BK101
Knowledge Base
Tools for a Healthy Environment - Energy Saving Tools
The age of restoration has begun - Reconstruction 2.0
Energy Independence - The Greening of America. A step by step process that is done simultaneously with other improvemnts. Continually learning and continually improving.
 Energy Monitoring -
Efficiency - Heat
Energy Monitoring -
Efficiency - HeatEMF - EMP - Cellphones - Noise - Air Quality
Light Communication (Li-Fi - Photonics)
Green Building - Environmental Education
Eco-Initiatives (actions you can take)
Green Products - Ideas - Sustainability
Environmental Awareness Books - Lawns
Sayings about the Environment - Environmental Quotes
Efficient Energy Use
Before you buy energy saving devices or clean energy producing products you should first have your home inspected by a building analyst who could perform an energy audit to determine building performance so that you are aware of the improvements that you can make to your house in order for it to be energy efficient as possible.
Big 5 Needs - Energy (electrical power) - Energy Efficient Appliances
Building Analyst performs a comprehensive energy audit and whole-home assessments to identify problems at the root cause and prescribes and prioritizes solutions based on building science. which is the collection of scientific knowledge and experience that focuses on the analysis and control of the physical phenomena affecting buildings and architecture. It traditionally includes areas such as building materials, building envelope, heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, natural and electrical lighting, acoustic, indoor air quality, passive strategies, fire protection, and renewable energies in buildings. In Europe, building physics and applied physics are terms used for the knowledge domain that overlaps with building science. The practical purpose of building science is to provide predictive capability to optimize the building performance of new and existing buildings, understand or prevent building failures, and guide the design of new techniques and technologies.
Building Codes - Energy Conservation - Location - Architectural Lighting Design
Energy Audit is an inspection, survey and analysis of energy flows, for energy conservation in a building, process or system to reduce the amount of energy input into the system without negatively affecting the output(s). In commercial and industrial real estate, an energy audit is the first step in identifying opportunities to reduce energy expense and carbon footprints.
Building Performance is the efficiency of functioning of buildings and the construction industry, its impact on natural environment, urban environment and its users. It is achieved through means such as architectural design values, building science, architectural engineering, efficient energy use and sustainability. Waste.
Energy Savings Performance Contract also known as Energy Performance Contracts, are an alternative financing mechanism authorized by the United States Congress designed to accelerate investment in cost effective energy conservation measures in existing Federal buildings. Smart Home.
Energy Conservation is the effort made to reduce the consumption of energy by using less of an energy service. This can be achieved either by using energy more efficiently (using less energy for a constant service) or by reducing the amount a service used (for example, by driving less).
Derating is the operation of a device at less than its rated maximum capability in order to prolong its life. Typical examples include operation below the maximum power rating, current rating, or voltage rating.
Safe Operating Area is defined as the voltage and current conditions over which the device can be expected to safely operate without self-damage.
Underclocking is modifying a computer or electronic circuit's timing settings to run at a lower clock rate than is specified. Underclocking is used to reduce a computer's power consumption, increase battery life, reduce heat emission, and it may also increase the system's stability and compatibility. Underclocking may be implemented by the factory, but many computers and components may be underclocked by the end user.
Energy Monitoring
Install an Energy Monitor so that you are fully aware how of much energy you use and what Appliances and Devices are using the most energy. You should also have a monitor that measures Temperature, Humidity, Pressure and Carbon Monoxide.
 Energy Use Monitor (amazon)
Energy Use Monitor (amazon)Whole House Energy Monitors
Smart Homes
Home Energy Monitor
Power Meters
The Parce
ALYT, Self-learning, DIY installation, smart home & security manager
The Energy Detective
Constellation
Energy Efficiency Programs
Home Energy Audit
Home Energy Assessment
Learn how to Measure your Energy use and Energy Costs
Energy Management System is a system of computer-aided tools used by operators of electric utility grids to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of the generation and/or transmission system. Appliances.
Energy Monitoring and Targeting is an energy efficiency technique based on the standard management axiom stating that “you cannot manage what you cannot measure”. M&T techniques provide energy managers with feedback on operating practices, results of energy management projects, and guidance on the level of energy use that is expected in a certain period. Importantly, they also give early warning of unexpected excess consumption caused by equipment malfunctions, operator error, unwanted user behaviours, lack of effective maintenance and the like. The foundation of M&T lies in determining the normal relationships of energy consumptions to relevant driving factors (HVAC equipment, production though puts, weather, occupancy available daylight, etc.) and the goal is to help business managers: Identify and explain excessive energy use. Detect instances when consumption is unexpectedly higher or lower than would usually have been the case. Visualize energy consumption trends (daily, weekly, seasonal, operational…). Determine future energy use and costs when planning changes in the business. Diagnose specific areas of wasted energy. Observe how changes to relevant driving factors impact energy efficiency. Develop performance targets for energy management programs. Manage energy consumption, rather than accept it as a fixed cost. The ultimate goal is to reduce energy costs through improved energy efficiency and energy management control. Other benefits generally include increased resource efficiency, improved production budgeting and reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Some Electronic Energy Meters can give False Readings that are up to 582% Higher than Actual Energy Consumption
Units of Energy is defined via work, the SI unit for energy is the same as the unit of work – the joule (J).
Electricity Meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or an electrically powered device.
Power Usage Effectiveness is a measure of how efficiently a computer data center uses energy; specifically, how much energy is used by the computing equipment (in contrast to cooling and other overhead).
Voltage Sweet Spot is when appliances use as little energy as possible. Like when you drive your car between 10mph to 90mph, it operates most efficiently at 50mph.
Power Analysis is a form of side channel attack in which the attacker studies the power consumption of a cryptographic hardware device (such as a smart card, tamper-resistant "black box", or integrated circuit). The attack can non-invasively extract cryptographic keys and other secret information from the device.
Energy Use of Appliances and Estimating Energy Consumption
Home Energy Saver
Energy Savers
Home Improvement Audits
Wattio
Energy House
Energy Hub
Shaspa
Nest Learning Thermostat
Control 4
Think Eco Smart Outlet
Energy Alternatives
Green Living Ideas
Home Monitors for Elderly
Sense installs in your home's electrical panel and provides insight into your energy use and home activity through our free iOS/Android apps.
The Contros: Control your Appliances from Anywhere
Ecoisme: Intelligent Energy Monitoring System
Intelligent Energy Systems - Stanford University (PDF)
Location, Location, Location
CURB is a home energy monitoring system that helps you take control of your home and all the energy it uses.
P3 P4400 Kill A Watt Electricity Usage Monitor (amazon)
Neur Home Energy Monitor
Smart Strip LCG5 Energy Saving Power Strip with Auto-Switching Technology and Modem/Coaxial Surge Protection (amazon)
Blue Line Innovations BLI 28000 PowerCost Monitor (amazon)
Noria: window air conditioner designed entirely with you in mind
Apps for Monitoring and Measuring Energy - Joulebug - Leafully - Kill ur Watts - Green-button - Smart Things Control Apps - The Internet of Things - Sensors
Ohm Connect Pays you for saving energy at specific times. Save Energy. Get Paid.
Watt Rebate search by zip code to find loans or tax rebates for becoming more energy efficient by state.
Watt - Solar Power - Human Energy
In 2010, the average annual electricity consumption for a U.S. residential utility customer was 11,496 kWh a year, an average of 958 Kilowatt Hours (kWh) per month. Tennessee had the highest annual consumption - 16,716 kWh.
Maine the lowest at 6,252 kWh.
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio of a unit is the cooling output during a typical cooling-season divided by the total electric energy input during the same period. The higher the unit's SEER rating the more energy efficient it is. In the U.S., the SEER is the ratio of cooling in British thermal unit (BTU) to the energy consumed in watt-hours. The coefficient of performance (COP), a more universal unit-less measure of efficiency, is discussed in the following section. The annual total cooling output would be:
5000 BTU/h × 8 h/day × 125 days/year = 5,000,000 BTU/year. With a SEER of 10 BTU/W·h, the annual electrical energy usage would be about: 5,000,000 BTU/year / 10 BTU/(W·h) = 500,000 W·h/year. The average power usage may also be calculated more simply by: Average power = (BTU/h) / (SEER) = 5000 / 10 = 500 W. If your electricity cost is 20¢/kW·h, then your cost per operating hour is: 0.5 kW * 20¢/kW·h = 10¢/h.
Weather Monitors
WeatherFlow Smart Weather Stations: AIR detects lightning and warns you of approaching storms. AIR also measures temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure, wind speed and direction, measure sunlight (including UV Index), Rain (haptic rain sensor), WiFi and Bluetooth, Low Energy connectivity, Long Battery Life. Sensors.
Lightning-Prediction System detects atmospheric conditions likely to produce lightning strikes and sounds an alarm, warning those nearby that lightning is imminent and giving them the chance to find safety before the storm arrives in the area. Lightning protection systems are often installed in outdoor areas which are often congested with people, lack sufficient shelter, and are difficult to evacuate quickly (such as water parks, college campuses, and large swimming pool or athletic field complexes). These locations are particularly dangerous during lightning storms. Prediction systems are prone to false alarms as they respond to conditions that are not always attributed to a developing thunderstorm. Electric field data is typically used in conjunction with detection information to limit false positives.
Acurite Weather Station
WeatherAtPoint - World's Smallest Weather Station Real-time, accurate weather measurements straight to your mobile device at the blink of an eye. Temperature, humidity, UV, atmospheric pressure and ambient light to your mobile device without a battery or internet connection, to help you go through your day without any weather surprises.
Indoor Weather Monitor (amazon)
Weather (world) - Atmosphere - Weather Effects on Mood
OVAL smart sensor system for your home or office. Each sensor monitors motion, light, temp, moisture, proximity & flood - sending you instant alerts!
Heat
Radiant Barrier are a type of thermal (heat) insulations that prevents heat transfer by Thermal Radiation. Thermal Energy may also be transferred via Conduction, which is the transfer of heat (internal energy) by microscopic collisions of particles and movement of electrons within a body. Or Convection, which is the heat transfer due to bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids, including molten rock (rheid). Convection takes place through advection, diffusion or both.
, however, and radiant barriers do not necessarily protect against Heat Transfer via conduction (without airspace facing the heat source) or convection (perforated). There are many definitions of thermal/heat insulation and it is commonly misinterpreted as “Bulk/Mass/Batt Insulation”, which is actually used to resist conduction heat transfer with certain R-values. Heat/thermal insulation is a barrier material which resists/blocks/reflects heat energy (either one or more of conduction, convection or radiation) to prevent its transfer through the boundary between two systems which are at different temperatures. Heat transfer always occurs from a region of higher temperature to one of lower temperature. Radiant barrier (or reflective) insulation is heat/thermal insulation which reflects radiation heat (radiant heat), preventing transfer from one side to another due to a reflective (or low emittance) surface. As such materials reflect radiant heat with negligible “R-values” they should also be classified as thermal/heat insulation.
Thermal Bridge is an area or component of an object which has higher thermal conductivity than the surrounding materials, creating a path of least resistance for heat transfer. Thermal bridges result in an overall reduction in thermal resistance of the object. The term is frequently discussed in the context of a building's thermal envelope where thermal bridges result in heat transfer into or out of conditioned space. Thermal bridges in buildings may impact the amount of energy required to heat and cool a space, cause condensation (moisture) within the building envelope, and result in thermal discomfort. There are strategies to reduce or prevent thermal bridging, such as limiting the amount of building members that span from unconditioned to conditioned space and applying continuous insulation materials to create thermal breaks.
Thermal Break is an element of low thermal conductivity placed in an assembly to reduce or prevent the flow of thermal energy between conductive materials. The opposite of a thermal barrier is a thermal bridge. In architecture and building construction some examples include the following: A thermal break is also a load-bearing thermal insulation system used in reinforced concrete structures to form a thermal break between cantilever structures and internal floor. Insulated glazing – the air or gas between the panes stops the conductive thermal energy from passing through the glass. Metal window or curtain wall framing – a separator material is used between the inner and outer frames to prevent the temperature transfer through the frame and condensation on the inside frame. Concrete work – a single row of concrete masonry units (CMU block) is commonly set between the inner concrete slab and exterior concrete work to prevent the transfer of heat or cold through the slab. Garage doors – in some doors that have high R-rating insulation, a vinyl thermal break is used along the edges of each segment instead of rolled steel. Metal and wood framed buildings - an insulation material installed on the roof, walls and floor prevents thermal short circuit creating the heat transfer through the framing material and controls when desired (winter/summer)resulting in energy savings. Metal windows and doors (Aluminium, Steel etc.) - separating the frame into two separate interior and exterior pieces joined with a less conductive material reduces temperature transfer. Thermal breaks (made of substantially rigid, low thermal conductive polyamide or polyurethane which is mechanically locked in aluminum window framing can be more than a thousand times less conductive than aluminum and a hundred times less than steel. In addition thermal breaks can have the added benefit of reducing sound transmittance by dampening vibration. With outstanding thermal breaks, aluminium frames are able to be used for passive houses. The geometry and material of thermal breaks are aimed to decrease heat loss because of conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction is decreased by using materials with minimum lambda values and also using profiles with hollow chambers. Convection is decreased by using flags on insulation profiles. And radiation is decreased by using low-e folio (e.g. insulbar LEF) on these flags.
Aerogel is a synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas. The result is a solid with extremely low density and low thermal conductivity. Nicknames include frozen smoke, solid smoke, solid air, solid cloud, blue smoke owing to its translucent nature and the way light scatters in the material. It feels like fragile expanded polystyrene to the touch. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds. By making tube aerogel out of carbon tubes, we can design an analogous elastic and lightweight material that traps heat without degrading noticeably over its lifetime.
Expansion Joint is an assembly designed to safely absorb the temperature-induced expansion and contraction of construction materials, to absorb vibration, to hold parts together, or to allow movement due to ground settlement or earthquakes. They are commonly found between sections of buildings, bridges, sidewalks, railway tracks, piping systems, ships, and other structures. Building faces, concrete slabs, and pipelines expand and contract due to warming and cooling from seasonal variation, or due to other heat sources. Before expansion joint gaps were built into these structures, they would crack under the stress induced.
Heat Recovery Ventilation also known as mechanical ventilation heat recovery (MVHR), is an energy recovery ventilation system using equipment known as a heat recovery ventilator, heat exchanger, air exchanger, or air-to-air heat exchanger which employs a cross flow or counter-flow heat exchanger (countercurrent heat exchange) between the inbound and outbound air flow. By recovering the residual heat in the exhaust gas, the fresh air introduced into the air conditioning system is pre-heated (pre-cooled), and the fresh air enthalpy is increased (reduced) before the fresh air enters the room or the air cooler of the air conditioning unit performs heat and moisture treatment. A typical heat recovery system in buildings consists of a core unit, channels for fresh air and exhaust air, and blower fans. Building exhaust air is used as either a heat source or heat sink depending on the climate conditions, time of year and requirements of the building. Heat recovery systems typically recover about 60–95% of the heat in exhaust air and have significantly improved the energy efficiency of buildings.
Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) are closely related; however, ERVs also transfer the humidity level of the exhaust air to the intake air.
Heat Exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.
Passive Heating and Cooling - Stoves - House Heating
Heat Pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to a destination called a "heat sink". Heat pumps are designed to move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer by absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. A heat pump uses a small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink. While air conditioners and freezers are familiar examples of heat pumps, the term "heat pump" is more general and applies to many HVAC (heating, ventilating, and air conditioning) devices used for space heating or space cooling. When a heat pump is used for heating, it employs the same basic refrigeration-type cycle used by an air conditioner or a refrigerator, but in the opposite direction - releasing heat into the conditioned space rather than the surrounding environment. In this use, heat pumps generally draw heat from the cooler external air or from the ground. In heating mode, heat pumps are three to four times more effective at heating than simple electrical resistance heaters using the same amount of electricity. The typical installation cost of a heat pump is about 20 times greater than that of resistance heaters.
AI-Designed Heat Pumps compressors consume 25% less energy using a machine-learning process called symbolic regression to come up with simple equations for quickly calculating the optimal dimensions of a turbocompressor for a given heat pump. Fans.
Energy Quest USA (youtube) - Earth The Operators Manual
District Heating is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating and water heating.
Coefficient of Performance of a heat pump, refrigerator or air conditioning system is a ratio of useful heating or cooling provided to work required. Higher COPs equate to lower operating costs. The COP usually exceeds 1, especially in heat pumps, because, instead of just converting work to heat (which, if 100% efficient, would be a COP of 1), it pumps additional heat from a heat source to where the heat is required. For complete systems, COP calculations should include energy consumption of all power consuming auxiliaries. COP is highly dependent on operating conditions, especially absolute temperature and relative temperature between sink and system, and is often graphed or averaged against expected conditions. Performance of Absorption refrigerator chillers is typically much lower, as they are not heat pumps relying on compression, but instead rely on chemical reactions driven by heat. Thermal Energy.
