BK101
Knowledge Base
Time
 Time
is the indefinite continued
progress
of
existence and
events that occur in apparently
irreversible succession from the
past
through the
present
to the future.
Time
is the indefinite continued
progress
of
existence and
events that occur in apparently
irreversible succession from the
past
through the
present
to the future.
Time Perception - Time is Relative - Time Travel - Time Saving
What does Time mean to a Human? Time is a tool that humans use to measure changes and predict events. Human time is based on one full rotation of the earth on it's axis and one full orbit around our sun, which are then scaled into readable numbers. Time is also measured by the speed of light. Time is a way of measuring biological decay so that we can measure how old something is and estimate how long our body will survive and how much time we have left in our lifetime. We can also use time to estimate how long matter and other molecules will last. Time comes in handy. There's a Time and Place for Everything. Time waits for no one, and temporary may be longer or shorter than you think. Time is of the Essence.
 Time is an Amount of Successive Moments considered as a resource under your
control and
sufficient enough to accomplish something.
An instance or single occasion for some event. A suitable
moment. Regulate or set the time of.
An indefinite period (usually marked by specific attributes or
activities). The
continuum of experience in which events pass from the future
through the present to the past.
A person's experience on a particular occasion. A reading
of a point in time as given by a clock.
The fourth coordinate that is required (along with
three spatial
dimensions) to specify a physical event
Rhythm as given by division into parts of equal duration. Measure the time or duration of an event or action or the person
who performs an action in a certain period of time. Assign a
time for an activity or event. Set the
speed,
duration, or execution of.
Adjust so that a force is applied and an
action occurs at the
desired time.
Time is an Amount of Successive Moments considered as a resource under your
control and
sufficient enough to accomplish something.
An instance or single occasion for some event. A suitable
moment. Regulate or set the time of.
An indefinite period (usually marked by specific attributes or
activities). The
continuum of experience in which events pass from the future
through the present to the past.
A person's experience on a particular occasion. A reading
of a point in time as given by a clock.
The fourth coordinate that is required (along with
three spatial
dimensions) to specify a physical event
Rhythm as given by division into parts of equal duration. Measure the time or duration of an event or action or the person
who performs an action in a certain period of time. Assign a
time for an activity or event. Set the
speed,
duration, or execution of.
Adjust so that a force is applied and an
action occurs at the
desired time. Seconds - Minutes - Days - Years - Clocks
Past is the time that has elapsed. Events which occurred before a given point in time. An earlier period in someone's life. History. Precede is to be earlier in time or to go back further or come before. To be the predecessor of something. To move ahead of others in time or space. Predecessor is someone who precedes you in time. Preceding is something existing before or coming before at an earlier time. To go back further in time.
Present is a period of time between the past and the future. Something existing now or happening now. The time that is associated with the events perceived directly and in the first time. Meantime.
Future are events or states that have not yet happened. The time yet to come or yet to be. What will happen in the time after the present. Futures arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics.
Medium Future is relating to a period of time that is neither very soon nor very far.
Long-Term is usually above 3 years, with medium-term usually between 1 and 3 years and short-term usually under 1 year.
Timeline of some of the things that will happen in the Near Future (wiki) - an incomplete list that leaves lot of things out, no vision.
Timeline of the Far Future (wiki) - an incomplete list that leaves a lot of things out, no vision.
Father Time is the indefinite continued progress of existence and events in the past, present, and future regarded as a whole. The personification of time, typically as an old man with a scythe and hourglass.
Forever
Forever is for a limitless time or a very long or seemingly endless time. Without interruption.
Eternity is time without end. A state of eternal existence believed in some religions to characterize the afterlife. A seemingly endless time interval (waiting).
Eternal is continuing forever or indefinitely. Having no beginning and no end in time. Lasting forever and existing at all times. Tiresomely long and seemingly without end. Eternal can also mean always true or valid.
Interminably is something happening all the time; seemingly without stopping.
Continuing is to move ahead and travel onward in time, space, place, position, or situation. To do something repeatedly and showing no intention to stop. Exist over a prolonged period of time or to continue after an interruption. Time Crystals.
Continuity is an uninterrupted connection or union. Detailed instructions in order to avoid discontinuities. The property of a continuous and connected period of time. Continuum - Steady State (sustainable).
Atoms - Infinity - Continuum - Time Travel - Time Perception
Permanent is something continuing or enduring without marked change in status or condition or place. Not capable of being reversed or returned to the original condition.
Permanence is the property of being able to exist for an indefinite duration. Lack of Chaos (consistency)
Protracted is lasting for a long time or longer than expected or usual. Lengthen in time; cause to be or last longer.
Prolong is to cause something to last longer. Lengthen in time or the extend in duration or space.
Indefinitely is something for an unlimited or unspecified period of time. To an indefinite extent or for an indefinite time.
Preservation is avoiding decay or loss. Thermodynamics - Food Preservation.
Perseveration is the tendency for a memory or idea to persist or recur without any apparent stimulus for it. The repetition of a particular response such as a word, phrase, or gesture regardless of the absence or cessation of a stimulus. The act of persisting or persevering; continuing or repeating behavior.
Perseverance is to continue or to keep repeating something of importance. Maintain.
Determination is deciding or controlling something's outcome or nature. Being determined to do or achieve something. Having firmness of purpose. Determining is to establish something after a calculation, investigation, experiment, research, inquiry, survey, or study in order to come to a decision, shape, influence or give direction to. Devoting your strength and concentrated attention to something important. Making up your mind about something and coming to terms. Goal.
Recurring - Repeating - Cycles
 Periodic is something
happening or
recurring at regular intervals.
Recurring or reappearing from time to time.
Periodic is something
happening or
recurring at regular intervals.
Recurring or reappearing from time to time.
Periodically is something that happens at regular time intervals or a definite length of time marked off by two instants.
Sleep - Reboot - Time Loop
Period is an amount of time. The interval taken to complete one cycle of a regularly repeating phenomenon. A unit of geological time during which a system of rocks formed. The end or completion of something.
Perennial is something recurring again and again. A self-renewal plant lasting for three seasons or more.
Triennially is something occurring at intervals three years apart.
Annual is a plant that completes its entire life cycle within a year, and must be replanted.
Succession is following of one thing after another in time. The action of following in order. The gradual and orderly process of change in an ecosystem brought about by the progressive replacement of one community by another until a stable climax is established. Successive is things happening in regular succession without gaps.
Duration is the period of time during which something continues. The property of enduring or continuing in time.
Cycles - Seasons - Rhythms - Reincarnation - Patterns - Schedule
Instant is a very short time, as the time it takes the eye to blink or the heart to beat. A particular point in time. Occurring with no delay.
Increment is the amount by which something increases. Increase by some amount or by one. A process of becoming larger or longer or more numerous or more important.
Interval is a definite length of time marked off by two instants. Interval in music is the difference in pitch between two notes. Interval in math is set containing all points or all real numbers between two given endpoints.
Duration - Time-Lapse
Interim is serving during an intermediate interval of time. The time between one event, process, or period and another.
Intermediate is lying between two extremes in time, space or state.
Intermittent is something occurring at irregular intervals, not continuous or steady.
Soon is something happening in the near future.
A Little While means that something will happen in a short time.
Jiffy is an informal term for any unspecified short period of time, as in "I will be back in a jiffy". From this it has acquired a number of more precise applications for short, very short, extremely short, ultra short or hyper short periods of time. First attested in 1785, the word's origin is unclear, though one suggestion is that it was thieves' cant for lightning.
Once in a Blue Moon is something that happens very rarely. The phrase refers to the appearance of a second full moon within a calendar month, which actually happens about every thirty-two months.
Predictions - Free Time - Spare Time - Time Management
Critical Path Method is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT).
Retroactively is something happening after the fact and affecting things in the past or taking effect from a date in the past. Descriptive of any event or stimulus or process that has an effect on the effects of events or stimuli or process that occurred previously. Ex post facto law.
Regulated is to fix or adjust the time, amount, degree, or rate of. Shape or influence; give direction to. Controlled or governed according to rule or principle or law. Principles or usage.
Destiny - Fate
Destiny is an event or a course of events that will inevitably happen in the future. Your overall circumstances or condition in life including everything that happens to you. Something's are not just random events, something's could just be fate because something's do happen for a reason.
Fate is the belief that certain events are destined to happen in a particular and are beyond a person's control because they are determined by a supernatural power or intervention. Sometimes bad things are also destined to happen, but you can still do something. Fatalism (pessimism) - Perception.
Predeterminism is the belief that all events of history, past, present and future, have been already decided or are already known, by either God, fate, or some other force, including human actions. Simulation Hypothesis.
Inevitably is something that is most likely to happen in the future, something that is impossible to avoid or evade. Inevitable is something incapable of being avoided or prevented. An unavoidable event. Invariably occurring or appearing. Adapt.
Meant to Be - Bebe Rexha (youtube) - If it's meant to be, it'll be, it'll be, Baby, just let it be.
Milestone is a significant event in your life or in a project. Baby Milestones (child development) - Milestone (project management).
Juncture is an event that occurs at a critical time. A particular point in events or time. A crisis situation or point in time when a critical decision must be made. The shape or manner in which things come together and a connection is made.
Temporary
Impermanence is the fact that all things are subject to decline and destruction, and permanence is mostly an illusion. Temporal things, whether material or mental, are compounded objects in a continuous change of condition. Though many things in life are in a cycle of death and rebirth, many things eventually disintegrate or fade away, but exactly where "away" is, is mostly undefined.
Entropy - Conservation of Mass - Transitions - Death
Temporal are things that are limited by time and of this world as opposed to the spiritual world.
Temporary is something that is intended to be not permanent or not lasting. Lacking continuity or regularity.
Transitory is something lasting a very short time.
Sand Mandala is a Tibetan Buddhist tradition involving the creation and destruction of mandalas or Sand Painting made from coloured sand. A sand mandala is ritualistically dismantled once it has been completed and its accompanying ceremonies and viewing are finished to symbolize the Buddhist doctrinal belief in the transitory nature of material life. Unhealthy Attachments. Dust in the Wind - Kansas (youtube). The material world is over rated, living forever is better.
Basic Units of Time - Time Language
 Second is defined as 1⁄86,400 of a day – this factor derived from the
division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to
60 seconds each. Another intuitive understanding is that it is about the
time between beats of a human heart.
Second is defined as 1⁄86,400 of a day – this factor derived from the
division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to
60 seconds each. Another intuitive understanding is that it is about the
time between beats of a human heart.Millisecond is a thousandth of a second. (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000). 100 milliseconds is one tenth of a second. Units of Time (wiki).
