BK101
Knowledge Base
Vertical Farming - Indoor Agriculture
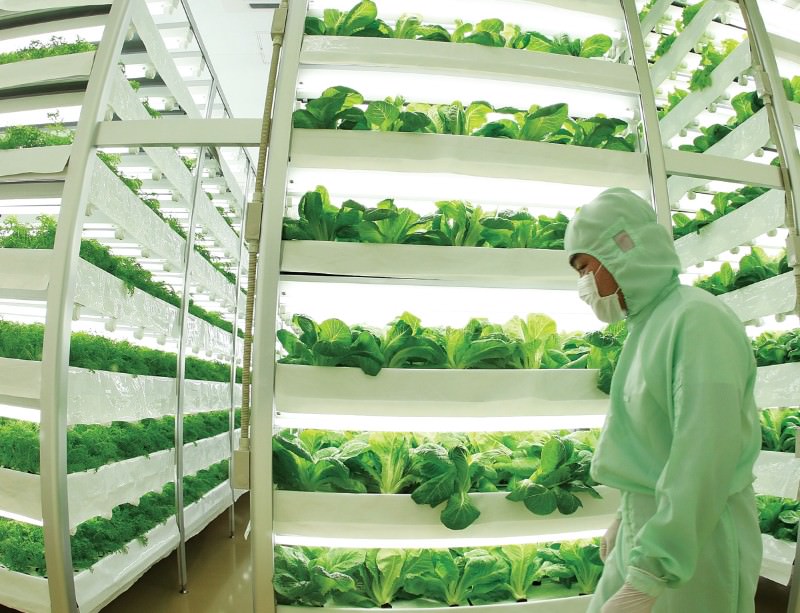
Vertical Farms are modular and can be adjusted to fit any building. Vertical Farms can also feed more people then regular farming can because they grow 75 times more food per square foot then a traditional farm. Vertical Farms also use no pesticides and no fungicides so the food is healthier and safer. Vertical Farms also reduce water consumption because indoor farms use 90 percent less water than outdoor farms, so having a wet or dry season doesn't matter. Indoor farming can also control plant fertilizing nutrients so the food that is grown is highly nutritious. Grow a large volume of food in a relatively small space and use less water. 6,500 square meters = 900,000-kilo harvest. Vertical Farming methods could help preserve lands and rain forests and also give time for other lands to recover and replenish topsoil and also help reduce carbon consumption. Better use of world’s existing cropland could feed 3 billion more people. Green Houses.
Food Security - Food Trucks - Vending Machines - Farm to Fridge - City Farming - Seeds - Lights
 Controlled Environment Agriculture is a
technology-based approach toward food production. The aim of CEA is to
provide protection and maintain optimal growing conditions throughout the
development of the crop. Production takes place within an enclosed growing
structure such as a greenhouse or building. Plants are often grown using
hydroponic methods in order to supply the
proper amounts of water and nutrients to the root zone. CEA optimizes the
use of resources such as water, energy, space, capital and labor. CEA
technologies include hydroponics, aquaculture, and aquaponics.
Controllable variables: Temperature (air, nutrient solution, root-zone),
Humidity (%RH), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Light (intensity, spectrum,
interval), Nutrient concentration (PPM, EC)
Fertilizers, Nutrient pH (acidity).
CEA facilities can range from fully automated glasshouses with computer
controls for watering, lighting and ventilation, to low-tech solutions
such as cloches or plastic film on field grown crops and plastic-covered
tunnels. CEA is used in research so that a specific aspect of production
can be isolated while all other variables remain the same. Tinted glass
could be compared to plain glass in this way during an investigation into
photosynthesis. Another possibility would be an investigation into the use
of supplementary lighting for growing lettuce under a hydroponic system.
Controlled Environment Agriculture is a
technology-based approach toward food production. The aim of CEA is to
provide protection and maintain optimal growing conditions throughout the
development of the crop. Production takes place within an enclosed growing
structure such as a greenhouse or building. Plants are often grown using
hydroponic methods in order to supply the
proper amounts of water and nutrients to the root zone. CEA optimizes the
use of resources such as water, energy, space, capital and labor. CEA
technologies include hydroponics, aquaculture, and aquaponics.
Controllable variables: Temperature (air, nutrient solution, root-zone),
Humidity (%RH), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Light (intensity, spectrum,
interval), Nutrient concentration (PPM, EC)
Fertilizers, Nutrient pH (acidity).
CEA facilities can range from fully automated glasshouses with computer
controls for watering, lighting and ventilation, to low-tech solutions
such as cloches or plastic film on field grown crops and plastic-covered
tunnels. CEA is used in research so that a specific aspect of production
can be isolated while all other variables remain the same. Tinted glass
could be compared to plain glass in this way during an investigation into
photosynthesis. Another possibility would be an investigation into the use
of supplementary lighting for growing lettuce under a hydroponic system.Vertical Farming is the practice of producing food in vertically stacked layers, such as in a skyscraper, used warehouse, or shipping container. The modern ideas of vertical farming use indoor farming techniques and controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) technology, where all environmental factors can be controlled. These facilities utilize artificial control of light, environmental control (humidity, temperature, gases...) and fertigation. Some vertical farms use techniques similar to greenhouses, where natural sunlight can be augmented with artificial lighting and metal reflectors.
Microclimates - Green Houses
Hydroponics - Mediums - Aeroponics - Aquaponics
Aquaculture - Micro Greens - Sprouts
LED Grow Lights
Ski town turns car park into Vertical Farm for Local Jobs/Food (youtube) - Vertical Harvest Jackson produces 100,000 pounds of vegetables a year on a plot 30 feet by 150 feet long; their 1/10th of an acre site grows an annual amount of produce equivalent to 10 acres of traditional farming. Relying on hydroponics and moving carousels, the farm uses 90% less water than conventional farming and doesn’t use any pesticides (only sticky traps).
Biofortification is the idea of breeding crops to increase their nutritional value. This can be done either through conventional selective breeding, or through genetic engineering. Biofortification differs from ordinary fortification because it focuses on making plant foods more nutritious as the plants are growing, rather than having nutrients added to the foods when they are being processed. Food Security.
