BK101
Knowledge Base

Pee - Poo - Bowel Movements
Number One or Number Two? - Toilets - Hygiene - Toilet Training
Excretion is the process by which metabolic wastes and other non-useful materials are eliminated from an organism.
Pee - Urine
 Urine is a liquid by-product of
metabolism
in the bodies of many animals, including humans. It is expelled from the
kidneys and flows through the ureters to the urinary bladder, from which
it is soon excreted from the body through the urethra during urination.
Hydration.
Urine is a liquid by-product of
metabolism
in the bodies of many animals, including humans. It is expelled from the
kidneys and flows through the ureters to the urinary bladder, from which
it is soon excreted from the body through the urethra during urination.
Hydration.Urination is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion.
Most people urinate between six and eight times a day. But if you're drinking plenty, it's not abnormal to go as many as 10 times a day or in 24 hours. The normal range for 24-hour urine volume is 800 to 2000 milliliters per day (with a normal fluid intake of about 2 liters per day). 2000 milliliters or 0.528344 US Gallons or 67.628 fl oz.
Oliguria is the low output of urine. In humans, it is clinically classified as an output more than 80 ml/day but less than 400ml/day. The decreased output of urine may be a sign of dehydration, kidney failure, hypovolemic shock, HHNS hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, urinary obstruction/urinary retention, DKA, pre-eclampsia, and urinary tract infections, among other conditions. Beyond oliguria is anuria, which represents an absence of urine, clinically classified as below 80 or 100 ml/day. Inflammation.
Urethra is a duct through which urine is discharged in most mammals and which serves as the male genital duct. Urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis and also carries semen. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in non-primates, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus.
Prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals. It differs considerably among species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. The function of the prostate is to secrete a slightly alkaline fluid, milky or white in appearance, that in humans usually constitutes roughly 30% of the volume of semen along with spermatozoa and seminal vesicle fluid. Semen is made alkaline overall with the secretions from other contributing glands, including, at least, seminal vesicle fluid. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ejaculate, together with most of the sperm. In comparison with the few spermatozoa expelled together with mainly seminal vesicular fluid, those in prostatic fluid have better motility, longer survival, and better protection of genetic material. The prostate also contains some smooth muscles that help expel semen during ejaculation. Prostate Gland is a firm partly muscular chestnut sized gland in males at the neck of the urethra; produces a viscid secretion that is the fluid part of semen.
Polyuria is a condition usually defined as excessive or abnormally large production or passage of urine (greater than 2.5 or 3 L over 24 hours in adults).
I Go to to Go. I Got to take a Leak. I Have to take a Number 1.
Frequent Urination is the need to urinate more often than usual. It is often, though not necessarily, associated with urinary incontinence and polyuria (large total volume of urine). However, in other cases, urinary frequency involves only normal volumes of urine overall. A frequent need to urinate at night is called nocturia. Frequent urination is strongly associated with frequent incidents of urinary urgency. Dehydration (needing water).
Overactive Bladder is a condition where there is a frequent feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person's life. The frequent need to urinate may occur during the day, at night, or both. If there is loss of bladder control then it is known as urge incontinence.
Urinary Urgency is a sudden, compelling urge to urinate. It is often, though not necessarily, associated with urinary incontinence, polyuria, nocturia, and interstitial cystitis. It tends to increase with age. When uncontrollable, it causes urge incontinence.
Urinary Incontinence is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: Urge incontinence due to an overactive bladder
Stress incontinence due to poor closure of the bladder. Overflow incontinence due to either poor bladder contraction or blockage of the urethra. Functional incontinence due to medications or health problems making it difficult to reach the bathroom. Treatments include pelvic floor muscle training, bladder training, surgery, and electrical stimulation. Behavioral therapy generally works better than medication for stress and urge incontinence. The benefit of medications is small and long term safety is unclear. Urinary incontinence is more common in older women.
Diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, that is, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis.
Plasma Osmolality measures the body's electrolyte-water balance.
Clinical Urine Tests are various tests of urine for diagnostic purposes. The most common is a Urinalysis or UA, one of the most common methods of medical diagnosis. The word is a portmanteau of the words urine and analysis. Other tests are urine culture (a microbiological culture of urine) and urine electrolyte levels. The target parameters that can be measured or quantified in urinalysis include naked-eye (gross) examination for color and smell plus analysis for many substances and cells, as well as other properties, such as specific gravity. A part of a urinalysis can be performed by using urine test strips, in which the test results can be read as color changes. Another method is light microscopy of urine samples.
