BK101
Knowledge Base
Teeth - Dentist
Teeth Health are extremely important, especially for Heart Health and Brain Health.
Teeth Care Instructions - Cavities - Fillings - Pain
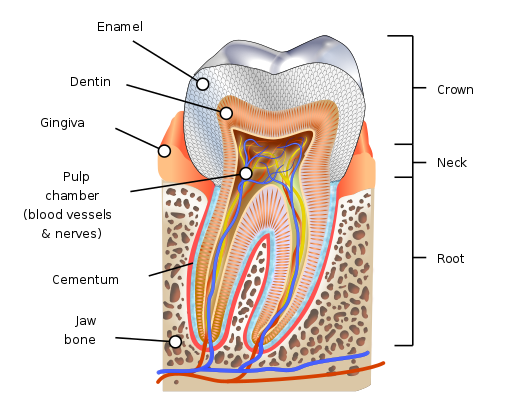 Human
Teeth are hard bonelike structures in the
mouth that function to
mechanically break down items of food by cutting and
crushing them in preparation for swallowing and
digesting. Humans have
four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each with a
specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food
and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are
embedded in the maxilla (upper jaw) or the mandible (lower jaw) and are
covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and
hardness. Teeth are among the most distinctive (and long-lasting) features
of mammal species. Humans, like other mammals, are diphyodont, meaning
that they develop two sets of teeth. The first set (called the "baby",
"milk", "primary", or "deciduous" set) normally starts to appear at about
six months of age, although some babies are born with one or more visible
teeth, known as natal teeth. Normal tooth eruption at about six months is
known as teething and can be painful. Fluoride.
Human
Teeth are hard bonelike structures in the
mouth that function to
mechanically break down items of food by cutting and
crushing them in preparation for swallowing and
digesting. Humans have
four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each with a
specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food
and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are
embedded in the maxilla (upper jaw) or the mandible (lower jaw) and are
covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and
hardness. Teeth are among the most distinctive (and long-lasting) features
of mammal species. Humans, like other mammals, are diphyodont, meaning
that they develop two sets of teeth. The first set (called the "baby",
"milk", "primary", or "deciduous" set) normally starts to appear at about
six months of age, although some babies are born with one or more visible
teeth, known as natal teeth. Normal tooth eruption at about six months is
known as teething and can be painful. Fluoride.
 Humans usually have 20 primary (deciduous, "baby" or "milk") teeth, and 32 permanent (adult)
teeth. Teeth are classified as incisors, canines, premolars (also called
bicuspids), and molars. Incisors are primarily used for biting pieces from
foods such as raw carrots or apples and peeled but uncut bananas, while
molars are used primarily for grinding foods after they are already in
bite size pieces inside the mouth.
Humans usually have 20 primary (deciduous, "baby" or "milk") teeth, and 32 permanent (adult)
teeth. Teeth are classified as incisors, canines, premolars (also called
bicuspids), and molars. Incisors are primarily used for biting pieces from
foods such as raw carrots or apples and peeled but uncut bananas, while
molars are used primarily for grinding foods after they are already in
bite size pieces inside the mouth.
Incisor are the front teeth present in most mammals.
Premolar are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth.
Molar are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth.
Wisdom Tooth is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through (erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, one in each of the four quadrants, but it is possible to have none, fewer, or more, in which case the extras are called supernumerary teeth. Wisdom teeth may get stuck (impacted) against other teeth if there is not enough space for them to come through normally. Impacted wisdom teeth are still sometimes removed for orthodontic treatment, believing that they move the other teeth and cause crowding, though this is not held anymore as true. Impacted wisdom teeth may suffer from tooth decay if oral hygiene becomes more difficult. Wisdom teeth which are partially erupted through the gum may also cause inflammation and infection in the surrounding gum tissues, termed pericoronitis. Some more conservative treatments, such as operculectomies, may be fitting for some cases, yet impacted wisdom teeth are commonly extracted as treatment for these problems, many times before these problems even occur. Some oppose this prophylactic removal of disease-free impacted wisdom teeth, including among them the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the UK.