Vertical Growing Resources
Vertical Farm
Growing Crops in Vertical Farms
Vertical Farming
LA Leadership
Gotham Greens
Skyland Vertical Farming (youtube)
Vertical Forest (youtube) - Vertical Forest
Plant Lab
High-Tech Grow Room
Localize Vertical Farm
Forest Garden (permaculture) - City Farming - Plant Intelligence
Plenty strives to grow the best tasting, most nutritious produce possible.
App Harvest is massive indoor farms Year-Round. No Chemical Pesticides, use only recycled rainwater and distribute it more efficiently, reducing water usage by 90%.
Small Scale Vertical Food Growing
 Window Farm is a hydroponic urban gardening system is
an indoor garden that allows for year-round growing in almost any window.
It lets plants use natural light, the climate control of your living
space, and organic “liquid soil.” Uses open-source designs.
Window
Farms -
Window Farms
Window Farm is a hydroponic urban gardening system is
an indoor garden that allows for year-round growing in almost any window.
It lets plants use natural light, the climate control of your living
space, and organic “liquid soil.” Uses open-source designs.
Window
Farms -
Window FarmsUpside-Down Tomato Planter
Micro-Gardening
Lighting (growlights)
Vertical Gardening (youtube)
Plants on Walls - Woolly Pocket
Urban Gardens Web
Vertical Farming - Vertigro
Agrivolution - MIT City Farm - Grow Food
Herbert is a wall mounted hydroponic vertical farm for your home. Simple, clean and 40% more efficient.
Small Indoor Growing Systems
Compact Growing Kits for Growing Small Plants and Herbs Indoors
Biopod - World's First Smart Microhabitat
Seedo Lab Auto Grow Hydroponics Device.
AVA Byte: Automated Smart Garden
Aero Garden
Chia Herb Garden
Citysens Modular Vertical Garden
EcoQube Air - The World's First Desktop Greenhouse
FogBox Desktop Aeroponics System that Grows Plants and your fresh kitchen Herbs with Fog.
mart Garden 3 by Click & Grow
City Hydro Indoor Growing System - Microgreens.
Zip Grow Vertical Growing System - Modular Farming Systems - Brightagrotech
Grow 53 Plants in 4 Sq Ft with a Garden Tower Vertical Container Garden.
Altifarm is a modular, all-season home farm with self-watering, grow lights, greenhouse cover and mobility.
Shipping Container Growing Systems
GrowFrame Collapsible Hydroponic Farm that grows food in empty shipping containers that are shipped around the world everyday.
Square Roots Grow uses shipping containers to help local farmers to grow GMO-free, pesticide-free, real food. $85,000 high-tech growing chambers pre-loaded with sensors, exotic lighting, precision plumbing for irrigation, vertical growing towers, a climate control system, and, now, leafy greens. It’s even possible to design taste.
Vertical Harvest Hydroponics builds enclosed systems out of transformed shipping containers. Around $200,000, including the customized freight container and the price to fly it in a C-130 transport plane.
Large Scale Vertical Farming
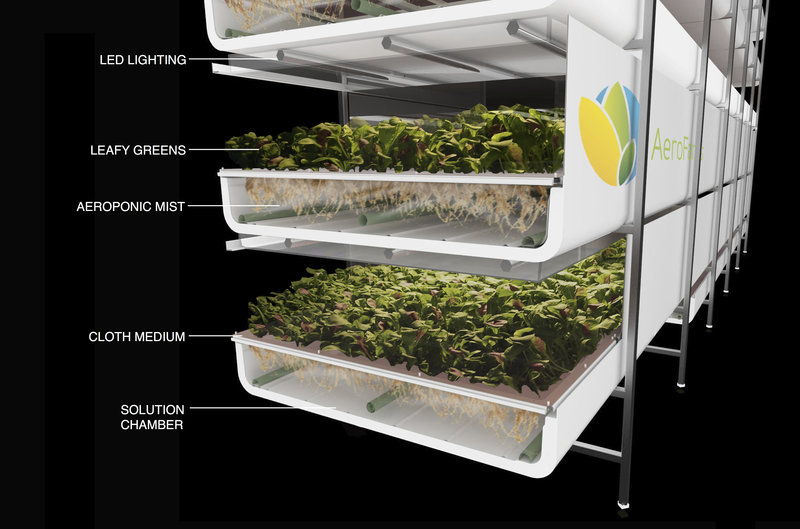 AeroFarms turned
an abandoned steel mill into the World’s Largest Vertical Farm in Newark,
N.J. - 12 layers of growth on 3½ acres, producing 2 million pounds of food
per year. Growing a plant in about 16 days instead of 30 days in the
field. Aero Farms Vertical Farming.
AeroFarms turned
an abandoned steel mill into the World’s Largest Vertical Farm in Newark,
N.J. - 12 layers of growth on 3½ acres, producing 2 million pounds of food
per year. Growing a plant in about 16 days instead of 30 days in the
field. Aero Farms Vertical Farming.WWII Bomb Shelter Becomes Hi-Tech Salad Farm Deep Under London
Combination of Aquaponic and Vertical Growing Technologies.
Green Sense Farms uses 0.1% of the water, land and fertilizer of an outdoor farm, No pesticides or herbicides, 26 Harvests a year, 46 pounds of 02 produces daily with tons of CO2 captured each month.
Mirai Vertical Farming - Tokyo (youtube)
Plenty (vertical Farming)
Hydroponics
This computer will grow your food in the future (video and text)
The Open Agriculture Initiative (OpenAG)
Plantagon productive agriculture solutions in urban environments. Retro-fitting empty areas and buildings into sustainable food production. Can use office buildings basements, Residential buildings basements or underground parking, Factories, Custom made Concepts. Combination building, growing food on one side of a building and selling food on the other side, along with an exercise floor, health services, office space, science space, library, learning center, and so on. A Symbiotic System that combines municipal infrastructure such as cooling, heating, biogas, waste, water and energy with food production.
Kennett Township Pennsylvania region produces half the mushroom crop in the U.S., known as the Mushroom Capital of
the World. In a small section of Pennsylvania, indoor farms are producing more than a million pounds of mushrooms every day. Kennett Mushrooms are the largest producer in the world of fresh mushrooms. Not only produce, but pack and ship all across North America, with delivery typically within 48 hours. That’s about a half a billion pounds of mushrooms a year. And that represents about 50 percent of the U.S. mushroom crop.