Urine Test reveals quality of your diet. Metabolites are considered to be an objective indicator of diet quality -- and are produced as different foods are digested by the body. The findings revealed an association between 46 metabolites in urine, and types of foods or nutrients in the diet. For instance, certain metabolites correlated with alcohol intake, while others were linked to intake of citrus fruit, fructose (fruit sugar), glucose and vitamin C. The team also found metabolites in urine associated with dietary intake of red meats, other meats such as chicken, and nutrients such as calcium. Certain metabolites were also linked with health conditions -- for instance compounds found in urine such as formate and sodium (an indicator of salt intake) are linked with obesity and high blood pressure. an individual's urine 'fingerprint', could enable people to receive healthy eating advice tailored to their individual biological make-up. This is known as "precision nutrition," and could provide health professionals with more specific information on the quality of a person's diet. Diet is a key contributor to human health and disease, though it is notoriously difficult to measure accurately because it relies on an individual's ability to recall what and how much they ate.
With Nanoparticles, a simple Urine Test could diagnose Bacterial Pneumonia. The results could also indicate whether antibiotics have successfully treated the infection. Pneumonia, a respiratory disease that kills about 50,000 people in the United States every year, can be caused by many different microbes, including bacteria and viruses. The team developed nanoparticles coated with peptides (short proteins) that can be chopped up by certain proteases, such as those expressed by cancer cells. When these particles are injected into the body, they accumulate in tumors, if any are present, and proteases there chop the peptides from the nanoparticles. These peptides are eliminated as waste and can be detected by a simple urine test. The researchers also developed a second nanoparticle-based sensor that can monitor the host's immune response to infection. These nanoparticles are covered in peptides that are cleaved by a type of protease called elastase, which is produced by immune cells called neutrophils. The sensors can help you distinguish between whether there's an infection and inflammation, versus inflammation and no infection.
Urine Therapy refers to various applications of human urine for medicinal or cosmetic purposes, including drinking of one's own urine and massaging one's skin, or gums, with one's own urine. There is no scientific evidence to support its use.
Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. Each kidney consists of millions of functional units called nephrons. The purpose of the Renal System is to eliminate wastes from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes (in the form of urine) exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibers that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination (voiding). The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra. Urine is formed in the kidneys through a filtration of blood. The urine is then passed through the ureters to the bladder, where it is stored. During urination, the urine is passed from the bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. 800–2,000 milliliters (mL) of urine are normally produced every day in a healthy human. This amount varies according to fluid intake and kidney function.
Human Body Systems
Kidney are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body in vertebrates. They filter the blood in order to make urine, to release and retain water, and to remove waste. They also control the ion concentrations and acid-base balance of the blood. Each kidney feeds urine into the Bladder by means of a tube known as the ureter. The kidneys regulate the balance of ions known as electrolytes in the blood, along with maintaining acid base homeostasis. They also move waste products out of the blood and into the urine, such as nitrogen-containing urea and ammonium. Kidneys also regulate fluid balance and blood pressure. They are also responsible for the reabsorption of water, glucose, and amino acids. The kidneys also produce hormones including calcitriol and erythropoietin. The kidneys also make an important enzyme, renin, which affects blood pressure through negative feedback. Located at the rear of the abdominal cavity in the retroperitoneal space, the kidneys receive blood from the paired renal arteries, and drain into the paired renal veins. Dialysis.
Vesicoureteral Reflux is a condition in which urine flows retrograde, or backward, from the bladder into the ureters/kidneys. Urine normally travels in one direction (forward, or anterograde) from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters, with a 1-way valve at the vesicoureteral (ureteral-bladder) junction preventing backflow. The valve is formed by oblique tunneling of the distal ureter through the wall of the bladder, creating a short length of ureter (1–2 cm) that can be compressed as the bladder fills. Reflux occurs if the ureter enters the bladder without sufficient tunneling, i.e., too "end-on".
Urinary Tract Infection is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is Escherichia coli, though other bacteria or fungi may rarely be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney infection, if it occurs, usually follows a bladder infection but may also result from a blood-borne infection. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In those with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult because bacteria may be present without there being an infection. In complicated cases or if treatment fails, a urine culture may be useful.
