BK101
Knowledge Base
Stress
Stress is a state of mental or emotional strain. Stress is a difficult experience that causes worry or emotional tension. Stress is a result of a mentally demanding activity or experience, or from a physically demanding activity or experience that has a high degree of uncertainty or risk. Stressor is any agent that causes stress to an organism.
Stress Management - Stress Relief - Triggers
 Stress
is a feeling of strain and pressure. Excessive amounts of stress may lead
to bodily harm.
Stress can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, dwarfism,
and mental illnesses such as depression.
Stress can be external and related to the
environment, but may also be created by internal
perceptions that cause an individual to
experience
anxiety or other negative
emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc.,
which they then deem stressful. Humans experience stress, or perceive
things as threatening, when they do not believe that their resources for
coping with obstacles
(stimuli, people, situations, etc.) are enough for what the circumstances
demand. When we think the demands being placed on us exceed our ability to
cope, we then perceive stress. But not all stress has
negative
effects. Small amounts of stress may be desired, beneficial, and even
healthy. Positive stress helps improve
athletic performance. It also plays a factor in motivation, adaptation,
and reaction to the environment.
Stress
is a feeling of strain and pressure. Excessive amounts of stress may lead
to bodily harm.
Stress can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, dwarfism,
and mental illnesses such as depression.
Stress can be external and related to the
environment, but may also be created by internal
perceptions that cause an individual to
experience
anxiety or other negative
emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc.,
which they then deem stressful. Humans experience stress, or perceive
things as threatening, when they do not believe that their resources for
coping with obstacles
(stimuli, people, situations, etc.) are enough for what the circumstances
demand. When we think the demands being placed on us exceed our ability to
cope, we then perceive stress. But not all stress has
negative
effects. Small amounts of stress may be desired, beneficial, and even
healthy. Positive stress helps improve
athletic performance. It also plays a factor in motivation, adaptation,
and reaction to the environment.
Signs of Stress - PTSD - Harassment (abuse) - Body Burden (stressors)
Distress is psychological suffering or extreme physical pain. A state of difficulties, danger, affliction or need.
Stress in biology is an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition. Stress is a body's method of reacting to a challenge. According to the stressful event, the body's way to respond to stress is by sympathetic nervous system activation which results in the fight-or-flight response. Because the body can not keep this state for long periods of time, the parasympathetic system returns the body's physiological conditions to normal (homeostasis). In humans, stress typically describes a negative condition that can affect a person's mental and physical well-being. Stress either physiological or biological is an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition. Stress is the body's method of reacting to a condition such as a threat, challenge or physical and psychological barrier. Stimuli that alter an organism's environment are responded to by multiple systems in the body. The autonomic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis are two major systems that respond to stress.
Chronic Stress is the response to emotional pressure suffered for a prolonged period of time in which an individual perceives he or she has little or no control. It involves an endocrine system response in which corticosteroids are released. While the immediate effects of stress hormones are beneficial in a particular short-term situation, long-term exposure to stress creates a high level of these hormones. This may lead to high blood pressure (and subsequently heart disease), damage to muscle tissue, inhibition of growth, suppression of the immune system, and damage to mental health.
Biological Stressors are conditions that make it hard for your body to take part in daily activities. This could involve illness, disability, biochemical changes in the body, or injuries. For instance, a biological stressor could be that you are sick with the flu.
Stress in Early Childhood. Early childhood is a critical period in a child’s life that includes ages from conception to five years old. Psychological stress is an inevitable part of life. Human beings can experience stress from an early age. Although stress is a factor for the average human being, it can be a positive or negative molding aspect in a young child’s life. stress can be beneficial by helping children develop skills needed to adapt to a new set of circumstances and deal with dangerous and intimidating situations. Some experts have theorized that there is a point where prolonged or excessive stress becomes harmful and can lead to serious health effects. When stress builds up in early childhood, neurobiological factors are affected. In turn, levels of the stress hormone cortisol exceed normal ranges. This theory however is based on animal studies and cross-sectional studies in humans, and the proposed impacts on brain centers have not been found in a landmark twin study and studies where neurobiological factors were measured in humans prior to stress or trauma exposure. Researchers have proposed three distinct types of responses to stress in young children: positive, tolerable, and toxic. These labels are based on theorized differences in lasting physiological changes occurring as a result of the intensity and duration of the stress response. Stress is caused by internal or external influences that disrupt an individual’s normal state of well-being. These influences are capable of affecting health by causing emotional distress and leading to a variety of physiological changes. Internal stressors include physiological conditions such as hunger, pain, illness or fatigue. Other internal sources of stress consist of shyness in a child, emotions, gender, age and intellectual capacity. Childhood trauma has lifelong impact. Exposure to adverse childhood experiences can include separation from family, home violence, neighborhood violence, mental illness or substance use disorder of caregiver, physical/sexual abuse, neglect divorce, a new home or school, illness and hospitalization, death of a loved one, poverty, natural disasters, and adults’ negative discipline techniques (e.g. spanking). Additional external stressors include prenatal drug exposure, such as maternal methamphetamine use, other maternal and paternal substance abuse, maternal depression, posttraumatic stress and psychosis.