Heating Seasonal Performance Factor is a term used in the heating and cooling industry. HSPF is specifically used to measure the efficiency of air source heat pumps. HSPF is defined as the ratio of heat output (measured in BTUs) over the heating season to electricity used (measured in watt-hours). It therefore has units of BTU/watt-hr. The higher the HSPF rating of a unit, the more energy efficient it is. An electrical resistance heater, which is not considered efficient, has an HSPF of 3.41. Depending on the system, an HSPF = 8 can be considered high efficiency and worthy of a US Energy Tax Credit.
Power Usage Effectiveness is a ratio that describes how efficiently a computer data center uses energy; specifically, how much energy is used by the computing equipment (in contrast to cooling and other overhead). PUE is the ratio of total amount of energy used by a computer data center facility to the energy delivered to computing equipment. PUE is the inverse of data center infrastructure efficiency (DCIE).
Insulation
Insulation is a material that reduces or prevents the transmission of heat or sound or electricity. The act of protecting something by surrounding it with material that reduces or prevents the transmission of sound or heat or electricity.
Building Insulation is any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation (e.g. for vibrations caused by industrial applications). Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.
Building Insulation Materials (wiki).
Thermal Insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e. the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials. Heat flow is an inevitable consequence of contact between objects of different temperature. Thermal insulation provides a region of insulation in which thermal conduction is reduced or thermal radiation is reflected rather than absorbed by the lower-temperature body. The insulating capability of a material is measured as the inverse of thermal conductivity (k). Low thermal conductivity is equivalent to high insulating capability (Resistance value). In thermal engineering, other important properties of insulating materials are product density (ρ) and specific heat capacity (c).
Vacuum Insulated Panel is a form of thermal insulation consisting of a gas-tight enclosure surrounding a rigid core, from which the air has been evacuated. It is used in building construction, refrigeration units, and insulated shipping containers to provide better insulation performance than conventional insulation materials.
Building Envelope is the physical separator between the conditioned and unconditioned environment of a building including the resistance to air, water, heat, light, and noise transfer.
Windows (double pane or triple pane?) - Smart Home
Winterization is the process of preparing something for winter.
Weatherization - WAP - Weatherization
R-Value in insulation is a measure of thermal resistance, or ability of heat to transfer from hot to cold, through materials (such as insulation) and assemblies of materials (such as walls and floors). The Higher the R-Value, the Greater the Insulating Effectiveness and the more a material prevents heat transfer. The R-value depends on the type of insulation, its thickness, and its density, it also depends on materials' resistance to heat conduction, as well as the thickness and (for loose or porous material) any heat losses due to convection and radiative heat transfer. However, it does not account for the radiative or convective properties of the material's surface, which may be an important factor for some applications. R varies with temperature, but in construction it is common to treat it as being constant for a given material (or assembly). It is closely related to the thermal transmittance (U-value) of a material or assembly, but is easier to manipulate in some calculations, since it can be simply added for materials and assemblies that are arranged in layers, or scaled proportionately if the thickness of a material changes. R-values expressed in United States customary units are about 5.68 times larger than those expressed in metric (SI) units. R-Value of 50 is considered to be Good and Effective.
Super-Insulating Aerogel for Windows and Mars. A new gel could increase energy efficiency in skyscrapers and help scientists to build habitats on Mars. The gel looks like a flattened plastic contact lens, is so resistant to heat that you could put a strip of it on your hand and a fire on top without feeling a thing. But unlike similar products on the market, the material is mostly see-through. Aerogels are at least 90 percent gas by weight. Their thin films are made up of crisscrossing patterns of solid material that trap air inside billions of tiny pores, similar to the bubbles in bubble wrap. It's that trapping capacity that makes them such good insulators. We're envisioning a retrofitting product that would basically be a peel-and-stick film that a consumer would buy at Home Depot.
How much Energy do Appliances use - Energy Efficient Appliances - Energy
Keep House Cool Tips - Cool Yourself
Water Saving Tools - Thermal Energy
Organic Window Caulking - PCB's in Caulk - Organic Building
Organic Spray Foam Insulation
5 Green Insulation Options
Sustainable Sources
This Old House
Green Alternative Insulation Materials
M-D Building Products 71548 Replaceable Cord Weatherstrip, 90 Feet, Gray (amazon)
W. J. Dennis MJ Replacement Steel Door Bottom Weatherstrip (amazon)
Red Devil 0876 Window & Door Siliconized Acrylic Clear Caulk 10.1 Oz. Cartridge (amazon)
Duck Brand 281504 Indoor 5-Window Shrink Film Kit, 62-by-210-Inch (amazon)
Organic Insulation Materials may not have as high an R-value per inch as Polystyrene and Fiberglass, but when they are used in sufficient quantity, they can provide sufficient insulation. You need to consider the other advantages of organic materials, in that they breathe, they absorb and give off moisture, they are non-toxic, fire proof, insect proof, they take very little energy to process, they can be easily recycled, and they store carbon.
Thermal Efficiency is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, a steam turbine or a steam engine, a boiler, furnace, or a refrigerator for example. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the fraction of the energy added by heat (primary energy) that is converted to net work output (secondary energy). In the case of a refrigeration or heat pump cycle, thermal efficiency is the ratio of net heat output for heating, or removal for cooling, to energy input (the coefficient of performance).
Mold - Air Barriers
Indoor Mold should be avoided. Mold reproduce by means of tiny spores. The spores are like seeds, but invisible to the naked eye, that float through the air. Mold may begin growing indoors when spores land on moist surfaces. There are many types of mold, but all require moisture and a food source for growth. It may be found behind wallpaper or paneling, on the inside of ceiling tiles, the back of drywall, or the underside of carpets or carpet padding. Piping in walls may also be a source of mold, since they may leak (causing moisture and condensation). Mold is detectable by smell and signs of water damage on walls or ceiling and can grow in places invisible to the human eye. It may be found behind wallpaper or paneling, on the inside of ceiling tiles, the back of drywall, or the underside of carpets or carpet padding. Piping in walls may also be a source of mold, since they may leak (causing moisture and condensation). Spores need three things to grow into mold: nutrients - cellulose (the cell wall of green plants) is a common food for indoor spores; moisture - To begin the decaying process caused by mold; time -mold growth begins from 24 hours to 10 days after the provision of growing conditions. Mold colonies can grow inside buildings, and the chief hazard is the inhalation of mycotoxins. After a flood or major leak, mycotoxin levels are higher even after a building has dried out. Food sources for mold in buildings include cellulose-based materials such as wood, cardboard and the paper facing on drywall and organic matter such as soap, fabrics and dust-containing skin cells. If a house has mold, the moisture may originate in the basement or crawl space, a leaking roof or a leak in plumbing pipes. Insufficient ventilation may accelerate moisture buildup. Visible mold colonies may form where ventilation is poorest and on perimeter walls (because they are nearest the dew point). If there are mold problems in a house only during certain times of the year, the house is probably too airtight or too drafty. Mold problems occur in airtight homes more frequently in the warmer months (when humidity is high inside the house, and moisture is trapped), and occur in drafty homes more frequently in the colder months (when warm air escapes from the living area and condenses). If a house is artificially humidified during the winter, this can create conditions favorable to mold. Moving air may prevent mold from growing, since it has the same desiccating effect as low humidity. Mold grow best in warm temperatures, 77 to 86 °F (25 to 30 °C), although growth may occur between 32 and 95 °F (0 and 35 °C). Removing one of the three requirements for mold reduces (or eliminates) new mold growth: moisture; food for the mold spores (for example, dust or dander); and warmth since mold generally does not grow in cold environments. HVAC systems can produce all three requirements for mold growth. The air conditioning system creates a difference in temperature, encouraging condensation. The high rate of dusty air movement through an HVAC system may furnish ample food for mold. Since the air-conditioning system is not always running, warm conditions are the final component for mold growth. Mold is part of the natural environment. Mold play an important part in nature by breaking down dead organic matter such as fallen leaves and dead trees. Space station mold survives high doses of ionizing radiation.
Vapor Barrier is any material used for damp proofing, typically a plastic or foil sheet, that resists diffusion of moisture through wall, ceiling and floor assemblies of buildings to prevent interstitial condensation and of packaging. Technically, many of these materials are only vapor retarders as they have varying degrees of permeability. Moisture or water vapor moves into building cavities in three ways: 1) With air currents, 2) By diffusion through materials, 3) By heat transfer. Of these three, air movement accounts for more than 98% of all water vapor movement in building cavities. A vapor retarder and an air barrier serve to reduce this problem, but are not necessarily interchangeable. Vapor retarders slow the rate of vapor diffusion into the thermal envelope of a structure. Other wetting mechanisms, such as wind-borne rain, capillary wicking of ground moisture, air transport (infiltration), are equally important. Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate is a measure of the passage of water vapor through a substance. Vapor should open and close when needed.
Vapor Retarders in brick, concrete, stucco walls | Everything you need to know (youtube - Belinda Carr)
What are Vapor Barriers, Vapor Retarders & Perm Ratings? (youtube - Belinda Carr)
Climate Zone Building Guide (Inside vapor barrier or Outside vapor barrier?) (Water - Air - Vapor - Thermal)
Air Barrier control air leakage into and out of the building envelope. Air barrier products may take several forms: Mechanically-attached membranes, also known as housewraps, usually a polyethylene-fiber or spun-bonded polyolefin, such as Tyvek is a generally accepted moisture barrier and an air barrier (ASTM E2178). Self-adhered membranes, which are typically also a water-resistant barrier and a vapor barrier. Fluid-applied membranes, such as heavy-bodied paints or coatings including polymeric based and asphaltic based materials. Closed-cell medium density spray-applied polyurethane foam, which typically provides insulation as well. Some open-cell spray-applied polyurethane foam that are of high density. Boardstock, which includes 12 mm plywood or OSB, 25 mm extruded polystyrene, etc. Air barriers are divided into air barrier materials, air barrier accessories, air barrier components, air barrier assemblies and air barrier systems. Air barrier materials – Building materials that are designed and constructed to provide the principal plane of airtightness through an environmental separator, which has an air permeance rate no greater than 0.02 L/(s•m²) at a pressure difference of 75 Pa when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2178. Air barrier materials meet the requirements of the CAN/ULC S741 Air Barrier Material Specification. The air barrier materials are typically the "big" pieces of material used in an air barrier assembly. Air barrier accessories – Products designated to maintain air tightness between air barrier materials, assemblies and components, to fasten them to the structure of the building, or both (e.g., sealants, tapes, backer rods, transition membranes, nails/washers, ties, clips, staples, strapping, primers) and which has an air permeance rate no greater than 0.02 L/(s•m²) at a pressure difference of 75 Pa when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2178. Air barrier components are used to connect and seal air barrier materials and/or air barrier assemblies together. Air barrier components – Pre-manufactured elements such as windows, doors and service elements that are installed in the environmental separator and sealed by air barrier accessories and which have an air leakage rate no greater than 0.20 L/(s•m²) at a pressure difference of 75 Pa when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2357. Air barrier assemblies – Combinations of air barrier materials and air barrier accessories that are designated and designed within the environmental separator to act as a continuous barrier to the movement of air through the environmental separator and which has an air leakage rate no greater than 0.20 L/(s•m²) at a pressure difference of 75 Pa when tested in accordance with ASTM E 2357. Air barrier systems – Combinations of air barrier assemblies and air barrier components, connected by air barrier accessories, that are designed to provide a continuous barrier to the movement of air through an environmental separator, which has an air leakage rate no greater than 2.00 L/(s•m²) at a pressure difference of 75 Pa when tested in accordance with ASTM E 779 or CAN/CGSB 149.10 or CAN/CGSB 149.15. Air barriers and water vapor. Some air barriers may be water vapor permeable, while others perform the function of a vapour barrier. This is because water fits through narrower pores than the other main constituents of air, oxygen(O2) and nitrogen. Air and moisture can be forced into wall and ceiling cavities where water vapor condenses and fosters the growth of mold. Warm air exiting the top of the house can draw in cold air to replace it, wasting heat and energy. Home Ventilation.
Fresh Air System (reduce indoor air pollutants) - Mold - Air Conditioning
Building Airtightness can be defined as the resistance to inward or outward air leakage through unintentional leakage points or areas in the building envelope. This air leakage is driven by differential pressures across the building envelope due to the combined effects of stack, external wind and mechanical ventilation systems. Airtightness is the fundamental building property that impacts infiltration and exfiltration (the uncontrolled inward and outward leakage of outdoor air through cracks, interstices or other unintentional openings of a building, caused by pressure effects of the wind and/or stack effect). An airtight building has several positive impacts when combined with an appropriate ventilation system (whether natural, mechanical, or hybrid): Lower heating bills due to less heat loss, with potentially smaller requirements for heating and cooling equipment capacities. Better performing ventilation system. Reduced chance of mold and rot because moisture is less likely to enter and become trapped in cavities. Fewer drafts and thus increased thermal comfort. Leakage typically occurs at the following locations on the building envelope: Junctions between walls and other walls or floors. Junctions between window frames and walls. Electrical equipment. Access doors and other wall penetrations. Tight houses need mechanical ventilation to ensure a supply of fresh air to keep people healthy; and existing houses should not be tightened without assessing whether the existing combustion appliances have an adequate source of combustion makeup air.
USG-Tremco Securock ExoAir Air Barrier System using gypsum sheathing panel integrated with a pre-applied fluid air-barrier membrane that controls air, water and vapor in a very efficient way.
Sheathing is a protective casing or covering. Joint Sealant.
Membrane is a pliable or flexible sheet like structure acting as a boundary, lining, or partition in an organism. A selective barrier that allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles.
Air Quality - Clean Air
 Indoor Air Quality
refers to the air quality within and around buildings and structures,
especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants.
IAQ can be affected by gases (including carbon monoxide, radon,
volatile
organic compounds), particulates, microbial contaminants (mold, bacteria),
or any mass or energy stressor that can induce adverse
health conditions.
Source control, filtration and the use of ventilation to dilute
contaminants are the primary methods for improving indoor air quality in
most buildings. Residential units can further improve indoor air quality
by routine cleaning of carpets and area rugs. Determination of IAQ
involves the collection of air samples, monitoring human exposure to
pollutants, collection of samples on building surfaces, and computer
modelling of air flow inside buildings. IAQ is part of indoor
environmental quality (IEQ), which includes IAQ as well as other physical
and psychological aspects of life indoors (e.g., lighting, visual quality,
acoustics, and thermal comfort). Indoor
air pollution in developing
nations is a major health hazard. A major source of indoor air pollution
in developing countries is the burning of biomass (e.g. wood, charcoal,
dung, or crop residue) for heating and cooking. The resulting exposure to
high levels of particulate matter resulted in between 1.5 million and 2
million deaths in 2000. The average human spends
40 years of their life indoors.
Indoor Air Quality
refers to the air quality within and around buildings and structures,
especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants.
IAQ can be affected by gases (including carbon monoxide, radon,
volatile
organic compounds), particulates, microbial contaminants (mold, bacteria),
or any mass or energy stressor that can induce adverse
health conditions.
Source control, filtration and the use of ventilation to dilute
contaminants are the primary methods for improving indoor air quality in
most buildings. Residential units can further improve indoor air quality
by routine cleaning of carpets and area rugs. Determination of IAQ
involves the collection of air samples, monitoring human exposure to
pollutants, collection of samples on building surfaces, and computer
modelling of air flow inside buildings. IAQ is part of indoor
environmental quality (IEQ), which includes IAQ as well as other physical
and psychological aspects of life indoors (e.g., lighting, visual quality,
acoustics, and thermal comfort). Indoor
air pollution in developing
nations is a major health hazard. A major source of indoor air pollution
in developing countries is the burning of biomass (e.g. wood, charcoal,
dung, or crop residue) for heating and cooking. The resulting exposure to
high levels of particulate matter resulted in between 1.5 million and 2
million deaths in 2000. The average human spends
40 years of their life indoors.Indoor Environmental Assessment
Indoor Air Quality Services - CO2
Industrial Hygiene - Services
Air Filter is a device composed of fibrous or porous materials which removes solid particulates such as dust, pollen, mold, and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines. Asthma Allergies.
Air Purifier is a device which removes contaminants from the air in a room. These devices are commonly marketed as being beneficial to allergy sufferers and asthmatics, and at reducing or eliminating second-hand tobacco smoke.
HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air. A HEPA filter is a type of mechanical air filter; it works by forcing air through a fine mesh that traps harmful particles such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and tobacco smoke. Selecting and Using an Air Filter. You can find HEPA filters in most air purifiers. To qualify as HEPA by industry standards, an air filter must remove (from the air that passes through) 99.97% of particles that have a size greater-than-or-equal-to 0.3 µm.