New AI can detect urinary tract infections using a technique called Non-negative Matrix Factorisation to find hidden clues of possible UTI cases.
Mesoamerican Nephropathy is a currently unexplained epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown origin (CKDu), prevalent in the Pacific Ocean coastal low lands of the Mesoamerican region, including southern Mexico, Guatemala, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Honduras and Costa Rica. In rural areas of Nicaragua the disease is colloquially called creatinina. This CKD epidemic in Central America spans along a nearly 1000 kilometer stretch of the Pacific coast. In El Salvador and Nicaragua alone, the reported number of men dying from this painful disease has risen five-fold in the last 20 years, although some researchers believe hidden cases have always been there and this increment in official data could be partially due to the recent increase in reports and improved case search, pushed by the growing social and political interest in the disease. In El Salvador, the disease has become the second leading cause of death among adult men, and according to a recent editorial, it has been estimated that this largely unknown epidemic has caused the premature death of at least 20,000 men in the region. Science Magazine reports: "In El Salvador alone, PAHO's latest figures say CKD of all causes kills at least 2,500 people in the country each year". The people affected by the epidemic are mainly young and middle-aged male laborers in the agricultural sector, particularly sugarcane workers. The disease has also been found to be prevalent in other occupations with a high risk of heat stress, implying strenuous work (miners, construction, port and transportation workers) in the high temperatures of the coastlands. The epidemic appears to affect particular Pacific coastal regions of Nicaragua, El Salvador, Costa Rica,and Guatemala.
Liver located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, has a wide range of functions, including detoxification of various metabolites, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion - Regeneration.
Drug reverses signs of Liver Disease in people living with HIV. Researchers report that the injectable hormone tesamorelin reduces liver fat and prevents liver fibrosis (scarring) in people living with HIV.
Fatty Liver Disease is a condition in which fat builds up in your liver. Alcoholic Steatohepatitis is a chronic, progressive liver disease characterized by thickening and scarring (fibrosis) of the liver as well as possible death (necrosis) of the liver tissue, brought on by excessive, prolonged alcohol use.
Natural compound cruciferous in vegetables helps fight fatty liver disease. Cabbage, kale, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts.
Bile is a dark green to yellowish brown fluid, produced by the liver of most vertebrates, that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine.
Liver fibrosis 'off switch' discovered in mice. Researchers identified several genetic switches, or transcription factors, that determine whether or not liver cells produce collagen -- providing a new therapeutic target for liver fibrosis.
Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process. This can be a reactive, benign, or pathological state. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, fibrosis results in scarring and thickening of the affected tissue, it is in essence an exaggerated wound healing response which interferes with normal organ function.
Men (body) - Women (body)
Analysis - Lab Tests
Poop and Pee Chart
Uroscopy is visually examining a patient's urine for pus, blood, or other symptoms of disease.
Urology is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the male and female urinary tract system and the male reproductive organs.
Maple Syrup Urine Disease is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting branched-chain amino acids. It is one type of organic acidemia. The condition gets its name from the distinctive sweet odor of affected infants' urine, particularly prior to diagnosis, and during times of acute illness.
Bubbles in Urine that disappear within seconds are not usually significant but if the bubbles last that is almost always a sign of protein being inappropriately allowed to leak through the kidney filtering mechanism and end up in your urine. That can be either from kidney disease or an infection which can generate protein from damaged tissue like the urinary tract and bladder. Your medications may also indicate an increased risk for production of bubbly or foamy urine. Foamy urine may occur due to dehydration or a fast flow of urine. Foamy urine may be a sign of kidney damage. Urine can foam up briefly every once in a while. This is usually due to the speed of urine flow. Foamy urine is more likely to be a sign of disease if it happens often or it gets worse over time.
Water (knowledge and Quality)
Paruresis is a type of phobia in which the sufferer is unable to urinate in the real or imaginary presence of others, such as in a public restroom. The analogous condition that affects bowel movement is called parcopresis.
