BK101
Knowledge Base
Hygiene - Bathing - Staying Clean
Hygiene is a set of practices performed for the preservation of health and for the prevention of illness. Hygiene is to cleanse the entire body so that you can look clean and smell clean. Sanitary is to be free from filth and pathogens.
Personal Grooming - Bathing - Skin Care - Nails - Hair - Toilet Training - Toilet (#1 and #2).
Hygiene Hypothesis is a hypothesis that states that a lack of early childhood exposure to infectious agents, symbiotic microorganisms (such as the gut flora or probiotics), and parasites increases susceptibility to allergic diseases by suppressing the natural development of the immune system. In particular, the lack of exposure is thought to lead to defects in the establishment of immune tolerance. Personal Hygiene.
Hand Washing
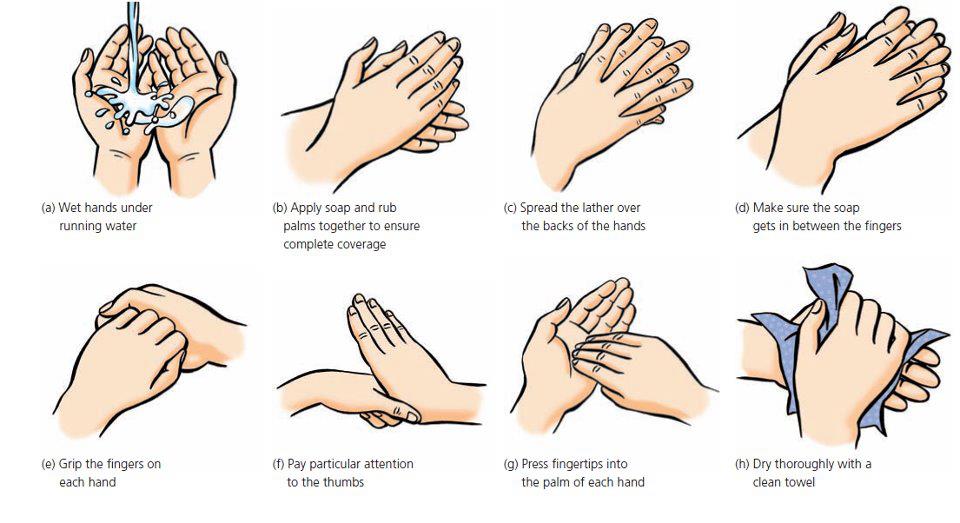 Hand Washing (cdc) -
Hand Hygiene (cdc)
Hand Washing (cdc) -
Hand Hygiene (cdc)CDC Hand Washing Tips - Washing Hands Tips
Washing Hands Saves Lives (video with interactive text)
Global Handwashing Day is an international handwashing promotion campaign to motivate and mobilize people around the world to improve their handwashing habits. Washing hands at critical points during the day and washing with soap are both important. Global Handwashing Day occurs on 15 October of each year. The global campaign is dedicated to raising awareness of handwashing with soap as a key factor in disease prevention. Respiratory and intestinal diseases can be reduced by 25-50%. Global Hand Washing - Wash Advocates.
Soap - Disinfect (clean) - Body Oder (sweat)
Soaps can be Recycled - How Used Hilton Hotel Soaps Get Recycled (youtube) - Clean the World is a nonprofit organization that recycles used soaps, lotions, and other toiletries from hotels. Its partners include Hilton, Marriott, and Walt Disney World Resorts, among others. Clean the World has donated over 50 million bars of recycled soap to people in need in 127 countries since its founding in 2009. The organization has had to adapt as more hotel chains move away from single-use toiletries in favor of bulk offerings. Hilton’s partnership with Clean the Word began in 2009, not 2019. The data presented in the video reflects the first seven months of the Clean the World Challenge — a promise to donate 1 million bars of Soap by October 15, 2019 (Global Handwashing Day). Insider regrets the error.
If you sleep for 12 hours a day, you will have 720 minutes to do things in your day. You should use a couple of those minutes in your day to do some simple tasks that would benefit you. A couple of minutes a day to do something positive. And you still have 718 minutes left.
Allergies - Colds - Flu - Hospital Infections - Viruses
Cholera is spread mostly by unsafe water and unsafe food that has been contaminated with human feces containing the bacteria. Undercooked seafood is a common source. Humans are the only animal affected. Risk factors for the disease include poor sanitation, not enough clean drinking water, and poverty. Cholera can be diagnosed by a stool test. A rapid dipstick test is available but is not as accurate. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Wiping your Butt.
Hand Sanitizer a alcohol-based type hand washing gel.
WHO: How to Hand Rub with alcohol-based formulation (youtube)
Zylast Hands Sanitizer - Nano Touch Materials
Hands
 Hand is a
prehensile, which is the quality of an appendage or organ that has
adapted for grasping or holding. A multi-fingered
organ located at the end of the
forearm or forelimb.
The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27
bones.
Hand is a
prehensile, which is the quality of an appendage or organ that has
adapted for grasping or holding. A multi-fingered
organ located at the end of the
forearm or forelimb.
The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27
bones.Index Finger is the first finger and the second digit of a human hand. (pointer finger).
Middle Finger is the third digit of the human hand, located between the index finger and the ring finger. It is usually the longest finger.
Ring Finger is the fourth proximal digit of the human hand, and the second most ulnar finger, located between the middle finger and the little finger.
Little Finger or pinky, is the most ulnar and usually smallest finger of the human hand, opposite the thumb, and next to the ring finger.
Thumb is the first digit of the hand. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit.
Male Ring Finger is typically longer than the Index Finger. Female Ring Finger and Index Finger are about the Same Length. Testosterone.
Reflexology is an alternative medicine involving application of pressure to the feet and hands with specific thumb, finger, and hand techniques without the use of oil or lotion. It is based on a system of zones and reflex areas that purportedly reflect an image of the body on the feet and hands, with the premise that such work effects a physical change to the body.
Feet
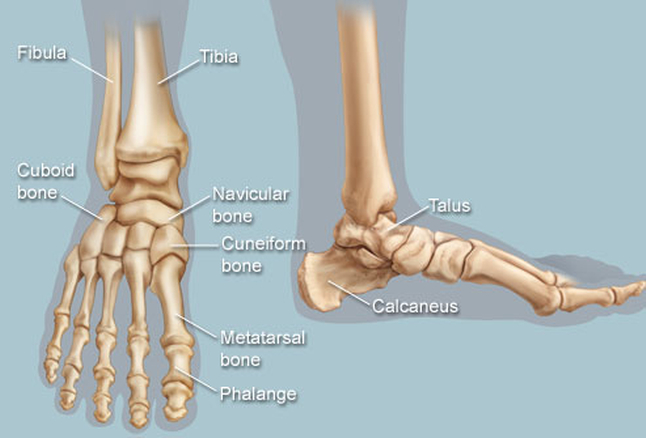
 Foot is an anatomical
structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb
which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the
foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or
more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. The human foot
is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing
26 bones, 33
joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred
muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The joints of the foot are the ankle and subtalar joint and the interphalangeal articulations of the foot.
Sweat.
Foot is an anatomical
structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb
which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the
foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or
more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. The human foot
is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing
26 bones, 33
joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred
muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The joints of the foot are the ankle and subtalar joint and the interphalangeal articulations of the foot.
Sweat. Take off your Shoes when in your Home. Shoes can carry 421,000 different types of Bacteria.
Footwear refers to garments worn on the feet, which originally serves to purpose of protection against adversities of the environment, usually regarding ground textures and temperature. Footwear in the manner of shoes therefore primarily serves the purpose to ease the locomotion and prevent injuries. Secondly footwear can also be used for fashion and adornment as well as to indicate the status or rank of the person within a social structure. Socks and other hosiery are typically worn additionally between the feet and other footwear for further comfort and relief.
Carhartt Boot Review (youtube) - Has carhart turned into a fast fashion brand? If not, these boots are a step in that unfortunate direction.
Shoe Size is an indication of the fitting size of a shoe for a person. There are a number of different shoe-size systems used worldwide. While all of them use a number to indicate the length of the shoe, they differ in exactly what they measure, what unit of measurement they use, and where the size 0 (or 1) is positioned. Some systems also indicate the shoe width, sometimes also as a number, but in many cases by one or more letters. Some regions use different shoe-size systems for different types of shoes (e.g. men's, women's, children's, sport, and safety shoes). This article sets out several complexities in the definition of shoe sizes. In practice, shoes should be tried on for size and fit before they are purchased.
 Barleycorn is an old English unit that equates to 1⁄3 inch (8.47 mm).
This is the basis for current UK and North American shoe sizes, with the
largest shoe size taken as twelve inches (a size 12) i.e. 30.5 cm, and
then counting backwards in barleycorn units, so a size 11 is 11.67 inches or 29.6 cm.
Barleycorn is an old English unit that equates to 1⁄3 inch (8.47 mm).
This is the basis for current UK and North American shoe sizes, with the
largest shoe size taken as twelve inches (a size 12) i.e. 30.5 cm, and
then counting backwards in barleycorn units, so a size 11 is 11.67 inches or 29.6 cm.
Shoelaces is a system commonly used to secure shoes, boots and other footwear. They typically consist of a pair of strings or cords, one for each shoe, finished off at both ends with stiff sections, known as aglets. Each shoelace typically passes through a series of holes, eyelets, loops or hooks on either side of the shoe. Loosening the lacing allows the shoe to open wide enough for the foot to be inserted or removed. Tightening the lacing and tying off the ends secures the foot within the shoe.
 Podoconiosis also
known as nonfilarial elephantiasis, is a disease of the lymph vessels of
the lower extremities that is caused by chronic exposure to irritant
soils. It is the second most common cause of tropical lymphedema after
filariasis, and it is characterized by prominent swelling of the lower
extremities, which leads to disfigurement and disability. Prior to the
development of lymphatic failure and frank lymphedema, a prodrome
consisting of itching, burning, hyperkeratosis, plantar edema, and rigid
digits may occur. As with other forms of tropical lymphedema, chronic
disease can lead to fusion of the toes, ulceration, and bacterial
superinfection. The disease has an acute component, and sufferers may
experience recurrent episodes of lower extremity warmth, firmness, and
pain. The cornerstone of prevention and treatment of podoconiosis is
avoidance of exposure to irritant soils. Wearing shoes in the presence of
irritant soils is the primary method of exposure reduction. In Rwanda,
a country of high disease prevalence, the government has banned walking
barefoot in public, in order to curtail podoconiosis and other soil-borne
diseases. Once the disease has developed, rigorous foot hygiene including
daily washing with soap and water, application of an emollient, and
nightly elevation of the affected extremity has been shown to reduce
swelling and disability. Compression wrapping and decongestive
physiotherapy of the affected extremity has been shown to be effective in
other forms of lymphedema, but the benefits of these therapies have not
been rigorously studied in podoconiosis. Nodules will not resolve with
these conservative measures, although surgical removal of the nodules can be performed.