Microsecond equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is μs. (0.000001 or 10−6 or 1/1,000,000).
Picosecond is an SI unit of time equal to 10−12 or 1/1,000,000,000,000 (one trillionth) of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to approximately 31,689 years. Lasers.
Zeptosecond is a unit of time equal to 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 001 seconds, that is, 10−21 second, and with symbol zs.
A Zeptosecond stopwatch for the microcosm. Physicists have recorded an internal atomic event with an accuracy of a trillionth of a billionth of a second.
Attoseconds is a thousandths of a Femtosecond, or quintillionths of a second.
Minute is 60 Seconds. There are 1,440 minutes in one earth day. - Clocks
A second isn’t what you think it is. Scientifically, it’s not defined as 1/60th of a minute, but as “the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom”.
Hour is 60 Minutes or 1/24 of a day or 24 hours in one earth day. Sun Dial.
Day is equal to 24 hours or when Earth completes one rotation with respect to the Sun. There are 365 Days in a Year, which is when Earth makes one full Orbit around the Sun. Solar Time - Calendar.
Yesterday is the day immediately before today or the day preceding today. The recent past. Only a short time ago.
Today is the day that includes the present moment between yesterday and tomorrow. The present time or age.
Tomorrow is the day after today. The next day following the present day. The near future.
Week is 7 Days. There are 4 weeks in 1 Month. There are 12 months in 1 Year. There are 1,440 minutes in one day. There are 525,600 minutes in one year. Names of the days of the week origin and history (wiki). ISO 8601 (wiki).
Month is a unit of time, used with calendars, which is approximately as long as a natural period related to the motion of the Moon; A month and Moon are related and both derive from the same word in an ancestral language. The traditional concept arose with the cycle of moon phases; such months or lunations are synodic months and last approximately 29.531 days. From excavated tally sticks, researchers have deduced that people counted days in relation to the Moon's phases as early as the Paleolithic age.
Lunar Month is the time between two successive syzygies or new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Synodic Month is based on the Moon's orbital period with respect to the Earth-Sun line, and is still the basis of many calendars today, and are used to divide the year. Synodic month is the average period of the Moon's orbit with respect to the line joining the Sun and Earth. This is the period of the lunar phases, because the Moon's appearance depends on the position of the Moon with respect to the Sun as seen from the Earth. Tropical Month is customary to specify positions of celestial bodies with respect to the vernal equinox. Because of Earth's precession of the equinoxes, this point moves back slowly along the ecliptic. Therefore, it takes the Moon less time to return to an ecliptic longitude of 0° than to the same point amid the fixed stars: 27.321582 days (27 d 7 h 43 min 4.7 s). This slightly shorter period is known as the tropical month; compare the analogous tropical year. Anomalistic Month is the Moon's orbit approximates an ellipse rather than a circle. However, the orientation (as well as the shape) of this orbit is not fixed. In particular, the position of the extreme points (the line of the apsides: perigee and apogee), rotates once (apsidal precession) in about 3,233 days (8.85 years). It takes the Moon longer to return to the same apsis because it has moved ahead during one revolution. This longer period is called the anomalistic month and has an average length of 27.554551 days (27 d 13 h 18 min 33.2 s). The apparent diameter of the Moon varies with this period, so this type has some relevance for the prediction of eclipses (see Saros), whose extent, duration, and appearance (whether total or annular) depend on the exact apparent diameter of the Moon. The apparent diameter of the full moon varies with the full moon cycle, which is the beat period of the synodic and anomalistic month, as well as the period after which the apsides point to the Sun again. Sidereal Month is the period of the Moon's orbit as defined with respect to the celestial sphere of apparently fixed stars. Sun Dial.
Year is the orbital period of the Earth moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the Seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mean year) across the complete leap cycle of 400 years is 365.2425 days.
Great Year is the period of one complete cycle of the equinoxes around the ecliptic, about 25,800 years.
Light Year is about 5.9 trillion miles. Julian Year is a time interval of exactly 365.25 Earth days. Light.
Sidereal Time is a timekeeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time, it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coordinates in the night sky. Briefly, sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars that are light years away".
Aeon is a relatively long period of time.
Timeline of Earth History (our moment in the sun) - Ages - Knowledge Preservation
Orders of Magnitude in Reference to Time is a description of the quantity of a time in respect to comparison between differing magnitudes. In common usage, the scale is usually the base10 or base−10 exponent being applied to an amount, making the order of magnitude 10 times greater or smaller. As the differences are measured in factors of 10, a logarithmic scale is applied. In terms of time, the relationship between the smallest limit of time, the Planck time, and the next order of magnitude larger is 10.
The Primacy of Consciousness (youtube)
2 Kalpas constitute a day and night of Brahma, 8.64 billion human years. Hindu Units of Time (wiki).
Real-Time Types (wiki) - Real Time Monitoring
Space Time - Time Dilation
86,400 seconds in a day. (1+8=9) - 10,080 Minutes in a Day (1+8=9) - 525,600 Minutes in a Year. Number 9.
1,000 seconds is about 16 minutes. - A million seconds is about 11 days. - A billion seconds is about 32 years.
2012 Phenomenon was a range of eschatological beliefs that cataclysmic or otherwise transformative events would occur on or around 21 December 2012.
Clocks - Time Measuring - What Time is it
 Clocks
is an instrument to indicate time, keep time, and co-ordinate time. Any
device for measuring time and displaying the time.
Seconds - Minutes -
Hours.
Clocks
is an instrument to indicate time, keep time, and co-ordinate time. Any
device for measuring time and displaying the time.
Seconds - Minutes -
Hours.Automaton Clock is a type of striking clock featuring automatons. Clocks like these were built from the 1st century BC through to Victorian times in Europe. A Cuckoo clock is a simple form of this type of clock. The first known mention is of those created by the Roman engineer Vitruvius, describing early alarm clocks working with gongs or trumpets. Later automatons usually perform on the hour, half-hour or quarter-hour, usually to strike bells. Common figures in older clocks include Death (as a reference to human mortality), Old Father Time, saints and angels. In the Regency and Victorian eras, common figures also included royalty, famous composers or industrialists.
Mechanical Watch is a watch that uses a clockwork mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to quartz watches which function electronically via a small battery. A mechanical watch is driven by a mainspring which must be hand-wound periodically. Its force is transmitted through a series of gears to power the balance wheel, a weighted wheel which oscillates back and forth at a constant rate. A device called an escapement releases the watch's wheels to move forward a small amount with each swing of the balance wheel, moving the watch's hands forward at a constant rate. The escapement is what makes the 'ticking' sound which is heard in an operating mechanical watch. Mechanical watches evolved in Europe in the 17th century from spring powered clocks, which appeared in the 15th century. Mechanical watches are typically not as accurate as modern electronic quartz watches, and they require periodic cleaning by a skilled watchmaker. Since the 1970s, quartz watches have taken over most of the watch market, and mechanical watches are now mostly a high-end product, purchased for aesthetic reasons, for appreciation of their fine craftsmanship, or as a status symbol.
Clockwork refers to the inner workings of either mechanical machines called clocks (where it is also called the movement) or other mechanisms that work similarly, using a complex series of gears. A clockwork mechanism is often powered by a clockwork motor consisting of a mainspring, a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon. Energy is stored in the mainspring manually by winding it up, turning a key attached to a ratchet which twists the mainspring tighter. Then the force of the mainspring turns the clockwork gears, until the stored energy is used up. The adjectives wind-up and spring-powered refer to mainspring-powered clockwork devices, which include clocks and watches, kitchen timers, music boxes, and wind-up toys.
Movement in clockwork also known as a caliber, is the mechanism of a watch or timepiece, as opposed to the case, which encloses and protects the movement, and the face, which displays the time. The term originated with mechanical timepieces, whose clockwork movements are made of many moving parts. It is less frequently applied to modern electronic or quartz timepieces, where the word module is often used instead.
Horology is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clocks are all examples of instruments used to measure time. In current usage, horology refers mainly to the study of mechanical time-keeping devices, while chronometry more broadly includes electronic devices that have largely supplanted mechanical clocks for the best accuracy and precision in time-keeping. People interested in horology are called horologists. That term is used both by people who deal professionally with timekeeping apparatus (watchmakers, clockmakers), as well as aficionados and scholars of horology. Horology and horologists have numerous organizations, both professional associations and more scholarly societies. The largest horological membership organisation globally is the NAWCC, the National Association of Watch and Clock Collectors, which is USA based, but also has local chapters elsewhere.
Cuckoo Clock is typically a pendulum-regulated clock that strikes the hours with a sound like a common cuckoo's call and has an automated cuckoo bird that moves with each note. Some move their wings and open/close their beaks while leaning forward, whereas in others, only the bird's body leans forward. The mechanism to produce the cuckoo call has been in use since the middle of the 18th century and has remained almost without variation until the present.
Digital Clock is a type of clock that displays the time digitally (i.e. in numerals or other symbols), as opposed to an analogue clock, where the time is indicated by the positions of rotating hands. Digital clocks are often associated with electronic drives, but the "digital" description refers only to the display, not to the drive mechanism. (Both analogue and digital clocks can be driven either mechanically or electronically, but "clockwork" mechanisms with digital displays are rare). A digital watch keeps time using a quartz movement. A tiny piece of quartz crystal is cut into the shape of a tuning fork, which vibrates at 32,768 times per second when electricity from the watch battery is passed through it. A circuit in the watch then counts 1 second for every 32,768 vibrations. Digital clocks typically use the 50 or 65 hertz oscillation of AC power or a 32,768 hertz crystal oscillator as in a quartz clock to keep time. Most digital clocks display the hour of the day in 24-hour format; in the United States and a few other countries, a commonly used hour sequence option is 12-hour format (with some indication of AM or PM). Some timepieces, such as many digital watches, can be switched between 12-hour and 24-hour modes. Emulations of analog-style faces often use an LCD screen, and these are also sometimes described as "digital".
Quartz Clock is a clock that uses an electronic oscillator that is regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. This crystal oscillator creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks are at least an order of magnitude more accurate than mechanical clocks. Generally, some form of digital logic counts the cycles of this signal and provides a numeric time display, usually in units of hours, minutes, and seconds. The world's first quartz clock was built in 1927 by Warren Marrison and J. W. Horton at Bell Telephone Laboratories. The world's first quartz watch, however, was unveiled by Japanese watchmaker Seiko as the Astron in December 1969. Since the 1980s, when the advent of solid-state digital electronics allowed them to be made compact and inexpensive, quartz timekeepers have become the world's most widely used timekeeping technology, used in most clocks and watches as well as computers and other appliances that keep time.