Gas Mask - Breathing - Choking or Not Breathing
Air Sanitizer is a sanitizer that acts on airborne microbiological organisms or microorganisms. In the United States, a sanitizer is a disinfectant that is intended to disinfect or sanitize, reducing or mitigating growth or development of microbiological organisms including bacteria, fungi or viruses on inanimate surfaces in the household, institutional, and/or commercial environment and whose labeled directions for use result in the product being discharged to publicly owned treatment works (POTWs).
Air Ionizer is a device that uses high voltage to ionise (electrically charge) air molecules. Negative ions, or anions, are particles with one or more extra electron, conferring a net negative charge to the particle. Cations are positive ions missing one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. Some commercial air purifiers are designed to generate negative ions. Another type of air ioniser is the electrostatic discharge (ESD) ioniser (balanced ion generator) used to neutralise static charge. In 2002, in an obituary in The Independent newspaper, Cecil Alfred 'Coppy' Laws was credited with being the inventor of the domestic air ioniser. Air ionisers have been used to eliminate the occurrence of air-borne bacterial infections and to reduce static electricity buildup in electronics.
Cold Plasma can Kill 99.9% of Airborne Viruses. Dangerous airborne viruses are rendered harmless on-the-fly when exposed to energetic, charged fragments of air molecules. Non-thermal plasma device that has previously been proven to achieve greater than 99% inactivation of an airborne viral surrogate, MS2 phage, a virus that infects E.coli bacteria.
Ventilation in architecture is the intentional introduction of ambient air into a space and is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants; it can also be used for purposes of thermal comfort or dehumidification. The correct introduction of ambient air will help to achieve desired indoor comfort levels although the measure of an ideal comfort level varies from individual to individual. The intentional introduction of outdoor air can be categorized as either mechanical ventilation, or natural ventilation. Mechanical ventilation uses fans to drive the flow of outdoor air into a building. This may be accomplished by pressurization (in the case of positively pressurized buildings), or by depressurization (in the case of exhaust ventilation systems). Many mechanically ventilated buildings use a combination of both, with the ventilation being integrated into the HVAC system. Natural ventilation is the intentional passive flow of outdoor air into a building through planned openings (such as louvers, doors, and windows). Natural ventilation does not require mechanical systems to move outdoor air, it relies entirely on passive physical phenomena, such as diffusion, wind pressure, or the stack effect. Mixed mode ventilation systems use both mechanical and natural processes. The mechanical and natural components may be used in conjunction with each other or separately at different times of day or season of the year. Since the natural component can be affected by unpredictable environmental conditions it may not always provide an appropriate amount of ventilation. In this case, mechanical systems may be used to supplement or to regulate the naturally driven flow. In many instances, ventilation for indoor air quality is simultaneously beneficial for the control of thermal comfort. At these times, it can be useful to increase the rate of ventilation beyond the minimum required for indoor air quality. Two examples include air-side economizer strategies and ventilative pre-cooling. In other instances, ventilation for indoor air quality contributes to the need for - and energy use by - mechanical heating and cooling equipment. In hot and humid climates, dehumidification of ventilation air can be a particularly energy intensive process. Ventilation should be considered for its relationship to "venting" for appliances and combustion equipment such as water heaters, furnaces, boilers, and wood stoves. Most importantly, the design of building ventilation must be careful to avoid the backdraft of combustion products from "naturally vented" appliances into the occupied space. This issue is of greater importance in new buildings with more air tight envelopes. To avoid the hazard, many modern combustion appliances utilize "direct venting" which draws combustion air directly from outdoors, instead of from the indoor environment. Natural ventilation can also be achieved through the use of operable windows, this has largely been removed from most current architecture buildings due to the mechanical system continuously operating. The United States current strategy for ventilating buildings is to rely solely on mechanical ventilation. In Europe designers have experimented with design solutions that will allow for natural ventilation with minimal mechanical interference. These techniques include: building layout, facade construction, and materials used for inside finishes. European designers have also switched back to the use of operable windows to solve indoor air quality issues. "In the United States, the elimination of operable windows is one of the greatest losses in contemporary architecture.
Building Airtightness - Air Barrier - Heat Exchanger
Natural Ventilation is the process of supplying air to and removing air from an indoor space without using mechanical systems. It refers to the flow of external air to an indoor space as a result of pressure differences arising from natural forces. There are two types of natural ventilation occurring in buildings: wind driven ventilation and buoyancy-driven ventilation. Wind driven ventilation arises from the different pressures created by wind around a building or structure, and openings being formed on the perimeter which then permit flow through the building. Buoyancy-driven ventilation occurs as a result of the directional buoyancy force that results from temperature differences between the interior and exterior. Since the internal heat gains which create temperature differences between the interior and exterior are created by natural processes, including the heat from people, and wind effects are variable, naturally ventilated buildings are sometimes called "breathing buildings". Green Building.
Balanced Ventilation System usually has two fans and two duct systems. Fresh air supply and exhaust vents can be installed in every room, but a typical balanced ventilation system is designed to supply fresh air to bedrooms and living rooms where occupants spend the most time.
Negative Room Pressure is an isolation technique used in hospitals and medical centers to prevent cross-contaminations from room to room. It includes a ventilation that generates negative pressure to allow air to flow into the isolation room but not escape from the room, as air will naturally flow from areas with higher pressure to areas with lower pressure, thereby preventing contaminated air from escaping the room. This technique is used to isolate patients with airborne contagious diseases such as tuberculosis, measles, or chickenpox.
Positive Pressure is a pressure within a system that is greater than the environment that surrounds that system. Consequently, if there is any leak from the positively pressured system it will egress into the surrounding environment. Use is also made of positive pressure to ensure there is no ingress of the environment into a supposed closed system. A typical example of the use of positive pressure is the location of a habitat in an area where there may exist flammable gases such as found on an oil platform or laboratory cleanroom. This kind of positive pressure is also used on operating theaters and in vitro fertilisation (IVF) labs. Hospitals may have positive pressure rooms for patients with compromised immune systems. Air will flow out of the room instead of in, so that any airborne microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) that may infect the patient are kept away. This process is important in human and chick development. Positive pressure, created by the closure of anterior and posterior neuropores of the neural tube during neurulation, is a requirement of brain development. Amphibians use this process to respire, whereby they use positive pressure to inflate their lungs.
Register is a grille with moving parts, capable of being opened and closed and the air flow directed, which is part of a building's heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. The placement and size of registers is critical to HVAC efficiency. Register dampers are also important, and can serve a safety function.
Window Screen is designed to cover the opening of a window. It is usually a mesh made of plastic wire, or other pieces of plastic and stretched in a frame of wood or metal. It serves to keep leaves, debris, spiders, insects, birds, and other animals from entering a building or a screened structure such as a porch, without blocking fresh air-flow.
Infiltration is the unintentional or accidental introduction of outside air into a building, typically through cracks in the building envelope and through use of doors for passage. Infiltration is sometimes called air leakage. The leakage of room air out of a building, intentionally or not, is called exfiltration. Infiltration is caused by wind, negative pressurization of the building, and by air buoyancy forces known commonly as the stack effect, which is the movement of air into and out of buildings, chimneys, flue-gas stacks, or other containers, resulting from air buoyancy. Buoyancy occurs due to a difference in indoor-to-outdoor air density resulting from temperature and moisture differences. The result is either a positive or negative buoyancy force. The greater the thermal difference and the height of the structure, the greater the buoyancy force, and thus the stack effect. The stack effect helps drive natural ventilation, air infiltration, and fires (e.g. the Kaprun tunnel fire and King's Cross underground station fire).
Fan is a powered machine used to create flow within a fluid, typically a gas such as air. A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades which act on the air. The rotating assembly of blades and hub is known as an impeller, a rotor, or a runner. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing or case. This may direct the airflow or increase safety by preventing objects from contacting the fan blades. Most fans are powered by electric motors, but other sources of power may be used, including hydraulic motors, handcranks, internal combustion engines, and solar power. A Bladeless Fan is not bladeless. Its vanes are hidden in its base and directs the collected airflow through a hollow tube or toroid, blowing a thin high-velocity smooth airflow from holes or a continuous slot across the surface of the tube or toroid. A bladeless fan blows air from a ring with no external blades.
Dedicated Outdoor Air System is a type of heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) system that consists of two parallel systems: a dedicated system for delivering outdoor air ventilation that handles both the latent and sensible loads of conditioning the ventilation air, and a parallel system to handle the (mostly sensible heat) loads generated by indoor/process sources and those that pass through the building enclosure.
Occupational Hygiene is the anticipation, recognition, evaluation, control and prevention of hazards from work that may result in injury, illness, or affect the well being of workers. These hazards or stressors are typically divided into the categories biological, chemical, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial. The risk of a health effect from a given stressor is a function of the hazard multiplied by the exposure to the individual or group. For chemicals, the hazard can be understood by the dose response profile most often based on toxicological studies or models. Occupational hygienists work closely with toxicologists for understanding chemical hazards, physicists for physical hazards, and physicians and microbiologists for biological hazards. Tropical medicine Infection) Environmental and occupational hygienists are considered experts in exposure science and exposure risk management. Depending on an individual's type of job, a hygienist will apply their exposure science expertise for the protection of workers, consumers and/or communities.
Sick Building Syndrome is used to describe a situation in which the occupants of a building experience acute health- or comfort-related effects that seem to be linked directly to the time spent in the building. No specific illness or cause can be identified.
Breathing - Air - Mold - Air Quality Reports (pollution)
How architects can stop COVID-19 from spreading indoors. Introduce more outside air, increase air exchange, maintain relative humidity of 40% to 60%, open windows to provide natural ventilation and flush out indoor spaces, increase access to daylight, and implement targeted disinfection techniques, such as UV-C light in healthcare settings. Containment.
Pollution Absorbing Buildings (green building)
Sustainable Building Design Software
Building Design Guide - Green Building - Applications
Motor Vehicle Emissions usually constitute the most Significant Source of Ultrafine Particles (diameter <0.1 microm) in an urban environment, particle number concentration and size distribution in the size range from 6 to 220 nm were measured by a condensation particle counter (CPC) and a scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS). Each spherical aerosol particle has a density of 2 grams/cm3. If the soot particle has a diameter of 20 nanometers, how much mass is in a single soot particle.
Condensation Particle Counter is a particle counter that detects and counts aerosol particles by first enlarging them by using the particles as nucleation centers to create droplets in a supersaturated gas.
Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer is an analytical instrument that measures the size and number concentration of aerosol particles with diameters from 2.5 nm to 1000 nm. They employ a continuous, fast-scanning technique to provide high-resolution measurements.
Aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets, in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog, dust, forest exudates and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols are haze, particulate air pollutants and smoke.
Bioaerosol are a subcategory of particles released from terrestrial and marine ecosystems into the atmosphere. They consist of both living and non-living components including organisms, dispersal methods of organisms, and excretions.
Particulates are microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the atmosphere of Earth. The term aerosol commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health. Particle pollution includes: PM10 : inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometers and smaller; and PM2.5 : fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller. How small is 2.5 micrometers? Think about a single hair from your head. The average human hair is about 70 micrometers in diameter – making it 30 times larger than the largest fine particle.
Particulate Matter contains microscopic solids or liquid droplets that are so small that they can be inhaled and cause serious health problems. Particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter pose the greatest problems, because they can get deep into your lungs, and some may even get into your bloodstream.
Road Dust is made up of components such as exhaust emissions from vehicles, tire tread particles, debris from the road itself, and runoff from nearby parks and yards. Contaminants in road dust react with singlet oxygen, that means that sunlight could change the lifetime and potency of those contaminants in ways we don't yet understand. One group of chemicals that could react with singlet oxygen are a set of toxic components of combustion emissions, known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Toxins (out-gassing)
Chemical Pollutants and Environmental Contaminants found in the home and diet have the same adverse effects on Male Fertility in both humans and in domestic dogs.
Air Quality Testing
Outdoor Air Quality Reports is your one-stop source for air quality data. A new interactive map even lets you zoom out to get the big picture or drill down to see data for a single air quality monitor. Current and forecast air quality maps and data for more than 500 cities across the U.S.. Current and historical data for U.S. Embassies and Consulates around the world. Current fire conditions including fire locations, smoke plumes, and air quality data from permanent and temporary air quality monitors. Air quality data for Canada and Mexico. Enviroflash emails, apps, widgets, and an API. Health and air quality information for the public, healthcare professionals, teachers and students, weather reporting. American Air Testing - Air Quality Index - Air Quality Monitoring - Amateur Guide - Air Quality Report.
The EPA maintains a repository of air quality data through the Air Quality System stores data from over 10,000 monitors in the United States. Monitors for all criteria pollutants (CO, Pb, NO2, Ozone, PM10, PM2.5, and SO2). PM2.5 Chemical Speciation. Network monitors. IMPROVE (Interagency Monitoring of PROtected Visual Environments) monitors. NATTS (National Air Toxics Trends Stations). NCORE (Multipollutant Monitoring Network). Nonattainment areas for all criteria pollutants. Tribal areas. Federal Class I areas (national parks and wilderness areas). While use of these sensors was expensive in the past, the 2010s saw a recent trend towards the development of cheaper portable air-quality sensors that can be worn by individuals to monitor local air quality levels. These sensors, can then, in turn, help measure the spatiotemporal coverage and variety of chemical species, and empower individuals and communities to better understand their exposure environments and risks from air pollution. A research group led by William Griswold at UCSD handed out portable air pollution sensors to 16 commuters, and found "urban valleys" where buildings trapped pollution. The group also found that passengers in buses have higher exposures compared to those in automobiles. Pollen Count Forecast.
Air Pollution Sensor are devices that monitor the presence of air pollution in the surrounding area. They can be used for both indoor and outdoor environments. These sensors can be built at home, or bought from certain manufactures. Although there are various types of air pollution sensors, and some are specialized in certain aspects, the majority focuses on five components: ozone, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrous oxide. The sensors were very expensive in the past, but with technological advancements these sensors are becoming more affordable and more widespread throughout the population. These sensors can help serve many purposes and help bring attention to environmental issues beyond the scope of the human eye. Water Quality.
Air Quality Index is used by government agencies to communicate to the public how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. Public health risks increase as the AQI rises. Different countries have their own air quality indices, corresponding to different national air quality standards. Some of these are the Air Quality Health Index (Canada), the Air Pollution Index (Malaysia), and the Pollutant Standards Index (Singapore).
Air Pollution Test Kit (amazon)
Cube Sensors - Sensors
Speck Air Quality Monitor
Flow, by Plume Labs - The First Smart Air Quality Tracker
Air Quality Monitoring Tools - Dust Measuring Device
Comparison of five methods for measuring particulate matter concentrations in cold winter climate
Air Labs Clean Air Bench Filters Pollution in Public Spaces.
Cleanout Guide for Safe Disposal of Household Chemicals
Home Air Check - Healthy Products - Environmental Hazards
Tzoa wearable enviro-tracker
Atmotube: The Portable Air Pollution Monitor
Kanomax 2211 Indoor Air Quality Monitor
Carbon Monoxide Detector is a device that detects the presence of the carbon monoxide (CO) gas in order to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. CO is a colorless, tasteless and odorless compound produced by incomplete combustion of carbon-containing materials. It is often referred to as the "silent killer" because it is virtually undetectable by humans without using detection technology. Sixty percent of Americans can not identify any potential signs of a CO leak in the home.
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the respiratory gases. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care.
Air Purifying Technology
Airdog X5 Air cleaner for your Home using reusable filter that's easy-to-wash in a dishwasher or by hand.
Evapolar Personal Air Conditioner cools, humidifies and cleans the air creating your local perfect microclimate.
Emerald Air: The Smartest Sensor and Air Purifier Get rid of viruses, allergens and airborne threats. Filters up odors, smoke, PM2.5, VOCs and allergens.
iBaby Air Smart Air Quality Monitor & Ion Purifier Smart Wi-Fi air monitor that detects VOCs & purifies the air for a healthier life.
Clairy Natural Air Purifier that combines the power of nature and technology to eliminate indoor pollution and analyze it.
Wynd - Air Purifier
Coway AP-1512HH Mighty Air Purifier with True HEPA and Eco Mode
Molekule air purifier breaks down harmful microscopic pollutants like allergens, mold, bacteria, viruses and even airborne chemicals.
Dyson Air Treatment Purifiers
The World's Best HEPA Air Purifier Systems - IQAir
Build a Do-It-Yourself Air Purifier for about $25 (youtube) - Using a HEPA Filter for a furnace and a Box fan the same size as the filter.
