated with the religion and philosophy of Buddhism. Buddhist meditation encompasses a variety of meditation techniques that aim to develop mindfulness, concentration, supramundane powers, tranquility, and insight. Specific Buddhist meditation techniques have also been used to remove unwholesome qualities thought to be impediments to spiritual liberation, such loving kindness to remove ill-will, hate, and anger, equanimity to remove mental clinging, and reflection on 31-parts-of-the-body and corpses to remove sensual lust for the body and cultivate annica or impermanence. Spiritual.
Buddhist Philosophy refers to the philosophical investigations and systems of inquiry that developed among various Buddhist schools in India following the parinirvana (i.e. death) of the Buddha and later spread throughout Asia. The Buddhist path combines both philosophical reasoning and meditation. The Buddhist traditions present a multitude of Buddhist paths to liberation, and Buddhist thinkers in India and subsequently in East Asia have covered topics as varied as phenomenology, ethics, ontology, epistemology, logic and philosophy of time in their analysis of these paths.
Tantra denotes the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that co-developed most likely about the middle of the 1st millennium AD. The term tantra, in the Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". Tantra literally means "loom, warp, weave".
Six Yogas of Naropa are a set of advanced Tibetan Buddhist tantric practices and a meditation sādhanā compiled in and around the time of the Indian monk and mystic Nāropa (1016-1100 CE) and conveyed to his student Marpa Lotsawa. The six yogas were intended in part to help in the attainment of Buddhahood in an accelerated manner.
Mettā Meditation means benevolence, loving-kindness, friendliness, amity, good will, and active interest in others. It is the first of the four sublime states (Brahmavihāras) and one of the ten pāramīs of the Theravāda school of Buddhism.
Bodhi in Buddhism is the understanding possessed by a Buddha regarding the true nature of things. It is traditionally translated into English with the word enlightenment, although its literal meaning is closer to "awakening." The verbal root "budh" means to awaken.
Dhyana Buddhism commonly translated as meditation, is a state of no mind, which lead to "state of perfect equanimity and awareness.
Techniques of Knowledge is a formulation of four specific techniques that were imparted in a process of initiation. "Light" involves careful pressure on the eyes, seeking to open the "third eye" after a long period of training and practice. This is comparable to similar Tantric practices. "Sound" involves positioning the hands over the ears and temples, with the goal of hearing the "heavenly music". This is reported to be related to sabda-brahman meditation. "Name", or "Word", is a meditation concentrating on breath. Kranenborg additionally states that it employs mantras while exhaling. "Nectar" involves tongue positioning, eventually leading the student to taste the "nectar of life". Michael Drury, describes these techniques as helping the practitioner to develop "a deep and spiritual self-knowledge."
Yoga
 Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or
disciplines which originated in ancient India. There is a broad variety of
Yoga schools, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.
Among the most well-known types of yoga are Hatha yoga and Rāja yoga.
Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or
disciplines which originated in ancient India. There is a broad variety of
Yoga schools, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.
Among the most well-known types of yoga are Hatha yoga and Rāja yoga. Yoga Poses with names Chart (image)
Yoga Moves - Yoga Poses - Yoga for Kids
Yoga is a process for internal listening and a form of measuring and maintaining physical strength and mental awareness.
Breathing Exercises - Exercise - Plank - Isometric
Pranayama is the practice of breath control in yoga. In modern yoga as exercise, it consists of synchronising the breath with movements between asanas, but is also a distinct breathing exercise on its own, usually practised after asanas. In texts like the Bhagavad Gita and the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, and later in Hatha yoga texts, it meant the complete cessation of breathing.
A lack of flexibility is often related to lack of strength.