Electronic Oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments (like calculators) and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games. Crystal Oscillator - Counters.
Time Clock is a device that records start and end times for hourly employees at a place of business.
Standard Time is the synchronization of clocks within a geographical area or region to a single time standard, rather than using solar time or a locally chosen meridian (longitude) to establish a local mean time standard.
Time Zone is a region of the globe that observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries of countries and their subdivisions because it is convenient for areas in close commercial or other communication to keep the same time.
On December 31, 2016, a "leap second" will be added to the world's clocks at 23 hours, 59 minutes and 59 seconds.
Can you really Turn Back Time?
Daylight Saving Time is the practice of advancing clocks during summer months so that evening daylight lasts longer, while sacrificing normal sunrise times. Typically, regions that use daylight saving time adjust clocks forward one hour close to the start of spring and adjust them backward in the autumn. In effect, DST causes a lost hour of sleep in the spring and an extra hour of sleep in the fall. AAA reports that Car Crashes rise 159 percent after Daylight Saving Time ends. AAA reports that Car Crashes rise 159 percent after Daylight Saving Time ends. Studies show that there is an increase in both heart attacks and road accidents the days after clocks are set forward one hour in Spring. Losing one hour of sleep disrupts the Body Clock. Being tired can decrease productivity, concentration and general well-being. Children may feel tired and cranky for several days after an hour's change in their bedtime routines. There doesn't seem to be any health benefits to daylight savings time, so what do we need it for? And do the reasons out weigh the adverse effects. Daylight Saving Time was instituted by corporate lobbies, not farmers. The US first enacted Daylight Saving Time during World War I, ostensibly to conserve energy by cutting down on the time people would artificially light their homes. Back when daylight saving was first enacted, “golf ball sales skyrocketed and there was a $200 million in additional sales of golf clubs and greens fees. Petroleum lobby was a keen supporter, because it has known since 1930 that daylight saving makes people drive their cars more in the evening—so they use more gasoline. The candy lobby was convinced an extra hour of evening light on Halloween would make kids collect more candy, and in turn get adults to buy more of it in anticipation.
A Norwegian island is campaigning to get rid of the concept of time, allowing residents to do “what we want, when we want”. The sun doesn’t rise in winter or set in summer on Sommaroy, leading most of the island’s 300 residents to back a bid for it to become the world’s first time-free zone. Kjell Ove Hveding, leader of the Time-Free Zone campaign, said the aim is to provide flexibility. Seasons - Time Perception.
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary Time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about 1 second of mean solar time at 0° longitude, and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. In some countries where English is spoken, the term Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is often used as a synonym for UTC.
Time Standard is a specification for measuring time: either the rate at which time passes; or points in time; or both. In modern times, several time specifications have been officially recognized as standards, where formerly they were matters of custom and practice. An example of a kind of time standard can be a time scale, specifying a method for measuring divisions of time. A standard for civil time can specify both time intervals and time-of-day. Standardized time measurements are made using a clock to count periods of some period changes, which may be either the changes of a natural phenomenon or of an artificial machine.
Atomic Clock is a clock device that uses an electronic transition frequency in the microwave, optical, or ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum of atoms as a frequency standard for its timekeeping element. Atomic clock ticks about a quadrillion times per second or 10 to the 15th.
Equation of Time describes the discrepancy between two kinds of Solar Time. The word equation is used in the medieval sense of "reconcile a difference". The two times that differ are the apparent solar time, which directly tracks the diurnal motion of the Sun, and mean solar time, which tracks a theoretical mean Sun with noons 24 hours apart. Apparent solar time can be obtained by measurement of the current position (hour angle) of the Sun, as indicated (with limited accuracy) by a sundial. Mean solar time, for the same place, would be the time indicated by a steady clock set so that over the year its differences from apparent solar time would resolve to zero. The equation of time is the east or west component of the analemma, a curve representing the angular offset of the Sun from its mean position on the celestial sphere as viewed from Earth. The equation of time values for each day of the year, compiled by astronomical observatories, were widely listed in almanacs and ephemerides.
History of Timekeeping Devices (wiki)
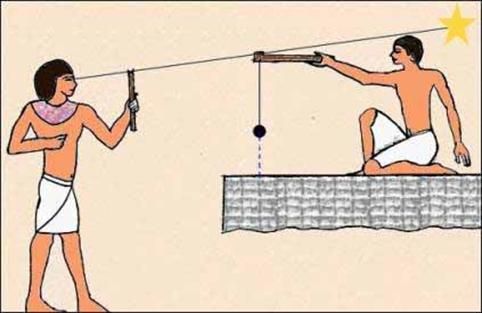 Merkhet
was an ancient timekeeping instrument. It involved the use of a bar with a
plumb line, attached to a wooden handle. It was used to track the
alignment of certain stars
which are known as Decans or "Baktiu" in the Ancient Egyptian Language, if
they were visible, in order to approximate the time at night (10 stars for
the 10 hours of the night, with a total of 24 hours including 12 hours for
the day, 1 hour for sunset, 1 hour for sunrise). In this way, it was more
efficient than other contemporary devices, such as
sundials, which were rendered useless at night
when it's dark. The exact design of the merkhet consists of a
horizontal bar, usually carved from wood or bone, with a plumb line
hanging from a transverse hole at one raised end of the bar, attached to a
controlling wooden handle. As deduced by texts and engravings on the inner
walls of the temples of Dendera and Edfu, the merkhet was typically used
in conjunction with a corresponding sighting tool, which the Egyptians
called a bay, itself made from a specially cut palm-rib with a sliced "V"
shape at one end. The two together could also be used, as appropriate, to
determine North. For the operation to work, two merkhets were required,
one aligned with Polaris, the North Pole star. If erected properly, and if
a bay was on hand, one could estimate quite accurately the time by
observing the transits of certain stars as they crossed the meridian and
came into alignment with the two merkhets.
Sextant.
Merkhet
was an ancient timekeeping instrument. It involved the use of a bar with a
plumb line, attached to a wooden handle. It was used to track the
alignment of certain stars
which are known as Decans or "Baktiu" in the Ancient Egyptian Language, if
they were visible, in order to approximate the time at night (10 stars for
the 10 hours of the night, with a total of 24 hours including 12 hours for
the day, 1 hour for sunset, 1 hour for sunrise). In this way, it was more
efficient than other contemporary devices, such as
sundials, which were rendered useless at night
when it's dark. The exact design of the merkhet consists of a
horizontal bar, usually carved from wood or bone, with a plumb line
hanging from a transverse hole at one raised end of the bar, attached to a
controlling wooden handle. As deduced by texts and engravings on the inner
walls of the temples of Dendera and Edfu, the merkhet was typically used
in conjunction with a corresponding sighting tool, which the Egyptians
called a bay, itself made from a specially cut palm-rib with a sliced "V"
shape at one end. The two together could also be used, as appropriate, to
determine North. For the operation to work, two merkhets were required,
one aligned with Polaris, the North Pole star. If erected properly, and if
a bay was on hand, one could estimate quite accurately the time by
observing the transits of certain stars as they crossed the meridian and
came into alignment with the two merkhets.
Sextant. Calendar is a system of organizing days for social, religious, commercial or administrative purposes. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months, and years. A date is the designation of a single, specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record (often paper) of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills. Periods in a calendar (such as years and months) are usually, though not necessarily, synchronized with the cycle of the sun or the moon. The most common type of pre-modern calendar was the lunisolar calendar, a lunar calendar that occasionally adds one intercalary month to remain synchronised with the solar year over the long term. History of Calendars. The calendar in most widespread use today is the Gregorian calendar, introduced in the 16th century by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of the Julian calendar, which was itself a modification of the ancient Roman calendar. The term calendar itself is taken from calendae, the term for the first day of the month in the Roman calendar, related to the verb calare "to call out", referring to the "calling" of the new moon when it was first seen. Latin calendarium meant "account book, register" (as accounts were settled and debts were collected on the calends of each month). The Latin term was adopted in Old French as calendier and from there in Middle English as calendery the 13th century (the spelling calendar is early modern).by the 13th century (the spelling calendar is early modern).
Calendar Date is a reference to a particular day represented within a calendar system. The calendar date allows the specific day to be identified. The number of days between two dates may be calculated. For example, "24 September 2019" is ten days after "14 September 2019" in the Gregorian calendar. The date of a particular event depends on the observed time zone. For example, the air attack on Pearl Harbor that began at 7:48 a.m. Hawaiian time on 7 December 1941 took place at 3:18 a.m. Japan Standard Time, 8 December in Japan. A particular day may be represented by a different date in another calendar as in the Gregorian calendar and the Julian calendar, which have been used simultaneously in different places. In most calendar systems, the date consists of three parts: the day of the month, the month, and the year. There may also be additional parts, such as the day of the week. Years are usually counted from a particular starting point, usually called the epoch, with era referring to the particular period of time (note the different use of the terms in geology). The most widely used epoch is a conventional birthdate of Jesus (which was established by Dionysius Exiguus in the sixth century). A date without the year may also be referred to as a date or calendar date (such as "2 September" rather than "2 September 2019"). As such, it defines the day of an annual event, such as a birthday on 31 May, holiday on 1 September, or Christmas on 25 December. Many computer systems internally store points in time in Unix time format or some other system time format. The date (Unix) command—internally using the C date and time functions—can be used to convert that internal representation of a point in time to most of the date representations shown here. The current date in the Gregorian calendar is 2 September 2019. If this is not really the current date, then click here to update it.
Leap Year is a calendar year containing one additional day (or, in the case of lunisolar calendars, a month) added to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical or seasonal year. Because seasons and astronomical events do not repeat in a whole number of days, calendars that have the same number of days in each year drift over time with respect to the event that the year is supposed to track. By inserting (also called intercalating) an additional day or month into the year, the drift can be corrected. A year that is not a leap year is called a common year.
Sundial is a device that tells the time of day when there is sunlight by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat plate (the dial) and a gnomon, which casts a shadow onto the dial. As the Sun appears to move across the sky, the shadow aligns with different hour-lines, which are marked on the dial to indicate the time of day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, though a single point or nodus may be used. The gnomon casts a broad shadow; the shadow of the style shows the time. The gnomon may be a rod, wire, or elaborately decorated metal casting. The style must be parallel to the axis of the Earth's rotation for the sundial to be accurate throughout the year. The style's angle from horizontal is equal to the sundial's geographical latitude. In a broader sense, a sundial is any device that uses the Sun's altitude or azimuth (or both) to show the time. In addition to their time-telling function, sundials are valued as decorative objects, literary metaphors, and objects of mathematical study. It is common for inexpensive, mass-produced decorative sundials to have incorrectly aligned gnomons and hour-lines, which cannot be adjusted to tell correct time. Navigation.