Natural Air Purifiers - Mother Natures Plants
 Houseplant is a
Plant that is grown indoors in places such as
residences and offices. Houseplants are commonly grown for decorative
purposes, but studies have also shown them to have positive psychological
effects. Houseplants also help with indoor air purification. Plants used
in this fashion are most commonly, though not always, tropical or
semi-tropical epiphytes, succulents or cacti. Houseplants need the correct
moisture, light levels, soil mixture, temperature, and humidity. As well,
houseplants need the proper fertilizer and correct-sized pots.
Indoor Farming.
Houseplant is a
Plant that is grown indoors in places such as
residences and offices. Houseplants are commonly grown for decorative
purposes, but studies have also shown them to have positive psychological
effects. Houseplants also help with indoor air purification. Plants used
in this fashion are most commonly, though not always, tropical or
semi-tropical epiphytes, succulents or cacti. Houseplants need the correct
moisture, light levels, soil mixture, temperature, and humidity. As well,
houseplants need the proper fertilizer and correct-sized pots.
Indoor Farming.Using the right plants can reduce indoor pollution and save energy. Home have potentially toxic gases, including carbon monoxide, ozone, and volatile organic compounds, from sources such as furniture, paints, carpets, and office equipment accumulate. Plants absorb toxins and can improve indoor air quality. Integrating plants with smart sensors networks and other computerized technologies could make those air cleaning more cost-effective and sustainable.
NASA Clean Air Study results suggest that certain common indoor plants may provide a natural way of removing toxic agents such as benzene, formaldehyde and trichloroethylene from the air, helping neutralize the effects of sick building syndrome. The first list of air-filtering plants was compiled by NASA as part of a clean air study published in 1989, which researched ways to clean air in space stations. As well as absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, as all plants do, these plants also eliminate significant amounts of benzene, formaldehyde and trichloroethylene. The second and third lists are from B. C. Wolverton's book and paper and focus on removal of specific chemicals. NASA researchers suggest efficient air cleaning is accomplished with at least one plant per 100 square feet of home or office space. While the original study only considered plants grown hydroponically (ie without soil), more recent research has shown that micro-organisms in the potting mix (soil) of a potted plant remove benzene from the air, and that some plant species also contribute to removing benzene.
House Plants that improve indoor Air Quality
Plants that Purify Indoor Air
How To Be An Adult: Choosing The Perfect Plant For Your Home (youtube)
Houseplants could one day monitor home health as a Biosensor and Phytosensor.
 5 Indoor Plants that are easy to take care of
5 Indoor Plants that are easy to take care of
ZZ plant Zamioculcas
Ripple Peperomia Peperomia caperata
Pothos Epipremnum aureum
Snake plant Sansevieria trifasciata
Bird's Nest Fern
How To Repot A Houseplant (youtube) - 1 to 2 inches larger pot in diameter and deeper. Add fresh potting soil to the bottom of the new pot, packing it well around the drainage hole that has a drain cover. Then transfer the plant to the new pot. Adjust the amount of soil mix so that the plant is at the same level as it was in the old pot. Loosen the roots on the plant. Position the plant, add soil mix to fill and pack tightly around the plant roots, and then water plant thoroughly. Plant Diseases.
Landscaping Sustainably - Sustainable Landscape Architecture
Instructions for taking care of plants are similar in ways to the instructions needed to take care of yourself in Life. Plants need clean water, and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little. Plants need clean food, and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little. Plants need light, and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little. Plants need room to grow, and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little. Plants need protection from harsh environments, and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little. Plants need love and so does life. Just enough, but not too much or too little.
Transitions - Adapting
We need to retrofit old homes and cities so that we can help maximize this transition and make it easy for everyone during these improvements. And of course we have to come up with a way to educate people so that these improvements are clearly understood by everyone and why we need to make these improvements as quick as possible. Renovate.
Germany is supporting steps to increase energy efficiency in buildings, with subsidies and incentives worth 6 billion euros ($7.2 billion) this year in 2021, the economy minister said on Monday. Modernize existing buildings with better insulation and more efficient heating.
Future Cities - Electric Cars - Advancing - Progressing - Adapting
We must also change the laws so that building energy wasting houses, buildings, cars and products is illegal. Buildings must be able to have multiple uses too incase the original use is no longer necessary. People should also know how to retrofit or modify buildings for other uses.
Major Cities only take up 2% of the usable land on earth. But Major Cities are home to 50% of the worlds population, consume 75% of the worlds energy and emit 80% of CO2 Carbon Dioxide. So fixing cities are a good place to start.
Energy Saving Building Designs - Green Products - Green Building - Basic Knowledge 101
Transition is the act of passing from one state or place to the next. Enjoy your soon to be new and invigorating planet. What will we think of next?
Retrofit gas saving devices in all cars, trucks, lawn mowers and machines.
Make boats run on biodiesel fuel. Add a natural and proven safe weed killer to the fuel if the lake has a weed problem.
Next step is to show people how to have low maintenance homes and possibly a Maintenance-Free House.
Environmental Tools - Earth Easy
We must improve education in every way possible, because a poor education is the root of all problems.
Electromagnetic Radiation
 Trifield Meter
can detect and measure
Electromagnetic Radiation Field and Radio/Microwaves from
Appliances and Power Lines.
Trifield Gauss Meters
and Magnetometers.
Trifield Meter
can detect and measure
Electromagnetic Radiation Field and Radio/Microwaves from
Appliances and Power Lines.
Trifield Gauss Meters
and Magnetometers.EMF - Electro Magnetic Field - Radiation
Magnetometer is an instrument that measures magnetism—either magnetization of magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or the strength and, in some cases, direction of the magnetic field at a point in space. Compass - Geophysical Surveys.
Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity is a claimed sensitivity to electromagnetic fields, resulting in negative symptoms.
Biofield is the field of energy and information that surrounds and interpenetrates the human body. It is composed of both measurable electromagnetic energy and hypothetical subtle energy, or chi. Bio-Battery - Human Energy - Life Force.
Biomodulator is a portable neurostimulation device that contains unique frequencies to produce microcurrent, electrical impulses that are transmitted by electrodes in the device through the skin to interface with the body’s internal peripheral nervous system. Bioelectricity.
Magnetoception (born to use magnetism to navigate) - Bio-Electro-Magnetics.
Cellphone Dangers - Microwave News
High Exposure to Radiofrequency Radiation linked to tumor malignant schwannomas activity in male rats
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
Aura - Human Energy - Brain
Solar plexus, torsion field, manifestation, make the subconscious conscious.
Optical magnetic field sensor can detect signals from the nervous system.
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart is the normal electrical conduction in the Heart that allows the impulse that is generated by the sinoatrial node (SA node) of the heart to be propagated to, and stimulate, the cardiac muscle (myocardium). The myocardium contracts after stimulation. It is the ordered, rhythmic stimulation of the myocardium during the cardiac cycle that allows efficient contraction of the heart, thereby allowing blood to be pumped throughout the body.
Faraday Cage (Electromagnetic Radiation Protection)
Electromagnetic Interference is when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: automobile ignition systems, cell phones, thunderstorms, the Sun, and the Northern Lights. EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect cell phones, FM radios, and televisions. EMI can be used intentionally for radio jamming, as in electronic warfare.
Electromagnetic Pulse
The Hum a phenomena involving widespread reports of a persistent and invasive low-frequency humming, rumbling, or droning noise not audible to all people.
Extremely Low Frequency is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. (ELF)
Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs
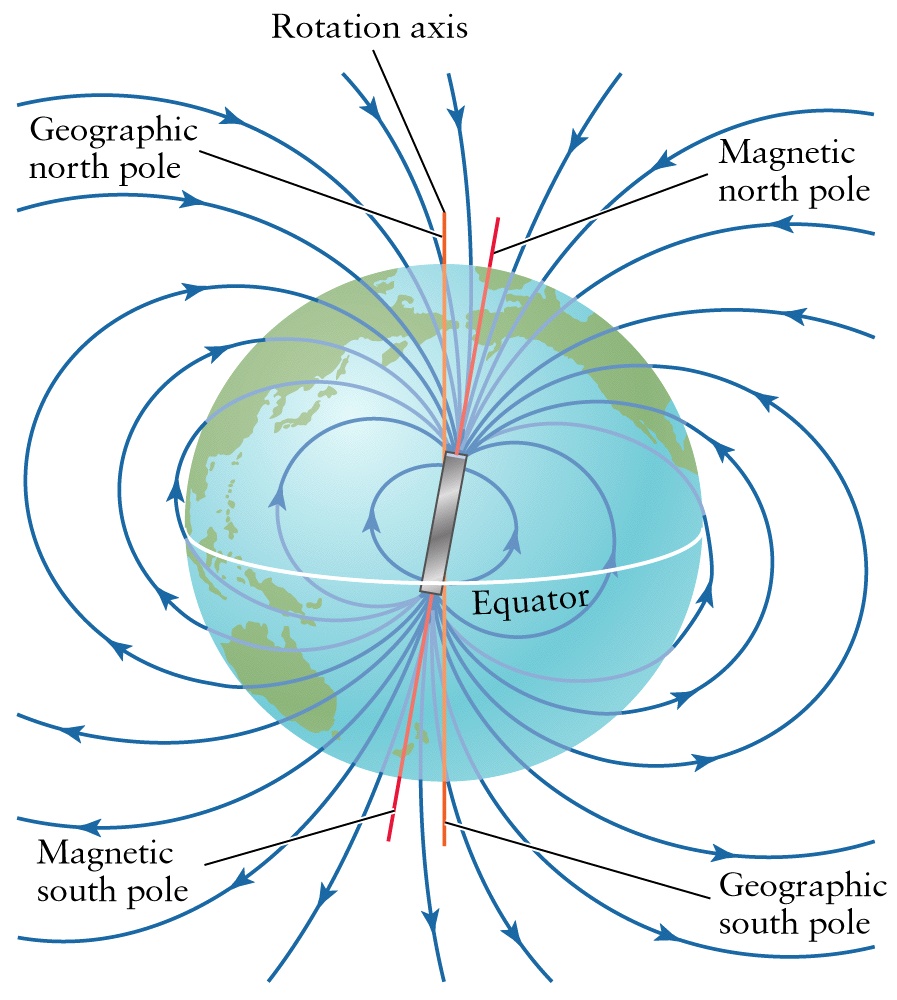 Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electrical Generator
Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Field
Electronics Knowledge
Torus
Cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e. an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive.
Bioacoustics is a cross-disciplinary science that combines biology and acoustics. Usually it refers to the investigation of sound production, dispersion and reception in animals (including humans). This involves neurophysiological and anatomical basis of sound production and detection, and relation of acoustic signals to the medium they disperse through. The findings provide clues about the evolution of acoustic mechanisms, and from that, the evolution of animals that employ them.
Biophoton (luminescence) - Organisms.
Morphic-Resonance is a process whereby self-organising systems inherit a memory from previous similar systems. In its most general formulation, morphic resonance means that the so-called laws of nature are more like habits.
Light - Melatonin
Ideophone are words that evoke an idea in sound, often a vivid impression of certain sensations or sensory perceptions, e.g. sound, movement, color, shape, or action. Ideophones are found in many of the world's languages, though they are claimed to be relatively uncommon in Western languages.
Cellphone Technology
Wireless Communication - Radio Waves - Smartphones (uses)
All Cellphones have a warning inside that tells the minimum separation distance a cellphone should be held from the head and body. The Federal Communication Commission recommends keeping your phone 5 to 25 mm away from head and body. Use speaker phone or earplugs. millimeters. Mobile Phone Radiation and Health (wiki)
Cellphones and Cancer Risk - Cordless Phones Too. Directed-Energy Weapon.
Glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the brain or spine. It is called a glioma because it arises from glial cells. The most common site of gliomas is the brain. Gliomas make up about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of all malignant brain tumors. Acoustic Neuroma.
Cancer - 13 ways to Reduce Cell Phone Radiation
All wireless devices from smartphones to wireless laptops to baby monitors come with FCC warnings that they are NOT safe to use if held directly on the body because the radio frequency emissions can exceed government limits. Very importantly, if you place a cell phone at body contact, you can exceed radiation limits up to 9 times US FCC limits according to reports of the French government after testing hundreds of cell phones. Dr. Hugh Taylor Chief of OB GYN at Yale has shown that pregnant mice exposed to this radiation have offspring with increased hyperactivity, decreased memory and altered brain development. Cell Phone Microwave Radiation To Cancer, Low Birth Weight and Sperm Damage.
Electromagnetic Radiation Safety- 5G Wireless Technology- Is 5G Harmful to Our Health-It's the non-thermal effects and not the thermal. 2.4 GHZ- 5 GHZ - 60 GHZ.
5GHz provides faster data rates at a shorter distance. 2.4GHz offers coverage for farther distances, but may perform at slower speeds.
Hertz is the unit of frequency; one hertz has a periodic interval of one second. Terahertz.
Beamforming is a technique that focuses a wireless signal towards a specific receiving device, rather than having the signal spread in all directions from a broadcast antenna, as it normally would. The resulting more direct connection is faster and more reliable than it would be without beamforming.
Extremely High Frequency the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It lies between the super high frequency band, and the far infrared band, the lower part of which is also referred to as the terahertz gap. Radio waves in this band have wavelengths from ten to one millimetre, so it is also called the millimetre band and radiation in this band is called millimetre waves, sometimes abbreviated MMW or mmW. Millimeter waves propagate solely by line-of-sight paths. They are not reflected by the ionosphere nor do they travel along the Earth as ground waves as lower frequency radio waves do. At typical power densities they are blocked by building walls and suffer significant attenuation passing through foliage. Absorption by atmospheric gases is a significant factor throughout the band and increases with frequency. However, it is maximum at a few specific absorption lines, mainly those of oxygen at 60 GHz and water vapor at 24 GHz and 184 GHz. There are tentative plans to use millimeter waves in future 5G Mobile Phones. With Raytheon the U.S. Air Force has developed a nonlethal weapon system called Active Denial System (ADS) which emits a beam of radiation with a wavelength of 3 mm. The weapon is reportedly not dangerous and causes no physical harm, but is extremely painful and causes the target to feel an intense burning pain, as if their skin is going to catch fire. The ranged weapon damages its target with highly focused energy, including laser, microwaves and particle beams. Potential applications of this technology include weapons that target personnel, missiles, vehicles, and optical devices.
Millimeter Wave Scanner is a whole-body imaging device used for detecting objects concealed underneath a person’s clothing using a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Roughly 21 Million Adult Americans Don't Own a Cellphone.
Wi-Fi or Wireless Fidelity, is technology for radio wireless local area networking of devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. Wi‑Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term Wi-Fi Certified to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. Wi-Fi most commonly uses the 2.4 gigahertz (12 cm) UHF and 5.8 gigahertz (5 cm) SHF ISM radio bands, these bands are subdivided into multiple channels.
Wi-Fi is an important threat to human health. Established Wi-Fi effects, include apoptosis, oxidat. testis/sperm dysfunct; Neuropsych; DNA impact; hormone change; Ca2+ rise. Wi-Fi is thought to act via voltage-gated calcium channel activation. Claims of no Wi-Fi effects was found is deeply flawed.
Mobile Phone Radiation and Health Mobile phones use electromagnetic radiation in the microwave range (450–3800 MHz). If you carry or use your phone in a pants or shirt pocket or tucked into a bra when the phone is ON and connected to a wireless network, you may exceed the federal guidelines for exposure to RF radiation. Use hands-free to decrease the radiation to the head. Keep the mobile phone away from the body. Do not use telephone in a car without an external antenna.
Wireless Warfare Exposed - Declassified Military Doc Proves Smart Phones Are Killing Mankind (youtube)
Cellular Phone Towers and Cancer
Task Force
Is wi-fi a mini cell phone tower?
Electro-Stress
Cell-Phone Towers, the invisible Danger
Resonance Beings of Frequency (youtube)
History of Radar (wiki)
Hollow Air Tube Anti-Radiation Headset Stereo Model EMF Protector (amazon)
International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP)
FEB
How to turn on or turn off Bluetooth and WIFI in Windows (youtube)
Ionization of Atoms and Molecules
 Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths
ranging from one meter to one millimeter; with frequencies between 300 MHz
(100 cm) and 300 GHz (0.1 cm).
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths
ranging from one meter to one millimeter; with frequencies between 300 MHz
(100 cm) and 300 GHz (0.1 cm).Terahertz wave activates filamentation of actin. Researchers have discovered that Terahertz (THz) wave irradiation activates the filamentation of actin protein. The discovery offers a new possibility for the manipulation of cellular functions.