Podoconiosis also
known as nonfilarial elephantiasis, is a disease of the lymph vessels of
the lower extremities that is caused by chronic exposure to irritant
soils. It is the second most common cause of tropical lymphedema after
filariasis, and it is characterized by prominent swelling of the lower
extremities, which leads to disfigurement and disability. Prior to the
development of lymphatic failure and frank lymphedema, a prodrome
consisting of itching, burning, hyperkeratosis, plantar edema, and rigid
digits may occur. As with other forms of tropical lymphedema, chronic
disease can lead to fusion of the toes, ulceration, and bacterial
superinfection. The disease has an acute component, and sufferers may
experience recurrent episodes of lower extremity warmth, firmness, and
pain. The cornerstone of prevention and treatment of podoconiosis is
avoidance of exposure to irritant soils. Wearing shoes in the presence of
irritant soils is the primary method of exposure reduction. In Rwanda,
a country of high disease prevalence, the government has banned walking
barefoot in public, in order to curtail podoconiosis and other soil-borne
diseases. Once the disease has developed, rigorous foot hygiene including
daily washing with soap and water, application of an emollient, and
nightly elevation of the affected extremity has been shown to reduce
swelling and disability. Compression wrapping and decongestive
physiotherapy of the affected extremity has been shown to be effective in
other forms of lymphedema, but the benefits of these therapies have not
been rigorously studied in podoconiosis. Nodules will not resolve with
these conservative measures, although surgical removal of the nodules can be performed.
Nails
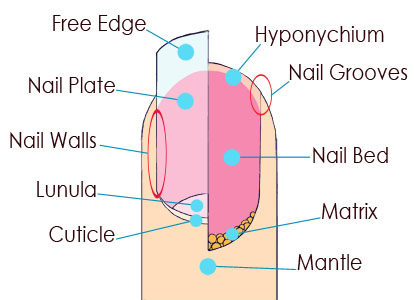 Nail is a horn-like envelope
covering the tips of the fingers and toes in humans. Nails are similar to
claws in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough
protective protein called
keratin
which is a
fibrous structural proteins that protects epithelial cells from damage
or stress. It is the key structural material making up the outer layer of
human skin.
Nail is a horn-like envelope
covering the tips of the fingers and toes in humans. Nails are similar to
claws in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough
protective protein called
keratin
which is a
fibrous structural proteins that protects epithelial cells from damage
or stress. It is the key structural material making up the outer layer of
human skin.Fingernails can be indicators of Health or Disease (image info-graph)
Nails can Reveal your Health - Unhealthy Nails and Disease
Identifying Nutritional Deficiencies Through Nails, Skin & Hair (youtube)
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail. - YMCA Feet Photo (nail fungus)
Nail Biting (bad habits)
Fingernail Care: To keep your fingernails looking their best: Keep fingernails dry and clean. This prevents bacteria from growing under your fingernails. Repeated or prolonged contact with water can contribute to split fingernails. Wear cotton-lined Rubber Gloves when washing dishes, cleaning or using harsh chemicals. Practice good nail hygiene. Use a sharp manicure scissors or Clippers. Trim your nails straight across, then round the tips in a gentle curve using a Nail File. Use moisturizer. When you use hand lotion, rub the lotion into your fingernails and cuticles, too. Apply a protective layer. Applying a nail hardener might help strengthen nails. Ask your doctor about biotin. Some research suggests that the nutritional supplement biotin might help strengthen weak or brittle fingernails. Baby's nails are softer and more pliable than adults, but they still can cause scratches and need trimming regularly. A baby's fingernails grow fast, so you may have to trim them weekly or even more frequently. Toenails grow more slowly and therefore require less maintenance. If you scratch yourself a lot, you should trim your nails short and file your fails so that your nails are smooth with no sharp edges. So if you do scratch yourself, at least you will be less likely to damage the skin or break the skin.
Manicure is trimming the fingernails carefully and neatly or cutting and shaping the nails. Manicure consists of filing and shaping the free edge, pushing and clipping (with a cuticle pusher and cuticle nippers) any nonliving tissue (but limited to the cuticle and hangnails), treatments with various liquids, massage of the hand, and the application of fingernail polish. When the same is applied to the toenails and feet, the treatment is referred to as a pedicure, which is treatment of the feet and toenails that include care not only for the toenails; dead skin cells are rubbed off the bottom of the feet using a rough stone (often a pumice stone). Skin care is often provided up to the knee, including granular exfoliation, moisturizing, and massage.
Nail Clipper is a hand tool used to trim fingernails, toenails and hangnails.
Nail File is a tool used to gently grind down and shape the edges of nails. They are often used in manicures and pedicures after the nail has been trimmed using appropriate nail clippers. Nail files may either be emery boards, ceramic, glass, crystal, plain metal files or metal files coated with corundum.
Nail Buffing is the act of polishing the nail using buffers of successively finer grit in order to make nails look more consistent and shiny. A paste is used to fill ridges on nail surfaces.
Nail Polish is a lacquer that can be applied to the human fingernail or toenails to decorate and protect the nail plates.
How long does a nail take to grow back? After a nail separates from the nail bed for whatever reason, it will not reattach. A new nail will have to grow back in its place. Nails grow back slowly. It takes about 6 months for a fingernail and up to 12 to 18 months for a toenail to grow back. The way a toenail grows is out of the matrix, which is the little pocket under the skin. It constantly is creating new cells, which lengthens the nails by forcing the old ones to get pushed together and grow out. When the cells finally grow out of the matrix, they are dead. The nail matrix is the area where your fingernails and toenails start to grow. The matrix creates new skin cells, which pushes out the old, dead skin cells to make your nails. As a result, injuries to the nail bed or disorders that affect the matrix can affect your nail growth.
Hair
 Hair is a
protein filament that grows from
follicles found in the
dermis,
or skin. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human
body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which
produce thick terminal and fine Vellus Hair. Most common interest in hair
is focused on Hair Growth, hair types and
Hair Care, but hair is also an
important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably
Keratin,
which is one of a family of fibrous structural
proteins. It is the key
structural material
making up hair, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of human skin.
Keratin is also the protein that protects
Epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble
in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to
form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized
epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals.
The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of
keratinized tissue is
Chitin,
which is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, is a derivative of
glucose. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi, the
exoskeletons of arthropods, such as crustaceans (e.g., crabs, lobsters and
shrimps) and insects, the radulae of molluscs, cephalopod beaks, and the
scales of fish and lissamphibians. The structure of chitin is comparable
to another polysaccharide - cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or
whiskers. In terms of function, it may be compared to the protein keratin.
Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and
biotechnological purposes.
Hair is a
protein filament that grows from
follicles found in the
dermis,
or skin. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human
body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which
produce thick terminal and fine Vellus Hair. Most common interest in hair
is focused on Hair Growth, hair types and
Hair Care, but hair is also an
important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably
Keratin,
which is one of a family of fibrous structural
proteins. It is the key
structural material
making up hair, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of human skin.
Keratin is also the protein that protects
Epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble
in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to
form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized
epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals.
The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of
keratinized tissue is
Chitin,
which is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, is a derivative of
glucose. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi, the
exoskeletons of arthropods, such as crustaceans (e.g., crabs, lobsters and
shrimps) and insects, the radulae of molluscs, cephalopod beaks, and the
scales of fish and lissamphibians. The structure of chitin is comparable
to another polysaccharide - cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or
whiskers. In terms of function, it may be compared to the protein keratin.
Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and
biotechnological purposes. Afro-Textured Hair is when each strand of this hair type grows in a tiny, angle-like helix shape. The overall effect is such that, compared to straight, wavy or curly hair, afro-textured hair appears denser. Curly hair is dominant, so someone is more likely to have curly or wavy hair if at least one of their parents does. Recent research points to trichohyalin, a protein in hair follicles, as having primary influence over hair curl. However, there are many genes contributing to hair curliness, most of them unknown. The main driver to have been identified is a gene that produces a protein called trichohyalin (TCHH), which strengthens the growing hair. Curly Hair is thought to protect the scalp as people walked in the intense African or equatorial UV light.
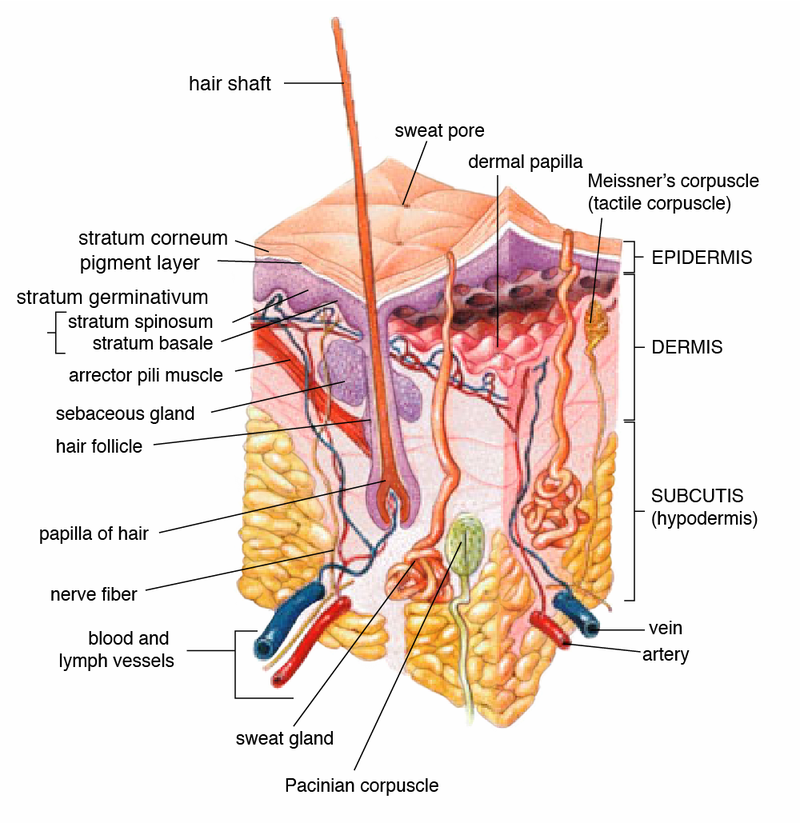
Hair Follicle resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between hormones, neuropeptides and immune cells. This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of hair as seen on different parts of the body. For example, terminal hairs grow on the scalp and lanugo hairs are seen covering the bodies of fetuses in utero and in some new born babies. The process of hair growth occurs in distinct sequential stages. The first stage is called anagen and is the active growth phase, catagen is the resting stage, telogen is the regression of the hair follicle phase, exogen is the active shedding of hair phase and lastly kenogen is the phase between the empty hair follicle and the growth of new hair. Hair Loss.