Solar Time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time or sundial time, and mean solar time or clock time. A sidereal day is the time it takes for a planet to complete a single rotation on its axis. A solar day is the time it takes for the Sun to return to the same place in the sky.
Subsolar Point is where the sun is perceived to be directly overhead in its zenith. Where the sun's rays are hitting the planet exactly perpendicular to its surface. It can also mean the point closest to the sun on an object in space, even though the sun might not be visible. Lahaina Noon is a tropical solar phenomenon when the Sun culminates at the zenith at solar noon, passing directly overhead (above the subsolar point).
Astronomical Clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets. The term is loosely used to refer to any clock that shows, in addition to the time of day, astronomical information. This could include the location of the sun and moon in the sky, the age and Lunar phases, the position of the sun on the ecliptic and the current zodiac sign, the sidereal time, and other astronomical data such as the moon's nodes (for indicating eclipses) or a rotating star map. The term should not be confused with astronomical regulator, a high precision but otherwise ordinary pendulum clock used in observatories. Astronomical clocks usually represent the solar system using the geocentric model. The center of the dial is often marked with a disc or sphere representing the earth, located at the center of the solar system. The sun is often represented by a golden sphere (as it initially appeared in the Antikythera Mechanism, back in the 2nd century BC), shown rotating around the earth once a day around a 24-hour analog dial. This view accorded both with the daily experience and with the philosophical world view of pre-Copernican Europe. Prague Astronomical Clock (wiki).
Beat the Clock is a television game show that involves people trying to complete challenges to win prizes while faced with a time limit.
Time Limit is a limit of time within which something must be done. A time limit or deadline is a narrow field of time, or a particular point in time, by which an objective or task must be accomplished. Once that time has passed, the item may be considered overdue (e.g., for work projects or school assignments). Time Management.
Hourglass is a device used to measure the passage of time. It comprises two glass bulbs connected vertically by a narrow neck that allows a regulated trickle of material (historically sand) from the upper bulb to the lower one. Factors affecting the time interval measured include sand quantity, sand coarseness, bulb size, and neck width. Hourglasses may be reused indefinitely by inverting the bulbs once the upper bulb is empty. Depictions of hourglasses in art survive in large numbers from antiquity to the present day, as a symbol for the passage of time.
Countdown is a sequence of backward counting to indicate the time remaining before an event is scheduled to occur.
Timer is a specialized type of clock used for measuring specific time intervals. Timers can be categorized into two main types. A timer which counts upwards from zero for measuring elapsed time is often called a stopwatch, while a device which counts down from a specified time interval is more usually called a timer. A simple example of this type is an hourglass. Working method timers have two main groups: Hardware and Software timers. Most timers give an indication that the time interval that had been set has expired. Time switches, timing mechanisms which activate a switch, are sometimes also called "timers".
Time Lapse - Frame Rate Frequency
Time-Lapse Photography is a technique whereby the frequency at which film frames are captured is much lower than that used to view the sequence. When played at normal speed, time appears to be moving faster and thus lapsing.
Frame Rate - Flowers Time Lapse (youtube)
Hyperlapse is a technique in time-lapse photography that allows the photographer to create motion shots. In its simplest form, a hyperlapse is achieved by manually moving the camera a short distance between each shot.
Lapse is a break or intermission in the occurrence of something. High-Speed Microscope.
Slit Scanning is an editing technique where each pixel row is delayed one frame more than the row below it.
Slow Motion is an effect in film-making whereby time appears to be slowed down. Hibernation.
Fast Forward is to move forward through a recording at a speed faster than that at which it would usually be played. Move forward in time at a faster than normal rate, e.g. to skip quickly to a later point when viewing or listening to a recording. Shift attention or focus to a later point in time. Entropy - Automaton.
In Real Time is something that happens at the present time and at normal speed. Something displayed nearly simultaneously when it is occurring. A live broadcast at the moment you are watching it.
Broadcast Delay is an intentional delay when broadcasting live material. Such a delay may be as short as seven seconds to prevent mistakes or unacceptable content from being broadcast. Longer delays lasting several hours can also be introduced so that the material is aired at a later scheduled time such as the prime time hours to maximize viewership. Tape delays lasting several hours can also be edited down to remove filler material or to trim a broadcast to the network's desired run time for a broadcast slot, but this isn't always the case.
Sound Recording and Reproduction is an electrical, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording.
Reverse is turning in the opposite direction or going back in time. Time Travel - Memory - Flash Back.
Instant Replay is a video reproduction of something that recently occurred which was both shot and broadcast live. The video, having already been shown live, is replayed in order for viewers to see again and analyze what had just taken place. Sometimes it's a slow motion replay so that it can be more accurately analyzed so that rulings can be reviewed by officials or challenged by coaches. Time Travel.
High-Speed Photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast. Macro Room (youtube).
High-Seed Camera is a device capable of capturing moving images with exposures of less than 1/1,000 second or frame rates in excess of 250 frames per second.
High-Speed 'Electron Camera' films Molecular Movie in HD.
High-Speed Surveillance in Solar Cells catches recombination red-handed. Using synchronized lasers pulses, researchers developed a new method of electrostatic force microscopy that can record movies with frames as fast as 300 nanoseconds. This is fast enough to watch electrons move inside solar cells, which can lead to more efficient solar power devices.
T-CUP is the world's Fastest Camera, capable of capturing 10 trillion Frames Per Second. Compressed ultrafast photography system using ultra-short pulses in the femtosecond range (10-15 s), combined with the image acquired it uses the Femtosecond streak camera, which is far too short to visualize, but it makes it possible to freeze time and create extremely slow motion images. Streak Camera is an instrument for measuring the variation in a pulse of light's intensity with time. They are used to measure the pulse duration of some ultrafast laser systems and for applications such as time-resolved spectroscopy and LIDAR.
The World's Fastest Camera. At 70 trillion frames per second, it's fast enough to document nuclear fusion and radioactive molecule decay. Wang's technique, which he calls compressed ultrafast spectral photography (CUSP), uses short pulses of laser light that each last for just one femtosecond, or one quadrillionth of a second. It's easiest to think of the advanced process in two steps: imaging and illumination.
Ultrafast camera films 3-D movies at 100 billion frames per second. In his quest to bring ever-faster cameras to the world, Caltech's Lihong Wang has developed technology that can reach blistering speeds of 70 trillion frames per second, fast enough to see light travel. Just like the camera in your cell phone, though, it can only produce flat images.
Studying chaos with one of the world's fastest cameras. Ultrafast camera technology might aid in the study of unpredictable systems. The camera makes use of a technology called compressed ultrafast photography.
Burst Mode in photography is when several photographs are captured in quick succession by either pressing the shutter button or holding it down.
Watching a video twice the playback speed or 2X Speed, is sometimes more effective for learning than watching it at normal playback speed. Information can be delivered a lot slower than we are capable of processing it, by speeding videos up you will consume more information, remember it better, and be less bored, and save time. TED Video Option.
1x speed is a video at normal speed. 2x speed would play a video twice as quickly. Lawn Mower Man.
Most of us speak at the rate of about 125 words per minute. However, we have the mental capacity to understand someone speaking at 400 words per minute, if that were possible. Speed Reading.
Clock Rate typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses, which are used to synchronize the operations of its components, and is used as an indicator of the processor's speed.
Space Time - Time and Space
Spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single interwoven continuum, which is an involving gradual quantitative transitions without abrupt changes or discontinuities.
Space-Time Continuum is a mathematical model that joins space and time into a single idea called a continuum. This four-dimensional continuum is known as Minkowski space, which is a four-dimensional manifold that has four dimensions: three dimensions of space (x, y, z) and one dimension of time.
Continuum as a measurement explains variation as involving gradual quantitative transitions without abrupt changes or discontinuities. In contrast, categorical theories or models explain variation using qualitatively different states.
Continuum is a continuous nonspatial whole or extent or succession in which no part or portion is distinct or distinguishable from adjacent parts. Continuity.
Continuous is something continuing in time or space without interruption. A function or curve that is extending without break or irregularity. Eternity.
Continuing is to move ahead and travel onward in time or space. Something remaining in force or being carried on without letup. To continue a certain state, condition, or activity. To keep or maintain something in unaltered condition and cause to remain or last.
Space-Time Crystal is a structure periodic in time and space. It extends the idea of a crystal to four dimensions. Analogues of the space-time crystal have been made that are in a non-equilibrium state that needs an external drive to repeat in time.
Spacetime Symmetries are features of spacetime that can be described as exhibiting some form of symmetry. The role of symmetry in physics is important in simplifying solutions to many problems. Spacetime symmetries are used in the study of exact solutions of Einstein's field equations of general relativity.
Theory of Relativity usually encompasses two interrelated theories by Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. Special relativity applies to all physical phenomena in the absence of gravity. General relativity explains the law of gravitation and its relation to other forces of nature. It applies to the cosmological and astrophysical realm, including astronomy.
General Relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time, or spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of partial differential equations.
Special Relativity describes how time and space are not absolute concepts. Time or light is relative depending on the speed of the observer. Time dilates, or slows down, the faster a person is moving in any direction. Time is flexible depending on your speed. If you are moving extremely fast, time will become slower, but to you everything will seem to be normal. If the Sun turned off, people on earth would know in 8 minutes, but if someone was on Pluto, they will not know that the sun turned off for 5 hours. We should not limit ourselves to only seeing things from the human perspective. From other perspectives outside the human experience, there can be several ways at looking at something and several ways of understanding something. There are known differences between each human, and everyone sees things a little different. But we can not assume that humans are the only ones who can see. So we should classify things that are known to be relative between humans, and we should also classify things that are not known, things that are from a non-human perspective. Special Relativity is the generally accepted and experimentally well-confirmed physical theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original pedagogical treatment, it is based on two postulates: The laws of physics are invariant (i.e., identical) in all inertial systems (i.e., non-accelerating frames of reference). The speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers who are in the vacuum, regardless of the motion of the light source. Relativistic Equations (wiki).
Relativity of Simultaneity is the concept that distant simultaneity, whether two spatially separated events occur at the same time, is not absolute, but depends on the observer's reference frame. Everything is relative. Time Dilation.
Galilean Invariance or Galilean Relativity states that the laws of motion are the same in all inertial frames. Galileo Galilei first described this principle in 1632 in his Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems using the example of a ship travelling at constant velocity, without rocking, on a smooth sea; any observer below the deck would not be able to tell whether the ship was moving or stationary.