Enamel is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the body. It is one of the four major tissues which make up the tooth, along with dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is normally visible and must be supported by underlying dentin. 96% of enamel consists of mineral, with water and organic material comprising the rest.
Baby Teeth in order of Appearance (photos) - Child Development
Dental Pulp Stem Cells are stem cells present in the dental pulp, the soft living tissue within teeth. They are multipotent, so they have the potential to differentiate into a variety of cell types. Other sources of dental stem cells are the dental follicle and the developed periodontal ligament.
Pulp in teeth is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue and cells called odontoblasts. The dental pulp is a part of the dentin–pulp complex (endodontium). The vitality of the dentin-pulp complex, both during health and after injury, depends on pulp cell activity and the signaling processes that regulate the cell’s behavior.
Human Tooth Development is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stages of fetal development. Primary (baby) teeth start to form between the sixth and eighth week of prenatal development, and permanent teeth begin to form in the twentieth week. If teeth do not start to develop at or near these times, they will not develop at all, resulting in hypodontia or anodontia. A significant amount of research has focused on determining the processes that initiate tooth development. It is widely accepted that there is a factor within the tissues of the first pharyngeal arch that is necessary for the development of teeth.
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have homodont dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have heterodont dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as diphyodont, while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is monophyodont. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed polyphyodont. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in sockets in the jawbones is termed thecodont.
Teeth Maintenance
 How to brush your teeth (youtube)
- How to Brush Teeth (youtube)
How to brush your teeth (youtube)
- How to Brush Teeth (youtube)
Toothbrush is an oral hygiene instrument used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard to reach areas of the mouth. Toothbrushes are available with different bristle textures, sizes, and forms. Most dentists recommend using a soft toothbrush since hard bristled toothbrushes can damage tooth enamel and irritate the gums.
Soft Bristle Tooth Brush? Pros and Cons - (webmd)
Bristl Phototherapy Rechargeable Electric Toothbrush
Brush your Teeth 2 Times a Day for 2 Minutes each time
Oral Care Tips (mayo clinic)
Teeth Care Tips (kids health)
Oral Health (webmd)
Oral Health (gov)
How to Floss (youtube) - Video 2 (youtube) - Video 3 (youtube)
Floss Holder Tool
Toothpaste alone does not prevent dental erosion or hypersensitivity. An analysis of nine toothpastes found that none of them protects enamel or prevents erosive wear. Specialists stress that diet and treatment by a dentist are key to avoid the problems originated by dentin exposure.
Dentistry is a branch of medicine that is involved in the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the oral cavity, commonly in the dentition but also the oral mucosa, and of adjacent and related structures and tissues, particularly in the maxillofacial (jaw and facial) area. Although primarily associated with teeth among the general public, the field of dentistry or dental medicine is not limited to teeth but includes other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temperomandibular and other supporting structures.
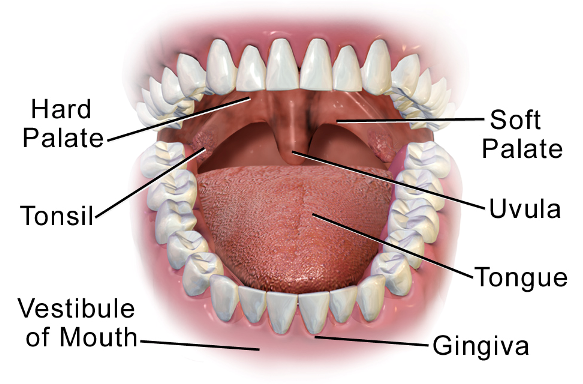
American Dental Association - Free Dental Clinics - Oral Cavity - Mouth
Pocket Dentistry answers for your clinical questions.
Dental Anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. (The function of teeth as they contact one another falls elsewhere, under dental occlusion.) Tooth formation begins before birth, and teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.
Dental Health Guide
American Dental Research - Dental Diseases
Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Orthodontics is a specialty that deals primarily with the diagnosis, prevention and correction of malpositioned teeth and the jaws.
Dental Arch are the two arches (crescent arrangements) of teeth, one on each jaw, that together constitute the dentition.
Malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close.