Netherlands Green Houses: 35% of Vegetables are grown on just 20 acres of land, 1% of farm land. 2 million pounds of tomatoes, double of outdoor farming. Growing 350 times more foof then a regular farm using 1/5 the water. 2nd in the world in exporting food. Dutch Greenhouse experts in greenhouse manufacturing.
Rank Country Value of Food Exports (US Dollars)
1 United States $149,122,000,000.00
2 Netherlands $92,845,387,781.00
3 Germany $86,826,895,514.00
4 Brazil $78,819,969,000.00
Largest Producing Countries of Agricultural Commodities (wiki)
Automated Robotic Greenhouse in San Carlos, California. Robots to carefully seed, water, and care for each plant.
machine learning algorithms that will automatically detect plant diseases.
Space Food for Astronauts - Food Grown in Outer Space
Space Food is a type of food product created and processed for consumption by astronauts during missions to outer space. The food has specific requirements of providing balanced nutrition for individuals working in space, while being easy and safe to store, prepare and consume in the machinery-filled weightless environments of crewed spacecraft. In recent years, space food has been used by various nations engaging on space programs as a way to share and show off their cultural identity and facilitate intercultural communication. Although astronauts consume a wide variety of foods and beverages in space, the initial idea from The Man in Space Committee of the Space Science Board in 1963 was to supply astronauts with a formula diet that would supply all the needed vitamins and nutrients. Designing food for consumption in space is an often difficult process. Foods must meet a number of criteria to be considered fit for space. Firstly, the food must be physiologically appropriate. Specifically, it must be nutritious, easily digestible, and palatable. Secondly, the food must be engineered for consumption in a zero gravity environment. As such, the food must be light, well packaged, fast to serve and require minimal cleaning up. (Foods that tend to leave crumbs, for example, are ill-suited for space.) Finally, foods require a minimum of energy expenditure throughout their use; they must store well, open easily and leave little waste behind. Meals Ready to Eat: Expedition 44 Crew Members Sample Leafy Greens Grown on Space Station. - Meal Ready to Eat (survival food).
Engineered Food for Space Travel. The Human Health and Performance Directorate's (HH&P) Space Food Systems capability is responsible for evaluating, producing and packaging food for each mission and developing menus. Required to be of high quality and meet the nutritional needs of each crew member while adhering to the requirements of limited storage space, limited preparation options. Designed containers and packaging appropriate for long-term storage. Space Travel.
Advanced Food Technologies Project is to develop, evaluate and deliver food technologies for human centered spacecraft that will support crews on missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Safe, nutritious, acceptable, and varied shelf-stable foods with a shelf life of 3 - 5 years will be required to support the crew during future exploration missions to the Moon or Mars. Concurrently, the food system must efficiently balance appropriate vehicle resources such as mass, volume, water, air, waste, power, and crew time. One of the objectives during the lunar outpost missions is to test technologies that can be used during the Mars missions. This subtopic will concentrate on two specific areas; food packaging and lunar outpost food preparation and food processing.
Airline Meal is a meal served to passengers on board a commercial airliner. These meals are prepared by specialist airline catering services and normally served to passengers using an airline service trolley.
Growing Food in Space for Space Travel
Plants in Space are plants grown in outer space typically in a weightless but pressurized controlled environment in specific space gardens. In the context of human spaceflight, they can be consumed as food and/or provide a refreshing atmosphere. Plants can metabolize carbon dioxide in the air to produce valuable oxygen, and can help control cabin humidity. Growing plants in space may provide a psychological benefit to human spaceflight crews.
Farming in Outer Space - Modern Farmer Information.
Growing Plants and Vegetables in a Space Garden
Veggie Plant Growth System Activated on International Space Station
Space cucumbers reveal secrets of plant survival
Bioregenerative Life Support System are artificial ecosystems consisting of many complex symbiotic relationships among higher plants, animals, and microorganisms. As the most advanced life support technology, BLSS can provide a habitation environment similar to the Earth's biosphere for space missions with extended durations, in deep space, and with multiple crews.
Agriculture is a Life Support System, which is a group of devices that allow a human being to survive in space. US government space agency NASA, and private spaceflight companies use the term environmental control and life support system or the acronym ECLSS when describing these systems for their human spaceflight missions. The life support system may supply air, water and food. It must also maintain the correct body temperature, an acceptable pressure on the body and deal with the body's waste products. Shielding against harmful external influences such as radiation and micro-meteorites may also be necessary. Components of the life support system are life-critical, and are designed and constructed using safety engineering techniques.
Leafy Green Astronauts
Space Greens beat the blues | Plants and psychological well-being in space. Plants may play a key role in maintaining the psychological well-being of space crews. Space travel can cause sleep disorders, a reduction in energy, inattentiveness and difficulty in problem-solving, and even memory loss. It can cause people to be more hostile, act more impulsively and, despite the danger and excitement, is sometimes boring. Any of these conditions and problems can lead to dangerous, if not tragic outcomes.
CEAC Lunar Greenhouse (youtube) - Full Scale Lunar Greenhouse Prototype (youtube)
Isolated Self Sustaining Living Earth Systems - Biosphere
Biosphere 2 is an Earth System Science Research Facility located in Oracle, Arizona. It has been owned by the University of Arizona since 2011. Its mission is to serve as a center for research, outreach, teaching, and lifelong learning about Earth, its living systems, and its place in the universe. It is a 3.14-acre (1.27-hectare) structure originally built to be an artificial, materially closed ecological system, or vivarium. It remains the largest closed system ever created. Earth is Biosphere 1.
Inside Biosphere 2: The World's Largest Earth Science Experiment (youtube)
Eden Project is a complex is dominated by two huge enclosures consisting of adjoining domes that house thousands of plant species, and each enclosure emulates a natural biome. The biomes consist of hundreds of hexagonal and pentagonal, inflated, plastic cells supported by steel frames. The largest of the two biomes simulates a rainforest environment and the second, a Mediterranean environment. The attraction also has an outside botanical garden which is home to many plants and wildlife native to Cornwall and the UK in general; it also has many plants that provide an important and interesting backstory, for example, those with a prehistoric heritage.