Human Hair Growth occurs everywhere on the body except for the soles of the feet, the lips, palms of the hands, some external genital areas, the navel, scar tissue, and, apart from eyelashes, the eyelids. Like skin, hair is a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium made of multi-layered flat cells whose rope-like filaments provide structure and strength to the hair shaft. Hair follows a specific growth cycle with three distinct and concurrent phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen phases. Each phase has specific characteristics that determine the length of the hair. All three phases occur simultaneously; one strand of hair may be in the anagen phase, while another is in the telogen phase. The body has different types of hair, including vellus hair and androgenic hair, each with its own type of cellular construction. The different construction gives the hair unique characteristics, serving specific purposes, mainly warmth and protection. Most humans develop the longest thickest hair on their scalps and (mostly observed in males) faces. This hair will usually grow to several feet before terminating, but many humans develop much longer hair.
Ingrown Hair is a condition where hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin. The condition is most prevalent among people who have coarse or curly hair. It may or may not be accompanied by an infection of the hair follicle (folliculitis) or "razor bumps" (pseudofolliculitis barbae), which vary in size. While ingrown hair most commonly appears in areas where the skin is shaved or waxed (beard, legs, pubic region), it can appear anywhere. Anything which causes the hair to be broken off unevenly with a sharp tip can cause ingrown hairs. Ingrown hairs are also caused because of lack of natural exfoliation in the skin.
Aging Changes Hair & Nails - Grey Hair
Body Hair, or androgenic hair, is the terminal hair that develops on the human body during and after puberty. It is differentiated from the head hair and less visible vellus hair, which are much finer and lighter in color. The growth of androgenic hair is related to the level of androgens (often referred to as male hormones; due to the production levels in males being higher on average, but it is actually present in both sexes, and therefore is a unisex hormone) in the individual.
Vellus Hair is short, thin, slight-colored, and barely noticeable thin hair that develops on most of a person's body during childhood. Exceptions include the lips, the back of the ear, the palm of the hand, the sole of the foot, some external genital areas, the navel, and scar tissue. The density of hair – the number of hair follicles per area of skin – varies from person to person. Each strand of vellus hair is usually less than 2 mm (1/13 inch) long and the follicle is not connected to a sebaceous gland. Vellus hair is most easily observed on children and adult women, as it generally has less terminal hair to obscure it. Vellus hair is not lanugo hair. Lanugo hair is a much thicker type of hair that normally grows only on fetuses. Vellus hair is differentiated from the more visible terminal or androgenic hair, which develops only during and after puberty, usually to a greater extent on men than it does on women. The Latin language uses the word vellus to designate "a fleece" or "wool". In slang usage, vellus hair is sometimes referred to as "peach fuzz" due to its resemblance to the downy epidermic growths on the peach fruit. Compared to other animals, humans appear relatively hairless, but you have more hair follicles crammed onto each square inch of your skin than the hairiest chimpanzee, monkey, or gorilla. The difference is that most of your hair (whether you’re a man or a woman) is nearly invisible. It consists of a fine, slow-growing, almost colorless covering of downy hair called vellus hair. Vellus hair blankets your body, insulating your skin and heightening your sensitivity to touch. It’s the reason you can sometimes “feel” a person moving past you in a darkened room—the passing air currents disturb your fine hairs and trigger the sensitive nerves attached to them. However, vellus hair is easily overlooked and nearly invisible without a magnifying glass. It’s sometimes known as “peach fuzz.”
Terminal Hair are thick, long, and dark, as compared with vellus hair. During puberty, the increase in androgenic hormone levels causes vellus hair to be replaced with terminal hair in certain parts of the human body. These parts will have different levels of sensitivity to androgens, primarily of the testosterone family. The Pubic area Hair is particularly sensitive to such hormones, as are the armpits which will develop axillary hair. Pubic and axillary hair will develop on both men and women, to the extent that such hair qualifies as a secondary sex characteristic, although males will develop terminal hair in more areas. This includes facial hair, chest hair, abdominal hair, leg and arm hair, and foot hair. Human females on the other hand can be expected to retain more of the vellus hair. Terminal Hair is the more obvious hair found on your body, including the hair on your head, your eyebrows, and your eyelashes. After puberty, terminal hair appears in many more places on your body—some where it’s wanted, and some where it’s decidedly inconvenient. Your eyebrow and eyelash hair also provide a home for a bizarre, sausage-shaped created called Demodex. It doesn’t spread disease or cause irritation, except in people who have severely compromised immune systems due to some other disease. The terminal hair on your eyelashes keeps dirt and insects out of your eyes. Your ear hairs and nose hairs play a similar role. The terminal hair on your eyebrows prevents sweat and rain from dripping onto your face. On your head, terminal hair helps prevent sunburns on sunny days and heat loss on cold ones. Pubic Hair is a type of terminal hair that serves as a secondary sexual characteristic. That means it’s there to advertise that you’re a fully functioning adult with the appropriate baby-making abilities. Hair doesn’t grow faster or thicker after you shave it (on any part of your body). Hair doesn’t grow faster at night. Female hair doesn’t grow faster during menstruation. Instead, all hair grows at a constant rate with a brief resting period. Frequent washing, blow drying, and dyeing your hair activities might make your current hair more brittle and fragile. But even if you damage a hair to the point of falling out, the same hair follicle will produce a new one to take its place. You’re born with all the hair follicles you’ll ever have. As you grow and your skin stretches from infant-sized to adult proportions, your hair follicles simply become more spread out. While you’re pregnant, each hair clings on a little bit longer, eventually giving you a fuller head of hair. After you give birth, your body sheds its hair more quickly to make up for lost time. The only ways to remove hair permanently are laser hair removal and electrolysis. Both treatments take numerous sessions over the course of many months, and neither treatment works for all people or all hair. Wearing hats doesn’t cause hair loss. Male-pattern baldness, which causes the infamous ring-around-the-bald-spot effect, develops gradually and eventually affects about two-thirds of all men. Its causes are genetic, and its treatments are few.
The average scalp has 100-150 thousand hairs. Hair is so strong that if you made all of your hair into a rope, it could hold 10-15 tons or about 3.5 ounces per strand. Hair also has the highest rate of cell division in the body. It grows at .3mm per day on average, and 1 cm per month. Thankfully, each hair has its own life cycle. If it didn’t, instead of losing hair randomly, we would molt. Hair grows in three phases: Anagen- The active growth stage (80-85% of hair is in this phase); Catagen- This phase is also known as the transitional phase, when hair begins to stop growing; and telogen- this phase is when hair growth is completely shut down and the fibers fall out (10-15% of our hair is in this phase at any given time). After your hair goes through the Telogen phase, Anagen begins again and voila! More hair! Melanin is a common amino acid in most all living organisms on planet Earth. Interestingly, spiders are one of only a few species that do not produce melanin.
Hair Care is an overall term for hygiene and cosmetology involving the hair which grows from the human scalp, and to a lesser extent facial, pubic and other body hair. Hair care routines differ according to an individual's culture and the physical characteristics of one's hair. Hair may be colored, trimmed, shaved, plucked, or otherwise removed with treatments such as waxing, sugaring, and threading. Hair care services are offered in salons, barbershops, and day spas, and products are available commercially for home use. Laser hair removal and electrolysis are also available, though these are provided (in the US) by licensed professionals in medical offices or specialty spas.
Hair Cutting - Styling Hair - Hair Washing - Hair Styles based on Head Shape (image) - Women Hairstyles (pdf)
Bowl Cut or bowl haircut, is a simple, plain, and short haircut where the hair is cut with a straight fringe on the front and the rest of the hair is the same length all the way around or is cut short on the sides and back. It is so named because it looks as though someone were to place a bowl on the head and cut off or trim all of the hair to a very short length. A bowl cut is also known for being a cheap and easy haircut often sported by children, typically in less developed countries worldwide. Historically, the bowl haircut was popular among common people of various nationalities as an easy and relatively neat cut by a non-professional. Indeed, it was done by putting a cooking pot of a fit size to the level of the ears, and all hair below the rim was cut or shaved off. In some cultures it was a normal type of haircut. In other cultures the bowl cut was viewed as an attribute of poverty, signifying that the wearer could not afford to visit a barber.
How To Cut Your Own Hair STEP BY STEP - Simple Faded Undercut Self-Haircut Tutorial (youtube)
QUICK & EASY HOME HAIRCUT TUTORIAL & TIPS (How to Cut Your Own Hair) (youtube)
Layered Hair is a hairstyle that gives the illusion of length and volume using long hair for the illusion of length and short hair for volume, as an easy style to manage. Hair is arranged into layers, with the top layers (those that grow nearer the crown) cut shorter than the layers beneath. This allows the tips of the top layers to blend apparently seamlessly with layers beneath.
Shaving is the removal of hair, by using a razor or any other kind of bladed implement, to slice it down—to the level of the skin or otherwise. Shaving is most commonly practiced by men to remove their facial hair and by women to remove their leg and underarm hair. A man is called clean-shaven if he has had his beard entirely removed.
Shave (wikihow) - Dollar Shave Club
Manscaping is when a man grooms, trims or shaves his pubic hair, or the hair on his body.
Pubic Hair Grooming Prevalence and Motivation Among Women in the United States.
Cosmetology is the study and application of beauty treatment.
Esthetician is a person skilled in giving beauty treatments (manicures and facials etc.).
Make up - Natural Products - Showering
Clean the Body from the Inside
Your hair stores a permanent record of the toxins you ingest. A standard hair drug test searches for traces of drugs consumed over the last 90 days. But take longer strands of hair or some slow-growing body hair and you can easily put the last year of your life under the microscope.
Nitpicking is the act of removing Nits (the eggs of Lice, generally Head Lice) from the host's hair. As the nits are cemented to individual hairs, they cannot be removed with most lice combs and before modern chemical methods were invented, the only options were to shave all the host's hair or to pick them free one by one. This is a slow and laborious process, as the root of each individual hair must be examined for infestation. It was largely abandoned as modern chemical methods became available; however, as lice populations can and do develop resistance, manual nitpicking is still often necessary. Nit-Picking as to criticism.