Feces - Shit Happens - What Poo Says About You
 Human Faeces are the feces (solid or
semisolid metabolic waste) of the human digestive system, including
bacteria. They vary significantly in appearance (i.e. size, color,
texture), according to the state of the digestive system, diet and general
health. Normally human feces are semisolid, with a mucus coating. Small
pieces of harder, less moist feces can sometimes be seen impacted on the
distal (leading) end. This is a normal occurrence when a prior
bowel
movement is incomplete, and feces are returned from the rectum to the
intestine, where water is absorbed. In the medical literature, the term
"stool" is more commonly used than "feces". Human feces together with
human urine are collectively referred to as human waste or
human excreta. Containing human feces, and
preventing spreading of pathogens from human feces via the fecal–oral
route, are the main goals of sanitation. -
Analyze-Poop.
Human Faeces are the feces (solid or
semisolid metabolic waste) of the human digestive system, including
bacteria. They vary significantly in appearance (i.e. size, color,
texture), according to the state of the digestive system, diet and general
health. Normally human feces are semisolid, with a mucus coating. Small
pieces of harder, less moist feces can sometimes be seen impacted on the
distal (leading) end. This is a normal occurrence when a prior
bowel
movement is incomplete, and feces are returned from the rectum to the
intestine, where water is absorbed. In the medical literature, the term
"stool" is more commonly used than "feces". Human feces together with
human urine are collectively referred to as human waste or
human excreta. Containing human feces, and
preventing spreading of pathogens from human feces via the fecal–oral
route, are the main goals of sanitation. -
Analyze-Poop.Stool Test involves the collection and analysis of fecal matter to diagnose the presence or absence of a medical condition.
Human Microbes
What someone might say if they need to go to a toilet: I Got to take a Dump. Take a Crap. Take a Shit. Take a Number Two. Take care of some paperwork. Have a bowel movement. Drop a deuce. Pinch off a loaf. Make an offering to the porcelain throne. I have a turtle head poking out.
Bowl Movement is the final act of digestion, by which organisms eliminate solid, semisolid, and/or liquid waste material from the digestive tract via the anus.
Defecation is the elimination of fecal waste through the anus. Defecate is to have a bowel movement.
Rectum is the final section of the large intestine, terminating at the anus.
Anus is the opening at the end of the alimentary canal through which solid waste matter leaves the body.
Wiping Tips: After you poop, the first wipe should be the lightest. The first wipe is to make sure there is nothing dangling. If the first wipe is too hard you might end up spreading poop around and make a mess. What you see on the first piece of toilet paper after the first wipe will determine how hard or soft the second wipe will be. Always end with a hole tap, but not too hard, your finger could breakthrough the toilet paper very easy. If you are not sure if you got it all, you may have to wipe again after an hour or so.
SKID MARKS: How To Wipe Your Butt (According to a Doctor) (youtube)
Skid Marks in your Underwear. Reasons why you might have skid marks in your underwear. You are not wiping properly or correctly (use a flushable moist Baby wipe if needed). You're not showering after you poop. Your poop is soft and sticky. (not enough Fiber). Your butt has a lot of hair. You sweat a lot. Underwear is too tight. You sit too long on your toilet. You have hemorrhoids. Fecal or Poop inconsistencies. You are not completely emptying your bowel. Toilet Training.
Wiping Your Butt - Bum Wiping Techniques - Clean Anus Bowel Movement
One of the main reason adults would have feces on their undies is because they do not wipe properly but this is compounded by the fact that you have soft sticky poop. Solid feces usually exit our anus with little or no residue for us to wipe unlike soft sticky poop which cause us to wipe several times and we just cannot seem to get rid of the mess . To get rid of our soft poop we need to add more soluble and insoluble fiber to our diet . Fiber helps to increase the bacteria in your colon and add bulk to your stool which improves the quality of your poop. Men need an average of 31 to 38 grams of fiber daily and women 21 to 25 grams of fiber daily which we can get from fruits vegetables , oats ,whole wheat . If you cannot get this amount from your food you can add fiber supplements such as psyllium and methylcellulose. Fecal inconsistencies this is the inability to control your bowel movement in most adults it is temporarily caused by Diarrhea, Constipation, Gas and bloating. While in other it can be a long term problem caused by a number of issues such as anxiety , nervousness, damage to their rectum , dementia, IBS and a list of other underlying diseases . If you are not sure if the cause you should see your doctor. For the persons aware of their problem the best solution is to wear sanitary napkins. Wear dark color underwear to hide the stains. Trying controlling your bowel to come in the morning so you can shower after using the toilet. This can be done by drinking a large glass of warm lemon water on an empty stomach in the morning a cup of coffee can also do the job. Constipation can prevent you from fully emptying your bowel thus leaving pieces of poop in your rectum. Which can slip out as you start to sweat and move around. Increase your water intake and also your fiber to avoid this problem. Synonyms for Shitting your Pants.