Orthotropics is a branch of dentistry that specializes in treating malocclusion by guiding the growth of the facial bones and correcting the oral environment. This treatment creates more space for the teeth and tongue. The main focus of this approach is to correct a patients oral and head posture.
Orthotropic Material have material properties that differ along three mutually-orthogonal twofold axes of rotational symmetry. They are a subset of anisotropic materials, because their properties change when measured from different directions.
Periodontology is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A person who practices this specialty is known as a periodontist.
Gums consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Periodontitis also known as gum disease and pyorrhea, is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth.
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that occurs around the teeth.
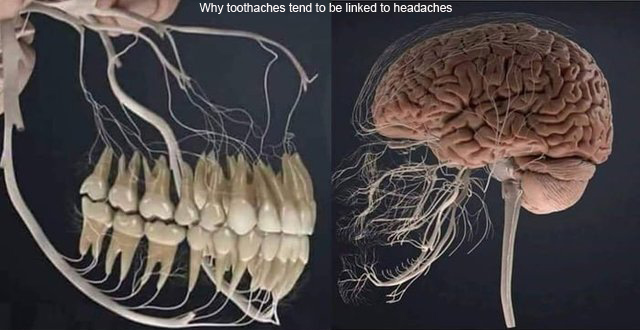
An untreated dental abscess can invade the tissues of the head and chest. It can infect and clot the veins of the neck, and spread between the skull’s many sinuses. If it reaches the brain, it can result in a brain abscess or meningitis.
Dental Abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by tooth decay, broken teeth or extensive periodontal disease (or combinations of these factors). A failed root canal treatment may also create a similar abscess.
High Levels of Oral Disease among elite Athletes affecting performance. Nearly half (49.1%) of the athletes were found to have untreated tooth decay, 77% had gingivitis, an early indicator of gum disease, and 39% self-reported having bleeding gums while cleaning their teeth, a sign of gum inflammation. Only 1.1% of the participants had ‘excellent’ periodontal health. More than a third (32%) reported that these conditions had impacted negatively on their sporting performance, along with their ability to eat (34.6%), relax and sleep (15.1%) and smiling and self-confidence (17.2%).
Good Hygiene - Bathing
Oral Microbiology is the study of the microorganisms or microbiota of the oral cavity and their interactions between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment present in the human mouth allows the growth of characteristic microorganisms found there. It provides a source of water and nutrients, as well as a moderate temperature. Resident microbes of the mouth adhere to the teeth and gums to resist mechanical flushing from the mouth to stomach where acid-sensitive microbes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid.
Fluoride Warnings
Swallowing Fluoride provides no (or very little) benefit. Fluoride may damage the brain. Substantial evidence of developmental neurotoxicity. Fluoride may lower IQ. Fluoride may cause non-IQ neurotoxic effects. Fluoride affects the pineal gland. Fluoride affects thyroid function. Fluoride causes arthritic symptoms. Fluoride damages bone. Fluoride may increase hip fractures in the elderly. Fluoride may cause bone cancer (osteosarcoma). Fluoride may cause reproductive problems. Topical Fluoride is much safer. Some individuals are highly sensitive to low levels of fluoride. Other subsets of population are more vulnerable to fluoride’s toxicity. Review panels hand-picked to deliver a pro-fluoridation result. Tooth decay was coming down before fluoridation started. Tooth decay does not go up when fluoridation is stopped. So Fluoridation in the water is unethical. Informed consent is standard practice for all medication, and one of the key reasons why most of Western Europe has ruled against fluoridation. With water fluoridation we are allowing governments to do to whole communities (forcing people to take a medicine irrespective of their consent) what individual doctors cannot do to individual patients. Put another way: Does a voter have the right to require that their neighbor ingest a certain medication (even if it is against that neighbor’s will). The dose cannot be controlled. Once fluoride is put in the water it is impossible to control the dose each individual receives because people drink different amounts of water. In the U.S., about 70% of public water supplies are fluoridated. This equates to approximately 185 million people, which is over half the number of people drinking artificially fluoridated water worldwide. Some countries have areas with high natural fluoride levels in the water. These include India, China and parts of Africa. In these countries measures are being taken to remove the fluoride because of the health problems that fluoride can cause. In Europe, only Ireland (73%), Poland (1%), Serbia (3%), Spain (11%), and the U.K. (11%) fluoridate any of their water. Most developed countries, including Japan and 97% of the western European population, do not consume fluoridated water. Fluorine is a chemical element that is very poisonous. Fluoride is the reduced form of fluorine.