The Hawaii Space Exploration Analog and Simulation is an analog habitat for human spaceflight to Mars. HI-SEAS is located in an isolated position on the slopes of the Mauna Loa volcano on the island of Hawaii. The area has Mars-like features and an elevation of approximately 8,200 feet (2,500 m) above sea level. The first HI-SEAS study was in 2013 and NASA's Human Research Program continues to fund and sponsor follow-up studies. The missions are of extended duration from four months to a year. The purpose of the detailed research studies is to determine what is required to keep a space flight crew happy and healthy during an extended mission to Mars and while living on Mars. Research into food, crew dynamics, behaviors, roles and performance, and other aspects of space flight and a mission on Mars itself is the primary focus. The HI-SEAS researchers also carry out studies on a variety of other topics as part of their daily activities. One thing under study by NASA is trying to understand crew dynamics such as morale, stress management, and how they solve problems as group.
Human Exploration Research Analog or HERA is a unique three-story habitat designed to serve as an analog for isolation, confinement, and remote conditions in exploration scenarios. Environment: Closed Habitat. Continually educating yourself throughout the entire space travel adventure will be the best defense against going stir crazy.
Solitude Skills - Boredom - Isolation Tank - Quarantine
Earth System Science is the application of systems science to the Earth sciences. In particular, it considers interactions between the Earth's "spheres"—atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, biosphere, and, even, the magnetosphere—as well as the impact of human societies on these components. At its broadest scale, Earth system science brings together researchers across both the natural and social sciences, from fields including ecology, economics, geology, glaciology, meteorology, oceanography, paleontology, sociology, and space science. Like the broader subject of systems science, Earth system science assumes a holistic view of the dynamic interaction between the Earth's spheres and their many constituent subsystems, the resulting organization and time evolution of these systems, and their stability or instability. Subsets of Earth system science include systems geology and systems ecology, and many aspects of Earth system science are fundamental to the subjects of physical geography and climate science. Systems Science.
Earth Science is a widely embraced term for the fields of science related to the planet Earth. It is the branch of science dealing with the physical constitution of the earth and its atmosphere. Earth science is the study of our planet’s physical characteristics, from earthquakes to raindrops, and floods to fossils. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. “Earth science” is a broad term that encompasses four main branches of study, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields.
Systems Geology emphasizes the nature of geology as a system – that is, as a set of interacting parts that function as a whole. The systems approach involves study of the linkages or interfaces between the component objects and processes at all levels of detail in order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the solid Earth. A long-term objective is to provide computational support throughout the cycles of investigation, integrating observation and experiment with modeling and theory, each reinforcing the other. The overall complexity suggests that systems geology must be based on the wider emerging cyberinfrastructure, and should aim to harmonize geological information with Earth system science within the context of the e-science vision of a comprehensive global knowledge system (see Linked Data, Semantic Web).
Systems Ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, a subset of Earth system science, that takes a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem is a complex system exhibiting emergent properties. Systems ecology focuses on interactions and transactions within and between biological and ecological systems, and is especially concerned with the way the functioning of ecosystems can be influenced by human interventions. It uses and extends concepts from thermodynamics and develops other macroscopic descriptions of complex systems.
Systems Biology is the computational and mathematical modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach (holism instead of the more traditional reductionism) to biological research.
Biological System s a complex network of biologically relevant entities. As biological organization spans several scales, examples of biological systems are populations of organisms, or on the organ- and tissue scale in mammals and other animals, the circulatory system, the respiratory system, the nervous system, etc. On the micro to the nanoscopic scale, examples of biological systems are cells, organelles, macromolecular complexes and regulatory pathways. A biological system is not to be confused with a living system, which is commonly referred to as life. For further information see e.g. definition of life or synthetic biology. Food in Space.
Microclimates - Green House
 Create
Microclimates in a sterile environment that uses less water than field grown crops.
Bees are allowed in to pollinate, but other bugs are kept out,
eliminating the need for pesticides.
Create
Microclimates in a sterile environment that uses less water than field grown crops.
Bees are allowed in to pollinate, but other bugs are kept out,
eliminating the need for pesticides.
Greenhouse - Cold Frames - Hoop Houses - Cloches - Row Covers - Pop-ups
Greenhouse is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown. These structures range in size from small sheds to industrial-sized buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame. The interior of a greenhouse exposed to sunlight becomes significantly warmer than the external ambient temperature, protecting its contents in cold weather. Many commercial glass greenhouses or hothouses are high tech production facilities for vegetables or flowers. The glass greenhouses are filled with equipment including screening installations, heating, cooling, lighting, and may be controlled by a computer to optimize conditions for plant growth. Different techniques are then used to evaluate optimality-degrees and comfort ratio of greenhouse micro-climate (i.e., air temperature, relative humidity and vapor pressure deficit) in order to reduce production risk prior to cultivation of a specific crop.
Dalsem - High-Tech Greenhouses. (High Quality, High Yield, Short Growing Season). Desalination
Polytunnel or Hoop House, is a tunnel made of polyethylene, usually semi-circular, square or elongated in shape. The interior heats up because incoming solar radiation from the sun warms plants, soil, and other things inside the building faster than heat can escape the structure. Air warmed by the heat from hot interior surfaces is retained in the building by the roof and wall. Temperature, humidity and ventilation can be controlled by equipment fixed in the polytunnel or by manual opening and closing of flaps. Polytunnels are mainly used in temperate regions in similar ways to glass greenhouses and row covers. Besides the passive solar heating that every polytunnel provides, every variation of auxiliary heating (from hothouse heating through minimal heating to unheated houses) is represented in current practice. The nesting of row covers and low tunnels inside high tunnels is also common. Caterpillar Tunnel Hoophouse
Bioshelters is a solar greenhouse managed as an indoor ecosystem. A bioshelter (life-shelter) involves two fields of knowledge and design. The first is architecture designed to nurture an ecosystem within. A bioshelter structure uses glazing to contain and protect the living biology inside, control air exchange and absorb energy. The building exchanges nutrients, gases and energy with the surrounding environment, produces crops, and recycles waste organic material into the soil. Solar energy is stored as heat energy in thermal mass such as water, stone, masonry, soil and plant biomass. The second is the biology inside the bioshelter. Earle Barnhart of the New Alchemy Institute has compared a bioshelter to a contained ecosystem. Solar heat is absorbed and stored in thermal mass to moderate air temperatures and provide heat for later use. Water moves from rainfall to fishponds to soil to plants and finally to water vapor. Year-round habitat is provided for beneficial insects . Ecological relationships between pests and their predators reduce the number of pests. Gases are exchanged among the animals, insects, micro-organisms, soil and plants. Nutrient cycles are developed between fish, plant & soil. Within the bioshelter are a variety of microclimates. The south areas receive the most direct sunlight. The east and west areas can be shaded for a portion of the day. Higher levels in a growing space will be warmer. A well-designed bioshelter, managed by human intelligence, can shelter a community of people, food crops, edible fish, and a diverse ecosystem of plants, animals and soil life.