Spray Fart or a wet fart that has some poop matter mixed in that sometimes makes a mess. Forcing a fart can be dangerous.
Fecal Incontinence is the inability to control or the lack of control of bowel movements, causing involuntary loss of stool (feces) to leak unexpectedly from the rectum, including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. Common causes of fecal incontinence include diarrhea, constipation, and muscle or nerve damage in some forms encopresis, which is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents.
Toilets - Best Toilet Positions (PDF) - Squatty Potty
Anal Cleansing is the hygienic practice that a person performs on the anal area of himself or herself after defecation. The anus and buttocks may be either washed with liquids or wiped with toilet paper or other solid materials. In many Muslim, Hindu and Sikh cultures, as well as Southeast Asia, water is usually used for anal cleansing using a jet, as with a bidet, or splashed and washed with the hand. Some people follow this up with toilet paper afterwards for drying purposes.
How Often should I Change my Underwear? It's definitely relevant. Change your underwear after intense physical activity and before going out for social events, and right after shower. You should change your underwear on a daily basis, unless you are pooping clean and you're not sweating too much. You might get 2 or 3 days.
How often should I replace my underwear? Consider fully replacing your underwear once a year if you are a hard worker. Stained underwear should be thrown out. Underwear should be replaced every year for health reasons to reduce the risk of urinary tract and other infections. A 3 week supply is around 20 pairs of underwear. You need at least 14 pairs if you launder your clothes once a week. A pair for each day of the week and backups for exercise or travel.
Laxative are substances that loosen stools and increase bowel movements. They are used to treat and prevent constipation, which refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass.
Suppository is a solid dosage form that is inserted into the rectum (rectal suppository), vagina (vaginal suppository) or urethra (urethral suppository), where it dissolves or melts and exerts local or systemic effects. Suppositories are used to deliver both systemically and locally acting medications.
Enemas - Cleansing the Inside
How often should I Pee and Poo?
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement. Complications from constipation may include hemorrhoids, anal fissure or fecal impaction. The normal frequency of bowel movements in adults is between three per day and three per week. (I poop once a day in the morning before my shower, and some days I poop twice). Babies often have three to four bowel movements per day while young children typically have two to three per day. I poop once everyday in the morning after coffee, and sometimes twice in one day.
Microbes - Fiber - Gas - Digestive Tract
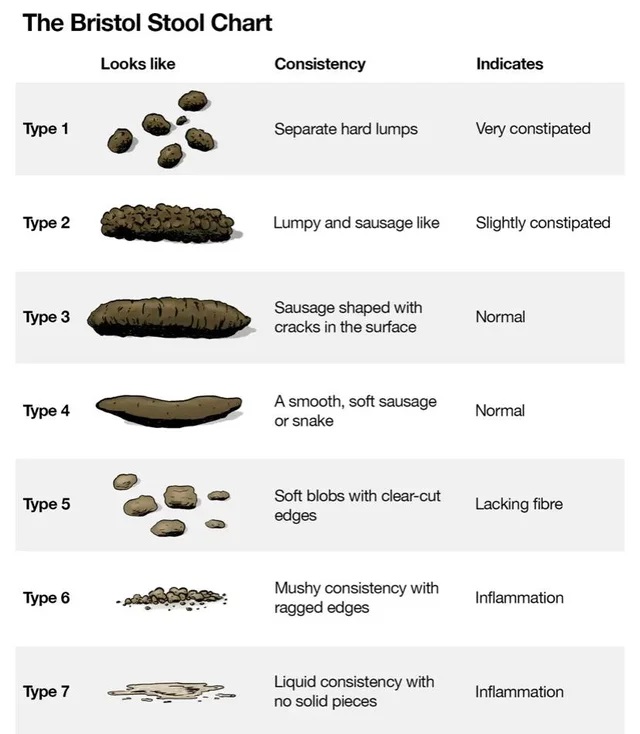 Diarrhea is the condition of having at
least three loose or liquid bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a
few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of
dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin
and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of
skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it
becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are
breastfed, however, may be normal. Viruses.