Fluoride Dangers (50 Reasons)
The Biophysics of Fluoride by Neurosurgeon Dr. Jack Kruse (youtube) - Redox
Maternal Fluoride Consumption During Pregnancy Lower Children's Intelligence.
Simple Test could prevent Fluoride-Related Disease. Method uses synthetic biology to detect dangerous levels of fluoride in drinking water. Synthetic biologists developed a simple, inexpensive new test that can detect dangerous levels of fluoride in drinking water.
Drugs in Water - Toxins - Documentaries
Pesticides - Pollution - Side Effects
Fluoride Varnish is a highly concentrated form of fluoride which is applied to the tooth's surface, by a dentist, dental hygienist or other health care professional, as a type of topical fluoride therapy.
Topical Medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body, as opposed to systemically, or forced on people by contaminating the water.
Mouthwash is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swilled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargled, where the head is tilted back and the liquid bubbled at the back of the mouth.
Gargling is the process of exhaling a slow and steady small amount of air from the lungs in order to bubbled a liquid in the mouth. It usually requires that the head be tilted back, allowing a mouthful of liquid to sit in the upper throat. The head can be tilted by tilting either the neck or the back, depending on what is comfortable for the gargler. Vibration caused by the muscles in the throat and back of the mouth cause the liquid to bubble and percolate through the throat and mouth cavity. A study in Japan has shown that gargling water a few times a day will lower the chance of upper respiratory infections such as colds, though some medical authorities are skeptical.
A common ingredient found in Toothpastes and Handwashes could make antibiotics less effective in treating conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs), which, if left untreated, can become life-threatening. According to the study, led by researchers at the Washington University in St. Louis, triclosan exposure may inadvertently drive bacteria into a state in which they are able to tolerate normally lethal concentrations of antibiotics, including those that are commonly used to treat UTIs.
Triclosan is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of action to triclocarban. Its efficacy as an antimicrobial agent, the risk of antimicrobial resistance, and its possible role in disrupted hormonal development remains controversial. Additional research seeks to understand its potential effects on organisms and environmental health. Triclosan is an ingredient added to many consumer products intended to reduce or prevent bacterial contamination. It is added to some antibacterial soaps and body washes, toothpastes, and some cosmetics.
Tooth Decay
Dental Cavities is a breakdown of teeth due to activities of bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss, and infection or abscess formation. The cause of caries is bacterial breakdown of the hard tissues of the teeth (enamel, dentin and cementum). This occurs due to acid made from food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjogren's syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antidepressants. Caries is also associated with poverty, poor cleaning of the mouth, and receding gums resulting in exposure of the roots of the teeth. Prevention of dental caries includes regular cleaning of the teeth, a diet low in sugar, and small amounts of topical fluoride. Brushing the teeth twice per day and flossing between the teeth once a day is recommended by many. Fluoride may be from water, salt or toothpaste among other sources. Treating a mother's dental caries may decrease the risk in her children by decreasing the numbers of certain bacteria. Screening can result in earlier detection. Depending on the extent of destruction, various treatments can be used to restore the tooth to proper function or the tooth may be removed. There is no known method to grow back large amounts of tooth. The availability of treatment is often poor in the developing world. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) or ibuprofen may be taken for pain. Worldwide, approximately 2.3 billion people (32% of the population) have dental caries in their permanent teeth. The World Health Organization estimates that nearly all adults have dental caries at some point in time. In baby teeth it affects about 620 million people or 9% of the population. They have become more common in both children and adults in recent years. The disease is most common in the developed world due to greater simple sugar consumption and less common in the developing world. Caries is Latin for "rottenness".
Dental Caries Detection
Caries Management System - PDF
Streptococcus Mutans is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay.