Bioshelter: Greenhouse (youtube) - Bioshelter-Greenhouse
Vertical Growing Stations
Greenhouse Evaporative Cooler Build (youtube) - Hot Temperatures
Geothermal Greenhouse: It worked. It REALLY Worked! (youtube) - Cold Temperatures
98-Page Guide Alaska Greenhouses
Heating a greenhouse with biomass - wood chips
Biomass - Alaska Energy Authority
Eco Forms - Grow Tent 5-x-5 - Grow Tents Box
Exotic Foods (PDF) - Five Exotic Greenhouse Crops
Root Zone Cooling and Heating to achieve greater profitability and stability in crop production and reduce energy consumption. Plant climate management and the shortage of water for irrigation.
Greenhouse Garden - Greenhouse Megastore
Greenhouse (amazon) - Greenhouse Magazine
Why Purchase a Green House?
Plant Nursery is a building with glass walls and roof used for the cultivation and exhibition of plants under controlled conditions, a place where plants are propagated and grown to usable size. They include retail nurseries which sell to the general public, wholesale nurseries which sell only to businesses such as other nurseries and to commercial gardeners, and private nurseries which supply the needs of institutions or private estates. Nurseries may supply plants for gardens, for agriculture, for forestry and for conservation biology.
Master Gardening - Garden - Village Farms
Growing Underground - Zero Carbon Food
Controlled-Environment Agriculture (wiki)
Cornell Controlled Environment Agriculture
University of Arizona Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
How much Land do we have to grow Food?
Building Kits: Barns, loafing sheds, single slope loafing shed
Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a subset of hydroculture, the method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent. Terrestrial plants may be grown with only their roots exposed to the mineral solution, or the roots may be supported by an inert medium, such as perlite or gravel. The nutrients in hydroponics can be from fish waste, duck manure, or normal nutrients.
Hydroculture is the growing of plants in a soilless medium, or an aquatic based environment. Plant nutrients are distributed via water. Aquaponics.
Hydroponics
Water Systems
Hydroasis
We Grow Hydro
We Grow Store
Hydroponics
Bright Farms
Sustainable Micro-Farms
Hydroponics Genesis Controller
Hydroponics for Beginners (youtube)
Hydroponic Gardening (youtube)
Hydroponics Europe: Nutriculture Aeroponic System Assembly (youtube)
Using 90% less water, 70% less nutrients and getting 10X yields.
Growing Medium
Growing Medium is a substance through which roots can grow and extract water and nutrients. Growing medium's can consist of native soils or artificial soils. Growth Medium.
Coconut Coir Growing Medium
Growing Mediums
Epic Gardening Coconut Coir
Air Max Aerated Coco Premium Soil Blend, 1.5 cf
PRO-MIX BX MYCORRHIZAE
Coconut Coir Nature’s perfect growing media!
Hydroponics is the science of growing plants without soil-- although the plants may or may not be suspended in a solid medium such as gravel, or expanded clay balls.
Soil retains minerals and nutrients, which "feed" flora, as we all know. Plant roots can't absorb dirt, however; when water passes through soil, it dissolves and collects some of the nutrient particles embedded. This "food" solution is absorbable as a liquid. As you can see, the soil itself is not an integral part of a plant's feeding cycle-- it is simply a stabilizer for the roots, and a convenient filter. Why eliminate the soil? Plants breathe air, just like humans. School children are taught a simple lesson: plants take in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen. The entire plant-- not just leafy material-- contributes to this process. If not properly maintained, soil can retain too much moisture, effectively suffocating ("drowning") a plant's root system. Alternatively, if the soil doesn't contain enough moisture, the plant will be unable to absorb the nutrients it needs to survive.
The roots of a hydroponic plant have constant access to both air and water, and it can be much easier to maintain that balance since the roots are typically visible.
The average plant needs at least five things to survive. Air, water, nutrients, minerals, and light. So long as you can provide these things in plenty, your plants should stay healthy.
Growing your own food can be a rewarding experience. If your hydroponic system is indoors, you can grow food during the off-season too. You'll also save money on pesticide-free produce and knowing your food wasn't shipped from a third-world farm that may be supporting bad business practices, like farm worker abuse
Although not necessary for the survival of a plant, substrate can help to support a plant physically and hold it upright, either by securing the root system, or by outweighing the plant itself. There are many kinds of substrates commercially available. Check your local greenhouse or hardware store. Alternatively, there are plenty to be found outdoors, especially near bodies of water. Even simple rock can alter the PH of your system. When checking your PH balance, be sure to check it after it has circulated through your substrate.
In the moisture-rich conditions hydroponics typically provide, substrate can be generally classified into the following categories: sandy, granular, and pebbled.
Sandy environments consist of particles between .06 (fine) and 2mm (coarse) in diameter. Even coarse sand retains a considerable amount of water (except in comparison to soil), and is not generally considered appropriate for use in a hydroponic system. If you use a pump, for example, the small particle size may lead to clogging. However, it is cheap and readily available, and, when wet, is heavy enough to provide a reasonable anchor for plant roots. There is some absorbable nutrient in sand. Typically speaking, the nutrients latent in sand culture vary widely on the substrate's color and origin. Most sand contains a large quantity of shell fragments, and thus has a high calcium content. Black sand usually has a high magnetite content originating from volcanic rock, known for its fertility. Orange or yellow sand might be an indicator of a high iron content. White sand tends to be very high in silica, which helps build healthy cell walls in plantlife. Diahydro, for example, is made from diatoms, a type of algae. Sand is semi-reusable. Sterilizing it between uses can be messy. (Sand can be sterilized by boiling it in water for extended periods of time.)