Hair Loss - Baldness
Hair Loss refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Typically inflammation or scarring is not present. Hair loss in some people causes psychological distress. Common types include: male-pattern hair loss, female-pattern hair loss, alopecia areata, and a thinning of hair known as telogen effluvium. The cause of male-pattern hair loss is a combination of genetics and male hormones, the cause of female pattern hair loss is unclear, the cause of alopecia areata is autoimmune, and the cause of telogen effluvium is typically a physically or psychologically stressful event. Telogen effluvium is very common following pregnancy. Less common causes of hair loss without inflammation or scarring include the pulling out of hair, certain medications including chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, hypothyroidism, and malnutrition including iron deficiency. Causes of hair loss that occurs with scarring or inflammation include fungal infection, lupus erythematosus, radiation therapy, and sarcoidosis. Diagnosis of hair loss is partly based on the areas affected. Treatment of pattern hair loss may simply involve accepting the condition. Interventions that can be tried include the medications minoxidil (or finasteride) and hair transplant surgery. Alopecia areata may be treated by steroid injections in the affected area, but these need to be frequently repeated to be effective. Hair loss is a common problem. Pattern hair loss by age 50 affects about half of males and a quarter of females. About 2% of people develop alopecia areata at some point in time.
Pattern Hair Loss is also known as male-pattern hair loss (MPHL) when it affects males and female-pattern hair loss (FPHL) when it affects females, is hair loss that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In males, the hair loss often presents as a receding hairline, while in females, it typically presents as a thinning of the hair. Male pattern hair loss is believed to be due to a combination of genetics and the male hormone dihydrotestosterone. The cause in female pattern hair loss remains unclear. Management may include simply accepting the condition. Otherwise, treatments may include minoxidil, finasteride, or hair transplant surgery. Evidence for finasteride in women, however, is poor and it may result in birth defects if taken during pregnancy. Pattern hair loss by the age of 50 affects about half of males and a quarter of females. It is the most common cause of hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia is a common form of hair loss in both men and women. In men, this condition is also known as male-pattern baldness. Hair is lost in a well-defined pattern, beginning above both temples. Over time, the hairline recedes to form a characteristic "M" shape. Hair also thins at the crown (near the top of the head), often progressing to partial or complete baldness.
Alopecia Areata also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress may result. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp or all body hair is lost and loss can be permanent. Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins if one is affected the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize its own cells with subsequent immune mediated destruction of the hair follicle.
Traction Alopecia is a form of alopecia, or gradual hair loss, caused primarily by pulling force being applied to the hair. Hair Pulling.
Eyes
Eyes (seeing is not believing)
Ears
Clean Your Ears (wikihow) - How to clean your Ears.
Ear is the organ of Hearing and balance.
Teeth
Brush 2 Times a Day - Bad Breath - Digestion Tract
Bathing - Taking a Bath - Showering -
How often you should bathe depends on many different factors.
 Bathing is the washing of the body with a fluid, usually
water or an aqueous solution, or the
immersion of the body in water.
Soap
- Disinfect (clean).
Bathing is the washing of the body with a fluid, usually
water or an aqueous solution, or the
immersion of the body in water.
Soap
- Disinfect (clean).Personal Grooming is the art of cleaning, grooming, and maintaining parts of the body.
Experts tend to agree that most people should avoid showering too frequently and in fact, if they reduce the frequency it can be an incredibly healthy decision for their skin. The exceptions to this rule are people who commute in the subway or other crowded spaces, go to the gym daily or are in contact with potentially sick people (such as those coughing, sneezing or sniffling during the flu season). In most cases you only need to shower twice out of each three days and some people can do so just every other day. When you avoid showering daily, your skin is better able to maintain its balance, making it radiant and healthy. The important thing is to remember to use a wash cloth on any specific areas that need daily attention for hygienic or smell-related reasons. Washing your hair no more than two times a week should help maintain the natural oil production, while achieving moisture balance. And if you have coarse or curly hair, try once every seven days. If you feel the need to wash your hair every day because you use public places that are filled with bacteria (like the subway or buses), or have a job that is physically demanding, or exercise regularly, don't worry. Try to use sulfate-free shampoos and protein conditioning treatment.
Shower Cap is a cover worn on top of the head while showering or bathing to protect hair from becoming wet.
Bathing Tips: Don't forget to clean your feet. Shampoo your hair no more than two times a week. Apply hair conditioner on your roots first. A long shower can actually remove much-needed moisture from the skin, especially a hot shower. This can leave your skin feeling dry and itchy. A shower should be 5 to 10 minutes long. A burst of cold water at the end of your shower can be quite good for you. helps increased tolerance to stress, can boost your immune system, increased fat burning, and has anti-depressant effects. Use a fluffy towel to lightly pat, not scrub or rub, your body. Moisturize your skin while it is still damp.
Elta md hydrating moisturizing facial and uv sunscreen with transparent zinc oxide. (amazon)
Mindfulness Showering: When taking a shower you should use that moment to notice your senses, feel the temperature of the water, intimately experiencing the soap against your skin and the sensual experience of a showering. Smell the aromas of the soap, listen to the running water or the feeling of rubbing shampoo into your scalp. Think of your showering as a metaphor for washing away stale irrelevant thoughts, feelings and bad memories. Negative ions produced by running water can also cleanse the aura. Meditation.
Skin
 Skin is the soft outer covering of vertebrates. An organ of the
integumentary system made up of multiple
layers of ectodermal tissue, and guards the underlying
muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs.
Cuts.
Skin is the soft outer covering of vertebrates. An organ of the
integumentary system made up of multiple
layers of ectodermal tissue, and guards the underlying
muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs.
Cuts.Skin Color - Pore Sweat Glands - Skin Picking - Touching - Skin Product Warnings - Skin Cancer - Shower
Epidermis is the outer two layers that make up the skin (or cutis), the inner layer being the dermis. It provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss (TEWL). The outermost part of the epidermis is composed of a stratified layer of flattened cells, that overly a basal layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. Stratum Corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis, consisting of dead cells (corneocytes). This layer is composed of 15–20 layers of flattened cells with no nuclei and cell organelles. Their cytoplasm shows filamentous keratin. These corneocytes are embedded in a lipid matrix composed of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Stratum Spinosum is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and Stratum Basale, which is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the outer covering of skin in mammals. Hair.
Dermis is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix. It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, lymphatic vessels and blood vessels are present in the dermis. Those blood vessels provide nourishment and waste removal for both dermal and epidermal cells. Your Fingerprints were formed while you were still in your mother’s womb. To biologists, fingerprints are known as friction ridges, and they’re thought to improve our sense of touch. They might also give you a better grip on small, wet objects. And thanks to your sebaceous glands and your sweat glands, your fingerprints leave wet, oily tracks wherever they’ve been.
Your skin makes a lightly acidic secretion to help protect itself. This is called the Acid Mantle. Because it is acidic, the most effective way to clean it off, along with excess oils, dirt and germs, is using an alkaline foaming system (soap!). Cold process soap is naturally alkaline with a pH of around 9-10. This pH helps to gently clean the skin.
Acid Mantle is a very fine, slightly acidic film on the surface of human skin acting as a barrier to bacteria, viruses and other potential contaminants that might penetrate the skin. Sebum is secreted by the sebaceous gland and when mixed with sweat becomes the acid mantle. The pH of the skin is between 4.5 and 6.2, slightly acidic. Since blood is slightly alkaline (7.4), pathogenic bacteria that become adapted to the pH of the skin and are able to reach internal tissues will encounter an environment to which they are less well adapted. This combination of acidic exterior and alkaline interior is one of the body's non-specific host defenses against bacterial pathogens.
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a single layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelial cells. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport, and sensing. Epithelial layers contain no blood vessels, so they must receive nourishment via diffusion of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane. Cell junctions are well employed in epithelial tissues.
Face Mites (youtube) - You probably have Demodex Mites living on your face. These tiny arachnids feast on sebum, the greasy oil in your pores.
Integumentary System is the organ system that protects the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or abrasion from outside. The system comprises the skin and its appendages (including hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails).
Skin Flora referred to as skin microbiota, refers to the microorganisms which reside on the skin, typically human skin. Many of them are bacteria of which there are around 1000 species upon human skin from nineteen phyla. Most are found in the superficial layers of the epidermis and the upper parts of hair follicles. Skin flora is usually non-pathogenic, and either commensal (are not harmful to their host) or mutualistic (offer a benefit). The benefits bacteria can offer include preventing transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them, or stimulating the skin's immune system. However, resident microbes can cause skin diseases and enter the blood system, creating life-threatening diseases, particularly in immunosuppressed people. A major non-human skin flora is Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.
Collagen is the main structural protein in the extracellular space in the various connective tissues in the body. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids wound together to form triple-helices of elongated fibrils. It is mostly found in fibrous tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and skin.
Collagen Peptides or Hydrolyzed Collagen are a hydrolyzed form of collagen. Peptan is produced by a carefully controlled enzymatic hydrolysis producing much smaller and easily digestible collagen peptides. Hydrolyzed collagen is well-known for its neutral taste and odor, which also makes it easy to consume. Consuming hydrolyzed collagen allows your body to maximize the benefits that collagen has to offer. Peptan is derived from 100 percent natural sources and is free from any side-effects. These bioactive peptides contain more than 97 percent protein (on a dry weight basis).
A newfound organ, the interstitium, is seen here beneath the top layer of skin, but is also in tissue layers lining the gut, lungs, blood vessels, and muscles. The organ is a body-wide network of interconnected, fluid-filled compartments supported by a meshwork of strong, flexible proteins.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin, nails, hair and its diseases. Academy of Dermatology.
Sun Burn - Degree of Burns
Lotion - Cream - Vitamins
Acne also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin disease that occurs when hair follicles are clogged with dead skin cells and oil from the skin. It is characterized by blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects areas of the skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. The role of diet and cigarette smoking is unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. During puberty, in both sexes, acne is often brought on by an increase in hormones such as testosterone. A frequent factor is excessive growth of the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes, which is normally present on the skin. Many treatment options for acne are available, including lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures. Eating fewer simple carbohydrates such as sugar may help. Treatments applied directly to the affected skin, such as azelaic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and salicylic acid, are commonly used. Antibiotics and retinoids are available in formulations that are applied to the skin and taken by mouth for the treatment of acne. However, resistance to antibiotics may develop as a result of antibiotic therapy. Several types of birth control pills help against acne in women. Isotretinoin pills are usually reserved for severe acne due to greater potential side effects. Early and aggressive treatment of acne is advocated by some in the medical community to decrease the overall long-term impact to individuals. In 2015, acne was estimated to affect 633 million people globally, making it the 8th most common disease worldwide. Acne commonly occurs in adolescence and affects an estimated 80–90% of teenagers in the Western world. Lower rates are reported in some rural societies. Children and adults may also be affected before and after puberty. Although acne becomes less common in adulthood, it persists in nearly half of affected people into their twenties and thirties and a smaller group continue to have difficulties into their forties.