Occupational Stress is stress related to one's job. Occupational stress often stems from unexpected responsibilities and pressures that do not align with a person's knowledge, skills, or expectations, inhibiting one's ability to Cope. Occupational stress can increase when workers do not feel supported by supervisors or colleagues, or feel as if they have little control over work processes.
Job Stress - Stress Brain
Tension in psychology is a state of mental or emotional strain or suspense. The physical condition of being stretched or strained. Feelings of hostility that are not manifest.
Stress Experienced by Nurses: Increased prevalence of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in critical care nurses. Alleviating job stress in nurses: approaches to reducing job stress in nurses. Depression, Anxiety and Symptoms of Stress among Hong Kong Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study. Comparison of the Value of Nursing Work Environments in Hospitals Across Different Levels of Patient Risk.
Alarm Fatigue
Techno-Stress is the negative psychological link between people and the introduction of new technologies. Where ergonomics is the study of how humans react to and physically fit with machines in their environment, technostress is a result of altered habits of work and collaboration that are being brought about due to the use of modern information technologies at office and home situations. People experience technostress when they cannot adapt to or cope with information technologies in a healthy manner. They feel compulsive about being connected and sharing constant updates, feel forced to respond to work-related information in real-time, and engage in almost habitual multi-tasking. They feel compelled to work faster because information flows faster, and have little time to spend on sustained thinking and creative analysis.
Why Stress Doesn't Always Cause Depression. Rats susceptible to anhedonia, a core symptom of depression, possess more serotonin neurons after being exposed to chronic stress, but the effect can be reversed through amygdala activation.
Not all Stress is Bad. Stress from certain exercises is beneficial. Stress from reducing food intake also has benefits. The human body is designed to experience stress and react to it. Stress can be positive, keeping us alert and ready to avoid danger. But stress can become a negative when a person faces continuous challenges without relief or relaxation between challenges. As a result, the person becomes overworked, and stress-related tension builds. Stress costs American industry more than $300 billion annually.
What doesn't kill you doesn't necessarily make you stronger - Exposure.
Humans naturally like to be in low pressure situations. Just like molecules in a high pressure zone, they naturally gravitate towards a low pressure area.
Cortisone is a pregnane (21-carbon) steroid Hormone. It is one of the main hormones released by the adrenal gland in response to stress. Cortisol - Adrenaline.
Cell Mechanism Regulating Protein Synthesis in Stress Conditions by Altering tRNA Abundance.
Effects of Stress on your Body - Suffering - Social Pressures - Resilience
How Stress causes Gray Hair. the type of nerve involved in the fight-or-flight response causes permanent damage to the pigment-regenerating stem cells in the hair follicle. The findings advance knowledge of how stress impacts the body, and are a first step toward blocking its negative effects. Sympathetic nerve system, which is responsible for the body's fight-or-flight response. Sympathetic nerves branch out into each hair follicle on the skin. The researchers found that stress causes these nerves to release the chemical norepinephrine, which gets taken up by nearby pigment-regenerating stem cells. Researchers found that the norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves causes the stem cells to activate excessively. The stem cells all convert into pigment-producing cells, prematurely depleting the reservoir. Grey Hair and Aging.