Terahertz Radiation can Disrupt Proteins in Living Cells. This finding implies that terahertz radiation, which was long considered impractical to use, may have applications in manipulating cell functions for the treatment of cancer, for example, but also that there may be safety issues to consider. Terahertz radiation is a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and infrared light, which is often known as the "terahertz gap" because of the lack so far of technology to manipulate it efficiently. Because terahertz radiation is stopped by liquids and is non-ionizing -- meaning that it does not damage DNA in the way that x-rays do -- work is ongoing to put it to use in areas such as airport baggage inspections. It has generally been considered to be safe for use in tissues, though some recent studies have found that it may have some direct effect on DNA, though it has little ability to actually penetrate into tissues, meaning that this effect would only be on surface skin cells.
There are No Publicly Available Maps for Cell Phone Towers in NYC. FCC and the FAA publish information about antenna registrations, and the NYC Department of buildings maintains a current record of building permits associated with mobile phone antennas.
Environmental Health Trust carries out cutting edge research to understand and reduce environmental health risks.
Effect of a Nighttime Magnetic Field Exposure on Sleep Patterns in Young Women. Since poor sleep quality is associated with multiple health problems, it is important to understand factors that may affect sleep patterns. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of a continuous, 60-Hz, nighttime magnetic field exposure on sleep outcomes in young women sleeping at home. The study was a randomized crossover trial, comparing intervention (0.5–1.0 µT above ambient levels) with ambient magnetic field levels, during two 5-night measurement periods. Subjects lived in the Seattle, Washington, area and were 20–40 years of age, had regular menstrual cycles, were not taking oral contraceptives, and had not breastfed or been pregnant during the previous year. The study was conducted between March and September of 2001. Sleep outcomes were measured via actigraphy. The range of magnetic field exposure was 0.001–0.50 µT during the ambient period and 0.41–1.21 µT during the intervention period. Sleep outcomes were not significantly different between the intervention and the ambient measurement periods. The intervention magnetic field had no effect on sleep patterns, suggesting that this exposure may not be an important factor in predicting sleep of young women who sleep at home.
The effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields on melatonin and cortisol, two marker rhythms of the circadian system. In the past 30 years the concern that daily exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic fields (ELF-EMF) (1 to 300 Hz) might be harmful to human health (cancer, neurobehavioral disturbances, etc) has been the object of debate, and has become a public health concern. This has resulted in the classification of ELF-EMF into category 2B, ie, agents that are “possibly carcinogenic to humans” by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Since melatonin, a neurohormone secreted by the pineal gland, has been shown to possess oncostatic properties, a “melatonin hypothesis” has been raised, stating that exposure to EMF might decrease melatonin production and therefore might promote the development of breast cancer in humans. Data from the literature reviewed here are contradictory. In addition, we have demonstrated a lack of effect of ELF-EMF on melatonin secretion in humans exposed to EMF (up to 20 years' exposure) which rebuts the melatonin hypothesis. Currently, the debate concerns the effects of ELF-EMF on the risk of childhood leukemia in children chronically exposed to more than 0.4 μT. Further research is thus needed to obtain more definite answers regarding the potential deleterious effects of ELF-EMF.
Magnetic Flux is a measurement of the total magnetic field which passes through a given area. It is a useful tool for helping describe the effects of the magnetic force on something occupying a given area. The measurement of magnetic flux is tied to the particular area chosen.
Electric fields can affect a body in three different ways: weak currents can be induced in the body, electric charges can build up on the surface of your skin and hair, and the body's voltage can increase. ... As a result, the field produces weak electric currents in the body.
Radio Waves - Smartphones (uses) - Electricity - Wireless Communication
Ground Wave Propagation is a method of radio wave propagation that uses the area between the surface of the earth and the ionosphere for transmission. The ground wave can propagate a considerable distance over the earth's surface particularly in the low frequency and medium frequency portion of the radio spectrum. Ground wave radio propagation is used to provide relatively local radio communications coverage.
Skywave refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.
An experiment by a handful of high school students in Denmark has sparked some serious international interest in the scientific community. They placed six trays of garden cress seeds next to Wi-Fi routers that emitted roughly the same microwave radiation as a mobile phone. Then they placed six more trays of seeds in a separate room without routers. The girls controlled both environments for room temperature, sunlight and water. After 12 days, they found the garden cress seeds in the routerless room had exploded into bushy greenery, while the seeds next to the Wi-Fi routers were brown, shriveled, and even mutated. Did the test twice with the same results. They were Painstakingly careful in keeping the conditions for both groups similar. The cress seeds in both groups were kept sufficiently moist during the whole experiment, and the temperature were controlled thermostatically.
Radio Frequency RF Radiation from Cordless Phones (youtube)
EMF Safety Network
WI-FRIED? (youtube)
Ants Circling Phone - Mysterious video of ants circling an iPhone -Ameisen umkreisen 7 (youtube)
Chi-O Phi: A Revolution of Active Jewelry Design protect yourself from unsettling EMF with this revolution of Active Jewelry Active Scalar Frequencies, Integrated Hologram Chip Technology, Radionic Imprinting, Bio-Friendly Frequencies.
Microwave Radiometer is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at sub-millimetre-to-centimetre wavelengths (at frequencies of 1–1000 GHz) known as microwaves. Microwave radiometers are very sensitive receivers designed to measure thermal electromagnetic radiation emitted by atmospheric gases. They are usually equipped with multiple receiving channels in order to derive the characteristic emission spectrum of the atmosphere or extraterrestrial objects. Microwave radiometers are utilized in a variety of environmental and engineering applications, including weather forecasting, climate monitoring, radio astronomy and radio propagation studies.
Hf35c Rf Analyze (800mhz - 2.5 Ghz) - Perfect for Smart Meters Detection
Acoustimeter RF Meter Model AM-10 Radio Frequency Microwave Detection Meter EMF Protection (amazon)
Cryptochrome are a class of flavoproteins that are sensitive to blue light. They are found in plants and animals. Cryptochromes are involved in the circadian rhythms of plants and animals, and in the sensing of magnetic fields in a number of species. The name cryptochrome was proposed as a portmanteau combining the cryptic nature of the photoreceptor, and the cryptogamic organisms on which many blue-light studies were carried out.
Alpha - Theta Waves in the Body
Specific Absorption Rate is a measure of the rate at which energy is absorbed by the human body when exposed to a radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic field.
Green Bank, West Virginia is a 13,000-square mile Radio Quiet Zone which is an area where radio transmissions are restricted in order to protect a Radio Telescope or a communications station from radio frequency interference. Equipment that can cause interference includes mobile phones, television transmitters, and CB radios, as well as other electrical equipment.
National Radio Quiet Zone in which radio transmissions are heavily restricted by law to facilitate scientific research. The National Radio Quiet Zone. Silence Benefits.
Millions of Humans are being Bombarded with Radio Waves and Microwaves continually everyday, and these waves all contain information. And if you had a radio receiver or a cellphone you can receive these messages being transmitted. But maybe humans don't need technology to receive the signals that are being transmitted by us and to us everyday, after all, human brains receive messages from several senses already. And I'm sure that the brain is capable of tuning in, it just hasn't learned how, just yet. Technology is just a stepping stone to discovering our own abilities.
New Technology Uses Wi-Fi Signals To See Through Walls. The device works by transmitting wireless signals that traverse the wall and reflect off a person’s body back to the device. (The emitted radiation is approximately 1/10,000 the amount given off by a standard cellphone.) The device captures these reflections and analyzes them in order to see the person’s silhouette.
Multiplexing Data carried on Terahertz Waves. Multiplexing is the ability to send multiple signals through a single channel, An international research team has demonstrated for the first time a method for multiplexing data carried on terahertz waves, high-frequency radiation that may enable the next generation of ultra-high bandwidth wireless networks. In The Journal Nature Communications, the researchers report the transmission of two real-time video signals through a terahertz multiplexer at an aggregate data rate of 50 gigabits per second, approximately 100 times the optimal data rate of today's fastest cellular network. Signals in terahertz communications networks will propagate as directional beams, not omnidirectional broadcasts like in existing wireless systems. This directional relationship between propagation angle and frequency is the key to enabling mux/demux in terahertz systems. A user at a particular location (and therefore at a particular angle from the multiplexing system) will communicate on a particular frequency. Researchers encoded two high-definition television broadcasts onto terahertz waves of two different frequencies: 264.7 GHz and 322.5 GHz. They then beamed both frequencies together into the multiplexer system, with a television receiver set to detect the signals as they emerged from the device. When the researchers aligned their receiver to the angle from which 264.7 GHz waves were emitted, they saw the first channel. When they aligned with 322.5 GHz, they saw the second. Further experiments showed that transmissions were error-free up to 10 gigabits per second, which is much faster than today's standard Wi-Fi speeds. Error rates increased somewhat when the speed was boosted to 50 gigabits per second (25 gigabits per channel), but were still well within the range that can be fixed using forward error correction, which is commonly used in today's communications networks. When a terahertz wave is modulated to encode data—meaning turned on and off to make zeros and ones—the main wave is accompanied by sideband frequencies that also must be detected by a receiver in order to transmit all the data. The research showed that the angle of the detector with respect to the sidebands is important to keeping the error rate down.
Terahertz Radiation THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of frequencies from 0.3 to 3 terahertz (THz; 1 THz = 1012 Hz). Wavelengths of radiation in the terahertz band correspondingly range from 1 mm to 0.1 mm (or 100 μm). Terahertz radiation occupies a middle ground between microwaves and infrared light waves known as the terahertz gap, It represents the region in the electromagnetic spectrum where the frequency of electromagnetic radiation becomes too high to be measured digitally via electronic counters, so must be measured by proxy using the properties of wavelength and energy.
A trick for taming terahertz transmissions. Researchers have invented a wireless communication receiver that can operate in the terahertz frequency band. By increasing the sensitivity 10,000-fold, they achieved the fastest Researchers invent a new receiver for terahertz-frequency radiation -- by implementing coherent detection, they achieve record transmission rates -- this work may lead to much faster wireless data speeds using less power. Real-time error-free transmission rates ever recorded. This work may be crucial for next generation cell phone standards and novel remote sensors.
Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum is a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly switching a carrier among many frequency channels, using a pseudorandom sequence known to both transmitter and receiver. It is used as a multiple access method in the code division multiple access (CDMA) scheme frequency-hopping code division multiple access (FH-CDMA). FHSS is a wireless technology that spreads its signal over rapidly changing frequencies. Each available frequency band is divided into sub-frequencies. Signals rapidly change ("hop") among these in a pre-determined order. Interference at a specific frequency will only affect the signal during that short interval. FHSS can, however, cause interference with adjacent direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) systems. A sub-type of FHSS used in Bluetooth wireless data transfer is adaptive frequency hopping spread spectrum (AFH). White Space.
Microwaves are a form of low energy electromagnetic radiation. Unlike x-rays or ultraviolet light, they don't have enough energy to break chemical bonds. They do, however, have the ability to interact with molecules that have positive and negative regions. WiFi wireless routers transmit at full power around 100mW on 2.4GHz. A Microwave oven is around 500 watts at the same frequency of 2 Ghz. The difference is the constant exposure to microwaves over long periods of time.
How Many Wireless Signals in Hospitals? There are more than 10 wireless devices in every patient room (i.e., heart monitors, telemetry, nurse call systems, and access control systems). All of them will rely on upgraded wireless networks. We need to strike a balance between convenience and safety — limiting wireless device usage within a specific distance from medical equipment and prohibiting their use in patient care areas where medical equipment is heavily used, while allowing their use in hospital waiting areas, lounges, private offices, and cafeterias. CADTH’s Rapid Response service undertook a review of the available evidence on the use of wireless devices in health care environments. The studies looked at several types of wireless devices — ultra-high frequency radios, various mobile phones, and a variety of Bluetooth-enabled devices — using a broad range of transmission technologies such as code division multiple access (CDMA), general packet radio service (GPRS), global system for mobile communication (GSM), Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA), universal mobile telecommunications system (UMTS), wireless local area network (WLAN) and analog. The effect of these devices on the performance of several types of medical equipment was investigated in the studies, including defibrillators, ventilators, brain stimulators, pumps, and ophthalmic equipment. The CADTH review found that electromagnetic emissions from wireless devices do frequently cause interference with medical equipment. This interference manifests itself in several ways — noises, screen distortions, false alarms, complete stoppages, and malfunctions in output parameters. Equipment is more likely to be affected if the wireless device is using the same radio frequency, transmitting a strong signal, or in close proximity to the equipment. Incidences of the interference affecting medical equipment to such an extent that it compromised patient safety were, however, found to be uncommon. Some hospitals have implemented Wi-Fi incrementally to support specific applications or areas within the facility — designs once were sufficient but now contribute to a fragmented WLAN infrastructure. Many other hospitals have poorly designed WLANs that are simply incapable of meeting the demands of the medical environment.
Wireless LAN is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building. LAN stands for Local Area Network.
EMP - E-Bomb - High Energy Pulse
Electro-Magnetic Pulse is a short burst of electromagnetic energy. Such a pulse's origination may be a natural occurrence or man-made and can occur as a radiated, electric or magnetic field or a conducted electric current, depending on the source.
Electronic Warfare is any action involving the use of the electromagnetic spectrum or directed energy to control the spectrum, attack of an enemy, or impede enemy assaults via the spectrum.
E-Bomb - Electromagnetic Weapon (wiki)
Nuclear Electromagnetic Pulse is a burst of electromagnetic radiation created by a nuclear explosion. The resulting rapidly varying electric and magnetic fields may couple with electrical and electronic systems to produce damaging current and voltage surges. The specific characteristics of a particular nuclear EMP event vary according to a number of factors, the most important of which is the altitude of the detonation. The term "electromagnetic pulse" generally excludes optical (infrared, visible, ultraviolet) and ionizing (such as X-ray and gamma radiation) ranges. In military terminology, a nuclear warhead detonated tens to hundreds of miles above the Earth's surface is known as a high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) device. Effects of a HEMP device depend on factors including the altitude of the detonation, energy yield, gamma ray output, interactions with the Earth's magnetic field and electromagnetic shielding of targets.
Effects of Nuclear Explosions
Directed-Energy Weapon is a ranged weapon system that inflicts damage at a target by emission of highly focused energy, including laser, microwaves and particle beams. Potential applications of this technology include anti-personnel weapon systems, missile defense system, and the disabling of lightly armored vehicles or mounted optical devices.
Havana Syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms experienced by United States and Canadian embassy staff in Cuba.
Diplomats experienced some form of brain injury, but did not determine the cause of the injuries. A co-author of the JAMA study considered microwave weapons to be "a main suspect" for the phenomenon
Active Denial System is a millimeter wave source that heats the water in a human target's skin and thus causes incapacitating pain.
Vigilant Eagle is a proposed airport defense system that directs high-frequency microwaves towards any projectile that is fired at an aircraft.
Bofors HPM Blackout is a high-powered microwave weapon that is said to be able to destroy at short distance a wide variety of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) electronic equipment and is purportedly non-lethal.
AESA radars mounted on fighter aircraft have been slated as directed energy weapons against missiles. Counter-electronics High Power Microwave Advanced Missile Project (wiki).
WIFI + Cell Phones Cause 100% Damage to Human Eggs. (DNA) (youtube) - Human immature eggs have ABSOLUTELY NO protection from microwave radiation. Damage/birth defects will be first apparent in the 3rd generation of a family regularly exposed to microwave radiation.
Recent advances in the effects of microwave radiation on brains. The brain has been recognized as one of the organs that is most vulnerable to microwave radiation.
Effect of Microwave Exposure on the Ovarian Development of Drosophila melanogaster.
Electromagnetic Interference - Electromagnetics - WiFi - Cell Phones
Coronal Mass Ejection (solar storms) - Geomagnetic Storm
Electronic Counter Countermeasures is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) on electronic sensors aboard vehicles, ships and aircraft and weapons such as missiles. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. In practice, EPM often means resistance to jamming.
Faraday Cage is an enclosure used to block electric fields. It is formed by conductive material or by a mesh of such materials.