Holistic Dermatology
Balance Me Beautiful Skin Care Tips - Healthy and Balanced Lifestyle Advice.
Dermatitis also known as eczema, is a group of diseases that results in inflammation of the skin. These diseases are characterized by itchiness, red skin, and a rash. In cases of short duration there may be small blisters while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to the entire body. Dermatitis was estimated to affect 245 million people globally in 2015. Some common emollients for the relief of eczema include Oilatum, Balneum, Medi Oil, Diprobase, bath oils and aqueous cream. Sebexol, Epaderm ointment, Exederm, and Eucerin lotion or cream may also be helpful with itching. Lotions or creams may be applied directly to the skin after bathing to lock in moisture. Moisturizing gloves (gloves which keep emollients in contact with skin on the hands) can be worn while sleeping. Generally, twice-daily applications of emollients work best. While creams are easy to apply, they are quickly absorbed into the skin, and therefore need frequent reapplication. Ointments, with less water content, stay on the skin for longer and need fewer applications, but they can be greasy and inconvenient. Recently, ceramides, which are the major lipid constituent of the stratum corneum, have been used in the treatment of eczema. They are often one of the ingredients of modern moisturizers. These lipids were also successfully produced synthetically in the laboratory. A randomized control trial in infants found that subjects with atopic dermatitis that were treated with emollients (e.g., Eucerin, Cetaphil, Nutraderm) had significantly decreased requirements for topical steroids compared with a control group who were not treated with them. Emollients are best applied immediately after bathing when the skin is well hydrated.
Rosacea is a chronic but treatable condition that primarily affects the central face, and is often characterized by flare-ups and remissions. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma. Rosacea is pronounced “roh-ZAY-sha”. Rosacea may develop in many ways and at any age. Although rosacea can affect all segments of the population and all skin types, individuals with fair skin who tend to flush or blush easily are believed to be at greatest risk. Recent studies have shown that the facial redness is likely to be the start of an inflammatory continuum initiated by a combination of neurovascular dysregulation and the innate immune system. Further research has now demonstrated that a marked increase in mast cells, located at the interface between the nervous system and vascular system, is a common link in all major presentations of the disorder. Beyond neurovascular and immune system factors, the presence of a microscopic mite called Demodex folliculorum has been considered as a potential contributor to rosacea. This mite is a normal inhabitant of human skin, but has been found to be substantially more abundant in the facial skin of rosacea patients. Researchers have also discovered that two genetic variants of the human genome may be associated with the disorder. Because the signs and symptoms of rosacea vary from one patient to another, treatment must be tailored. A gentle skin-care routine can also help control rosacea. Patients are advised to clean their face with a mild and non-abrasive cleanser, then rinse with lukewarm water and blot the face dry with a thick cotton towel. Never pull, tug or use a rough washcloth. Patients may apply non-irritating skin-care products as needed, and are advised to protect the skin from sun exposure using a sunscreen that delivers UVA/UVB protection with an SPF of 30 or higher. Mild or pediatric formulations are available for sensitive skin, and look for non-chemical (mineral) sunscreens that contain zinc or titanium dioxide. Rosacea patients should avoid any skin-care products that sting, burn or cause additional redness. rosacea patients can improve their chances of maintaining remission by identifying and avoiding lifestyle and environmental factors — often related to flushing — that may trigger flare-ups or aggravate their individual conditions. Identifying these factors is an individual process, however, because what causes a flare-up in one person may have no effect on another. To help identify personal trigger factors, rosacea patients are advised to keep a diary of daily activities or events and relate them to any flare-ups they may experience. National Rosacea Society.
Rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture. A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracked or blistered, swell, and may be painful. The causes, and therefore treatments for rashes, vary widely. Diagnosis must take into account such things as the appearance of the rash, other symptoms, what the patient may have been exposed to, occupation, and occurrence in family members. The diagnosis may confirm any number of conditions. The presence of a rash may aid diagnosis; associated signs and symptoms are diagnostic of certain diseases. For example, the rash in measles is an erythematous, morbilliform, maculopapular rash that begins a few days after the fever starts. It classically starts at the head, and spreads downwards.
Stress Rashes often take the form of hives, also called wheals or welts. Hives can appear anywhere on the body. Stress puts your body in a state of extreme tension and releases a great deal of cortisol and adrenaline into your bloodstream - both of which are known to lead to skin reactions.
Hives is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Often the patches of rash move around. Typically they last a few days and do not leave any long-lasting skin changes. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs. Hives frequently occur following an infection or as a result of an allergic reaction such as to medication, insect bites, or food. Psychological stress, cold temperature, or vibration may also be a trigger. In half of cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include having conditions such as hay fever or asthma. Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. Prevention is by avoiding whatever it is that causes the condition. Treatment is typically with antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and ranitidine. In severe cases, corticosteroids or leukotriene inhibitors may also be used. Keeping the environmental temperature cool is also useful. For cases that last more than six weeks immunosuppressants such as ciclosporin may be used. About 20% of people are affected. Cases of short duration occur equally in males and females while cases of long duration are more common in females. Cases of short duration are more common among children while cases of long duration are more common among those who are middle aged. Hives have been described at least since the time of Hippocrates. The term urticaria is from the Latin urtica meaning "nettle". Hives can also be classified by the purported causative agent. Many different substances in the environment may cause hives, including medications, food and physical agents. In perhaps more than 50% of people with chronic hives of unknown cause, it is due to an autoimmune reaction. The mainstay of therapy for both acute and chronic hives is education, avoiding triggers and using antihistamines, which are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis and other allergies.
Urticaria, also known as hives, is an outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques (wheals) on the skin that appear suddenly -- either as a result of the body's reaction to certain allergens, or for unknown reasons. Hives usually cause itching, but may also burn or sting. Urticaria is an itchy skin eruption characterized by weals with pale interiors and well-defined red margins; usually the result of an allergic response to insect bites, food or drugs.
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a rash that primarily occurs in people with asthma or allergies. Any red eruption of the skin. Atopic dermatitis or eczema is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It's common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever.
Necrosis is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis, which refers to the destruction of a cell through the action of its own enzymes, which are catalysts that increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Most enzymes are proteins.
Diagnosing and treating skin diseases of Patients with dark skin. Patients with dark skin can present with morphologic variants, subtle disease presentations, and disease manifestations requiring unique management and therapies. With African Americans, Asians, and Hispanic Americans becoming a significant portion of the population, dermatologists must be able to diagnose and manage skin conditions in people of color.
Swimmer's Itch is a short-term immune reaction occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomatidae. Symptoms, which include itchy, raised papules, commonly occur within hours of infection and do not generally last more than a week. It is common in freshwater, brackish and marine habitats worldwide. Incidence may be on the rise, although this may also be attributed to better monitoring. There are no permanent effects to people from this condition. Orally administered hydroxyzine, an antihistamine, is sometimes prescribed to treat swimmer's itch and similar dermal allergic reactions. In addition, bathing in oatmeal, baking soda, or Epsom salts can also provide relief of symptoms.
Scratching the Skin primes the gut for Allergic Reactions to Food. Research illuminates relationship between eczema and food allergy. Scratching the skin triggers a series of immune responses culminating in an increased number of activated mast cells -- immune cells involved in allergic reactions. This newly identified skin-gut communication helps illuminate the relationship between food allergy and atopic dermatitis (a type of eczema), a disease characterized by dry, itchy skin. Atopic dermatitis is a strong risk factor for developing food allergy. The researchers found that some cells in the skin respond to scratching -- simulated by applying and removing small strips of tape on the skin of mice -- by producing a cell-signaling protein called IL-33, which enters the bloodstream. When IL-33 reaches the gut, it works in concert with IL-25, a protein secreted by cells in the lining of the intestine, to activate type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). Activated ILC2s make two additional cell-signaling proteins, IL-13 and IL-4, which were found to be responsible for the expansion of intestinal mast cells. The researchers also found that as mast cells expanded, the intestinal lining became more permeable, making it easier for allergens to enter the tissues.
Scratching is a form of rubbing which may create scratches; living creatures that scratch their skin usually do so in response to itching, which response is sometimes called a scratch reflex.
If you scratch yourself a lot, you should trim your nails short and file your nails so that your nails are smooth with no sharp edges. Self Harm.
How your Brain senses an itch. A set of neurons in spinal cord help transmit a light-touch signal from skin to brain. Light touch plays a critical role in everyday tasks, such as picking up a glass or playing a musical instrument. The sensation is also an essential part of the body's protective defense system, alerting us to objects in our environment that could cause us to fall or injure ourselves. In addition, it is part of the detection system that has evolved to protect us from biting insects, such as those that cause malaria and Lyme disease, by eliciting a feeling of an itch when an insect lands on your skin.
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision.
Photodermatitis sometimes referred to as sun poisoning or photoallergy, is a form of allergic contact dermatitis in which the allergen must be activated by light to sensitize the allergic response, and to cause a rash or other systemic effects on subsequent exposure. The second and subsequent exposures produce photoallergic skin conditions which are often eczematous. It is distinct from sunburn.
Phototoxicity is a chemically induced skin irritation, requiring light, that does not involve the immune system. It is a type of photosensitivity.
Bathing in a Clean River can Boost Immunity and Mood.
Schistosomatidae is a family of digenetic trematodes with complex parasitic life cycles. Immature developmental stages of schistosomes are found in molluscs and adults occur in vertebrates. The best studied group, the blood flukes of the genus Schistosoma, infect and cause disease in humans. Other genera which are infective to non-human vertebrates can cause mild rashes in humans. Schistosomatids are dioecious (individuals are of separate sexes) which is exceptional with regards to their phylum, Platyhelminthes, in which most species are hermaphrodidic (individuals possess both male and female reproductive systems). Cercarial Dermatitis.
Germ Theory of Disease states that some diseases are caused by microorganisms.
Parasitic Skin Disease. Scientists use CRISPR to edit structural gene in organism that causes leishmaniasis. Scientists are planning for Phase 1 human trials of a vaccine they developed by using CRISPR gene-editing technology to mutate the parasite that causes leishmaniasis, a skin disease common in tropical regions of the world and gaining ground in the United States.
Exfoliation in cosmetology involves the removal of the oldest dead skin cells on the skin's outermost surface. Exfoliation is involved in the process of all facials, during microdermabrasion or chemical peels. Exfoliation can be achieved through mechanical or chemical means. You should exfoliate two to three times a week for normal and combination skin, and once a week for sensitive skin.