Principle of Relativity is the requirement that the equations describing the laws of physics have the same form in all admissible frames of reference. For example, in the framework of special relativity the Maxwell equations have the same form in all inertial frames of reference. In the framework of general relativity the Maxwell equations or the Einstein field equations have the same form in arbitrary frames of reference. Several principles of relativity have been successfully applied throughout science, whether implicitly (as in Newtonian mechanics) or explicitly (as in Albert Einstein's special relativity and general relativity.
Relativistic Mechanics refers to mechanics compatible with special relativity (SR) and general relativity (GR). It provides a non-quantum mechanical description of a system of particles, or of a fluid, in cases where the velocities of moving objects are comparable to the speed of light c. As a result, classical mechanics is extended correctly to particles traveling at high velocities and energies, and provides a consistent inclusion of electromagnetism with the mechanics of particles. This was not possible in Galilean relativity, where it would be permitted for particles and light to travel at any speed, including faster than light. The foundations of relativistic mechanics are the postulates of special relativity and general relativity. The unification of SR with quantum mechanics is relativistic quantum mechanics, while attempts for that of GR is quantum gravity, an unsolved problem in physics. As with classical mechanics, the subject can be divided into "kinematics"; the description of motion by specifying positions, velocities and accelerations, and "dynamics"; a full description by considering energies, momenta, and angular momenta and their conservation laws, and forces acting on particles or exerted by particles. There is however a subtlety; what appears to be "moving" and what is "at rest"—which is termed by "statics" in classical mechanics—depends on the relative motion of observers who measure in frames of reference.
The Speed of Light is a constant in our Universe. Though time in motion slows down time and strong gravity slows down time, light is mostly a constant, as far as we can see of course. Light Clock.
One Light Year is about 5.9 trillion miles, which is the distance that light travels in a vacuum, which is one Julian year or 365.25 days. What does a day mean to someone who never lived on Earth? What is a year? What is a mile? What is reality? You could being a one foot ruler and say light travels 983,571,056.4304 feet per second (9.836e+8). Then they would say, what is a million and what is a second? Voyager One?
Absolute Space and Time is a concept in physics and philosophy about the properties of the universe. In physics, absolute space and time may be a preferred frame.
Preferred Frame is usually a special hypothetical frame of reference in which the laws of physics might appear to be identifiably different (simpler) from those in other frames. In theories that apply the principle of relativity to inertial motion, physics is the same in all inertial frames, and is even the same in all frames under the general principle of relativity.
Inertial Frame of Reference is a frame of reference in which bodies, whose net force acting upon them is zero, are not accelerated; that is they are at rest or they move at a constant velocity in a straight line. In analytical terms, it is a frame of reference that describes time and space homogeneously, isotropically, and in a time-independent manner. Conceptually, in classical physics and special relativity, the physics of a system in an inertial frame have no causes external to the system. An inertial frame of reference may also be called an inertial reference frame, inertial frame, Galilean reference frame, or inertial space. All inertial frames are in a state of constant, rectilinear motion with respect to one another; an accelerometer moving with any of them would detect zero acceleration. Measurements in one inertial frame can be converted to measurements in another by a simple transformation (the Galilean transformation in Newtonian physics and the Lorentz transformation in special relativity). In general relativity, in any region small enough for the curvature of spacetime and tidal forces to be negligible, one can find a set of inertial frames that approximately describe that region. In a non-inertial reference frame in classical physics and special relativity, the physics of a system vary depending on the acceleration of that frame with respect to an inertial frame, and the usual physical forces must be supplemented by fictitious forces. In contrast, systems in non-inertial frames in general relativity don't have external causes, because of the principle of geodesic motion. In classical physics, for example, a ball dropped towards the ground does not go exactly straight down because the Earth is rotating, which means the frame of reference of an observer on Earth is not inertial. The physics must account for the Coriolis effect—in this case thought of as a force—to predict the horizontal motion. Another example of such a fictitious force associated with rotating reference frames is the centrifugal effect, or centrifugal force.
Our universe, space and time first started when there was energy that could move at the speed of light (c) and energy with resting mass (that includes planets, electrons, you/me, etc.). The difference in speed creates what we perceive as a temporal dimension where resting mass is always trying to catch up to the speed of light. The gap between the 2 types of energy is called 3D space. Time slows the faster you move until the point when you get to the speed of light (c) and time stops. It no longer moves forward or backward. This is time dilation and helps prove this is true. Because stuff with resting mass can never catch up the process is ongoing and fast moving energy continues to speed away in all directions, creating more space. This also explains the arrow of time and helps explain gravity as being a decrease in the expansion of or collapse of space.
A Brief History of Time is a popular-science book on cosmology (the study of the universe) by British physicist Stephen Hawking. It was first published in 1988. Hawking wrote the book for nonspecialist readers with no prior knowledge of scientific theories. In A Brief History of Time, Hawking writes in non-technical terms about the structure, origin, development and eventual fate of the universe, which is the object of study of astronomy and modern physics. He talks about basic concepts like space and time, basic building blocks that make up the universe (such as quarks) and the fundamental forces that govern it (such as gravity). He writes about cosmological phenomena such as the Big Bang and black holes. He discusses two major theories, general relativity and quantum mechanics, that modern scientists use to describe the universe. Finally, he talks about the search for a unifying theory that describes everything in the universe in a coherent manner. The book became a bestseller and sold more than 10 million copies in 20 years. It was also on the London Sunday Times bestseller list for more than five years and was translated into 35 languages by 2001. Stephen Hawking Extended Interview: Last Week Tonight with John Oliver (HBO) (youtube)
Philosophy of Space and Time is the branch of philosophy concerned with the issues surrounding the ontology, epistemology, and character of space and time. While such ideas have been central to philosophy from its inception, the philosophy of space and time was both an inspiration for and a central aspect of early analytic philosophy. The subject focuses on a number of basic issues, including whether time and space exist independently of the mind, whether they exist independently of one another, what accounts for time's apparently unidirectional flow, whether times other than the present moment exist, and questions about the nature of identity (particularly the nature of identity over time).
Wormhole or Spacetime Bridge, is a shortcut connecting two separate points in spacetime. Time Perception.
Time Translation Symmetry is a mathematical transformation in physics that moves the times of events through a common interval. Time translation symmetry is the hypothesis that the laws of physics are unchanged, (i.e. invariant) under such a transformation. Time translation symmetry is a rigorous way to formulate the idea that the laws of physics are the same throughout history. Time translation symmetry is closely connected, via the Noether theorem, to conservation of energy. In mathematics, the set of all time translations on a given system form a Lie group. There are many symmetries in nature besides time translation, such as spatial translation or rotational symmetries. These symmetries can be broken and explain diverse phenomena such as crystals, superconductivity, and the Higgs mechanism. However, it was thought until very recently that time translation symmetry could not be broken. Time crystals, a state of matter first observed in 2017, break time translation symmetry.
Noether's Theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system has a corresponding conservation law.
Invariant in physics is an observable of a physical system which remains unchanged under some transformation. Invariance, as a broader term, also applies to the no change of form of physical laws under a transformation, and is closer in scope to the mathematical definition. Invariants of a system are deeply tied to the symmetries imposed by its environment. Invariance is an important concept in modern theoretical physics, and many theories are expressed in terms of their symmetries and invariants.
What happens when you look up and see a ball headed toward you? Without even thinking about it, you flinch. That might be because our brains are constantly living our lives in fast-forward, playing out the action in our head before it happens.
Time Travel
Time Travel is the hypothetical idea that a person can travel back in time into the past or travel forward in time into the future. Time travel is the concept of a human being having the ability to move between certain points in time or move between different points in space. The ability to time travel is usually imagined when someone builds a hypothetical device known as a time machine that can enter a portal that connects distant points in time. Sometimes a time machine is imagined as a vehicle.
Reverse Motion is a visual effect in which reversing the order of the frames of a film or video makes time appear to run backward. A special effect in cinematography whereby the action that is filmed is shown backwards. Special effect are illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, video game, and simulator industries to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual world.
Reverse tape effects is an audio effect in which reversing the direction of an audio recording renders sounds backward.
T-symmetry or time reversal symmetry is the expected symmetry of physical laws independent of whether time runs forward or backward. T-Symmetry is the theoretical symmetry of physical laws under a time reversal transformation. Particles.
Time Reversibility is the ability of some processes to operate in either direction of time. Space Travel.
Time Reversal Signal Processing is a technique for focusing acoustic and electromagnetic waves by reversing in time a system's response signals.
If you could separate time from space, then what time would it be when you got there? Being here now is not the same as now somewhere else. Time and Space are linked together, so what happens when you unlink time and space?
Everyone is a Time Traveler. You time travel when you think about your past memories. You time travel when you think about past events in history. You time travel when you plan for the future. You time travel when you talk to someone younger or older then you. You time travel when you look at the stars at night. Second chances happen all the time, it's called learning from mistakes. I travel more now then I ever did. I travel into the future, I travel into the past, and then I travel back into the present to document my findings. Time Travel is real, as long as you learn not to associate time traveling with your physical self, like they portray in the movies, which is totally inaccurate and misleading. But movies themselves are a form of time travel, just like books, photos, TV, instant replay, time-lapse photography, fossils and stories. I am a time traveler, and I spend a lot of time in the future, but the weird part is, I have a feeling that I'm not alone. Many things in Life are traveling at different speeds, which depends on their size, their locations, the type of wave, frequency and their molecular properties. And these varying speeds is one of the reasons that makes life happen. And intelligent life such as humans can witness and interact with these varying speeds. Maybe time travel is a one way trip. Are you willing to abandon your time period for another time period that you know little about, without a chance to return?
Books about Time Travel (wiki) - Movies about Time Travel - Back To The Future (1985), Primer (2004), Groundhog Day (1993), Time Bandits (1981), Terminator 2: Judgement Day (1991), Donnie Darko (2001), Looper (2012), 12 Monkeys (1995), Bill & Ted’s Excellent Adventure (1989), Timecop (1994), Flight of the Navigator (1986), Edge of Tomorrow (2014), The Time Machine (1960), Hot Tub Time Machine (2010), Escape from the Planet of the Apes (1971), X-Men Days of Future’s Past (2014), Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home (1986), Star Trek Generations (1994), Avengers: Endgame (2019) - "If you travel back in time into the past, that past becomes your new future, and your former present self becomes the past, which can't be changed by your new future." Quantum Leap was a TV show that portrayed a physicist who leaps through spacetime during an experiment in time travel, by temporarily taking the place of other people to correct historical mistakes. Dean Stockwell co-stars as Admiral Al Calavicci, Sam's womanizing, cigar-smoking companion and best friend, who appears to him as a hologram.