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder - PTSD
Acute Stress Reaction is a psychological condition arising in response to a terrifying or traumatic event, or witnessing a traumatic event that arises a strong emotional response within the individual. It should not be confused with the unrelated circulatory condition of shock/ hypoperfusion, or the concept of shock value. Acute stress reaction may develop into delayed stress reaction or better known as PTSD if stress isn't correctly managed. Triggers.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental disorder that can develop after a person is exposed to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, or other threats on a person's life. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in how a person thinks and feels, and increased arousal. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event. Young children are less likely to show distress but instead may express their memories through play. Those with PTSD are at a higher risk of suicide.
The Post Traumatic Stress Center
Post Dramatic Stress Syndrome
Correlation between PTSD & Substance Abuse
We train soldiers for war. Let's train them to come home, too: Hector Garcia (video and interactive text)
PTSD Coach App
Psychedelic Therapy
Reconsolidation Therapy - Exposure Therapy - Memory Failures
Combat Stress Reaction is a term used within the military to describe acute behavioral disorganization seen by medical personnel as a direct result of the trauma of war. Also known as "combat fatigue" or "battle neurosis", it has some overlap with the diagnosis of acute stress reaction used in civilian psychiatry. It is historically linked to shell shock and can sometimes precurse post-traumatic stress disorder.
Survivor Guilt is a mental condition that occurs when a person perceives themselves to have done wrong by surviving a traumatic event when others did not. It may be found among survivors of murder, terrorism, combat, natural disasters, epidemics, among the friends and family of those who have died by suicide, and in non-mortal situations such as among those whose colleagues are laid off. FOMO - Anxiety.
Psychological Trauma is a type of damage to the mind that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event. Trauma is often the result of an overwhelming amount of stress that exceeds one's ability to Cope, or integrate the emotions involved with that experience. A traumatic event involves one's experience, or repeating events of being overwhelmed that can be precipitated in weeks, years, or even decades as the person struggles to cope with the immediate circumstances, eventually leading to serious, long-term negative consequences.
Complex Post-traumatic Stress Disorder is a proposed diagnostic term for a variant of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) that results from repetitive, prolonged trauma involving harm or abandonment by a caregiver or other interpersonal relationship with an uneven power dynamic, such as intimate partner violence (IPV). C-PTSD is associated with child abuse or neglect, IPV, hostages or prisoners of war, concentration camp survivors, defectors of certain organizations that some considered cults. Situations involving captivity or entrapment (a situation lacking a viable escape route for the victim) can lead to C-PTSD-like symptoms, which include prolonged feelings of helplessness and deformation of one's identity and sense of self.
TSRI Researchers Discover How the Brain Turns Chronic Stress into Pathological Anxiety
Endocannabinoid or eCB system include natural lipid signaling molecules that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, a peptide molecule called corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF). Anandamide clearance enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) override the stress-reducing capabilities of a major eCB called N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide). Increased CRF was also associated with drops in anandamide levels in the central nucleus of the amygdala. Together, increased FAAH activity and decreased anandamide signaling reduce inhibitory control of excitatory neurotransmission in this critical region, and lower the brain's ability to regulate stress and anxiety.
Brain Sciences Researcher Pinpoints Brain Circuit That Triggers Fear Relapse. Hippocampus-driven feed-forward inhibition of the prefrontal cortex mediates relapse of extinguished fear. The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) has been implicated in the extinction of emotional memories, including conditioned fear. We found that ventral hippocampal (vHPC) projections to the infralimbic (IL) cortex recruited parvalbumin-expressing interneurons to counter the expression of extinguished fear and promote fear relapse. Whole-cell recordings ex vivo revealed that optogenetic activation of vHPC input to amygdala-projecting pyramidal neurons in the IL was dominated by feed-forward inhibition. Selectively silencing parvalbumin-expressing, but not somatostatin-expressing, interneurons in the IL eliminated vHPC-mediated inhibition. In behaving rats, pharmacogenetic activation of vHPC→IL projections impaired extinction recall, whereas silencing IL projectors diminished fear renewal. Intra-IL infusion of GABA receptor agonists or antagonists, respectively, reproduced these effects. Together, our findings describe a previously unknown circuit mechanism for the contextual control of fear, and indicate that vHPC-mediated inhibition of IL is an essential neural substrate for fear relapse.
Related Subject Pages: Depression - Grieving - Anxiety - Anger - Emotions - Crime - Violence - The Human Brain - Bad Memories - Attention Restoration - Know Thyself.
Stress Relief
Stress Management refers to the wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's levels of stress, especially chronic stress, usually for the purpose of improving everyday functioning.