Granular particles range between 2 and 4mm. This may consist of gravel, or plant mulch. Stone gravel makes a heavy, non-biodegradable anchor for plant roots, and is highly recommended for use in hydroponic systems. Stone gravel contains very little latent plant nutrition, just like sand. There are several grades of gravel readily available to choose from.
Creek rock and Pea Gravel consist of round, shiny stones. The smooth shape of these stones allows for great aeration and root growth, although the drainage may be excessive. Crushed rock is typically made by crushing large chunks of limestone or dolomite into smaller pieces. Crushed rock has sharper edges than creek rock, and tends to interlock better. This tighter knit makes for higher water retention, although limestone tends to weigh less. Limestone is a strong alkali. Check your PH, and balance accordingly.
Stone-based substrate is highly re-useable. It is considerably less messy than sand to boil for sterilization. If weight is not a concern (ie: the plants you grow are not expected to reach considerable heights) you might consider using a plant mulch, such as peat mulch, cedar shavings, or coir (coconut peat). Mulches retain a high quantity of water, but also breathe very well. Mind you, they are also highly degradable, which can lead to clogged pumps, and wood shavings often contain aromatic oils which can inhibit plant growth. Mould and algae growth poses a higher risk when mulches are involved, but pose one considerable advantage over rocky substrate: they can be composted and replaced with fresh material. It does not need to be stored. I wouldn't suggest re-using 'em, anyway. This is especially convenient if you use hydroponic systems exclusively to start seeds, or grow during the off-season.
Pebbled substrate measures between 4 and 64mm. Stone pebbles have the basic characteristics of creek rock. They are typically smooth, often shiny, and the gaps between the stones make for low water retention and high aeration. The shinier the stone, the worse the water retention will be. A matte or pockmarked surface indicates a porous stone, which will stay damper, longer, whilst still providing excellent aeration. Pebbles-- especially the porous variety-- can explode when heated for sterilization.
You should boil your substrate between uses to sterilize it. Bacteria love warm, wet environments and will probably thrive in a hydroponic system. Algae loves wet and warm (and lukewarm... and cold) systems, too, and it can look unsightly. If you care about appearances, boiling your substrate between uses will discourage blossoming, but if you use grey (recycled from previous use) water you'll be fighting a losing battle.
Mirabel Boston Premium Lettuce enriches the water with vitamins and minerals needed for growth and health of the plants, along with controlled for optimal results, such as temperature, light, humidity, etc. This technique requires strict safety procedures and sanitation. Avoiding the waste of water through reuse, eliminating the use of herbicides and fungicides and greatly reduces the use of pesticides. When all these conditions are combined, the lettuces are more tender, less fibrous than conventional agricultural methods.
I love farms that can supply Living lettuce with its roots intact. Delivering fresh lettuce with roots still attached lets moisture and nutrients continue to supply nourishment. Grown in a greenhouse using no pesticides or herbicides, delicious!
Aquaponics
Aquaponics refers to any system that combines conventional aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as snails, fish, crayfish or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) in a symbiotic environment. In normal aquaculture, excretions from the animals being raised can accumulate in the water, increasing toxicity. In an aquaponic system, water from an aquaculture system is fed to a hydroponic system where the by-products are broken down by Nitrifying bacteria initially into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates , which are utilized by the plants as nutrients, and the water is then recirculated back to the aquaculture system. Hydroponics.
 How to Build a Tilapia Pond
How to Build a Tilapia PondHome Aquaponics Kit
Aqua-ponics
Aquaponics
Center for Cooperative Aquaculture Research
EcoQube C - Your Window To Nature a miniature learning tool.
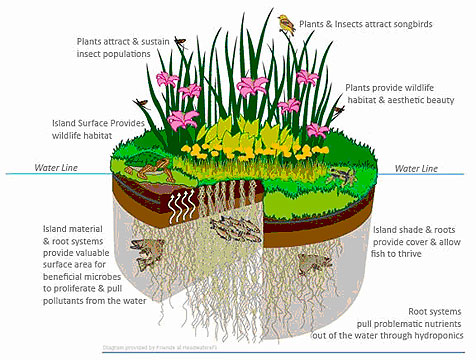
Aqua Biofilter Floating Wetlands & Floating Islands treats waste water, stormwater, aquaculture water, waterways, ponds, dams and lakes. Bio-Accumulation
Floating Wetlands help boost nitrogen removal in lagoons
Seaweed
Growing Spirulina at Home
Growing Spirulina at Home. Blue green algae for fish and people too! (youtube)
"If you compare spirulina to meat it will take six months to grow a kilogram of beef, but spirulina can grow in a week."
Edible Algae
Edible Seaweed are algae that can be eaten and used in the preparation of food. They typically contain high amounts of fiber and are a complete protein. They may belong to one of several groups of multicellular algae: the red algae, green algae, and brown algae.
Peeponics - Hydroponics without the Chemicals, Aquaponics without the Fish (youtube)
Carrageenan are a family of linear sulphated polysaccharides that are extracted from red edible seaweeds. They are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. Their main application is in dairy and meat products, due to their strong binding to food proteins. There are three main varieties of carrageenan, which differ in their degree of sulphation. Kappa-carrageenan has one sulphate group per disaccharide, Iota-carrageenan has two, and Lambda-carrageenan has three.
Seaweed Farms suck carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and counteract ocean acidification. Seaweed grows at 30 to 60 times the rate of land-based plants, so it can draw out lots of C02, and grows enough protein to feed a population of 10 billion people.
Strong Arm Farm sustainably Harvested Sonoma Coast Seaweeds in Sonoma County, California.
O'Leary Aquaponic Farms
Aquaponic balcony garden with the power of Arduino
Ecoqube desktop ecosystem that uses basil to filter water aquaponics.
American Society for Horticultural Science - Farming Knowledge
Improving Ecosystems with Aquatic Plants. Study shows how to grow aquatic plants in large-scale plant production systems.