Static Electricity - EMF (electro magnetic frequencies)
Voltage Spike are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit. Fast, short duration electrical transients (overvoltages) in the electric potential of a circuit are typically caused by Lightning strikes, Power outages, Tripped circuit breakers, Short circuits, Power transitions in other large equipment on the same power line, Malfunctions caused by the power company, Electromagnetic pulses with electromagnetic energy distributed typically up to the 100 kHz and 1 MHz frequency range. Inductive spikes. In the design of critical infrastructure and military hardware, one concern is of pulses produced by nuclear explosions, whose nuclear electromagnetic pulses distribute large energies in frequencies from 1 kHz into the gigahertz range through the atmosphere. The effect of a voltage spike is to produce a corresponding increase in current (current spike). However some voltage spikes may be created by current sources. Voltage would increase as necessary so that a constant current will flow. Current from a discharging inductor is one example. For sensitive electronics, excessive current can flow if this voltage spike exceeds a material's breakdown voltage, or if it causes avalanche breakdown. In semiconductor junctions, excessive electric current may destroy or severely weaken that device. An avalanche diode, transient voltage suppression diode, varistor, overvoltage crowbar, or a range of other overvoltage protective devices can divert (shunt) this transient current thereby minimizing voltage. Voltage spikes, also known as surges, may be created by a rapid buildup or decay of a magnetic field, which may induce energy into the associated circuit. However voltage spikes can also have more mundane causes such as a fault in a transformer or higher-voltage (primary circuit) power wires falling onto lower-voltage (secondary circuit) power wires as a result of accident or storm damage. Voltage spikes may be longitudinal (common) mode or metallic (normal or differential) mode. Some equipment damage from surges and spikes can be prevented by use of surge protection equipment. Each type of spike requires selective use of protective equipment. For example, a common mode voltage spike may not even be detected by a protector installed for normal mode transients. Power increases or decreases which last multiple cycles are called swells or sags, respectively. An uninterrupted voltage increase that lasts more than a minute is called an overvoltage. These are usually caused by malfunctions of the electric power distribution system.
Overcurrent is a situation where a larger than intended electric current exists through a conductor, leading to excessive generation of heat, and the risk of fire or damage to equipment. Possible causes for overcurrent include short circuits, excessive load, incorrect design, an arc fault, or a ground fault. Fuses, circuit breakers, and current limiters are commonly used overcurrent protection (OCP) mechanisms to control the risks. Circuit breakers and fuses protect circuit wiring from damage caused by overcurrent.
Short Circuit is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit, which could damage electronics or cause an open circuit and be disconnected with no external electrical current flowing between the terminals, which could cause the electronic device not work because of an infinite resistance between two nodes.
Ground Fault or Earth Fault is any failure that allows unintended connection of power circuit conductors with the earth.
Just like with lightning strikes, things that are plugged in will get damaged from the power surge or voltage spike. And if you are very close to a EMP, even some things that are not plugged in that are sensitive to static electricity like integrated circuit chips (IC), transistors, resistors, could be damage by compton scattering. An EMP surge is also “front loaded.” meaning that it doesn’t do a build up for a couple of micro-seconds, which would allow enough time for the circuit breaker to “read” that trouble is on the way and shut down. This is why a surge protector may not give you the protection that you need. So certain appliances will need to be repaired or need to be replaced. The main damage from EMPs comes from collapsing magnetic field across the metal in electronics and cause shorts. Being unplugged has the advantage that you aren't vulnerable to surges coming in on long lines such as the AC mains or any sort of telecommunications wire. Dedicated suppression components such as fuses and MOVs are likely to fail first, and in a way that stops further energy flow (fuses blow, MOVs fail short) -- these sacrificial failures may help by absorbing the brunt of the surge energy incoming to the device, especially if it's being conducted in by long lines. Spare boards may be less prone than live equipment to exhibiting certain destructive failure modes that require an existing energy source. ICs are almost universally equipped with I/O protection structures on their pads, which will absorb the brunt of the surge energy and fail first, usually as opens or dead shorts. This makes it possible to "go/no-go" test the ICs for surge damage by testing all the I/O protection structures.
Electrometric burst will disrupt services and certain electronics, and our lack of computer systems will leave us extremely vulnerable, but life will go on. A lot of things like electrical appliances are a quality of life luxury, they are not totally necessary for survival, unless the power grid and communications fail, then just like any disaster or emergency, you need good planning, and you also need to know your options.
Li-Fi - The Power of Light
 There has to be a Safer and more Healthier way of
transmitting data without radiation and microwaves from Cellular
Towers, Wi-Fi and Wireless Phones?
There has to be a Safer and more Healthier way of
transmitting data without radiation and microwaves from Cellular
Towers, Wi-Fi and Wireless Phones?
Li-Fi Light Fidelity is a bidirectional, high-speed and fully networked wireless communication technology similar to Wi-Fi. a form of visible light communication and a subset of optical wireless communications (OWC) and could be a complement to RF communication (Wi-Fi or cellular networks), or even a replacement in contexts of data broadcasting.
Harald Haas: Wireless Data from Every Light Bulb (video)
Visible Light Communication is a data communications variant which uses visible light between 400 and 800 THz (780–375 nm). VLC is a subset of optical wireless communications technologies.
Squeezing Light into a Tiny Channel brings Optical Computing a step closer. Developing technologies that run on light. Researchers are designing a nanoscale photon diode, a necessary component that could bring us closer to faster, more energy-efficient computers and communications that replace electricity with light.
Optical Computing uses photons produced by lasers or diodes for computation. For decades, photons have promised to allow a higher bandwidth than the electrons used in conventional computers. Most research projects focus on replacing current computer components with optical equivalents, resulting in an optical digital computer system processing binary data. This approach appears to offer the best short-term prospects for commercial optical computing, since optical components could be integrated into traditional computers to produce an optical-electronic hybrid. However, optoelectronic devices lose 30% of their energy converting electronic energy into photons and back; this conversion also slows the transmission of messages. All-optical computers eliminate the need for optical-electrical-optical (OEO) conversions, thus lessening the need for electrical power. Application-specific devices, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and optical correlators, have been designed to use the principles of optical computing. Correlators can be used, for example, to detect and track objects, and to classify serial time-domain optical data.
Optical Engineering is the field of study that focuses on applications of optics. Optical engineers design components of optical instruments such as lenses, microscopes, telescopes, and other equipment that utilizes the properties of light. Other devices include optical sensors and measurement systems, lasers, fiber optic communication systems, optical disc systems (e.g. CD, DVD), etc.
LED's - Light - Wireless Energy
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.
Do you See the Light?
Li-Fi will eventually be used for transmitting information directly into the brain. It would most likely go directly to the brains memory first and then from there it would have to be sorted using the brains preferred processes for learning. The person receiving the information would need training first, and would also need to be an adult with a brain that's fully developed. We already take in information through light by what we see, things like pictures, text, and by way of video, computer screens and TV, which some of it is mostly subliminal without much benefit, unless you can deconstruct it effectively. Lawn Mower Man (AI).
Photonics - Optogenetics
Photonics is the science of light generation, detection, and manipulation through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and detection/sensing.
Nanophotonics is the study of the behavior of Light on the nanometer scale, and of the interaction of nanometer-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology. It often (but not exclusively) involves metallic components, which can transport and focus light via surface plasmon polaritons.
A new approach to trapping light in artificial photonic materials could lead to a tremendous boost in the transfer speed of data online.
Photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of all forms of electromagnetic radiation including Light.
Waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. They enable a signal to propagate with minimal loss of energy by restricting expansion to one dimension or two.
Biophoton are photons of light in the ultraviolet and low visible light range that are produced by a biological system. They are non-thermal in origin, and the emission of biophotons is technically a type of bioluminescence, though bioluminescence is generally reserved for higher luminance luciferin/luciferase systems. The term biophoton used in this narrow sense should not be confused with the broader field of biophotonics, which studies the general interaction of light with biological systems.
Biophotonics denotes a combination of biology and photonics, with photonics being the science and technology of generation, manipulation, and detection of photons, quantum units of light. Photonics is related to electronics and photons. Photons play a central role in information technologies such as fiber optics the way electrons do in electronics.
Physicists score double hit in LED research. In 2 breakthroughs in the realm of photonics, researchers are reporting the successful demonstration of an LED (light-emitting diode) based on half-light half-matter quasiparticles in atomically thin materials. This is also the first successful test of an electrically driven light emitter using atomically thin semiconductors embedded in a light trapping structure (optical cavity).
Polarization Waves (magnetics)
Eyes (sight)
Electromagnetics and Photonics Research - Optics Info Base
Intense Pulsed Light is a technology used by cosmetic and medical practitioners to perform various skin treatments for aesthetic and therapeutic purposes, including hair removal, photorejuvenation (e.g. the treatment of skin pigmentation, sun damage, and thread veins) as well as to alleviate dermatologic diseases such as acne.
Advance in intense pulsed light sintering opens door to improved electronics manufacturing. Intense pulsed light sintering allows for faster densification – in a matter of seconds – over larger areas compared to conventional sintering processes such as oven-based and laser-based. IPL can potentially be used to sinter nanoparticles for applications in printed electronics, solar cells, gas sensing and photocatalysis.
Photocatalysis is the acceleration of a photoreaction in the presence of a catalyst. In catalysed photolysis, light is absorbed by an adsorbed substrate. In photogenerated catalysis, the photocatalytic activity (PCA) depends on the ability of the catalyst to create electron–hole pairs, which generate free radicals (e.g. hydroxyl radicals: •OH) able to undergo secondary reactions.
Densification is to impregnate (wood) with additives under heat and pressure in order to achieve greater density and hardness.
Absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way in which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed into internal energy of the absorber, for example thermal energy. The reduction in intensity of a light wave propagating through a medium by absorption of a part of its photons is often called attenuation. Usually, the absorption of waves does not depend on their intensity (linear absorption), although in certain conditions (usually, in optics), the medium changes its transparency dependently on the intensity of waves going through, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs.
Computing at the Speed of Light, shuttle photons instead of electrons using ultra-compact Beam Splitters. Mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets built with this technology would consume less power, have longer battery life and generate less heat than existing mobile devices.
Optoelectronics is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that source, detect and control Light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics.
Tunable Optical Chip paves way for new Quantum Devices. Researchers have created a silicon carbide (SiC) photonic integrated chip that can be thermally tuned by applying an electric signal.
Atoms, molecules or even living cells can be manipulated with light beams.
Across the spectrum: Researchers find way to stabilize Color of Light in next-gen Material. Researchers believe this could be the basis for efficient and more cost-effective optoelectronic technologies that can turn light into electricity or vice versa.
When AI and Optoelectronics meet: Researchers take control of Light Properties. Researchers customize the properties of broadband light sources using an AI algorithm and a photonic chip. Spectro-temporal representation of femtosecond pulse patterns, prepared by a photonic chip to seed the generation of supercontinuum. The patterns are optimized via machine-learning to select and enhance desired properties in the output supercontinuum. Here, the pulses are separated by 1 picosecond, and measured experimentally via frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG). Using machine-learning and an integrated photonic chip, researchers from INRS (Canada) and the University of Sussex (UK) can now customize the properties of broadband light sources. Also called "supercontinuum," these sources are at the core of new imaging technologies and the approach proposed by the researchers will bring further insight into fundamental aspects of light-matter interactions and ultrafast nonlinear optics.
Silicon Photonics is the study and application of photonic systems which use silicon as an optical medium.
Parylene photonics enable future optical biointerfaces. Scientists have invented an optical platform that will likely become the new standard in optical biointerfaces. They labeled this new field of optical technology 'Parylene photonics.' Chamanzar's design was created with neural stimulation in mind, allowing for targeted stimulation and monitoring of specific neurons within the brain. Crucial to this, is the creation of 45-degree embedded micromirrors. While prior optical biointerfaces have stimulated a large swath of the brain tissue beyond what could be measured, these micromirrors create a tight overlap between the volume being stimulated and the volume recorded. These micromirrors also enable integration of external light sources with the Parylene waveguides.
Programming light on a chip. Research opens doors in photonic quantum information processing, optical signal processing and microwave photonics. Researchers have developed a new integrated photonics platform that can store light and electrically control its frequency (or color) in an integrated circuit.
Nanophysicists developed a high-performance Organic Phototransistor. Converting light into electrical signals is essential for a number of future applications including imaging, optical communication and biomedical sensing. Researchers have now developed a new molecular device enabling to detect light and translate it with high efficiency to detectable electronic current.
Phototransistor is a device that is able to sense light levels and alter the current flowing between emitter and collector according to the level of light it receives.
Physicists Write, Read and Erase using Light. A team of physicists has developed a new method of storing information in fully transparent plastic foils.
5000 times faster than a computer. Interatomic light rectifier generates directed electric currents. The absorption of light in semiconductor crystals without inversion symmetry can generate electric currents. Researchers have now generated directed currents at terahertz (THz) frequencies, much higher than the clock rates of current electronics. They show that electronic charge transfer between neighboring atoms in the crystal lattice represents the underlying mechanism.
Quantum manipulation and control of light. Creating different kinds of light with manipulable quantum properties.
Visible Light and Nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable Bioactive Molecules. Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics. Quantum dots behave more like organic molecules than metal nanoparticles. The nanoparticle catalysts use energy from visible light to activate molecules on their surfaces and fuse them together to form larger molecules in configurations useful for biological applications. The larger molecule then detaches easily from the nanoparticle, freeing the nanoparticle to be used again in another reaction cycle.
Internet Connection Types
Researchers develop new way to break reciprocity law by changing material properties periodically in time. The breakthrough could help to create efficient nonreciprocal devices, such as compact isolators and circulators, that are needed for the next generation of microwave technology by eliminating the need for bulky magnets, and in photonics or optical communications systems. When we look through a window and see our neighbor on the street, the neighbor can also see us. This is called reciprocity, and it is the most common physical phenomenon in nature.
The Story of Light - Bell Labs - Future Impossible (youtube)
Spatial Multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas. Therefore, the space dimension is reused, or multiplexed, more than one time.
Moonlight is 500,000 times less bright than the sun, but light cast by the moon has different optical properties than the Sun. Moonlight reflected from the sun presents a distinctive spectrum composed of more reds and yellows, and possesses a different frequency than sunlight. This specific light spectrum has never been artificially duplicated. Different tissue and cell types in the body each have their own particular light absorption dispositions (they will only absorb light of a specific wavelength); therefore different frequencies of light have distinct benefits and applications. Extensive research has shown that different wavelengths of light have beneficial therapeutic effects at the cellular level.
Electronic chip mimics the brain to make memories in a flash. Engineers have mimicked the human brain with an electronic chip that uses light to create and modify memories. Researchers from RMIT University drew inspiration from an emerging tool in biotechnology -- optogenetics -- to develop a device that replicates the way the brain stores and loses information.
Optogenetics allows scientists to delve into the body's electrical system with incredible precision, using light to manipulate neurons so that they can be turned on or off.
Optogenetics is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. Memories - Stanford.
Light flips genetic switch in bacteria inside transparent worms. Light-controlled genes could reveal how gut bacteria impact health. Researchers have shown that colored light can both activate and deactivate genes of gut bacteria in the intestines of worms. The research shows how optogenetic technology can be used to investigate the health impacts of gut bacteria.
Light can be used as an accurate method to control gene expression shows groundbreaking optogenetics study by University of Colorado, Duke University and University of Helsinki researchers.
Switching DNA functions on and off by means of light. Biochemists use protein engineering to transfer photocaging groups to DNA. Biochemists have developed a new strategy for controlling the biological functions of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by means of light and therefore provide a tool to investigate processes which take place in cells. The cell's functions depend on special molecules, the enzymes. Enzymes are proteins, which carry out chemical reactions in the cell. They help to synthesize metabolic products, make copies of the DNA molecules, convert energy for the cell's activities, change DNA epigenetically and break down certain molecules.
Luminescence - Light Therapy - Light
Photoreceptor Protein are light-sensitive proteins involved in the sensing and response to light in a variety of organisms.
Photocurrent is the electric current through a photosensitive device, such as a photodiode, as the result of exposure to radiant power.
Researchers "Reprogram" Network of Brain Cells with Thin Beam of Light.
Integrated Control of Predatory Hunting Circuits by the Central Nucleus of the Amygdala. Mice became aggressive predators when two sets of neurons in the Amygdala were activated with laser light.
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers use light to launch drugs from red blood cells. Scientists use light to control the logic networks of a cell in a breakthrough technique that uses light to activate a drug stored in circulating red blood cells so that it is released exactly when and where it is needed.
Stereotactic Surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually used to treat cancer. In stereotactic radiosurgery the word "stereotactic" refers to a three-dimensional coordinate system that enables accurate correlation of a virtual target seen in the patient's diagnostic images with the actual target position in the patient. Stereotactic radiosurgery may also be called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) when used outside the central nervous system (CNS).
Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation. A research team presents a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neuroscience research.
SLAC Study: Light Can Switch On Topological Materials. Computer Simulations Show How Light Pulses Can Create Channels that Conduct Electricity with No Resistance in Atomically Thin Semiconductors.
LumiWave: Delivers the power of 200 LEDS (light emitting diodes) deep-tissue, infrared-light therapy device wavelength, in a lightweight, portable and affordable package. Stimulating effect of photon penetration and cell absorption.
Penetration Depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the material falls to 1/e (about 37%) of its original value at (or more properly, just beneath) the surface. When electromagnetic radiation is incident on the surface of a material, it may be (partly) reflected from that surface and there will be a field containing energy transmitted into the material. This electromagnetic field interacts with the atoms and electrons inside the material. Depending on the nature of the material, the electromagnetic field might travel very far into the material, or may die out very quickly. For a given material, penetration depth will generally be a function of wavelength.