Time Loop is a plot device in which periods of time are repeated and re-experienced by the characters, and there is often some hope of breaking out of the cycle of repetition. Time loop is sometimes used to refer to a causal loop; although they appear similar, causal loops are unchanging and self-originating, whereas time loops are constantly resetting: when a certain condition is met, such as a death of a character or a clock reaches a certain time, the loop starts again, with one or more characters retaining the memories from the previous loop. Stories with time loops commonly center on the character learning from each successive loop through time. Time Loop Movies.
Chronostasis is a type of temporal illusion in which the first impression following the introduction of a new event or task demand to the brain appears to be extended in time. For example, chronostasis temporarily occurs when fixating on a target stimulus, immediately following a saccade (i.e., quick eye movement). This elicits an overestimation in the temporal duration for which that target stimulus (i.e., postsaccadic stimulus) was perceived. This effect can extend apparent durations by up to 500 ms and is consistent with the idea that the visual system models events prior to perception.
Spatial Intelligence - Space and the Universe
Temporal Pincer is a time-bending tactical technique for missions: you approach it moving forward in time, and then also approach it in reverse moving backwards from the future – each side using the knowledge that the other side gained from having already experienced it. Temporal is relating to time or limited by time. Pincer Movement is a military attack by two coordinated forces that close in on an enemy position from different directions.
Temporal Paradox or time travel paradox is a paradox, an apparent contradiction, or a logical contradiction that is associated with the idea of time and time travel. Temporal paradoxes fall into two broad groups: consistency paradoxes exemplified by the grandfather paradox; and causal loops.
Time Warp is the idea of changing the past is logically contradictory, and results in a grandfather paradox, which is a paradox of time travel in which inconsistencies emerge through changing the past. The name comes from the paradox's common description as a person who travels to the past and kills their own grandfather, preventing the existence of their father or mother and therefore their own existence. Any inconsistency in past events may be regarded as a grandfather paradox.
Time Perception
Autonoetic Consciousness is the human ability to mentally place ourselves in the past, in the future, or in counterfactual situations, and to thus be able to examine our own thoughts. Our sense of self affects our behavior, in the present, past and future. It relates to how we reflect on our own past behavior, how we feel about it, and this in turn determines if we do it again.
You Can't Change the Past, but you can change how you react to past events, and you can change how you remember past events, and you can also change which events in the past that you remember the most. If you want to change the past, you have to make changes in the present that will change your future, so that in the future, when you or other people remember your past, they will see more than just the horrible moments that happened in your life, but they will also see all the other great moments that happened in your life. We are not defined by past events, we are defined by what we have learned from past events, and how we adapted to the present. Knowledge Preservation.
What if you could travel back in time and talk to yourself when you were just 10 years old, what would you say and what advice would you give? "Hey dude I'm you 50 years from now in the future, I have to warn you, there is so much you still don't know and schools are not teaching everything that you need to know. And some of the things that you think you know, are actually wrong and not true. But your ignorance is not your fault, you didn't learn how important learning is or did you have access to the most valuable knowledge and information that you need to fully understand yourself and the world around you. So here is all the knowledge and information that I have accumulated so far in 50 years which will save you a lot of time and also reduce the mistakes that you don't need to make. Even 50 years from now there will still be many things to learn, so never stop learning. Good Luck and never forget how important you are, you are not alone, and you will always be loved, always."
When your future self is talking shit about you, let your future self know that the jokes on them, because you're going to ruin their life, and your future self will not be able to talk shit about you in the future. So take that my future self, time travel rules. Oh wait, forget that. I love you future self, please tell me the things that I'm doing wrong so that I can correct my mistakes now. I want my future self to say "I love you", and say "You did it you crazy bastard, you freaking did it. I'm not going to tell you your future or influence your decisions now, all can say is thanks for everything that you did and thanks for everything that you didn't do."
A lot of people said that if they had a chance to travel back in time they would kill Hitler. But if you were intelligent, you would go back in time to educate Hitler instead of killing him. Then he could have educated others. So by time that you are born, all the problems in the world would be solved. So that means that every person alive has the ability to time travel, they just have to choose the time they want to live in and understand that everything that they do now will affect their future self. But the reality is, it's not just you who gets affected by your past actions, it's everyone else and everything else that gets affected by your past actions.
What if you could go back in time to stop wars and crimes from happening? You can see the future, so you can also stop wars and crimes from happening. You might not know the exact day or how, but you know what causes wars and crimes, which is the ignorance of men. When we educate men more fully, then intelligent men will not start wars or commit crimes.
Time relates to motion of matter within space. Take away the matter, and there are no properties for time to measure, or time relative to the matter. The space may be infinite and may exist whether or not matter existed within it. Time and space may be already separate, as time itself is merely a concept to measure distance between between material objects and their related velocities. Concepts of space and time are linked by common dependence on the existence of objects. Every object is also a concept that is scale dependent with arbitrarily defined boundaries in both space and time. But every concept only has meaning in relation to all other concepts. No concept stands on it own. It is impossible also to think of a single thing as an object without a subject or a subject without an object. There two types of time, universal time which runs as a backdrop to everything which as yet we do not understand fully. Then relative time which man instigated and uses. Objects in space are described as three dimensional and can be measured, relative to their height, width and depth.
Scientists say the universe is expanding, expanding into what? Something of course is outside the universe, something much larger than the universe itself. So let's imagine standing outside the universe, and the universe is the size of a basketball. So if you were larger than the universe you could take a person from one end of the universe and transfer them to the other side of the universe. Maybe using a syringe like device, which would make it look like a wormhole to us. To this person outside the universe all time would exist always simultaneously. Time would be just a record of a particular moment that is saved within the universe like a hard drive.
Zeno's Arrow Paradox. If everything when it occupies an equal space is at rest, and if that which is in locomotion is always occupying such a space at any moment, the flying arrow is therefore motionless. (as recounted by Aristotle, Physics VI:9, 239b5). In the arrow paradox (also known as the fletcher's paradox), Zeno states that for motion to occur, an object must change the position which it occupies. He gives an example of an arrow in flight. He states that in any one (duration-less) instant of time, the arrow is neither moving to where it is, nor to where it is not. It cannot move to where it is not, because no time elapses for it to move there; it cannot move to where it is, because it is already there. In other words, at every instant of time there is no motion occurring. If everything is motionless at every instant, and time is entirely composed of instants, then motion is impossible. Whereas the first two paradoxes divide space, this paradox starts by dividing time—and not into segments, but into points. Paradox of Place From Aristotle: If everything that exists has a place, place too will have a place, and so on ad infinitum. Dessa - Fighting Fish (youtube).
Arrow of Time involves the "one-way direction" or "asymmetry" of time. This direction can be determined by studying the organization of atoms, molecules, and bodies, and might be drawn upon a four-dimensional relativistic map of the world.
Time is not absolute. There for there could be no time travel machine, only a time difference, or a perceived difference in time.
Absolute is perfect or complete or pure. Complete and without restriction or qualification; sometimes used informally as intensifiers. Expressing finality with no implication of possible change. Not capable of being violated or infringed. Something that is conceived or that exists independently and not in relation to other things; something that does not depend on anything else and is beyond human control; something that is not relative. Not limited by law.
All Time Exists all at once All the Time. The Past, Present And Future exist all at once simultaneously. Everyone is always alive.
The illusion of time : past, present and future all exist together (youtube)
Eternalism is a philosophical approach to the ontological nature of time, which takes the view that all existence in time is equally real, as opposed to presentism or the growing block universe theory of time, in which at least the future is not the same as any other time. Some forms of eternalism give time a similar ontology to that of space, as a dimension, with different times being as real as different places, and future events are "already there" in the same sense other places are already there, and that there is no objective flow of time. It is sometimes referred to as the "block time" or "block universe" theory due to its description of space-time as an unchanging four-dimensional "block", as opposed to the view of the world as a three-dimensional space modulated by the passage of time.
3 Simple Ways to Time Travel and 3 Complicated Ones (youtube)
Fourier Transform decomposes a function of time (a signal) into the frequencies that make it up, in a way similar to how a musical chord can be expressed as the amplitude (or loudness) of its constituent notes. The Fourier transform of a function of time itself is a complex-valued function of frequency, whose absolute value represents the amount of that frequency present in the original function, and whose complex argument is the phase offset of the basic sinusoid in that frequency.
Action Physics - Space Time - Time Management
"Objects can be traveling at different speeds depending on what reference point we take, time can alter from different reference perspectives, and mass can alter from different perspectives."
Time Dilation is a difference in the elapsed time measured by two observers, either due to a velocity difference relative to each other, or by being differently situated relative to a gravitational field. As a result of the nature of spacetime, a clock that is moving relative to an observer will be measured to tick slower than a clock that is at rest in the observer's own frame of reference. A clock that is under the influence of a stronger gravitational field than an observer's will also be measured to tick slower than the observer's own clock. Such time dilation has been repeatedly demonstrated, for instance by small disparities in a pair of atomic clocks after one of them is sent on a space trip, or by clocks on the Space Shuttle running slightly slower than reference clocks on Earth, or clocks on GPS and Galileo satellites running slightly faster. Time dilation has also been the subject of science fiction works, as it technically provides the means for forward time travel.
Light Clock is a simple way of showing a basic feature of Special Relativity. A clock is designed to work by bouncing a flash of light off a distant mirror and using its return to trigger another flash of light, meanwhile counting how many flashes have occurred along the way. It is easy to show that people on Earth watching a spaceship fly overhead with such a clock would see it ticking relatively slowly. This effect is called time dilation.
Time Passes Quicker at a Higher Altitudes
Gravitational Time Dilation is a form of time dilation, an actual difference of elapsed time between two events as measured by observers situated at varying distances from a gravitating mass. The higher the gravitational potential (the farther the clock is from the source of gravitation), the faster time passes. Albert Einstein originally predicted this effect in his theory of relativity and it has since been confirmed by tests of general relativity. Black Holes.
How can we be flying through space but at the same time feel like we are frozen in time? When we look up at the stars, year after year, the same stars are in the same place, almost looking like nothing has changed. Are we seeing the same stars that people saw a thousand years ago?
Noetic Sciences (beyond awareness)
Timeline of the Far Future predicts how life will evolve over time; and plate tectonics, which shows how continents shift over millennia.
Will our Knowledge be Preserved?