Wetland restoration is critical for improving ecosystem services, but many aquatic plant nurseries do not have facilities similar to those typically used for large-scale plant production. This study attempts to determine what methods would effectively benefit the large-scale production of aquatic plants as a possible resource of bolstering the improvement of the ecosystems.
Aquaculture
Aquaculture is the farming of fish, crustaceans, molluscs, aquatic plants, algae, and other aquatic organisms. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture refers to aquaculture practiced in marine environments and in underwater habitats.
Algaculture is the farming of species of Algae, which is an informal term for a large, diverse group of photosynthetic organisms which are not necessarily closely related, and is thus polyphyletic. Included organisms range from unicellular genera, such as Chlorella and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 m in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem, which are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and the stoneworts.
Microphyte, which are Microscopic Algae, typically found in freshwater and marine systems living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundreds of micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use simultaneously the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. Microalgae is the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels about it. Microalgae biomass is often measured with chlorophyll a concentrations and can provide a useful index of potential production. The standing stock of microphytes is closely related to that of its predators. Without grazing pressures the standing stock of microphytes dramatically decreases.
Mike Velings: The Case for Fish Farming (video and text)
Fish Farming Dangers
Fish Farming involves raising fish commercially in tanks or enclosures, usually for food. It is the principal form of aquaculture, while other methods may fall under mariculture. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement a species' natural numbers is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Worldwide, the most important fish species used in fish farming are carp, tilapia, salmon, and catfish.
Vero Blue Farms onshore, indoor fish farm growing multiple species of fish on land.
Handbook on small-scale freshwater fish farming
Freshwater Fish Farming in Virginia: Selecting the Right Fish to Raise
Growing Fish in Your Homemade Pond
How to Build a Fish Pond or how to dig a fishpond (youtube)
How to Build all Natural Pond without a Liner | Low Cost and Maintenance | Big Back Yard Water Lake Habitat (youtube)
Open Pond Systems - Macroalgae and Microalgae
Sea Lettuce a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.
Nori is the Japanese name for edible seaweed species of the red algae genus Pyropia, including P. yezoensis and P. tenera.
3D Under Water Vertical Ocean Farming
Seaweed Farming - Two x Sea - Sustainable Fishing Resources
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium (known as geoponics). Uses water and fish waste, aeroponics is conducted without a growing medium. It is sometimes considered a type of hydroponics, since water is used in aeroponics to transmit nutrients.
No Soil, Grows Faster, Uses 90% Less Water then outdoor Farms. Plant Food (PDF)
Backyard Aeroponics: self-sustaining farm for Wisconsin cold (youtube)
The world’s largest aeroponic farm, exploding with food in the middle of a “food desert” (youtube)
Low Pressure Aeroponics Tower Build - Part 1 (youtube)
Rockwool Starter Cubes 1.5" (49 Cubes (1/2 Sheet)
Does growing food Hydroponically or Aeroponically reduce heavy metals and toxins absorbed by food when it is grown in soil?
Micro Greens
Micro-Greens is a tiny vegetable green that is used both as a visual and flavor component or ingredient primarily in fine dining restaurants. Fine dining chefs use microgreens to enhance the beauty, taste and freshness of their dishes with their delicate textures and distinctive flavors. Smaller than “baby greens,” and harvested later than “sprouts,” microgreens can provide a variety of leaf flavors, such as sweet and spicy. They are also known for their various colors and textures. Among upscale markets, they are now considered a specialty genre of greens that are good for garnishing salads, soups, plates, and sandwiches. Edible young greens and grains are produced from various kinds of vegetables, herbs or other plants. They range in size from 1” to 3” including the stem and leaves. A microgreen has a single central stem which has been cut just above the soil line during harvesting. It has fully developed cotyledon leaves and usually has one pair of very small, partially developed true leaves. The average crop-time for most microgreens is 10–14 days from seeding to harvest.
How much to Grow?
Sprouting is the practice of germinating seeds to be eaten raw or cooked. Sprouts can be germinated at home or produced industrially. They are a prominent ingredient of the raw food diet and common in Eastern Asian cuisine. Sprouting, like cooking, reduces anti-nutritional compounds in raw legumes. Raw lentils for example contain lectins, antinutrional proteins which can be reduced by sprouting or cooking. Sprouting is also applied on a large scale to barley as a part of the malting process. A downside to consuming raw sprouts is that the process of germinating seeds can also be conducive to harmful bacterial growth.
Jonathans Sprouts - Sprout Net - Sprout Man - Sprout People
Germination - Seedling
Shoot consist of stems including their appendages, the leaves and lateral buds, flowering stems and flower buds. The new growth from seed germination that grows upward is a shoot where leaves will develop. In the spring, perennial plant shoots are the new growth that grows from the ground in herbaceous plants or the new stem or flower growth that grows on woody plants. In everyday speech, shoots are often synonymous with stems. Stems, which are an integral component of shoots, provide an axis for buds, fruits, and leaves. Young shoots are often eaten by animals because the fibres in the new growth have not yet completed secondary cell wall development, making the young shoots softer and easier to chew and digest. As shoots grow and age, the cells develop secondary cell walls that have a hard and tough structure. Some plants (e.g. bracken) produce toxins that make their shoots inedible or less palatable.
Micro Greens - Microgreens Kits and Growing Supplies
Do it Yourself Grow Kits - In Farm
Lights (LED'S) - Super Foods
Eden Works nutrient-rich Microgreens using aquaponic ecosystems that use 95% less water than conventional farms, no pesticides, and no GMOs. Located in Brooklyn, you’ll find us on the shelf within 24 hours of harvest.
Growing Broccoli Sprouts in a Jar.
Add 2 tablespoons of broccoli sprouting seeds to a wide-mouthed quart jar.
Cover with a few inches of filtered water and cap with the sprouting lid.
Store in a warm, dark place overnight. Can use a kitchen cabinet for this.
The next morning, drain the liquid off and rinse with fresh water. Be sure to drain all the water off.
Repeat this 3-4 times a day. Continue to store your seeds in a warm, dark place. After a few days, the seeds will start to break
open and grow.
Eventually, the sprouts will be an inch or so long and have yellow leaves. Now you can move the sprouts out into the sunlight.
Continue to rinse them 3-4 times a day until the leaves are dark green. Now they are ready to eat!