Using a Laser to Wirelessly Charge a Smartphone safely across a room - Wireless Energy
Photodielectric Detector using a Superconducting Cavity
Implanted Computer Chip - Fragmented - Brain Knowledge
Controlling Light with Light. Researchers develop a new platform for all-optical computing. Researchers developed a fundamentally new material that uses reversible swelling and contracting in a hydrogel under low laser power to change the refractive index. The hydrogel is composed of a polymer network that is swollen with water, like a sponge, and a small number of light-responsive molecules known as spiropyran (which is similar to the molecule used to tint transition lenses). When light is shone through the gel, the area under the light contracts a small amount, concentrating the polymer and changing the refractive index. When the light is turned off, the gel returns to its original state. When multiple beams are shone through the material, they interact and affect each other, even at large distances. Beam A could inhibit Beam B, Beam B could inhibit Beam A, both could cancel each other out or both could go through -- creating an optical logic gate. Not only can we design photoresponsive materials that reversibly switch their optical, chemical and physical properties in the presence of light, but we can use those changes to create channels of light, or self-trapped beams, that can guide and manipulate light.
Fiber Optics
Optical Fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than wire cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with lesser amounts of loss; in addition, fibers are also immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer excessively. Fibers are also used for illumination, and are wrapped in bundles so that they may be used to carry images, thus allowing viewing in confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.
Using Light for Communications was originally thought of over a 100 years ago.
Fiber Optic Sensor is a sensor that uses optical fiber either as the sensing element ("intrinsic sensors"), or as a means of relaying signals from a remote sensor to the electronics that process the signals ("extrinsic sensors").
Fiber Optic Super-Fast Internet by Harnessing Twisted Light Beams. Researchers say they have developed tiny readers that can detect information in light spirals to carry more data and process it faster. Fiber optic cables use pulses of light to transmit information, but currently information can only be stored through the color of the light, and whether the wave is horizontal or vertical. By twisting light into a spiral, engineers effectively create a third dimension for light to carry information: the level of orbital angular momentum, or spin. It’s like DNA, if you look at the double helix spiral, the more you can use angular momentum the more information you can carry.
1000 gigabits per second (1 gigabit = 1 billion bits) - Super Computers.
Putting on the pressure improves glass for fiber optics. Rapid, accurate communication worldwide is possible via fiber optic cables, but as good as they are, they are not perfect. Now, researchers suggest that the silica glass used for these cables would have less signal loss if it were manufactured under high pressure. Signal loss means that we have to use amplifiers every 80 to 100 kilometers (50 to 62 miles). Simulations showed that using pressure quenching of the glass, the Rayleigh scattering loss could be reduced by more than 50%.
Navigation using Light
Light-Field Camera captures information about the light field emanating from a scene; that is, the intensity of light in a scene, and also the direction that the light rays are traveling in space. This contrasts with a conventional camera, which records only light intensity. One type of light field camera uses an array of micro-lenses placed in front of an otherwise conventional image sensor to sense intensity, color, and directional information. Multi-camera arrays are another type of light field camera. Holograms are a type of film-based light field image.
Lidar is a surveying method that measures distance to a target by illuminating that target with a pulsed laser light, and measuring the reflected pulses with a sensor. Differences in laser return times and wavelengths can then be used to make digital 3D-representations of the target. The name lidar, sometimes considered an acronym of Light Detection And Ranging (sometimes Light Imaging, Detection, And Ranging) (also called LIDAR, LiDAR, and LADAR), was originally a portmanteau of light and radar, which is an object-detection system that uses radio waves to determine the range, angle, or velocity of objects.
Sound - Noise Control
Acoustical Engineering is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It is the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typically concerned with the design, analysis and control of sound. Noise Consultants.
How to Make High Performance Sound Absorption Panels for $5 (youtube)
Noise Pollution is the disturbing or excessive noise that may harm the activity or balance of human or animal life. The source of most outdoor noise worldwide is mainly caused by machines and transportation systems, motor vehicles, aircraft, and trains. Nuisance (crime).
The impact of human-caused Noise Pollution on Birds. Anthropogenic noise pollution (ANP) is a globally invasive phenomenon impacting natural systems, but most research has occurred at local scales with few species. Researchers in this study investigated continental-scale breeding season associations with ANP for 322 bird species to test whether local-scale predictions are consistent at broad spatial extents for an extensive group of North American bird species in the continental United States.
Anthropogenic Noise in the marine environment can be generally classed as either acute or chronic. Chronic noise refers to long term, low intensity noise, for example from shipping and industrial activity. Both have the potential to impact on cetacean behaviour and physiology.
Effects of Living in a Noisy World. Worldwide, noise-induced hearing impairment is the most prevalent irreversible occupational hazard, and it is estimated that 120 million people worldwide have disabling hearing difficulties. Brief exposure to sound levels exceeding 120 dBA without hearing protection may even cause physical pain.
Misophonia is when people irritated by certain sounds or have strong negative feelings, sensitivities, thoughts, and physical reactions to specific sounds, which the literature calls "trigger sounds". These sounds can be soft or loud. One study found that around 80% of the sounds were related to the mouth, like someone eating, slurping, chewing or popping gum, whispering, etc., and around 60% were repetitive. A visual trigger may develop related to the trigger sound. It also appears that a misophonic reaction can occur in the absence of an actual sound.
Hyperacusis is a highly debilitating rare hearing disorder characterized by an increased sensitivity to certain frequencies and volume ranges of sound (a collapsed tolerance to usual environmental sound). A person with severe hyperacusis has difficulty tolerating everyday sounds, which become painful or loud. Hyperacusis is often coincident with tinnitus. Both conditions have a prevalence of about 10–15% and hearing loss as a major risk factor. However, there also appear to be important differences between the mechanisms involved in tinnitus and hyperacusis.
Prepulse Inhibition is a neurological phenomenon in which a weaker prestimulus (prepulse) inhibits the reaction of an organism to a subsequent strong reflex-eliciting stimulus (pulse), often using the startle reflex. The stimuli are usually acoustic, but tactile stimuli (e.g. via air puffs onto the skin) and light stimuli are also used. When prepulse inhibition is high, the corresponding one-time startle response is reduced. The reduction of the amplitude of startle reflects the ability of the nervous system to temporarily adapt to a strong sensory stimulus when a preceding weaker signal is given to warn the organism. PPI is detected in numerous species including mice and humans. Although the extent of the adaptation affects numerous systems, the most comfortable to measure are the muscular reactions, which are normally diminished as a result of the nervous inhibition. Deficits of prepulse inhibition manifest in the inability to filter out the unnecessary information; they have been linked to abnormalities of sensorimotor gating.
 Noise Regulation includes statutes or guidelines relating to
sound
transmission established by national, state or provincial and municipal
levels of government. After the watershed passage of the United States
Noise Control Act of 1972, other local and state governments passed
further regulations.
Noise Pollution.
Noise Regulation includes statutes or guidelines relating to
sound
transmission established by national, state or provincial and municipal
levels of government. After the watershed passage of the United States
Noise Control Act of 1972, other local and state governments passed
further regulations.
Noise Pollution.Interactive Map of Road and Aviation Noise Pollution in the United States.
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of sound perception and audiology—how humans perceive various sounds. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound (including noise, speech, and music). Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field of many areas, including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science. Auditory Hallucination.
Why is the Brain disturbed by Harsh Sounds? Their results showed that the conventional sound-processing circuit is activated but that the cortical and sub-cortical areas involved in the processing of salience and aversion are also solicited. This explains why the brain goes into a state of alert on hearing this type of sound. Researchers from UNIGE and HUG played repetitive sounds of between 0 and 250 Hz to 16 participants closer and closer together in order to define the frequencies that the brain finds unbearable. The scientists were able to establish that the upper limit of sound roughness is around 130 Hz. Above this limit the frequencies are heard as forming only one continuous sound. The sounds considered intolerable were mainly between 40 and 80 Hz, i.e. in the range of frequencies used by alarms and human screams, including those of a baby. when the repetitions are spaced less than about 25 milliseconds apart, the brain cannot anticipate them and therefore suppress them. It is constantly on alert and attentive to the stimulus. When the sound is perceived as continuous (above 130 Hz), the auditory cortex in the upper temporal lobe is activated. But when sounds are perceived as harsh (especially between 40 and 80 Hz), they induce a persistent response that additionally recruits a large number of cortical and sub-cortical regions that are not part of the conventional auditory system. "These sounds solicit the amygdala, hippocampus and insula in particular, all areas related to salience, aversion and pain. This explains why participants experienced them as being unbearable. Alarm Fatigue.
Prolonged exposure to loud noise alters how the brain processes speech, potentially increasing the difficulty in distinguishing speech sounds.
Acute High-Intensity Noise induces rapid Arc protein expression butfails to rapidly change GAD expression in amygdala and hippocampusof rats: Effects of treatment with D-cycloserine.
Background Noise is any sound other than the sound being monitored (primary sound).
Ambient Noise Level is the background sound pressure level at a given location, normally specified as a reference level to study a new intrusive sound source. Ambient sound levels are often measured in order to map sound conditions over a spatial regime to understand their variation with locale. In this case the product of the investigation is a sound level contour map. Alternatively ambient noise levels may be measured to provide a reference point for analyzing an intrusive sound to a given environment. For example, sometimes aircraft noise is studied by measuring ambient sound without presence of any overflights, and then studying the noise addition by measurement or computer simulation of overflight events. Or roadway noise is measured as ambient sound, prior to introducing a hypothetical noise barrier intended to reduce that ambient noise level. Ambient noise level is measured with a sound level meter. It is usually measured in dB relative to a reference pressure of 0.00002 Pa, i.e., 20 µPa (micropascals) in SI units. A pascal is a newton per square meter. The centimeter-gram-second system of units, the reference sound pressure for measuring ambient noise level is 0.0002 dyn/cm2. Most frequently ambient noise levels are measured using a frequency weighting filter, the most common being the A-weighting scale, such that resulting measurements are denoted dB(A), or decibels on the A-weighting scale.
Atmospheric Sounding is a measurement of vertical distribution of physical properties of the atmospheric column such as pressure, temperature, wind speed and wind direction (thus deriving wind shear), liquid water content, ozone concentration, pollution, and other properties. Such measurements are performed in a variety of ways including remote sensing and in situ observations. The most common in situ sounding is a radiosonde, which usually is a weather balloon, but can also be a rocketsonde. Remote sensing soundings generally use passive infrared and microwave radiometers: airborne instruments, surface stations, Earth-observing satellite instruments such as AIRS and AMSU, observation of atmospheres on different planets, such as the Mars climate sounder on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Sound Level Meter is used for acoustic (sound that travels through air) measurements. It is commonly a hand-held instrument with a microphone. The diaphragm of the microphone responds to changes in air pressure caused by sound waves. That is why the instrument is sometimes referred to as a Sound Pressure Level (SPL) Meter. This movement of the diaphragm, i.e. the sound pressure deviation (pascal Pa), is converted into an electrical signal (volts V). While describing sound in terms of sound pressure (Pascal) is possible, a logarithmic conversion is usually applied and the sound pressure level is stated instead, with 0 dB SPL equal to 20 micropascals. A microphone is distinguishable by the voltage value produced when a known, constant sound pressure is applied. This is known as the microphone sensitivity. The instrument needs to know the sensitivity of the particular microphone being used. Using this information, the instrument is able to accurately convert the electrical signal back to a sound pressure, and display the resulting sound pressure level (decibels dB SPL). Sound level meters are commonly used in noise pollution studies for the quantification of different kinds of noise, especially for industrial, environmental, mining[1] and aircraft noise. The current international standard that specifies sound level meter functionality and performances is the IEC 61672-1:2013. However, the reading from a sound level meter does not correlate well to human-perceived loudness, which is better measured by a loudness meter. Specific loudness is a compressive nonlinearity that depends on level and also frequency, which can be calculated in a number of different ways.
Sound Pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone. The SI unit of sound pressure is the pascal (Pa).
Sound Pressure Level is a logarithmic measure of the effective pressure of a sound relative to a reference value.
Acoustical Society promotes the knowledge and practical applications of acoustics. Pitch Perception.
Quite Rock Sound Proofing Material
Echo Absorber Acoustic Panel
Soundproofing Insulation
Acoustimac
Acoustical Surfaces
Sound Transmission Class is an integer rating of how well a building partition attenuates airborne sound. In the US, it is widely used to rate interior partitions, ceilings/floors, doors, windows and exterior wall configurations (see ASTM International Classification E413 and E90). Outside the US, the Sound Reduction Index (SRI) ISO index or its related indices are used. As of 2012, these are defined in the ISO - 140 series of standards (under revision). The STC rating figure very roughly reflects the decibel reduction in noise that a partition can provide. Structurally decoupling the gypsum wallboard panels from the partition framing can result in a large increase in sound isolation when installed correctly. Examples of structural decoupling in building construction include resilient channels, sound isolation clips and hat channels, and staggered- or double-stud framing. The STC results of decoupling in wall and ceiling assemblies varies significantly depending on the framing type, air cavity volume, and decoupling material type. Great care must be taken in each type of decoupled partition construction, as any fastener that becomes mechanically (rigidly) coupled to the framing can short-circuit the decoupling and result in drastically lower sound isolation results.
Sound Reduction Index is used to measure the level of sound insulation provided by a structure such as a wall, window, door, or ventilator. It is defined in the series of international standards ISO 16283 (parts 1-3) and the older ISO 140 (parts 1-14), or the regional or national variants on these standards.
Soundproofing is any means of reducing the sound pressure with respect to a specified sound source and receptor. There are several basic approaches to reducing sound: increasing the distance between source and receiver, using noise barriers to reflect or absorb the energy of the sound waves, using damping structures such as sound baffles, or using active antinoise sound generators. Noise Reducing Window Treatments - Noise Reducing window Blinds - A triple pane window can eliminate 15-20% more noise.
Anechoic Chamber is a room designed to completely absorb reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from waves entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reverberant sounds), in effect simulating being inside an infinitely large room. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to RF anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges being tested.
Damping dissipates vibrational energy before it can build up and radiate as sound. Absorption is trapping the sound waves.
Noise Cancelation Headphones
Auditory Masking occurs when the perception of one sound is affected by the presence of another sound. Auditory masking in the frequency domain is known as simultaneous masking, frequency masking or spectral masking. Auditory masking in the time domain is known as temporal masking or non-simultaneous masking. Simultaneous masking occurs when a sound is made inaudible by a noise or unwanted sound of the same duration as the original sound. For example, a powerful spike at 1 kHz will tend to mask out a lower-level tone at 1.1 kHz. Also, two sine tones at 440 and 450 Hz can be perceived clearly when separated. They cannot be perceived clearly when presented simultaneously. Masking Threshold - White Noise.
Smell Masking - Synesthesia - Sound Perception - Problem Transference.
Sound Masking is the addition of natural or artificial sound (commonly, though inaccurately, referred to as "white noise" or "pink noise") into an environment to cover-up unwanted sound by using auditory masking. This is in contrast to the technique of active noise control. Sound masking reduces or eliminates awareness of pre-existing sounds in a given area and can make a work environment more comfortable, while creating speech privacy so workers can better concentrate and be more productive. Sound masking can also be used in the out-of-doors to restore a more natural ambient environment.
Informational Masking is broadly defined as a degradation of auditory detection or discrimination of a signal embedded ina context of other similar sounds.
Energetic Masking occurs when the neural excitation evoked by the competing speech exceeds the excitation produced by the target speech. It is largely a matter of the relative energies in the two signals. Energetic masking is caused by physical interactions between signal and masker.
 Active Noise Control is a method for reducing unwanted
sound by the
addition of a second sound specifically designed to cancel the first.
Sound is a
pressure wave, which consists of alternating periods of
compression and
rarefaction.
A noise-cancellation speaker emits a
sound wave with the same
amplitude
but with inverted phase (also known as
antiphase) to the original
sound. The waves combine to form a new wave, in a process called
interference, and
effectively cancel each other out – an effect which is called destructive
interference. Modern active noise control is generally achieved
through the use of analog circuits or digital signal processing.