Some of the things that help reduce some of the effects of Stress:
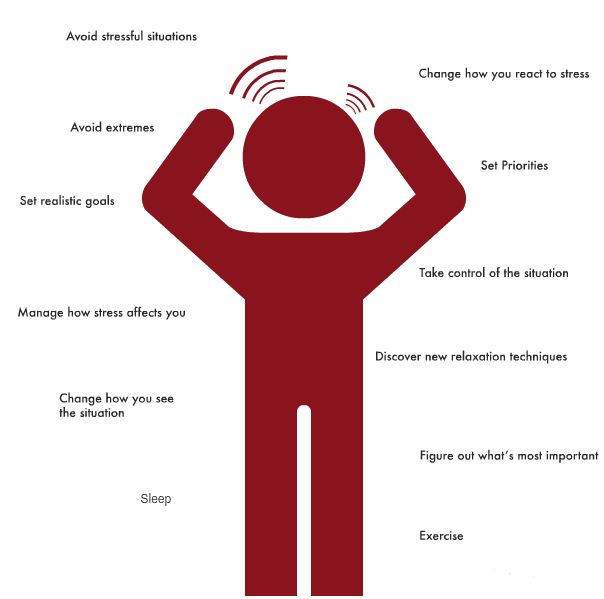 Sleep
- Meditation
Sleep
- MeditationExercise - Sports
Eating Healthy
Talking - Faith
Learning - Games
Humor - Chewing Gum
Music - Tea
Writing - Travel
Sex - Controls
Time Management
Decision Making
Planning - Goals
Controlling your breathing and being aware of your breathing can help control your emotions. Breathing Exercises.
Stress Management
Dealing with Stress
Relaxation Techniques
How to Handle Stressful Situations
Relaxation Techniques for Stress Relief
Relieve Stress Tips
Stress Network
Relieve-Stress
Stress
Punching Bag (wiki)
Coping
Patience
Balance
You have to learn how to adjust your comfort level because not all Pain is injury related.
Happy Thoughts are just logical thoughts.
Cortisol has been shown to damage and kill cells in the hippocampus (the brain area responsible for your episodic memory) and there is robust evidence that chronic stress causes premature brain aging. Stress Hormone Cortisol "Turning adversity into opportunity"
Cortisol Hormone is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Serotonin Transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein that transports serotonin from the synaptic cleft to the presynaptic neuron.
Morals - Philosophy - Reverse Placebo
Most stress is created in our mind, if it's not a Fight or Flight a Life or Death Situation, then the stress you're feeling is all created by you. Exercise is stressful, yet it's good for us. You can say that it's a different kind of stress but you can not ignore the fact that you can easily not enjoy exercising, so it's how you Perceive it. Fear can cause stress, but when I watch a horror movie I can experience some of the same effects that fear causes, even knowing it's a movie and it's not real. So the stress is not damaging but more entertaining. Again it's how you perceive it.
Awareness. Physical stress can easily influence the way you think and act. Mental stress can also control the way you think and act. A person needs to know when the body is stressed so that a person can protect themselves from injury by stopping and by taking a break and resting. A person also needs to know when the mind is stressed so they are aware of things accurately and not just reacting. We need to be aware of our body, but we also need to be aware of how our mind is reacting to stress. People can get angry or depressed very easy when the body or mind is under stress. Everyone needs to know how to be in control and be aware, if not, then you will be vulnerable to behaviors and actions that you are not aware of. People jump when they hear loud noises when other people don't. When your exercising your body is under stress, but a person will react differently to the stress of exercise then they do the stress from physical labor. Relative.
We all know about Second Chances. Everyone wishes at some point in their life that they would have had a second chance. What would you say? What would you do differently if you had a second chance? We need to stop defining our past experiences as being the only chances that we have. Everyday that you wakeup is a second chance. Second chances are everywhere. But you have to open your heart and open your mind and seek out second chance moments, because second chances will not always come to you. You need to learn from your past, share what you have learned, and create new futures. This way your past doesn't become someone's else's future.
"Life shouldn't be something that you have to endure, life should be something that you should love to explore."
"The Reality for most people is Sleep very little, Eat unhealthy, Work too much and then Repeat. Eat, Pray, Love must be about praying for a better world."
Under Pressure - Queen and David Bowie - with lyrics (youtube)