This whole process will take about a week. Patience is key!
Once they are ready, replace the sprouting lid with a standard mason jar lid and store in the refrigerator.
How to Grow Organic Broccoli Sprouts in a Mason Jar (youtube).
Broccoli sprout compound may restore brain chemistry imbalance linked to schizophrenia a set of chemical imbalances in the brains of people with schizophrenia related to the chemical glutamate. And they figured out how to tweak the level using a compound derived from broccoli sprouts.
Films about Growing Micro-Greens
Interviews & Insights: Chris Thoreau - Commercial Microgreens Operation (youtube)Food Pedalers Microgreens and Wheatgrass, Grown in Vancouver. Delivered by Bike. Since 2009.
Urban Farmer C.Stone (youtube)
74 Year Old Discovers the Fountain of Youth in Her Garden looks 40, John from Growing Your Greens with Annette Larkins (youtube 1 hour 13 mins.)
How to Grow a MicroGreens Vegetable Garden Year Round Inside Your Home (youtube)
Urban Hydrogreens
How to Grow Sprouts with Water or in Soil Any Time of the Year at Got Sprouts (youtube)
Got Sprouts
Red Cabbage Microgreens Lower ‘Bad’ Cholesterol in animal study
Speckled Pea Sprouts
Mung Bean Sprouts - Sprout People
Broccoli Sprouts
Broccoli Sprouts, A Delicious Sprout Variety High in Glucoraphanin (youtube)
Sulforaphane, a phytochemical in broccoli sprouts, improves obesity. Cancer prevention by detoxicating chemical compounds taken into the body and by enhancing anti-oxidation ability. Known to exert effects of cancer prevention by activating a transcription factor, Nrf2 (nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2), which regulates the balance of oxidation -- reduction in the cell, and by enhancing anti-oxidation ability of the body and detoxication of chemical compounds taken into the body. On the other hand, when the balance of oxidation -- reduction is deteriorated due to hyper nutrition and obesity, it has been known to be related to pathogenesis of various diseases. Kanazawa University.
Glucoraphanin enzyme myrosinase transforms glucoraphanin into raphanin, which is an antibiotic, and into sulforaphane, which exhibits anti-cancer and antimicrobial properties in experimental models.
Phytoestrogens are plant-derived xenoestrogens (estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system but consumed by eating phytoestrogenic plants. Also called "dietary estrogens", they are a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of their structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or/and antiestrogenic effects, by sitting in and blocking receptor sites against estrogen.
Wheatgrass Jointing Stage
Easy Sprout Sprouter for Home Growing
Urban Sprouts - Growing Mediums
A tablespoon of seeds can grow a 1/2 pound of sprouts. At the store it's around $18-$25 a pound, sprouts grown at home is around 0.50 cents a tray.
Books about Growing Sprouts
Victorio VKP1014 4-Tray Kitchen Seed SprouterGrowing Herbs
Sprouting Seeds Super Sampler- Organic- 2.5 Lbs of 10 Different Delicious Sprout Seeds: Alfalfa, Mung Bean, Broccoli, Green Lentil, Clover, Buckwheat, Radish, Bean Salad and More
The Sprout House Dozen Organic Sprouting Seeds Sampler Small Quantities of Each Seed Alfalfa, French Lentil, Mung, Daikon Radish, Clover, Green Pea, Garbanzo, Adzuki, Broccoli, Green Lentil, Hard Wheat, Black Sunflower
The Sprout House Organic Sprouting Seeds - Mung, Adzuki, Green Pea, Red Lentil, French Lentil, Green Lentil 1 pound
(amazon)
3 Part Salad Sprout Seed Mix - 1 Lbs - Handy Pantry Brand: Certified Organic Sprouting Seeds: Radish, Broccoli and Alfalfa: Cooking, Food Storage or Delicious Salad Sprouts
LED Lights - Growing Lights for Indoor Farming
Grow Light is an artificial light source, generally an electric light, designed to stimulate plant growth by emitting a light appropriate for photosynthesis. Grow lights are used in applications where there is either no naturally occurring light, or where supplemental light is required. For example, in the winter months when the available hours of daylight may be insufficient for the desired plant growth, lights are used to extend the time the plants receive light. If plants do not receive enough light, they will grow long and spindly.
Migrolight 2.0 Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD)
Photosynthetically Active Radiation or PAR, designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis. This spectral region corresponds more or less with the range of light visible to the human eye. Photons at shorter wavelengths tend to be so energetic that they can be damaging to cells and tissues, but are mostly filtered out by the ozone layer in the stratosphere. Photons at longer wavelengths do not carry enough energy to allow photosynthesis to take place.
Blue, Red, Far Red LED's
LED Grow Lights 101
LED Facts
LED Lights for Growing
Advanced LED Lights
Blue-Red LED 13.8 Watt Square Grow Light Panel (amazon)
LED Lighting Advances in Horticultural Applications boosts Productivity
LED's (Home Lighting)
1000 Bulbs - Green Electrical Supply - Earth LED
Intelligent Gro fully programmable color channels and automated 24 day/night schedules for all phases of plant growth or to replicate any lighting condition, sunrise/sunset, moon lighting, cloudy days or even make up your own spectrum to suit your personal needs. Certain color LED lights can cause food to grow differently.
Diamond Series LED's
In indoor growing, to grow 2 pounds of potato's or tomato's require about 1,200 kilowatt-hours of electricity for each kilogram of edible tissue they produce? 1,200 kilowatt-hours is the annual electricity consumption of the average American home refrigerator.
There are 3 factors to successfully grow crops with artificial light: Light Quality (recipe), Light Intensity (micromol), Light Duration (hours per day). This is different for every plant but generally the same species will do good under the same parameters. For lettuce we found that red/blue/warm white at a certain ratio seemed to work best for the flavor it gave the lettuce. The specific promotion of vitamin and carotenoid development such as lutein and zeaxanthin gives a good taste.
Engineered light to improve health, food. Intentionally controlled light can help regulate human health and productivity by
eliciting various hormonal responses. Tailored LED wavelengths and intensities also can efficiently stimulate plant growth, alter their shapes and increase their nutritional value, opening a new world of scientific and technological possibilities for indoor farming.
Seeds - Artificial Photosynthesis