Adaptive algorithms are designed to analyze the waveform of the
background aural or nonaural noise, then based on the specific
algorithm generate a signal that will either phase shift or invert the
polarity of the original signal. This inverted signal (in antiphase) is
then amplified and a transducer creates a sound wave directly
proportional to the amplitude of the original waveform, creating
destructive interference. This effectively reduces the volume of the
perceivable noise. A noise-cancellation speaker may be co-located with
the sound source to be attenuated. In this case it must have the same
audio power level as the source of the unwanted sound. Alternatively,
the transducer emitting the cancellation signal may be located at the
location where sound attenuation is wanted (e.g. the user's ear). This
requires a much lower power level for cancellation but is effective only
for a single user. Noise cancellation at other locations is more
difficult as the three-dimensional wavefronts of the unwanted sound
and the cancellation signal could match and create alternating zones
of constructive and destructive interference, reducing noise in some spots while doubling
noise in others. In small enclosed spaces (e.g. the passenger
compartment of a car) global noise reduction can be achieved via
multiple speakers and feedback microphones, and measurement of the
modal responses of the enclosure.
Active Noise Control is a method for reducing unwanted
sound by the
addition of a second sound specifically designed to cancel the first.
Sound is a
pressure wave, which consists of alternating periods of
compression and
rarefaction.
A noise-cancellation speaker emits a
sound wave with the same
amplitude
but with inverted phase (also known as
antiphase) to the original
sound. The waves combine to form a new wave, in a process called
interference, and
effectively cancel each other out – an effect which is called destructive
interference. Modern active noise control is generally achieved
through the use of analog circuits or digital signal processing.
Adaptive algorithms are designed to analyze the waveform of the
background aural or nonaural noise, then based on the specific
algorithm generate a signal that will either phase shift or invert the
polarity of the original signal. This inverted signal (in antiphase) is
then amplified and a transducer creates a sound wave directly
proportional to the amplitude of the original waveform, creating
destructive interference. This effectively reduces the volume of the
perceivable noise. A noise-cancellation speaker may be co-located with
the sound source to be attenuated. In this case it must have the same
audio power level as the source of the unwanted sound. Alternatively,
the transducer emitting the cancellation signal may be located at the
location where sound attenuation is wanted (e.g. the user's ear). This
requires a much lower power level for cancellation but is effective only
for a single user. Noise cancellation at other locations is more
difficult as the three-dimensional wavefronts of the unwanted sound
and the cancellation signal could match and create alternating zones
of constructive and destructive interference, reducing noise in some spots while doubling
noise in others. In small enclosed spaces (e.g. the passenger
compartment of a car) global noise reduction can be achieved via
multiple speakers and feedback microphones, and measurement of the
modal responses of the enclosure.Noise Control is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution or to reduce the impact of that noise, whether outdoors or indoors. Electronic Noise.
Cancel Noise without ear-blocking headphones using a behind-the-ear device that still achieves noise cancellation as good as the best headphones or earbuds available today. It involves combining wireless IoT networks with noise cancellation. A microphone is placed in the environment that senses sounds and sends them over wireless signals to an earpiece. Since wireless signals travel a million times faster than sound, the earphone can receive the sound information much faster than the actual sound itself. This is similar to lightning and thunder -- the lightning arrives much before the thunder, allowing people to prepare for the loud rumble, how this technology would work: The person who wants to cancel noise (Alice) would place the IoT microphone away from her, say on her office door. The noise from her coworkers' conversation in the hallway is picked up by this IoT device and transmitted to Alice's earpiece over a wireless connection. The actual sound arrives at the earpiece later, and because of this lead time, the noise can be fully canceled. As a result, it is no longer necessary to block the ear canal. Has a few limitations. The IoT microphone needs to be between the noise source and Alice. If noise is coming at her from all directions, a couple more IoT devices would need to be placed around her.
Noise (electronic errors) - Sound - Hearing
When does Noise become a Meaningful Message? Background noise is usually regarded as a nuisance that masks important sounds. But noise can convey information about important environmental conditions and allow animals to make informed decisions.
How to 3-D Print Your Own Sonic Tractor Beam
Silence is Good for You
Acoustic Camera - Sound Localization - Acoustic Location
Microphone Array is any number of microphones operating in tandem. There are many applications: Systems for extracting voice input from ambient noise (notably telephones, speech recognition systems, hearing aids). Surround sound and related technologies. Binaural recording. Locating objects by sound: acoustic source localization, e.g., military use to locate the source(s) of artillery fire. Aircraft location and tracking. High fidelity original recordings. Environmental Noise Monitoring. An omnidirectional (or nondirectional) microphone's response is generally considered to be a perfect sphere in three dimensions. In the real world, this is not the case. As with directional microphones, the polar pattern for an "omnidirectional" microphone is a function of frequency. The body of the microphone is not infinitely small and, as a consequence, it tends to get in its own way with respect to sounds arriving from the rear, causing a slight flattening of the polar response. This flattening increases as the diameter of the microphone (assuming it's cylindrical) reaches the wavelength of the frequency in question. Therefore, the smallest diameter microphone gives the best omnidirectional characteristics at high frequencies.
Radio Astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1932, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories observed radiation coming from the Milky Way.
Very Large Array is a centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy observatory located in central New Mexico on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, ~50 miles (80 km) west of Socorro. The VLA comprises twenty-seven 25-meter radio telescopes deployed in a Y-shaped array and all the equipment, instrumentation, and computing power to function as an interferometer. Each of the massive telescopes is mounted on double parallel railroad tracks, so the radius and density of the array can be transformed to adjust the balance between its angular resolution and its surface brightness sensitivity. Astronomers using the VLA have made key observations of black holes and protoplanetary disks around young stars, discovered magnetic filaments and traced complex gas motions at the Milky Way's center, probed the Universe's cosmological parameters, and provided new knowledge about the physical mechanisms that produce radio emission. Sonar.
Books about Environmental Awareness - Impacts - Solution
Some of the reading material and tools for the Environmental Education and Environmental Awareness Curriculum.
Understanding Environment Paperback – December 8, 2004 (amazon)
Protecting Public Health and the Environment: Implementing The Precautionary Principle Paperback – June 1, 1999 (amazon)
The Complete Idiot's Guide to Green Living Paperback – September 4, 2007 (amazon)
The Self-sufficient Life and How to Live It Hardcover – March 17, 2003 (amazon)
The Ecology of Commerce: A Declaration of Sustainability Paperback – June 3, 1994 (amazon)
Green to Gold: How Smart Companies Use Environmental Strategy to Innovate, Create Value, and Build Competitive Advantage Paperback – January 9, 2009 (amazon)
The Sustainability Revolution: Portrait of a Paradigm Shift Paperback – June 1, 2005 (amazon)
Living Without Electricity: People's Place Book No. 9 Hardcover – February 1, 1990 (amazon)
Easy Green Living: The Ultimate Guide to Simple, Eco-Friendly Choices for You and Your Home Paperback – April 1, 2008
Complete Guide to Reducing Energy Costs (Consumer Reports Complete Guide To...) Paperback – October 17, 2006
Earthship: How to Build Your Own, Vol. 1 Paperback – September, 1990 (amazon)
The Geography of Nowhere: The Rise and Decline of America's Man-Made Landscape Paperback – July 26, 1994
The Carbon Buster's Home Energy Handbook: Slowing Climate Change and Saving Money Paperback – November 1, 2006
How to Live a Low-Carbon Life: The Individual's Guide to Stopping Climate Change Paperback – March 30, 2007
The Carbon-Free Home: 36 Remodeling Projects to Help Kick the Fossil-Fuel Habit Paperback – July 15, 2008
Green from the Ground Up: Sustainable, Healthy, and Energy-Efficient Home Construction (Builder's Guide) Paperback – April 1, 2008
Cradle to Cradle: Remaking the Way We Make Things Paperback – April 22, 2002 (amazon)
Biomimicry: Innovation Inspired by Nature Paperback – September 17, 2002 (amazon)
Green Books
Related Pages - Green Car Ideas and Websites - Green News - Eco-Initiatives - Environmental Education - Recommended Documentaries and Films - Inspiration 101 - Green Building - Information Websites.
Environment Awareness Quotes - Sayings about the Environment
 We do not inherit the earth from our ancestors,
we borrow it from our children. (Native American Proverb)
We do not inherit the earth from our ancestors,
we borrow it from our children. (Native American Proverb)
Don't blow it - good planets are Hard to find. (Quoted in Time) - Seven Generations.
Nature provides a free lunch, but only if we control our appetites. (William Ruckelshaus Business Week, 18 June 1990).
All of humanity now has the option to "make it" successfully and sustainably, by virtue of our having minds, discovering principles and being able to employ these principles to do more with less. (Buckminster Fuller)
I think the environment should be put in the category of our national security. Defense of our resources is just as important as defense abroad. Otherwise what is there to defend? (Robert Redford, Yosemite National Park dedication, 1985)
Live within your Means - Living Modestly - Simplicity
The natural liberty of man is to be free from any superior power on earth, and not to be under the will or legislative authority of man, but to have only the law of nature for his rule. (John Locke)
What would be more inspiring then to begin the age of restoration, reweaving the wondrous diversity of life that still surrounds us? (Edward. O. Wilson)
You may think your actions are meaningless and that they won't help, but that is no excuse, you must still act.
(Mahatma Gandhi Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi)
Take only what you need and leave the land as you found it. (Arapaho)
We are made from Mother Earth and we go back to Mother Earth. (Shenandoah)
The wilderness is not just a home for every living thing on planet, it is everything that makes us human, it's our whole existence, and it's more than just a part of us, it is us.
So bleak is the picture... that the bulldozer and not the atomic bomb may turn out to be the most destructive invention of the 20th century. (Philip Shabecoff, New York Times Magazine, 4 June 1978)
Opie, you haven't finished your milk. We can't put it back in the cow, you know. (Frances Bavier, Aunt Bee Taylor, The Andy Griffith Show)
The activist is not the man who says the river is dirty. The activist is the man who cleans up the river. (Ross Perot)
It is horrifying that we have to fight our own government to save the environment. (Ansel Adams)
Take nothing but pictures. Leave nothing but footprints. Kill nothing but time. (Motto of the Baltimore Grotto, a caving society)
Humankind has not woven the web of life. We are but one thread within it. Whatever we do to the web, we do to ourselves. All things are bound together. All things connect. (Chief Seattle, 1855)
Every day is Earth Day. To demoralize the importance of protecting mother earth into an annual holiday is really ignorant. We have to except the fact that Every day is Earth Day, and not some holiday that makes you temporally aware.
I went to the woods because I wished to live deliberately and to front only the essential facts of life and learn what it had to teach, and did not want to wait till the end of my life just to discover that I had not lived. (Henry David Thoreau)
"Be the change you wish to see in the world." (Mahatma Gandhi)
If the success or failure of this planet, and of human beings, depended on how I am and what I do, how would I be? What would I do? (Buckminster Fuller)
It is now highly feasible to take care of everybody on Earth at a ‘higher standard of living than any have ever known.’ It no longer has to be you or me. Selfishness is unnecessary and henceforth unrationalizable as mandated by survival.
Humanity has the option to become successful on our planet if we reorient world production away from weaponry-- from killingry to livingry. Can we convince humanity in time? (Buckminster Fuller)
Some men see things as they are and say why? I dream of things that never were and say why not?
The time is out of joint: O cursed spite, That ever I was born to set it right! (Hamlet)
If you want things to improve in the world the first thing you have to do is make improvements in yourself, there is no other way. If you can’t be what you want the world to be you will never see improvements. Interpersonal intelligence.
Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. (Margaret Mead)
A human being is part of the whole, called by us "Universe," a part limited in time and space. He experiences himself, his thoughts and feelings as something separated from the rest - a kind of optical delusion of his consciousness. This delusion is a kind of prison for us, restricting us to our personal desires and to affection for a few persons nearest to us. Our task must be to free ourselves from this prison by widening our circle of compassion to embrace all living creatures and the whole [of] nature in its beauty. (Albert Einstein 1950)
"Creation manifests when balance is perfected between the opposites. By applying higher Law against lower laws, the Creation becomes divine." Summum - Philosophy.
Give a man a fish, and he can eat for a day. But teach a man how to fish, and he'll be dead of mercury poisoning inside of three years. (Charles Haas)
“When it occurs to a man that nature does not regard him as important, and that she feels she would not maim the universe by disposing of him, he at first wishes to throw bricks at the temple, and he hates deeply the fact that there are no bricks and no temples.” -- Stephen Crane, "The Open Boat".
The last 100 years has mostly been about exploration, but the next 100 years will be mostly about restoration. We have tried a million different things in a million different ways, and we will continue to use our creativity and our knowledge to advance our world, but now It's time choose the best of what we have accomplished and learned and stop wasting what the earth has given us on things that do not matter or things that do not provide us with stability. We can't continue to take more then we give. Because we now know that death and destruction will soon accelerate out of control and if we don't act appropriately and quickly, everything we ever cherish will die. - Liberation, Reservation, Celebration.
U.S. consumers and industry dispose of enough aluminum to rebuild the commercial air fleet every three months; enough iron and steel to continuously supply all automakers; enough glass to fill New York's World Trade Center every two weeks. (Environmental Defense Fund advertisement, Christian Science Monitor, 1990).
You go into a community and they will vote 80 percent to 20 percent in favor of a tougher Clean Air Act, but if you ask them to devote 20 minutes a year to having their car emissions inspected, they will vote 80 to 20 against it. We are a long way in this country from taking individual responsibility for the environmental problem. (William Ruckelshaus , former EPA administrator, New York Times, 30 November 1988)
We never know the worth of water 'til the well is dry."
"The frog does not drink up the pond in which he lives". (Sioux)
"Thousands have lived without love, not one without water"
You have to learn to understand the soil, what it needs and what it offers. The earth is our Mother and she’s the reason why we are all here. Take care of her and she’ll take care of you. And please don’t mind the occasional outbursts from Mother Nature,
she’s just reminding us that we should never take Life for Granted." Thank You Mom...(Howard Polley)
What we can tell so far is that Life is a Continuum and that we are all part of something really incredible. And Life, in a lot of ways, is not easily explainable. But one thing we do know is that humans have been blessed to have been given these amazing brains. So if we are ever going to understand all that we are, we would have to start using our brains. Brains are most likely the reason why humans have lasted so long on this earth. And brains will most likely be the reason why humans may ultimately avoid going extinct like the millions of other species who have lived before us.
Even if we are not the major contributor to this Mass Extinction, or to put it lightly "Climate Change", we can certainly counter act and possibly slow it down or even reverse some of the damage that has been done. We can also prepare ourselves for these changes instead of just sitting around watching 100's of millions of people die right in front of us. As all life forms have done before us, we will fight for our lives and we will not go down without a fight. It's time to start training our young, our survival depends on it. And we can start right now by spreading the word and informing people about the facts. People have always wanted to do what's right, but people need the necessary information and knowledge that will help them understand what is right. Luckily with all the Phones, TV's, Radios and News Papers that we have, we can communicate on a massive scale.
The number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. With the Permian Triassic Extinction Event taking up to 10 million years for the world to fully recover.
"As we have witnessed throughout our history, and also by learning how other animals survive, if we all live within our needs or means, we will, most of the time, have everything we need. And having everything you need for your entire life sounds pretty awesome."
 Every single little thing that you do in your life has an effect on the world, all your
actions causes something else to happen, that is what we call
cause and effect, that is life, that is science, that is
physics, that is a fact. Even the simple action of eating
food, if you consume
unhealthy food regularly, over time you will experience
negative effects, either reduced productivity, physical or mental
disabilities, disease or early death. Even if you live, the
fact that you supported an action that produced negative
effects throughout society and the world, you will still have
blood on your hands, and not just your own blood, but other
peoples blood as well. Your not just slowly killing yourself,
you are killing other people now and killing more people in the
future. Everyone needs to be aware of this Cause and effect
so that we can all stop treating ourselves and each other so
disrespectfully. There is no need for this. We can fix this. Let's get started.
Every single little thing that you do in your life has an effect on the world, all your
actions causes something else to happen, that is what we call
cause and effect, that is life, that is science, that is
physics, that is a fact. Even the simple action of eating
food, if you consume
unhealthy food regularly, over time you will experience
negative effects, either reduced productivity, physical or mental
disabilities, disease or early death. Even if you live, the
fact that you supported an action that produced negative
effects throughout society and the world, you will still have
blood on your hands, and not just your own blood, but other
peoples blood as well. Your not just slowly killing yourself,
you are killing other people now and killing more people in the
future. Everyone needs to be aware of this Cause and effect
so that we can all stop treating ourselves and each other so
disrespectfully. There is no need for this. We can fix this. Let's get started.
I Love the Wind
I love those cool gentle breezes on a hot summer day.
I love how the wind gives me that feeling of motion even when I'm standing still.
I love how the wind brushes against my skin, like mother nature is caressing me.
I love strong winds too, they seem to fill me with energy and enthusiasm, as if the wind is full of energy.
I love the wind.....except when it blows down my house of course.
Quote Pages - Activism Quotes - Inspiration Quotes - Life Quotes - Education Quotes - Writing Quotes - Adventure Quotes - Photography Quotes - Sports Quotes - Money Quotes - Environmental Education.