Flexibility refers to the absolute range of movement in a joint or series of joints, and length in muscles that cross the joints to induce a bending movement or motion. Flexibility varies between individuals, particularly in terms of differences in muscle length of multi-joint muscles. Flexibility in some joints can be increased to a certain degree by exercise, with stretching a common exercise component to maintain or improve flexibility. Quality of life is enhanced by improving and maintaining a good range of motion in the joints. Overall flexibility should be developed with specific joint range of motion needs in mind as the individual joints vary from one to another. Loss of flexibility can be a predisposing factor for physical issues such as pain syndromes or balance disorders. Gender, age, and genetics are important for range of motion. Exercise including stretching and yoga often improves flexibility. Many factors are taken into account when establishing personal flexibility: joint structure, ligaments, tendons, muscles, skin, tissue injury, fat (or adipose) tissue, body temperature, activity level, age and gender all influence an individual's range of motion about a joint. Individual body flexibility level is measured and calculated by performing a sit and reach test, where the result is defined as personal flexibility score. Elasticity.
Hyperflexion is deviation from a straight or normal course. Act of bending a joint; especially a joint between the bones of a limb so that the angle between them is decreased.
Injury Warnings - Posture
Articulation Joint is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.
Cracking Joints means bending a person's joints to produce a distinct cracking or popping sound, often followed by a feeling of satisfaction or relaxation to the person. It is sometimes done as part of a joint adjustment routine performed by a chiropractor. According to a folk belief, the popping of joints, especially knuckles, leads to arthritis or other joint problems. However, medical research has so far failed to demonstrate any connection between knuckle cracking and long-term joint problems. While the cracking mechanism and the resulting sound is not yet fully understood, it is mainly attributed to nitrogen or carbon dioxide bubbles building up between the joints.
What stretching actually does to your body ft. Sofie Dossi (youtube) - Physics Woman (youtube)
Changes in Elastic Characteristics of Human Muscle induced by Eccentric Exercise.
Contortion is a performance art in which performers, contortionists, showcase their skills of extreme physical flexibility. Contortion acts often accompany acrobatics, circus acts, street performers and other live performing arts. Contortion acts are typically performed in front of a live audience. An act will showcase one or more artists performing a choreographed set of moves or poses, often to music, which require extreme flexibility. The physical flexibility required to perform such acts greatly exceeds that of the general population. It is the dramatic feats of seemingly inhuman flexibility that captivate audiences. In some countries, such as Russia and Mongolia, contortion holds special cultural significance.
Beighton Score is a simple system to quantify joint laxity and hypermobility. It uses a simple 9 point system, where the higher the score the higher the laxity. Muscle Contraction.
Hypermobility in joints is a condition that features joints that easily move beyond the normal range expected for that particular joint. Hypermobile joints tend to be inherited. Symptoms of the joint hypermobility syndrome include pain in the knees, fingers, hips, and elbows.
The stretching of a muscle fiber begins with the sarcomere, the basic unit of contraction in the muscle fiber. As the sarcomere contracts, the area of overlap between the thick and thin myofilaments increases. As it stretches, this area of overlap decreases, allowing the muscle fiber to elongate.
Street Yoga - Yoga Trail Yoga Network
Gaiam Yoga (youtube) - OM Yoga (youtube)
Hatha Yoga is a branch of yoga. The word haṭha literally means "force" and thus alludes to a system of physical techniques.
Hatha Yoga (youtube).
Bikram Yoga is a system of yoga that Bikram Choudhury synthesized from traditional hatha yoga techniques and popularized beginning in the early 1970s. Copyright Trolls.
Hang upside down (youtube) - Anti-Gravity Yoga (youtube)
Asana refers both to the place in which a practitioner (yogi if male, yogini if female) sits and the posture in which he or she sits. In the Yoga Sutras, Patanjali defines "asana" as "to be seated in a position that is firm, but relaxed". Patanjali mentions the ability to sit for extended periods as one of the eight limbs of his system, known as ashtanga yoga.
Supermind in Integral Yoga is the intermediary between Spirit and the manifest world, which enables the transformation of common being into Divine being.
Goat Yoga - Animal Therapy
Yoga improves symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, which is a condition with chronic nervousness and worry. Yoga may be helpful in treating anxiety in some people. According to researchers, generalized anxiety disorder is a common, impairing, and undertreated condition, currently affecting an estimated 6.8 million Americans. Cognitive behavioral therapy.