Are we there yet? This question is really saying, "why don't I know where I am?" If I am here, then where is here? And if I am going somewhere, then where is there? I'm lost, or I'm just not paying attention and I'm definitely not managing time, or space. So to say, "are we there yet? Is really saying, "have I learned anything yet?"
Time is a measurement system, a process for learning and a very important Tool that helps us plan and predict. Though the timing of cycles, rhythms and development are essential for life, try not to spend to much time thinking about time, this is just one of many tools that we have.
The Primacy of Consciousness (youtube)
Delta-T is the time difference obtained by subtracting Universal Time or UT from Terrestrial Time or TT: ΔT=TT−UT.
Invariant Subspace of a linear mapping T : V - V from some vector space V to itself is a subspace W of V that is preserved by T; that is, T(W) - W.
Time Scale (universe)
Do you believe that time exists?
Time of Flight describes a variety of methods that measure the time that it takes for an object, particle or acoustic, electromagnetic or other wave to travel a distance through a medium. Action Physics.
Quasi-Biennial Oscillation is a quasiperiodic oscillation of the equatorial zonal wind between easterlies and westerlies in the tropical stratosphere with a mean period of 28 to 29 months.
Quasiperiodicity displays irregular periodicity. Periodic behavior is defined as recurring at regular intervals, such as "every 24 hours.
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. The term vibration is precisely used to describe mechanical oscillation. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current power. Hz - Brain Waves.
Time Perception
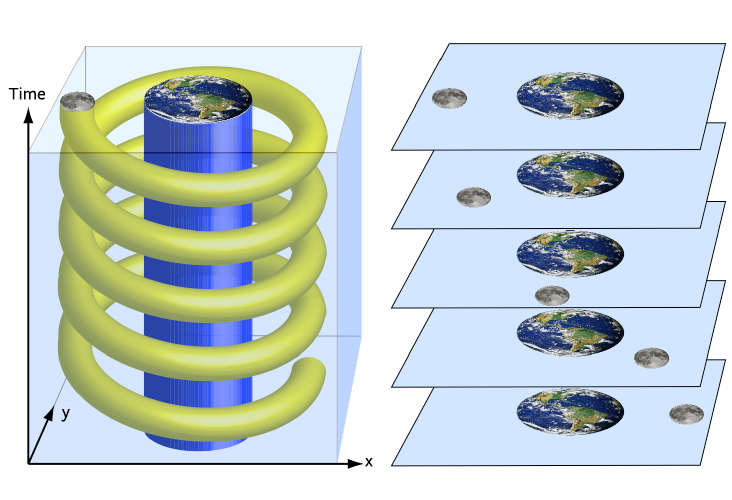
Time Perception refers to the subjective experience of life and the subjective experience, or sense, of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of change, distance the duration of the indefinite and unfolding of events.
I can have memories of the past, and I can live in the present moment, and I can make plans and predictions about the future. So I live in the past, present and future simultaneously, almost at the same time. But if I'm thinking about the past, then I'm not thinking about the present moment or the future. If I'm thinking about the present moment, then I'm not thinking about the past or the future. If I'm thinking about the future, then I'm not thinking about the present moment or the past. So in order to think about anything, I need to have a past, a present and a future. Philosophy of Mind - Multi-Tasking.
We don't experience time when we sleep or experience time when we are mediating deeply. Time and space seems to be nonexistent at these moments. Time and space exists for the living who are awake and have consciousness. Time is relative and not relative simultaneously.
Fourth Dimension is required to specify a physical event, along with three spatial dimensions.
Humans have a startling accurate sense of time, particularly when younger. The mechanism we use for this seems to be a distributed system involving the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. Long term time keeping seems to be monitored by the suprachiasmatic nuclei, which is responsible for the circadian rhythm or body clock. Short term time keeping is handled by other cell systems.
Hippocampal “time cells” bridge the gap in memory for discontiguous events. The hippocampus is critical to remembering the flow of events in distinct experiences and, in doing so, bridges temporal gaps between discontiguous events. Here we report a robust hippocampal representation of sequence memories, highlighted by “time cells” that encode successive moments during an empty temporal gap between the key events, while at the same times encoding location and ongoing behavior. Furthermore, just as most place cells “remap” when a salient spatial cue is altered, most time cells form qualitatively different representations (“re-time”) when the main temporal parameter is altered. Hippocampal neurons also differentially encode the key events and disambiguate different event sequences to compose unique, temporally organized representations of specific experiences. These findings suggest that hippocampal neural ensembles segment temporally organized memories much the same as they represent locations of important events in spatially defined environments. A fundamental feature of episodic memory is the temporal organization of serial events that compose a unique experience. How do hippocampal neurons represent the temporal organization of extended experiences and bridge temporal gaps between discontiguous events? Time cells in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex support episodic memory. Time cells are neurons in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex that fire at specific moments within a cognitive task or experience. Episodic memory describes our ability to weave temporally contiguous elements into rich and coherent experiences. The formation of these memories requires the brain to represent temporal information, and recent discoveries in animal models of episodic memory suggest that the activity of “time cells” in the mesial temporal lobe (MTL) fulfills this critical role in memory formation. Like place cells, which exhibit an increased probability of firing at specific locations, or “place fields,” within an environment, time cells reliably fire at specific and consistent moments, or “time fields,” within a longer time interval. Single Neurons in the Human Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex Encode the Passage of Time. To represent temporal information, time cells fire at a preferred time interval—their time field—that is defined relative to the beginning and end of a period of fixed duration. Both the encoding and retrieval periods of the free recall task were of relatively fixed duration. Time Cells in the Hippocampus Are Neither Dependent on Medial Entorhinal Cortex Inputs nor Necessary for Spatial Working Memory. A key function of the hippocampus and entorhinalcortex is to bridge events that are discontinuous intime, and it has been proposed that medial entorhinalcortex (mEC) supports memory retention by sustain-ing the sequential activity of hippocampal timecells.
How the brain remembers right place, right time. Studies could lead to new ways to enhance memory for those with traumatic brain injury or Alzheimer's disease. About a decade ago, a group of neurons known as "time cells" was discovered in rats. These cells appear to play a unique role in recording when events take place, allowing the brain to correctly mark the order of what happens in an episodic memory. Located in the brain's hippocampus, these cells show a characteristic activity pattern while the animals are encoding and recalling events. By firing in a reproducible sequence, they allow the brain to organize when events happen. The timing of their firing is controlled by 5 Hz brain waves, called theta oscillations, in a process known as precession. Investigations into whether humans also have time cells by using a memory task that makes strong demands on time-related information. Recruited volunteers from the Epilepsy Monitoring Unit at UT Southwestern's Peter O'Donnell Jr. Brain Institute, where epilepsy patients stay for several days before surgery to remove damaged parts of their brains that spark seizures. Electrodes implanted in these patients' brains help their surgeons precisely identify the seizure foci and also provide valuable information on the brain's inner workings.
Growing Block Universe states that the past and present exist while the future does not exist. The present is an objective property, to be compared with a moving spotlight. By the passage of time more of the world comes into being; therefore, the block universe is said to be growing. The growth of the block is supposed to happen in the present, a very thin slice of spacetime, where more of spacetime is continually coming into being.
Eternalism is a philosophical approach to the ontological nature of time, which takes the view that all existence in time is equally real, as opposed to presentism or the growing block universe theory of time, in which at least the future is not the same as any other time. Some forms of eternalism give time a similar ontology to that of space, as a dimension, with different times being as real as different places, and future events are "already there" in the same sense other places are already there, and that there is no objective flow of time. It is sometimes referred to as the "block time" or "block universe" theory due to its description of space-time as an unchanging four-dimensional "block", as opposed to the view of the world as a three-dimensional space modulated by the passage of time.
One million years in Human time might could be perceived as just being one day to another life form. Like when you see a Time Lapse video. Time is relative and time has different scales.
Even the speed of light is irrelevant. You might say the speed of light is the same everywhere, but it's how you measure it. Time on earth is only unique to us. Once you leave the planet or the solar system, time will need a new standard.
Frame Rate (flickers of light) - Space Time
Slow Motion Perception is a postulated mental state wherein time seems to be slowed down. People experiencing life-threatening situations sometimes report that time seemed to have slowed down.
Quintillionths of a Second in Slow Motion. Observing and controlling ultrafast processes with attosecond resolution. Many chemical processes run so fast that they are only roughly understood. To clarify these processes, researchers have now developed a methodology with a resolution of quintillionths of a second. The new technology stands to help better understand processes like photosynthesis and develop faster computer chips.
Areas of the Brain that Process Time (image)
"Time flies when you're having fun" ..when you don't notice the passage of time, time will feel like it passes quickly.
Time goes Faster when you're busy doing things and when you're happy, like when traveling, socializing, learning or doing activities that you like.
Time goes Slower when you're bored, unhappy or not busy doing anything important, like with some jobs or in prison.
Duration in philosophy is a theory of time and consciousness that the moment one attempted to measure a moment, it would be gone: one measures an immobile, complete line, whereas time is mobile and incomplete. For the individual, time may speed up or slow down, whereas, for science, it would remain the same. Hence Bergson decided to explore the inner life of man, which is a kind of duration, neither a unity nor a quantitative multiplicity. Duration is ineffable and can only be shown indirectly through images that can never reveal a complete picture. It can only be grasped through a simple intuition of the imagination.
Duration is the amount of elapsed time between two events. The period of time during which something continues.
Busy is being active or fully engaged or occupied. Characterized by much activity. Distracted.
"Life starts out slow then life gradually speeds up because we add more things into our timeframe, which sadly makes us pay more attention to the time than to life itself."
Funny how Time Flies when you're Having Fun is to perceive time as going by very quickly when you are enjoying something and not paying attention to the passing of time.
Cycles is an interval during which a recurring sequence of events occurs. A periodically repeated sequence of events.
Seasons - Rhythms - Patterns - Random
Time is related to the speed at which our Earth turns, and since most planets turn or rotate at different speeds, our perception of time, and our measurement of time, is only unique to Humans on Earth.
New experiences really do seem to be longer in the memory than familiar ones. It’s called the “oddball effect”, and it seems to be why time feels like it’s going faster as you get older – because more stuff is familiar to you.
Oddball Paradigm is an experimental design used within psychology research. Presentations of sequences of repetitive stimuli are infrequently interrupted by a deviant stimulus. The reaction of the participant to this "oddball" stimulus is recorded.
Take a day off, take a break, pause, unwind, regroup and relax.
Meditation - Awareness - Adventure
Timeline is a project artifact. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labeled with dates alongside itself.