Diarrhea is the condition of having at
least three loose or liquid bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a
few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of
dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin
and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of
skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it
becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are
breastfed, however, may be normal. Viruses.
Amoebiasis is an infection caused by any of the amoebas of the Entamoeba group. Symptoms are most common during infection by Entamoeba histolytica. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhoea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. People affected may develop anemia due to loss of blood.
Food Safety - Food Poison
Dysentery is a type of gastroenteritis that results in diarrhea with blood. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. It is caused by a number of types of infection such as bacteria, viruses, parasitic worms, or protozoa. The mechanism is an inflammatory disorder of the intestine, especially of the colon. Dysentery Kills 700,000 children a year.
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it leads within hours to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. This may result in sunken eyes, cold skin, decreased skin elasticity, and wrinkling of the hands and feet. Dehydration can cause the skin to turn bluish. Symptoms start two hours to five days after exposure. Prevention methods against cholera include improved
sanitation and access to clean water.
Cholera affects an estimated 3–5 million people worldwide and causes 28,800–130,000 deaths a year. There were 1,207,596 suspected cases of cholera in Yemen between April 2017 and April 2018. The total estimated number of cholera cases worldwide ranges from 1.4 million to 4 million. Clean Water.
Some people who have a strong gastrocolic reflex have a bowel movement the minute you feed them, and it's a normal response from them. Others have a bowel movement every day or every other day or so, it varies.
Typhoid Mary was an Irish-born cook believed to have infected 53 people, three of whom died, with typhoid fever, and the first person in the United States identified as an asymptomatic carrier of the disease. Because she persisted in working as a cook, by which she exposed others to the disease, she was twice forcibly quarantined by authorities, and died after a total of nearly three decades in isolation. Mary Mallon (September 23, 1869 – November 11, 1938).
Typhoid Fever is a bacterial infection due to a specific type of Salmonella that causes symptoms. Spreads through the fecal-oral route.
Fecal-Oral Route describes a particular route of transmission of a disease wherein pathogens in fecal particles pass from one person to the mouth of another person. Main causes of fecal–oral disease transmission include lack of adequate sanitation (leading to open defecation), and poor hygiene practices. If soil or water bodies are polluted with fecal material, humans can be infected with waterborne diseases or soil-transmitted diseases. Fecal contamination of food is another form of fecal-oral transmission. Washing hands properly after changing a baby's diaper or after performing anal hygiene can prevent foodborne illness from spreading. The common factors in the fecal-oral route can be summarized as five Fs: fingers, flies, fields, fluids, and food. Diseases caused by fecal-oral transmission include diarrhea, typhoid, cholera, polio and hepatitis.
Pelvic Floor Training (youtube) - Bladder and Bowel Foundation
Dyssynergia is any disturbance of muscular coordination, resulting in uncoordinated and abrupt movements.
Poo Therapy
Fecal Bacterio-Therapy or Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT), also known as a Stool Transplant, is the process of transplantation of fecal bacteria from a healthy individual into a recipient. FMT involves restoration of the colonic microflora by introducing healthy bacterial flora through infusion of stool, e.g. by colonoscopy, enema, orogastric tube or by mouth in the form of a capsule containing freeze-dried material, obtained from a healthy donor. The effectiveness of FMT has been established in clinical trials for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), whose effects can range from diarrhea to pseudomembranous colitis. Due to an epidemic of CDI in North America and Europe, FMT has gained increasing prominence, with some experts calling for it to become first-line therapy for CDI. In 2013 a randomized, controlled trial of FMT from healthy donors showed it to be highly effective in treating recurrent C. difficile in adults, and more effective than vancomycin alone. FMT has been used experimentally to treat other gastrointestinal diseases, including colitis, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has regulated human feces as an experimental drug since 2013. Transplants can be 90% effective.
Stool Donation - Open Biome
Fecal transplants could one day be used to restore cognitive decline among the elderly. A new study shows how fecal transplants from older to younger mice altered their gut microbiome, which in turn impacted their spatial learning and memory.
Fecal transplantation can restore the gut microbiota of C-section babies.