Facial is a family of skin care treatments for the face, including steam, exfoliation, extraction, creams, lotions, facial masks, peels, and massage. They are normally performed in beauty salons, but are also a common spa treatment. They are used for general skin health as well as for specific skin conditions. Types of facials include European facial, LED light therapy facials, and mini-facials.
Self-Healing Material are artificial or synthetically-created substances that have the built-in ability to automatically repair damage to themselves without any external diagnosis of the problem or human intervention.
Wart, Mole or Skin Cancer
Why is skin thick on the soles of the feet?
Callus is a toughened area of skin which has become relatively thick and hard in response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation.
Blister is a small pocket of lymph within the upper layers of the skin, typically caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood (known as blood blisters) or with pus (if they become infected).
Tissue in biology is a cellular organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.
 A few millimeters of tissue keeps their blood from oozing out of their body. It
helps keep water and nutrients inside your body, where they belong, and it
keeps undesirable elements—like toxins and marauding bacteria—outside most
of the time. Skin does far more than the obvious task of keeping your
insides on the inside. It’s a washable, stretchable, self-repairing fabric
that lasts a lifetime with minimal care. It’s also home to your hair,
nails, and sweat glands. If your skin was laid flat, your skin occupies
about 20 square feet of space.
A few millimeters of tissue keeps their blood from oozing out of their body. It
helps keep water and nutrients inside your body, where they belong, and it
keeps undesirable elements—like toxins and marauding bacteria—outside most
of the time. Skin does far more than the obvious task of keeping your
insides on the inside. It’s a washable, stretchable, self-repairing fabric
that lasts a lifetime with minimal care. It’s also home to your hair,
nails, and sweat glands. If your skin was laid flat, your skin occupies
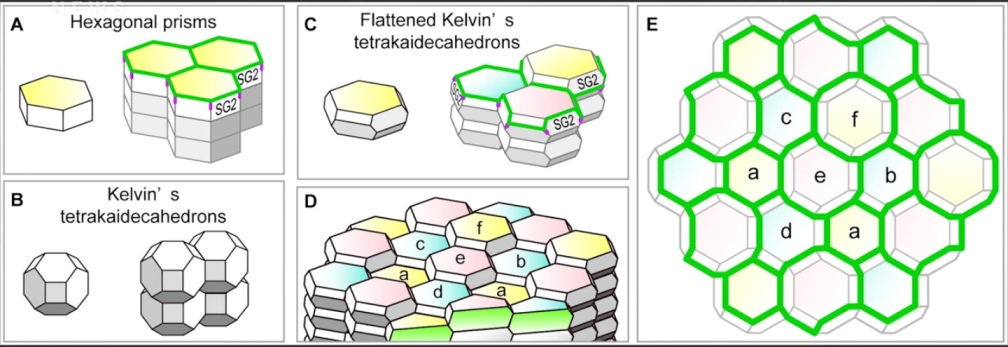
about 20 square feet of space.This Is How Your Skin Holds In Bodily Fluids (youtube) - A tight seal but still porous. Epidermis keeps you leak proof using the Stratum Granulosum, which are layers of Tetrakaidecahedrons in a Honeycomb pattern.
When your body produces fresh skin cells, these newcomers push the older cells out of the crowded neighborhood at the base of the epidermis and toward the surface of the skin. The trip takes anywhere from a couple of weeks to a month. By the time a skin cell reaches the surface, it’s little more than a dead, scale-like structure that’s filled with keratin but none of the ordinary cellular machinery. Each surface skin cell lasts about 30 days on the outside, which means you get an entirely new skin every month.
You lose millions of dead skin cells every day, that's 30,000 or so scales of skin that flake off your body every minute. Because skin flakes are thin and nearly transparent, your household dust almost always has a light, silvery-grey color. Dust mites are common, they're very tiny and distant relatives of the common household spider. Dust Mites live in our houses by the millions, with most of them taking up residence in upholstered furniture, drapery, carpets, and—above all—mattresses. Dust mites need just three things for a life of contentment: warmth, moisture, and a steady diet of skin flakes. In your bed, they get all three. Dust mites have absolutely no interest in crawling on your body. But dust-mites may cause allergies that include sore eyes, an itchy throat, and sneezing fits. You can wash your bedding at high temperatures—at least 130 degrees Fahrenheit, or use zippered covers for mattresses and pillows that can reduce the number of dust mites. Dust mites actually eat and excrete the same skin flake several times, until they’ve finally digested all the goodness out of it.
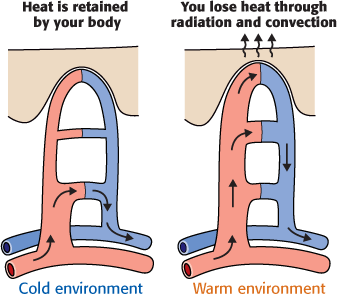 Body Temperature
Regulator. Using a design that’s the human equivalent of a hot-water
radiator, your body sends warm blood to the surface of your skin so it can
radiate heat away to the cooler world outside. When you need to conserve
heat, your body clamps down on this process, tightening the blood vessels
in your skin. That reduces the flow of blood near the skin and slows your
rate of heat loss. This system explains why people become flushed when
they’re hot (it’s from the increased blood flow). It also explains how
frostbite inflicts its damage. The cold itself doesn’t harm your
body—instead, the extremely reduced blood flow starves your cells of the
oxygen they need to survive.
Body Temperature
Regulator. Using a design that’s the human equivalent of a hot-water
radiator, your body sends warm blood to the surface of your skin so it can
radiate heat away to the cooler world outside. When you need to conserve
heat, your body clamps down on this process, tightening the blood vessels
in your skin. That reduces the flow of blood near the skin and slows your
rate of heat loss. This system explains why people become flushed when
they’re hot (it’s from the increased blood flow). It also explains how
frostbite inflicts its damage. The cold itself doesn’t harm your
body—instead, the extremely reduced blood flow starves your cells of the
oxygen they need to survive.Vitamin D: Sun exposure that you need to synthesize vitamin D is very little in the summer months (or in a tropical climate). But in late fall and winter, you can run around in boxer shorts without producing a microgram of vitamin D. But try not to linger in the sun between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. (11 a.m. and 4 p.m. during daylight-saving time). If you find yourself in strong sun, seek shade. Always wear a wide-brimmed hat, long-sleeved shirt, and long pants on sunny days. Use sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB Rays and offers a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15. Use sunscreen properly. Apply sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going out. Repeat every two or three hours, more often if you’re swimming.
Pheromones - Goose Bumps
How a member of a family of light-sensitive proteins adjusts skin color. Researchers have found that opsin 3 -- a protein closely related to rhodopsin, the protein that enables low-light vision -- has a role in adjusting the amount of pigment produced in human skin, a determinant of skin color. When humans spend time in the sun without proper skin protection, the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation signals the skin to produce more melanin -- which protects against the cancer-causing effects of the radiation -- and become darker. There are two parts to solar UV radiation: short wavelength radiation or UVB, and long wavelength radiation or UVA. Each part is detected by the skin in different ways; how UVB makes humans tan has been known for a while. Melanocytes, specialized skin cells that produce the pigment melanin, have an abundance of opsin 3, they thought that opsin 3 might be the receptor that detects UVA and signals increased melanin production.
Body Knowledge
Chameleon inspires 'smart skin' that changes color in the sun. A new concept in the field of photonic crystals
Chemists used photonic crystals to develop a flexible smart skin that reacts to heat and sunlight while maintaining a near constant volume.
Telangiectasia are also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter. These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere on the body but are commonly seen on the face around the nose, cheeks and chin. Dilated blood vessels can also develop on the legs, although when they occur on the legs, they often have underlying venous reflux or "hidden varicose veins". When found on the legs, they are found specifically on the upper thigh, below the knee joint and around the ankles. Many patients who suffer with spider veins seek the assistance of physicians who specialize in vein care or peripheral vascular disease. These physicians are called vascular surgeons or phlebologists. More recently, interventional radiologists have started treating venous problems. Some telangiectasias are due to developmental abnormalities that can closely mimic the behaviour of benign vascular neoplasms. They may be composed of abnormal aggregations of arterioles, capillaries or venules. Because telangiectasias are vascular lesions, they blanch when tested with diascopy. Telangiectasias, aside from presenting in many other conditions, are one of the features of the acronymically named CREST syndrome, a form of systemic scleroderma. The syndrome recognises the significantly co-presenting symptoms of calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly and telangiectasia.
Don't Shower too Much
1. Make the Skin Softer. Your skin receives its hydration from two main sources. It attracts moisture that is in the air and it also gets hydration from the beneficial oils and water found within your body. It is important to keep in mind that when the air outside gets dryer, your skin will as well as there is less moisture for it to attract. Some people decide to use a lot of moisturizer to solve the problem but a better option can be showering less often. That is because when you use hot water (which most people do, especially in cooler months), it will soften your skin’s oils, making it easier for them to wash away and therefore dry out your skin. This means that ideally you should shower less frequently and opt for a nontoxic soap in the locations you need it. If you do this, your skin should be able to find a happy healthy balance by itself. If you feel you need more, opt for pure shea butter creams or organic raw oils such as olive, jojoba and coconut. Hot water is bad for two reasons: First it removes too much of your natural oils, second, hot water brings blood circulation to your skin which is why your skin turns red like a lobster. With the circulation comes inflammatory building blocks to create more itch and even a rash. Water temperature should be tepid, meaning skin temperature or just a little warmer—especially if you have fragile skin that’s prone to dryness. You shouldn’t shower for more than 5 to 10 minutes, and use a non-drying soap only on the oily and odor-causing parts of your skin such as your face, armpits, buttocks, groin, and feet. Try not to soap your arms or legs. Sebaceous Gland are microscopic exocrine glands in the skin that secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals. In humans, they occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The type of secretion of the sebaceous glands is referred to as holocrine. Depending on the work or activities, some people shower once or twice a week to once every two to three days. Cleaning Hair with Just Water.
2. Give Off the Natural Scent. When talking about giving off your natural scent, it is important to clarify that this should only be obvious when someone gets close to you; if they can smell you from far away you should consider switching deodorants. Experts have linked smell with sexual attraction as well as selecting a mate both on the physiological and psychological level. This means that by showering less, you may actually do better at attracting a partner. Natural Mineral Salt Deodorant.
3. Preserve Helpful Bacteria. Most people realize that our stomachs need good bacteria to function but not everyone realizes that this is true of the skin cells as well. The New York Times had an article in which Dr. Richard Gallo who is the dermatology chief at the University of California pointed out that good bacteria in the skin cell help these cells learn how to produce their own antibiotics that can help protect us from bad bacteria. Body lotion and most soaps don’t provide this benefit; only showering less frequently does.