Yoga Poses - The Spider-Man - The Inchworm - The Hip Shifter - The Bretzel Lean - Mountain Pose - Downward Facing Dog - Adho Mukha Svanasana - Plank Pose - Upward Facing Dog - Warrior One - Warrior Two - Tree Pose - Chair Pose - Butterfly Pose - Reclining Spinal Twist - Bridge Pose - Child’s Pose.
Sleep Improvement Yoga Moves - Wind Relieving Pose (Pawanmuktasana) (on back). Rock-A-Bye Pose (on back, pull both legs into chest while exhaling). Legs and Feet Straight up in the Air while Laying on your Back (arms stretched out wide). Wave Exercise (on back, slowly swing legs and head side to side). Shava Asana (lay flat on back with legs and arms spread wide, palms facing upward).
Chair Yoga is a gentle form of yoga that is practiced sitting on a chair, or standing using a chair for support. It is in the process of being recognized formally as a type of yoga distinct from other types, such as Iyengar Yoga or Ashtanga yoga. Often the poses, or Asanas, are often adaptations of Hatha Yoga Poses. Frequently the chair yoga student is unable to participate in a traditional yoga class due to the effects of aging or disabilities. However, Chair yoga is a great practice for everyone, as it deepens flexibility and strengthens personal body awareness. Chair yoga classes are sometimes made available at senior fitness centers, retirement facilities, and adult daycare centers. Chair yoga is usually taught as a way to achieve physical and mental fitness, not as a way of life, seeing most other yoga classes in the Western world. Image (photo).
Hand Yoga - Yoga for your Hands (youtube) - 12 Hand and Finger Exercises
 Surya Mudra: This pose will help you lose
weight faster and improve your digestion, while also resolving any
eyesight problems. The technique will also help you in case of circulation
and trembling.
Surya Mudra: This pose will help you lose
weight faster and improve your digestion, while also resolving any
eyesight problems. The technique will also help you in case of circulation
and trembling.Prithvi Mudra: This strength pose can increase the earth element over the fire one. The earth element can influence the growth of tissues and muscle development while encouraging healing. It eliminates the fire element, meaning that it eliminates inflammation as well.
Vaayu Mudra: This pose will improve the oxygen transport to the body’s tissues and calm your mind.
Shunya Mudra: The Shunya Mudra pose will relax your body and help you with ear problems, vertigo or feeling of dullness.
Gyan Mudra: The pose of wisdom, as the Gyan Mudra is called, will boost your enthusiasm and creativity.
Varun Mudra: The pose can help people suffering from arthritis, hormonal disorders and dehydration.
Aakash Mudra: The pose of enlightenment can relax your mind and detoxify your body.
Exercise Benefits the Body and the Mind. Yoga is a type of exercise. Meditation is a type of exercise. The more you understand a particular type of exercise, the more you can benefit from it. The more time and learning that you put into an exercise, the more you can benefit from it. In order to receive you must first give. In order to receive the most benefits from any type of exercise you must first learn how to exercise effectively and efficiently, and also understand the physical and mental changes that you will experience. Benefits vary depending on the input, and also depending on how skillful and how knowledgeable you are. Practice and learning is essential.
Just because certain people do weird or incredible things with yoga or meditation or any other type of exercise, this does not mean in anyway shape or form, that you need to experience these particular levels of achievement in order to benefit from exercising.
Pilates the art of controlled movements, which should look and feel like a workout (not a therapy) when properly manifested. If practiced with consistency, Pilates improves flexibility, builds strength and develops control and endurance in the entire body. It puts emphasis on alignment, breathing, developing a strong core, and improving coordination and balance. The core, consisting of the muscles of the abdomen, low back, and hips, is often called the "powerhouse" and is thought to be the key to a person's stability. Pilates' system allows for different exercises to be modified in range of difficulty from beginner to advanced or to any other level, and also in terms of the instructor and practitioner's specific goals and/or limitations. Intensity can be increased over time as the body conditions and adapts to the exercises. Pilates.
Live, Learn, Love and Progress...