International Caries Detection and Assessment System is a standardized system, based on best available evidence for detecting early and later stage caries severity, should lead to the acquisition of better quality information which could then be used to inform decisions about appropriate diagnosis, prognosis, and clinical management of dental caries at both the individual and public health levels.
Dental Health (tooth decay)
Avoid Root Canals (youtube)
How To Heal Tooth Decay And Reverse Cavities Using This Easy Remedy (youtube)
SUDANTA: POWER of Ancient HERBS on Your Brush Introducing Ayurveda-powered, non-fluoride SUDANTA toothpaste for the first time GLOBALLY.
Mineralization Intervention - Remineralizing Tooth Gel
Homemade Remineralizing Toothpaste
Ingredients:
4 tablespoons coconut oil.
2 tablespoons baking soda.
1 tablespoon xylitol powder.
20 drops cinnamon or clove essential oil.
20 drops peppermint essential oil.
30 drops trace minerals.
toothpaste tube.
Peptide-Based Biogenic Dental Product may Cure Cavities by using proteins and remineralization guided by peptides to rebuild tooth enamel and treat dental cavities.
Keep 32
Small molecule inhibitor prevents or impedes tooth cavities in a preclinical model. The inhibitor blocks a key virulence enzyme in the oral bacterium Streptococcus mutans, making it unable to stick to a tooth surface.
Nitrate levels found in Beets are converted by the body into nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide not only prevents cavities, but also actually stops tooth decay.
Tideglusib can stimulate teeth to fix decay. When a tooth is damaged, the body produces a thin layer of dentine to seal tooth pulp and prevent infection. But this isn’t effective to repair large cavities. Man-made cement fillings patch the decayed tooth, but the tooth’s normal mineral level is never completely restored. Eventually, dentists have to remove old fillings and replace them with larger ones. And after several treatments, the decayed teeth may need to be pulled, he said placed biodegradable collagen sponges laced with a low dose of Tideglusib over holes drilled into the teeth of mice. Over six weeks, as the sponge degraded, it was replaced by new dentine, leading to complete, natural repair. Tideglusib is a potent, selective and irreversible small molecule non-ATP-competitive GSK3 inhibitor that has been investigated as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease and paralysis supranuclear palsy in Phase IIa and IIb clinical trials.
Oil Pulling is a traditional folk remedy where oil is "swished" (kavala graha) or "held" (snigda gandoosha) in the mouth. Practitioners of oil pulling claim it is capable of improving oral and systemic health, including a benefit in conditions such as headaches, migraines, diabetes mellitus, asthma, and acne, as well as whitening teeth. Its promoters claim it works by "pulling out" toxins, which are known as ama in Ayurvedic medicine, and thereby reducing inflammation.
Arginine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual. Preterm infants are unable to synthesize or create arginine internally, making the amino acid nutritionally essential for them. Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because their body produces sufficient amounts. Precursor for the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) Non-L-arginine derived NO can be generated by the nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway that is monitored through saliva testing. Reduces healing time of injuries (particularly bone). Quickens repair time of damaged tissue. Helps decrease blood pressure in clinical hypertensive subjects NO-mediated decrease in blood pressure is influenced by both the L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide synthase pathway and non-L-arginine or alternative pathway through nitrate-rich foods such as beets and spinach. Arginine is a potent agonist of the mTOR protein kinase that regulates growth and metabolism at both the cellular and organismal level. Arginine helps to activate mTORC1 by promoting its localization to the lysosome by binding to the CASTOR proteins.
Avoid Sugar!
Phytic Acid is bad for teeth. It's the principal storage form of phosphorus in many plant tissues, especially bran and seeds. It can be found in cereals and grains. (known as inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6), inositol polyphosphate, or phytate when in salt form), discovered in 1903, a saturated cyclic acid. Whole Grain Organic Bread.
Regeneration of Teeth
Tooth Regeneration is a stem cell based regenerative medicine procedure in the field of tissue engineering and stem cell biology to replace damaged or lost teeth by regrowing them from autologous stem cells. As a source of the new bioengineered teeth, somatic stem cells are collected and reprogrammed to induced pluripotent stem cells which can be placed in the dental lamina directly or placed in a reabsorbable biopolymer in the shape of the new tooth.