Personalized Donor Selection. Durable coexistence of donor and recipient strains after fecal Microbiota transplantation.
Leaky Gut Syndrome - Intestinal Permeability is the opening of intercellular tight junctions (increased intestinal permeability) can allow passage of microbes, microbial products, and foreign antigens into the mucosa and the body proper. This can result in activation of the immune system and secretion of inflammatory mediators.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are the principal types of inflammatory bowel disease. It is important to note that not only does Crohn's disease affect the small intestine and large intestine, it can also affect the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a group of symptoms—including abdominal pain and changes in the pattern of bowel movements without any evidence of underlying damage.
How a gut infection may produce chronic symptoms. A bout of intestinal distress like traveler's diarrhea leads to irritable bowel syndrome.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. SIBO is defined as excessive bacteria in the small intestine. Patients with SIBO vary in presentation, from being only mildly symptomatic to suffering from chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and malabsorption.
Crohn's Disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus. Signs and symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, and weight loss. Other complications may occur outside the gastrointestinal tract and include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and tiredness. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of bowel cancer.
Hemorrhoid also called piles, are vascular structures in the anal canal. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control. They become a disease when swollen or inflamed; the unqualified term "hemorrhoid" is often used to mean the disease. The signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids depend on the type present. Internal hemorrhoids usually present with painless, bright red rectal bleeding when defecating. External hemorrhoids often result in pain and swelling in the area of the anus. If bleeding occurs it is usually darker. Symptoms frequently get better after a few days. A skin tag may remain after the healing of an external hemorrhoid.
Pruritus Ani is the irritation of the skin at the exit of the rectum, known as the anus, causing the desire to scratch. The intensity of anal itching increases from moisture, pressure, and rubbing caused by clothing and sitting. At worst, anal itching causes intolerable discomfort that often is accompanied by burning and soreness. It is estimated that up to 5% of the population of the United States experiences this type of discomfort daily.
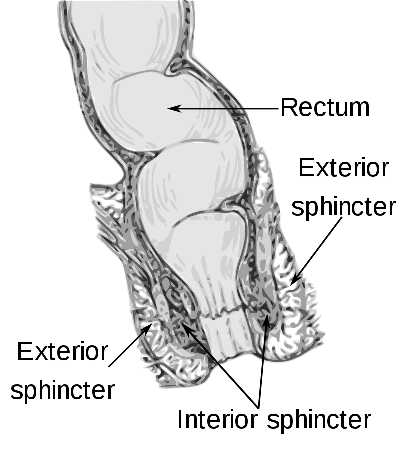 Anus is an opening at the opposite end
of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control
the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during
digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may include: matter
which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; food material after all the
nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested
matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and
dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts.
Anus is an opening at the opposite end
of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control
the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during
digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may include: matter
which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; food material after all the
nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested
matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and
dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts.Proctology is the branch of medicine dealing with the pathology of and surgery upon the colon, rectum and anus.
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (e.g. ulceration, polyps) and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected colorectal cancer lesions. Colonoscopy can remove polyps as small as one millimetre or less. Once polyps are removed, they can be studied with the aid of a microscope to determine if they are precancerous or not. It can take up to 15 years for a polyp to turn cancerous.
Colorectal Surgery is a field in medicine, dealing with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. The field is also known as proctology, but the latter term is now used infrequently within medicine, and is most often employed to identify practices relating to the anus and rectum in particular. Digestion Tract.
Fecal Immunochemical Test is designed to detect the protein hemoglobin, which is found in red blood cells. People who test positive with the FIT need to get a colonoscopy to determine whether they have cancer or pre-cancerous lesions. But those who test negative only need to keep getting the FIT each year to make sure they don’t develop colon cancer.
Functional Gastrointestinal Disorder include a number of separate idiopathic disorders which affect different parts of the gastrointestinal tract and involve visceral hypersensitivity and impaired gastrointestinal motility. Heightened mast cell activation is a common factor among all FGIDs that contributes to visceral hypersensitivity as well as epithelial, neuromuscular, and motility dysfunction.
Meta-genomic analysis of toilet waste from long distance flights; a step towards global surveillance of infectious diseases and antimicrobial resistance.
The Surprisingly Charming Science of your Gut (video and text)
Electrical Power of Poo - Waste Energy