Units of Time
A second isn’t what you think it is. Scientifically, it’s not defined as 1/60th of a minute, but as “the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom”.
The strontium clock would neither gain nor lose one second in some 15 billion years.
Slave Clock is a clock that depends for its accuracy on another clock, a master clock. Many modern clocks are synchronized, either through the Internet or by radio time signals, to a worldwide time standard called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) based on a network of master atomic clocks in many countries.
Europe's standard electrical frequency of 50 hertz has fallen ever so slightly to 49.996 hertz. For electric clocks that rely on the frequency of the power system — typically radio, oven and heating-panel clocks — the cumulative effect was close to six minutes.
Utility Frequency is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power station to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world. During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization. Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency. In practice, the exact frequency of the grid varies around the nominal frequency, reducing when the grid is heavily loaded, and speeding up when lightly loaded. However, most utilities will adjust the frequency of the grid over the course of the day to ensure a constant number of cycles occur. This is used by some clocks to accurately maintain their time. (also known as power line frequency in American English or mains frequency in British English).
The smallest standard scientific measure of time is the “Planck time”. It takes you about five hundred and fifty thousand trillion trillion trillion Planck times to blink once, quickly.
Time is measured by one complete Orbit around our Sun, which is called one Year. A 12 month calendar, which equals one year (365 Days, or 365 Earth Rotations), is an incremental tool which divides one earth orbit around our sun into Months and Days. Time is also measured by one complete rotation of the earth, which is called one day. A 24 Hour Clock is an incremental tool that divides one rotation of the earth into Seconds, Minutes and Hours. Time is also measure by Carbon Decay, which is then calculated into how many earth orbits around the Sun.
Can I make up for Lost Time?
"Tomorrow is not a mystical land where 99% of all human productivity, motivation and achievement is stored, that's today, so why wait?"
"The Past is all we know of the Future", which means that our past experiences helps us to determine the future.
How much is your time worth?
You may selfishly buy yourself some time, but time runs out for everyone. Everyone needs to stop stealing time from future generations. Our ancestors gave us this time that we have now, it is our duty to pass on time that is usable and valuable.
Time-Shift is to move from one period in time to another.
Time Shifting is the recording of programming to a storage medium to be viewed or listened to after the live broadcasting. Typically, this refers to TV programming but can also refer to radio shows via podcasts.
Place Shifting allows media, such as music or films, which are stored on one device, to be accessed from another place through another device.
Time-shifted inhibition helps electric fish ignore their own signals. African fish called mormyrids communicate using pulses of electricity. New research shows that a time-shifted signal in the brain helps the fish to ignore their own pulse. This skill has co-evolved with large and rapid changes in these signals across species. A solution to this problem is a brain function called a corollary discharge. It's sort of like a negative copy of the original message -- something that tells the fish: Ignore this. But an animal's brain doesn't have to block sensory inputs during the entire message to effectively ignore its own signal, according to new research from biologists at Washington University in St. Louis. Instead, the inhibitory signal -- that call to ignore -- is delayed in fish that communicate using longer electric pulses, versus those using shorter pulses.
Time is of the Essence
Time is of the Essence means that something must be done immediately and that time is an important, crucial and significant feature of a thing that is essential to a particular action or response, and failure to complete the required performance by a certain time or date will cause unnecessary consequences and maybe even suffering. Time is of the Essence when used in a contract law, places the other party on notice that failure to complete a required performance by a date certain set forth therein will constitute an incurable breach. Indicating that one or more parties to the agreement must perform by the time to which the parties have agreed if a delay will cause material harm.
Date Certain is a legal term for the date on or by which the actions of a contract can be reasonably completed, and is considered to be legally binding.
Hast is a condition of urgency making it necessary to hurry and move fast at a high rate of speed.
Haste makes Waste is used to say that doing something too quickly can cause mistakes that could result in time, effort and materials being wasted.
Haste is sometimes necessary. Though going to fast sometimes does increase the risks, vulnerabilities and mistakes. So go as fast as you possibly can while being safe as you possibly can. Haste not Waste - Time Management - Taking a Break.
"You don't want to rush into things, and you don't want to move too slowly either."
Essence is the choicest or most essential or most vital part of some idea or experience. The central meaning.
Of the Essence is something important, indispensable and crucial.
‘I only have a minute, 60 seconds in it, Forced upon me, I did not choose it, But I know that I must use it, Give account if I abuse it, Suffer if I lose it. Only a tiny little minute, But eternity is in it.’ - Benjamin Mays (wiki) - A pioneering civil rights leader who was the president of Morehouse College during Martin Luther King Jr. education there. Elijah Cummings - First House floor speech (1996). youtube video.
"Even when I'm doing all the things that I can, I still feel sometimes like I'm not doing enough, like there's another level of productivity that I haven't reached yet, where time management becomes more machine like, where every minute is correctly, effectively and efficiently calculated and divided up in a way that I can complete as many tasks that I can in one day. But I must do this without having time interfere with life, or have time interrupt life, or have time diminish life. So within that machine like management of time there has to be time set aside to just think and reflect, or you may risk not having a life, and not feel alive, or even feel human."
Reasonable Time is that amount of time which is fairly necessary, conveniently, to do whatever is required to be done, as soon as circumstances permit.
“Better late than never, but never late is better”
Don’t say "I Don’t have Enough Time". You have exactly the same number of hours per day that everyone else has, well almost everyone. Instead of saying "I don't have the time", you could say, "I currently have other responsibilities and other people are counting on me to fulfill those responsibilities, but when those commitments change, I would like to know more about what you do, as well as the ways that I could help you". 20 Minute Rule.
American Time Use Survey: How people spend their Time - PDF
Where our Time Goes (Info-graphic)
You Only have So Much Time. If you live to be 100 years old you'll live 876,000 hours in your life. Minus 300,000 hours sleeping, minus 73,000 hours eating, minus 120,000 hours working, minus 20,000 hours of school and so on. That leaves you less than 300,000 waking hours to do what you want, or less than 34 years being awake to live, and that's only if you live to 100 in good health? Don't waste your waking hours. And depending on where you live, you may have to spend more time working and spend more time getting food and water. And if you live to only 70 years old, that means you may have less than 20 years of life.
Other things happening in your life - What's the Meaning of Life?
Time Management is an extremely important tool when it comes to planning and predicting. But we cannot allow time to dictate and control all of our actions all of the time, if we did, we would disconnect from ourselves and reality, and become more machine like then human. We have to relax and connect to our inner self a couple of times a day. We have to separate our external time from our internal time. We need time to ourselves, where time has no meaning, and our mind is free to wander. Procrastination - Routines.
"There are many things in my life that I am not totally in control of. Even though I am getting better at controlling things in my life, I am still not in control of everything. I prioritize, but I have to learn how not to ignore things that still may be important. So I have to learn how to spend some more time on the lower priorities in my life, because they still may have significance. How many things do I need to be in control of in my life in order to feel that I am in control of my life? Without turning into a control freak or becoming a perfectionist."
Focus - Awareness - Action Physics
Value of Time is the opportunity cost of the time that a traveller spends on his/her journey. In essence, this makes it the amount that a traveller would be willing to pay in order to save time, or the amount they would accept as compensation for lost time.
Are we Frozen in Time, or are we Moving? Let go of the concept of time as if time did not exist. Now imagine the past, the present and the future being the same thing, occupying the same space. Now look out at the stars at night, you see the past, the present and the future, all at the same time. Now stay there for a moment, think, experience life without time.....can you explain it?
Suspended Animation is the slowing or stopping of life processes by exogenous or endogenous means without termination. Breathing, heartbeat, and other involuntary functions may still occur, but they can only be detected by artificial means.
Time (poem) - Time can be seen and time can be felt. Through the years of changes our world has endured, through the changes we experience in ourselves. Measured by moments and the rising of our Sun, it's the one thing we can be thankful for when the day is done. HP.
Only Time will Tell is the hope that people will eventually see the consequences or the benefits of their actions in the future. Will you be alive to hear time tell the results? Will time tell other people in the future that you were a hero? Or will time tell other people in the future that you were an ignorant person or a coward who did nothing. Or maybe time will not tell people anything because what time had to say was lost, or manipulated?
We have all had moments where we have helped someone in need, maybe saving someone's life, and we remember how great we felt because we know we did something that was needed, something that was special, because we know how important help can be to someone in need. I'm in one of those moments right now, except this is one big moment, a much larger picture, a moment stretching many lifetimes and encompassing many moments in time, eons. Except this type of time is not measured by our sun, this time stretches across the universe. Time on earth has been slowed down, giving humans a chance to see and experience life in a unique way. But our experience of time is only unique to earth. Beyond our planet time takes on a whole new meaning where time is not measured in seconds, hours, days or years, in fact it's not a measurement at all, time is something that is felt and experienced, which transcends all definitions of time and our understanding of what time is. It is the ultimate moment.
Broken Social Scene "Halfway Home" (youtube)
I don't dream about the future, the future dreams about me, and the future is smiling. The past is also smiling, because the past knows how far I've come and also sees what I'm doing now. We're halfway home.
Songs About Time
Time In A Bottle: Jim Croce, 1973 (youtube)
Time - Pink Floyd (youtube)
Does Anybody Really Know What Time It Is - Chicago (youtube)
Turn! Turn! Turn! - The Byrds (youtube)
Time Won't Let Me - The Outsiders (youtube) - I can't wait forever, even though you want me to.
Its Now or Never - Elvis Presley 1960 - Tomorrow will be too late, it's now or never, My love won't wait. So don't procrastinate.
Too Much Time On My Hands - Styx (youtube) - Having too much time is impossible, the same goes for Boredom.
Hazy Shade of Winter - The Bangles (youtube)
Time Has Come Today (Chambers Brothers-Long Version) with no cuts to song (youtube)
Out of Time - Chris Farlowe (youtube)
Time Is On My Side - The Rolling Stones (youtube)
Your Time Is Gonna Come - Led Zeppelin (youtube)
Fly Like An Eagle - Steve Miller Band (youtube) - Time keeps on slippin', slippin', slippin' Into the future.
No Time - The Guess Who (youtube) - On my way to better things, (No time left for you), I found myself some wings, (No time left for you), Distant roads are callin' me, (No time left for you), No time for a gentle rain, No time for my watch and chain, No time for revolving doors, No time for the killin' floor, No time for the killin' floor, There's no time left for you, No time left for you, No time for a summer friend, No time for the love you send, Seasons change and so did I, You need not wonder why, You need not wonder why, There's no time left for you, No time left for you.
"Even a stopped clock is right twice a day, but how would you know which two times during the day that the clock was right when you don't have a clock that works?"