Bone Structure Regeneration after low induction magnetic field treatment in teeth chosen for extraction. The use of slow variable magnetic fields contributed to bone structure regeneration and to preserve teeth with recorded endo-perio syndrome. Endodontic treatment of replanted teeth, aided with magnetostimulation has stopped the osteolisis process. Human Body Magnetic Field.
Natural Tooth Repair Method could Revolutionize Dental Treatments.
Activating Tooth Regeneration in Mice. Oral & Craniofacial Sciences now show that Wnt activity is absent in a rudimentary form of the dental lamina (RSDL) in mice. This structure forms in the mouse but then disappears, stopping the generation of
another set of teeth. Wound Healing.
Fillings for Teeth
Composite or Amalgam? The debate over whether dental amalgam (the "silver" in dental fillings) should be used. Supporters claim that it is safe, effective and long-lasting while critics argue that claims have been made since the 1840s that amalgam is unsafe because it may cause mercury poisoning and other toxicity.
Dental Fillings could last twice as Long. A compound used to make car bumpers strong and protect wood decks could
prevent return visits to the dentist's office.
Bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace a missing tooth (or several teeth) by joining an artificial tooth permanently to adjacent teeth or dental implants. Types of bridges may vary, depending upon how they are fabricated and the way they anchor to the adjacent teeth. Conventionally, bridges are made using the indirect method of restoration. However, bridges can be fabricated directly in the mouth using such materials as composite resin. A bridge is fabricated by reducing the teeth on either side of the missing tooth or teeth by a preparation pattern determined by the location of the teeth and by the material from which the bridge is fabricated. In other words, the abutment teeth—including portions which are otherwise perfectly healthy—are "reduced" in size using a high-speed rotary tool to accommodate the material to be used to restore the size and shape of the original teeth in a correct alignment and contact with the opposing teeth. The dimensions of the bridge are defined by Ante's Law: "The root surface area of the abutment teeth has to equal or surpass that of the teeth being replaced with pontics". The materials used for the bridges include gold, porcelain fused to metal, or in the correct situation porcelain alone. The amount and type of reduction done to the abutment teeth varies slightly with the different materials used. The recipient of such a bridge must be careful to clean well under this prosthesis. When restoring an edentulous space with a fixed partial denture that will crown the teeth adjacent to the space and bridge the gap with a pontic, or "dummy tooth", the restoration is referred to as a bridge. Besides all of the preceding information that concerns single-unit crowns, bridges possess a few additional considerations when it comes to case selection and treatment planning, tooth preparation and restoration fabrication.
Crown is used to cover a tooth to help restore it to its normal shape and size. A crown can make your tooth stronger and improve its appearance. A crown can help strengthen a tooth with a large filling when there isn’t enough tooth remaining to hold the filling. Crowns can also be used to attach bridges, protect a weak tooth from breaking or restore one that’s already broken. A crown is a good way to cover teeth that are discolored or badly shaped. It’s also used to cover a dental implant.
Dental Implant is a surgical component that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic.
Ceramic Inlays offer an aesthetic alternative to metal class I or II restorations.
Braces are devices used in orthodontics that align and straighten teeth and help to position them with regard to a person's bite, while also working to improve dental health. They are often used to correct underbites, as well as malocclusions, overbites, open bites, deep bites, cross bites, crooked teeth, and various other flaws of the teeth and jaw. Braces can be either cosmetic or structural. Dental braces are often used in conjunction with other orthodontic appliances to help widen the palate or jaws and to otherwise assist in shaping the teeth and jaws.
Time-Lapse Video of Braces Straightening Teeth over time (motion gif)
Periodontal Probe is an instrument in dentistry commonly used in the dental armamentarium. It is usually long, thin, and blunted at the end. The primary purpose of a periodontal probe is to measure pocket depths around a tooth in order to establish the state of health of the periodontium. There are markings inscribed onto the head of the instrument for accuracy and readability.