Mother Dirt biome-friendly products helps rebalance the skin and reduce its dependence on conventional products. Nitric Oxide.
4. Protect from Harmful Chemicals. You may be surprised to learn that having oils and dead skin cells on your skin is actually beneficial. These elements provide a kind of protection from harmful bacteria. They also make it more difficult for certain chemicals to penetrate the skin. This is crucial as these chemicals can damage the skin and in some cases other parts of the body as well. When you shower, you remove these oils and dead skin cells from your skin and in the process make it easier for chemicals to get in. this is even worse if you are using harsh soaps or body washes that contain chemicals. Because of this, experts suggest always selecting a nontoxic soap with a minimal number of ingredients and only using it when necessary and in the locations that truly need it.
5. Reduce Skin Irritations. Skin irritations are fairly common and people who deal with these issues such as rashes, general irritation or even something specific such as rosacea and eczema know that taking hot showers makes the problem worse. In fact, their Skin tends to behave better when they take fewer hot showers. Some people with psoriasis, eczema or other similar conditions will actually be allergic to the sensitizers found in shampoos and soaps. If you remove these toxic products from your routine, you are likely to notice a significant decrease in rashes and irritations. Some people will even see their problems completely disappear.
Avoid Hot Showers. Your shower water should be warm, especially on your face. Luke Warm is a liquid or food that is moderately warm or tepid. Warm is having or producing a comfortable and agreeable degree of heat or imparting or maintaining heat. Extremely Hot water is around 130 F (54.4 C) or above. Hot water in your home coming from the tap can be around 100 F (43.3 to 32.2 C), and can gradually get hotter sometimes, so be careful. Water temperature in your home can vary depending on the time of year and the hot water setting of your hot water heater. Warm water is around 80 F (26.7 to 15 C). Warm water is mixing one half hot water with one half cold water. Cold water in your house can vary too, usually cold water is around 70 F. Body Temperatures.
Take short showers if you shower more than once a day. Don't stand under water for minutes at a time. Hot water strips away natural oils and damages the skin faster, so stick to a lukewarm or cooler showers.
Cold Shower
Take more cold and cool showers then hot and warm showers. If you do take a occasional hot shower, the last couple of minutes of your shower should be cold water. Ending your shower with cold water will help lock in moisture, increase circulation, and benefit your skin and hair. Cold temperature decreases Transepidermal Water Loss, contributing to better skin hydration. Cold temperature also reduces your skin’s sensitivity to irritants. A chilled end to your shower may “cause superficial blood vessels to constrict, which can be beneficial to those who are prone to facial flushing or rosacea. Due to decreased facial redness, the skin tone/complexion may appear improved. Cold showers also speed up sore muscle recovery. Cold temperature also redirects blood flow to deep blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart. This improved blood return may help the body’s metabolism and processing of waste products. Lymphatic System. Cold water also increases your heart rate, so it wakes you up. Cold water can also improve your mood. Cold water could also increase your stores of brown fat (the “good” fat that burns calories/energy in order to produce heat) Cold water should not be so cold that it causes discomfort. Cold Shower for Health. Ice Water Therapy.
Moisturizing
Proper Moisturizing Protocol: Try not to wait longer than 3 minutes after leaving the shower to moisturize your skin. After stepping from the shower, gently pat excess water from your skin, leaving some droplets behind. Then apply a liberal amount of a moisturizer that contains ceramide (a natural oil found in skin). When skin gets dry and cracks, it lets in bacteria and allergens.
Moisturizer are complex mixtures of chemical agents (often occlusives help hold water in the skin after application, humectants attract moisture and emollients help smooth the skin.) specially designed to make the external layers of the skin (epidermis) softer and more pliable. They increase the skin's hydration (water content) by reducing evaporation. Naturally occurring skin lipids and sterols, as well as artificial or natural oils, humectants, emollients, lubricants, etc., may be part of the composition of commercial skin moisturizers. They usually are available as commercial products for cosmetic and therapeutic uses, but can also be made at home using common pharmacy ingredients. Mechanisms of actionare Occlusives: These work by forming a thin film on the surface of the skin to prevent loss of moisture. Humectants: These attract water vapor from the air to moisturize the skin. Restoration of deficient materials: These are more complex and try to restore natural moisturizing factors on the skin, such as amino-lipids. Antipruritic action (anti-itching): Down regulate cytokines and cooling effect from evaporation of water for water-based moisturizer. Antimitotic (mitoic inhibitor): Slow the process of mitosis (cell division) on the epidermis by mineral oil, which could be helpful for people who have psoriasis disease. UV Protection: Moisturizers also contain sunscreen which will protect your skin from UV light. Inhibit proinflammatory prostanoids production: Blocking cyclooxygenase activity which causes soothing and lower skin inflammation. Wound healing: Hyaluronic acid, Antimicrobial effect by act against microbe surface. Xeroderma. Two factors have to be considered when assessing the safety of a moisturizer: The safety of the ingredients it contains and The risk of bacterial contamination. Some people are sensitive or allergic to certain chemical components, which can cause irritation, rashes, and other allergic reactions. As with most skin-care products, there is a risk of moisturizers being contaminated with bacteria that can cause disease.
Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to unbroken skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, cotton wool, or gauze. While lotion may be used as a medicine delivery system, many lotions, especially hand lotions and body lotions are meant instead to simply smooth, moisturize and soften the skin. These may be used in anti-aging lotions, which can also be classified as a cosmetic in many cases, and may contain fragrances. The Food and Drug Administration voiced concern about lotions not classified as drugs that advertise anti-aging or anti-wrinkle properties.
Cream is a preparation usually for application to the skin. Creams for application to mucous membranes such as those of the rectum or vagina are also used. Creams may be considered pharmaceutical products as even cosmetic creams are based on techniques developed by pharmacy and unmedicated creams are highly used in a variety of skin conditions (dermatoses). The use of the finger tip unit concept may be helpful in guiding how much topical cream is required to cover different areas. Creams are semi-solid emulsions of oil and water. They are divided into two types: oil-in-water (O/W) creams which are composed of small droplets of oil dispersed in a continuous water phase, and water-in-oil (W/O) creams which are composed of small droplets of water dispersed in a continuous oily phase. Oil-in-water creams are more comfortable and cosmetically acceptable as they are less greasy and more easily washed off using water. Water-in-oil creams are more difficult to handle but many drugs which are incorporated into creams are hydrophobic and will be released more readily from a water-in-oil cream than an oil-in-water cream. Water-in-oil creams are also more moisturising as they provide an oily barrier which reduces water loss from the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin.
Gel is a solid jelly-like material that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state. By weight, gels are mostly liquid, yet they behave like solids due to a three-dimensional cross-linked network within the liquid. It is the crosslinking within the fluid that gives a gel its structure (hardness) and contributes to the adhesive stick (tack). In this way gels are a dispersion of molecules of a liquid within a solid in which liquid particles are dispersed in the solid medium.
Oil is any neutral, nonpolar chemical substance that is a viscous liquid at ambient temperatures and is both hydrophobic (immiscible with water, literally "water fearing") and lipophilic (miscible with other oils, literally "fat loving"). Oils have a high carbon and hydrogen content and are usually flammable and surface active.
Humectant is a hygroscopic substance used to keep things moist; it is the opposite of a desiccant. It is often a molecule with several hydrophilic groups, most often hydroxyl groups; however, amines and carboxyl groups, sometimes esterified, can be encountered as well (its affinity to form hydrogen bonds with molecules of water is the crucial trait).
Lubricant is a substance, usually organic, introduced to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking (oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination.
Aloe Vera is a succulent plant species of the genus Aloe. An evergreen perennial, it originates from the Arabian Peninsula but grows wild in tropical climates around the world and is cultivated for agricultural and medicinal uses. The species is also used for decorative purposes and grows successfully indoors as a potted plant. It is found in many consumer products including beverages, skin lotion, cosmetics, or ointments for minor burns and sunburns.
Tea Tree Oil is an essential oil with a fresh camphoraceous odor and a colour that ranges from pale yellow to nearly colourless and clear, it is also known as melaleuca oil or ti tree oil. It's derived from the leaves of the tea tree, Melaleuca alternifolia, native to Southeast Queensland and the Northeast coast of New South Wales, Australia. It is typically used as a topical medication in low concentrations for attempted treatments of skin conditions. Tea tree oil is claimed as useful for treating dandruff, acne, lice, herpes, insect bites, scabies, and skin fungal or bacterial infections. However, the quality of the evidence for efficacy in these conditions is minimal. Tea tree oil is neither a patented product nor an approved drug, and is poisonous if consumed by mouth.
Hair is made of dead skin cells and doesn't need as much washing as the rest of our skin. Wash your scalp at least weekly and wash your face, chest and back after conditioning the Hair.
Dry Hair Shampoo - Shaking corn starch into hair has achieved the same effect, but most current products deliver the drying agents via an aerosol spray.
Conditioner-Only Hair Washing or Co-Washing is the process of only using conditioner to wash, condition, and moisturize your hair. According to experts, conditioner is more gentle on the hair and still lifts dirt and product from strands, as a shampoo would. It must be a silicone-free conditioner to keep from weighing your hair down. Add a cleansing conditioner to your routine if your hair is dry.
You want to soften the hair before shaving, but not too much. Shaving should happen at the end of a short shower so the hairs are damp but not too swollen from too much heat and steam, which causes hair swelling that later leads to Ingrown Hair when the shaved hairs dry and shrink below the skin surface. Pat your skin with a towel instead of rubbing vigorously. Apply moisturizer right away, within two to three minutes of showering.
Bentonite is an absorbent aluminium phyllosilicate clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite. The different types of bentonite are each named after the respective dominant element, such as potassium (K), sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), and aluminium (Al). Experts debate a number of nomenclatorial problems with the classification of bentonite clays. Bentonite usually forms from weathering of volcanic ash, most often in the presence of water. However, the term bentonite, as well as a similar clay called tonstein, has been used to describe clay beds of uncertain origin. For industrial purposes, two main classes of bentonite exist: sodium and calcium bentonite. In stratigraphy and tephrochronology, completely devitrified (weathered volcanic glass) ash-fall beds are commonly referred to as K-bentonites when the dominant clay species is illite. In addition to montmorillonite and illite another common clay species that is sometimes dominant is kaolinite. Kaolinite-dominated clays are commonly referred to as tonsteins and are typically associated with coal. Bentonite has been prescribed as a bulk laxative, and it is also used as a base for many dermatologic formulas. Bentoquatam is a bentonate-based topical medication intended to act as a shield against exposure to urushiol, the oil found in plants such as poison ivy or poison oak. even use it internally. It has an alkalizing effect on the body and when taken correctly, it can help balance gut bacteria. Healing clays like bentonite have a high concentration of minerals including silica, calcium, magnesium, sodium, iron, and potassium. It also absorbs and removes toxins, heavy metals, impurities, and chemicals. Bentonite clay is a unique clay due to its ability to produce an “electrical charge” when hydrated. Upon contact with fluid its electrical components change, carrying a strong negative charge which bonds to the positive charge in many toxins.helping with skin and allergy issues said to be especially calming to skin itching from eczema, psoriasis, chickenpox, etc. Bentonite clay (montmorillonite) is a mudlike substance derived from volcanic ash. It's sometimes used in the personal care industry as a face mask. Bentonite clay can also be used for hair as a natural way to add moisture and remove toxins.