Dental X-Rays Radiography. Dental Radiographs are commonly called x-rays. Dentists use radiographs for many reasons: to find hidden dental structures, malignant or benign masses, bone loss, and cavities. A radiographic image is formed by a controlled burst of X-ray radiation which penetrates oral structures at different levels, depending on varying anatomical densities, before striking the film or sensor. Teeth appear lighter because less radiation penetrates them to reach the film. Dental caries, infections and other changes in the bone density, and the periodontal ligament, appear darker because X-rays readily penetrate these less dense structures. Dental restorations (fillings, crowns) may appear lighter or darker, depending on the density of the material. The dosage of X-ray radiation received by a dental patient is typically small (around 0.150 mSv for a full mouth series, according to the American Dental Association website), equivalent to a few days' worth of background environmental radiation exposure, or similar to the dose received during a cross-country airplane flight (concentrated into one short burst aimed at a small area). Incidental exposure is further reduced by the use of a lead shield, lead apron, sometimes with a lead thyroid collar. Technician exposure is reduced by stepping out of the room, or behind adequate shielding material, when the X-ray source is activated.
Bitewing Xrays (video)
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery specializes in treating many diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral (mouth) and maxillofacial (jaws and face) region.
Association of Oral Surgeons
Teeth Grinding (webmd) - Twitching
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common problem; reports of prevalence range from 8–31% in the general population. Several symptoms are commonly associated with bruxism, including hypersensitive teeth, aching jaw muscles, headaches, tooth wear, damage to dental restorations (e.g. crowns and fillings) and damage to teeth. However it may cause minimal symptoms, and therefore people may not be aware of the condition.
Tooth Pain Relief
 Analgesic is any member of
the group of drugs used to achieve analgesia, relief from
Pain. Analgesic
drugs act in various ways on the peripheral and central nervous systems.
They are distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily affect, and in some
instances completely eliminate, sensation. Analgesics include paracetamol
(known in North America as acetaminophen or simply APAP), the nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as the salicylates, and
opioid drugs
such as morphine and oxycodone. When choosing analgesics, the severity and
response to other medication determines the choice of agent; the World
Health Organization (WHO) pain ladder specifies mild analgesics as its
first step. Analgesic choice is also determined by the
type of pain: For
neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is
often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered
analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants.
Analgesic is any member of
the group of drugs used to achieve analgesia, relief from
Pain. Analgesic
drugs act in various ways on the peripheral and central nervous systems.
They are distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily affect, and in some
instances completely eliminate, sensation. Analgesics include paracetamol
(known in North America as acetaminophen or simply APAP), the nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as the salicylates, and
opioid drugs
such as morphine and oxycodone. When choosing analgesics, the severity and
response to other medication determines the choice of agent; the World
Health Organization (WHO) pain ladder specifies mild analgesics as its
first step. Analgesic choice is also determined by the
type of pain: For
neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is
often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered
analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants.Anesthesia is a state of temporary induced loss of sensation or awareness. It may include analgesia (relief from or prevention of Pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), or unconsciousness. A patient under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of medical procedures that would cause severe or intolerable pain to an unanesthetized patient. Three broad categories of anaesthesia exist: General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation. Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. Regional anesthesia and local anesthesia, which block transmission of nerve impulses between a targeted part of the body and the central nervous system, causing loss of sensation in the targeted body part. A patient under regional or local anesthesia remains conscious, unless general anaesthesia or sedation is administered at the same time. Two broad classes exist: Peripheral blockade inhibits sensory perception in an isolated part of the body, such as numbing a tooth for dental work or administering a nerve block to inhibit sensation in an entire limb. Central, or neuraxial, blockade administers the anesthetic in the region of the central nervous system itself, suppressing incoming sensation from outside the area of the block. Examples include epidural anaesthesia and spinal anaesthesia.