Activated Charcoal Soap with Calcium Bentonite Clay.
Water Therapy - Messaging the Skin
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. aged volcanic ash.
Sweat
Perspiration is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. Exocrine Gland are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Hydration.
Sweat Gland are small tubular structures of the Skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species: Echini Sweat Glands are distributed almost all over the human body, in varying densities, with the highest density in palms and soles, then on the head, but much less on the trunk and the extremities. Its water-based secretion represents a primary form of cooling in humans. Apocrine sweat glands are mostly limited to the axilla (armpits) and perianal areas in humans. They are not significant for cooling in humans, but are the sole effective sweat glands in hoofed animals, such as the camels, donkeys, horses, and cattle. Apocrine Sweat Gland is a type of merocrine sweat gland composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. In humans, apocrine sweat glands are found only in certain locations of the body: the axillae (armpits), areola and nipples of the breast, ear canal, eyelids, wings of the nostril, perianal region, and some parts of the external genitalia. Modified apocrine glands include the ciliary glands in the eyelids; the ceruminous glands, which produce ear wax; and the mammary glands, which produce milk. The rest of the body is covered by eccrine sweat glands. Sweat Glands are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Ceruminous glands (which produce ear wax), mammary glands (which produce milk), and ciliary glands in the eyelids are modified apocrine sweat glands.
Gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Pore is any tiny hole admitting passage of a liquid, fluid or gas. Any small opening in the skin or outer surface of an animal.
Heat Index is an index that combines air temperature and relative Humidity, in shaded areas, as an attempt to determine the human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the shade. Sometimes feeling like it's 30 degrees hotter then the actual temperature. The result is also known as the "felt air temperature" or "apparent temperature". For example, when the temperature is 32 °C (90 °F) with 70% relative humidity, the heat index is 41 °C (106 °F). This heat index temperature has an implied (unstated) humidity of 20%. This is the value of relative humidity for which the heat index formula indicates 41 °C feels like 41 °C. A heat index temperature of 32 °C has an implied relative humidity of 38%. The human body normally cools itself by perspiration, or sweating. Heat is removed from the body by Evaporation of that sweat. However, high relative humidity reduces the evaporation rate. This results in a lower rate of heat removal from the body, hence the sensation of being overheated. This effect is subjective, with different individuals perceiving heat differently for various reasons (such as obesity, metabolic differences, pregnancy, menopause, effects of drugs and/or drug withdrawal); its measurement has been based on subjective descriptions of how hot subjects feel for a given temperature and humidity. This results in a heat index that relates one combination of temperature and humidity to another. Because the humidity index is based on temperatures in the shade, while people often move across sunny areas, then the heat index can give a much lower temperature than actual conditions of typical outdoor activities. Also, for people exercising or active, at the time, then the heat index could give a temperature lower than the felt conditions. For example, with a temperature in the shade of only 82 °F (28 °C) at 60% relative humidity, then the heat index would seem 84 °F (29 °C), but movement across sunny areas of 102 °F (39 °C), would give a heat index of over 137 °F (58 °C), as more indicative of the oppressive and sweltering heat. Plus when actively working, or not wearing a hat in sunny areas, then the feels-like conditions would seem even hotter. Hence, the heat index could seem unrealistically low, unless resting inactive (idle) in heavily shaded areas. Heat Index is a measure of how hot it really feels when relative humidity is factored in with the actual air temperature. A quantity expressing the discomfort felt as a result of the combined effects of the temperature and humidity of the air. Bodies lose heat in water very fast due to the big heat capacity of water.
Heat Exhaustion - Exercising (sweat)
New microfluidic devices help athletes and enhance physical rehab. A new wearable system measures sweat and sweat biomarkers. It is a soft, flexible device that measures the bodies’ response to exercise.
Wearable device measures cortisol in sweat. By drawing in a bit of sweat, a patch can reveal how much cortisol a person is producing. Cortisol is known as the stress hormone but is involved in many important physiological functions.
Don't Sweat the Small Stuff (worrying)
Chloride compounds or chlorine atoms, often attached to sodium ones to form salt – are important for maintaining the body’s internal pH balance, regulating the movement of fluids in and out of cells, and transmitting impulses across nerve fibres. Also mixed in with sweat is urea, ammonia, proteins, sugars, potassium and bicarbonate. Not to mention trace metals like zinc, copper, iron, nickel, cadmium, lead, and even a tiny bit of manganese. For some of those metals, sweat is an important mechanism for excreting them from inside of the body. Sweat exits the body through one of two types of glands. Apocrine glands are found in the armpits and nostrils and on the nipples, ears and parts of the genitalia Eccrine Glands, millions of which are distributed over most of the rest of the human body When the body and skin get too warm, thermoreceptors send a message indicating as much to the brain. There, the hypothalamus – a small cluster of cells that controls our hunger, thirst, sleep, and body temperature – sends a message to the apocrine and eccrine glands, which begin pumping out sweat. Perspiration left behind on your skin can allow bacteria to grow, so you may need a shower after strenuous exercise or work.
Body Oder - B.O.
Body Odor is present in animals and humans, and its intensity can be influenced by many factors (behavioral patterns, survival strategies). Body odor has a strong genetic basis both in animals and humans, but it can be also strongly influenced by various diseases and physiological conditions. Body odor is generally considered to be an unpleasant odor among many human cultures. In humans, the formation of body odors is caused by factors such as diet, gender, health, and medication, but the major contribution comes from bacterial activity on skin gland secretions.
Pheromones (sense of smell). - Why I don't smell my own Stink?
Diet quality and the attractiveness of male body odor. Greater fruit and vegetable intake, was significantly associated with more pleasant smelling sweat (with more floral, fruity, sweet and medicinal qualities),and greater carbohydrate intake with stronger smelling less pleasant sweat.
The effect of meat consumption on body odor attractiveness. Women preferred the odor of men who ate a non-meat diet. Fresh odor samples were assessed for their pleasantness, attractiveness, masculinity, and intensity by 30 women not using hormonal contraceptives.
Pig-Pen effect: Mixing skin oil and ozone can produce a personal pollution cloud. A range of volatile and semi-volatile gases and substances are produced when ozone, a form of oxygen that can be toxic, reacts with skin oils carried by soiled clothes.
100% Pure, All Natural, Mineral Salts Deodorant Stone. Your perspiration, when it first leaves your body is sterile & odorless. When it comes in contact with bacteria on your skin, the bacteria multiplies, its the bacteria that causes the odor. The mineral salts leaves a thin film on your skin and the bacteria can not thrive in the salts environment. Mineral salts are mined out of the Ground; No Toxic Chemicals, No Carcinogens, Just 100% Mineral Salts; Will Easily last well Over 2 Years with Daily Use. It's a Huge Money Saver. Will Not Leave Stains on your Clothes EVER!
Ammonium Aluminium Sulfate, also known as ammonium alum or just alum, is a white crystalline double sulfate usually encountered as the dodecahydrate, formula (NH4)Al(SO4)2·12H2O. It is used in small amounts in a variety of niche applications. The dodecahydrate occurs naturally as the rare mineral tschermigite. Ammonium alum is made from aluminium hydroxide, sulfuric acid and ammonium sulfate. It forms a solid solution with potassium alum. Pyrolysis leaves alumina. Such alumina is used in the production of grinding powders and as precursors to synthetic gems. Ammonium alum is not a major industrial chemical or a particularly useful laboratory reagent, but it is cheap and effective, which invites many niche applications. It is used in water purification, in vegetable glues, in porcelain cements, in deodorants and in tanning, dyeing and in fireproofing textiles. The pH of the solution resulting from the topical application of ammonium alum with perspiration is typically in the slightly acid range, from 3 to 5. Ammonium alum is a common ingredient in animal repellant sprays. Alum was once a common pickling ingredient used to promote crispness in preserved vegetable, due to the way it reacts with natural pectin. It has fallen out of use from a suspected link to Alzheimer's Disease, and is no longer recommended for pickling. Aluminium sulfate, closely related to ammonium alum, is considered nontoxic up to LD50 of 6207 mg/kg. For reduced concentrations no human or ecological toxicity officially registered.
BO - An enzyme called C-T lyase, found in the bacterium Staphylococcus hominis, dwells in human armpits. These bacteria feed on odorless chemicals released in sweat, which the enzyme then converts into thioalcohols—a pungent compound responsible for the offending smell.
How many days in a row can a person wear the same clothes? It depends on the person and their health, it depends on the clothes or the type of fabric that the person is wearing, it depends on the climate where the person lives, it depends on the activities or the type of work that a person does. For those that wear the same bra every day for weeks on end, the guide recommends giving it a wash every three to four days, the same for trousers or pants or jeans. Everyday items such as tights, T-shirts and briefs need to be put in the laundry basket when they get used under harsh conditions, which could be after one day of use. Sleeping in the same clothes that you wear everyday can create an unhealthy hygiene level which could then lead to illness or skin/hair conditions that are not ideal. Dirt, dust, grime, oils, and dead skin cells of the day get caught up all over our face, and can start to harm our skin if we leave them there. Also, it’s bad if these get into/on your pillow and then you are re-exposed to them every night for hours at a time. This is the same idea with wearing the same clothes you did everything in the day before, while going to bed. The bugs, dirt, dust, skin cells, and germs from everyone else are stuck in them, and can be re-exposed to you over and over! Not to mention the bed bugs that can start eating at your own body.
Stain Removing
Oil-Based Stains: Use liquid dish soap. (mayonnaise, spaghetti sauce or salad dressings).
Pigment Stains: Use rubbing alcohol and blot the ink with a paper towel or cotton ball. White vinegar can also help.
Blood Stains: First try cold water. If that doesn't work, hydrogen peroxide.
Berry Stains: Running boiling hot water through the stain can help.