Local Anesthetic is a medication that causes reversible absence of Pain sensation, although other senses are often affected, as well. Also, when it is used on specific nerve pathways (local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle power) also can be achieved. Clinical LAs belong to one of two classes: aminoamide and aminoester local anesthetics. Synthetic LAs are structurally related to cocaine. They differ from cocaine mainly in that they have a very low abuse potential and do not produce hypertension or (with few exceptions) vasoconstriction. They are used in various techniques of local anesthesia such as: Topical anesthesia (surface). Topical administration of cream, gel, ointment, liquid, or spray of anaesthetic dissolved in DMSO or other solvents/carriers for deeper absorption. Infiltration. Brachial plexus block. Epidural (extradural) block. Spinal anesthesia (subarachnoid block). Iontophoresis.
Twilight Anesthesia is an anesthetic technique where a mild dose of general anesthesia is applied to induce anxiolysis (anxiety relief), hypnosis, and anterograde amnesia (inability to form new memories). The patient is not unconscious, but sedated. During surgery or other medical procedures, the patient is under what is known as a "twilight state", where the patient is relaxed and "sleepy", able to follow simple directions by the doctor, and is responsive. Generally, twilight anesthesia causes the patient to forget the surgery and the time right after. It is used for a variety of surgical procedures and for various reasons. Just like regular anesthesia, twilight anesthesia is designed to help a patient feel more comfortable and to minimize pain associated with the procedure being performed and to allow the medical practitioner to practice without interruptions.
Novocain Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is used primarily to reduce the Pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin, and it is also used in dentistry. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainly as a sodium channel blocker. Today it is used therapeutically in some countries due to its sympatholytic, anti-inflammatory, perfusion-enhancing, and mood-enhancing effects.
Bio Safe Dentistry - Holistic Dentistry
Hypnosis Pain Killer (youtube) - Hypnosis and Dentistry
Pain Management
Sedation Dentistry refers to the use of pharmacological agents to calm and relax a patient prior to and during a dental appointment. The pharmacological agents usually belong to a class of drugs called sedatives, which exert their action by depressing the central nervous system, specifically those areas concerned with conscious awareness. There are different degrees of central nervous system depression, each corresponding to a level of relaxation which ranges from minimal, moderate, to deep sedation. In general, minimal sedation refers to a patient who has reduced anxiety but readily responds to verbal or physical stimulation. With moderate sedation the patient is even more relaxed, and will respond to purposeful stimulation. In deep sedation, the patient may not exhibit any signs of consciousness and therefore be unresponsive to stimulation. Sedation by pharmacologic methods may be obtained by two general routes. The enteral route involves absorption of medication across enteric membranes which line the alimentary canal from the oral cavity, through the digestive tract, ending in the rectum. This route includes medications that are either swallowed, absorbed through the mucosa of the oral cavity, or inserted rectally. The parenteral route involves the administration of sedative drugs other than absorption across enteric membranes (outside of the alimentary canal). These methods include intravenous, inhalation, intramuscular, and submucosal administration, among others.
Fraud by Dentists
Complaints against Dentists should be filed by anyone who believes that a licensee Dentist has engaged in illegal activities which are related to his/her professional responsibilities.
The corrupting force in dentistry is profitability. When a dentist puts profit before a patient’s needs, optimum care becomes all about funneling people towards extensive care such as Implants and Extreme Makeovers. Less profitable services will be neglected and the profitable ones promoted heavily.
Excessive treatment. Dentist over-treats a tooth or your entire mouth.
Supervised Neglect. Under-serves your needs, don’t receive enough care, you’ll gradually run into more problems.
Dental Malpractice Lawyer (ct)
Wisdom-Teeth Fraud
How to Avoid Bad Dentists
National Board Dental Examination (wiki)
Heath Care Fraud
Funny Video Clips about Dentists
Little Shop of Horrors - Dentist Song (youtube)
Little Shop of Horrors - Dentist Scene - w/ Bill Murray (Good Quality) (youtube)
Kids got a god damn Revolver (youtube)
Commission on Dental Accreditation. A “formal” complaint is defined as a complaint filed in written (or electronic) form and signed by the complainant. This complaint should outline the specific policy, procedure or standard in question and rationale for the complaint including specific documentation or examples. Complainants who submit complaints verbally will receive direction to submit a formal complaint to the Commission in written, signed form following guidelines in the Evaluation and Operational Policies and Procedures manual.
Tongue Warning Signs
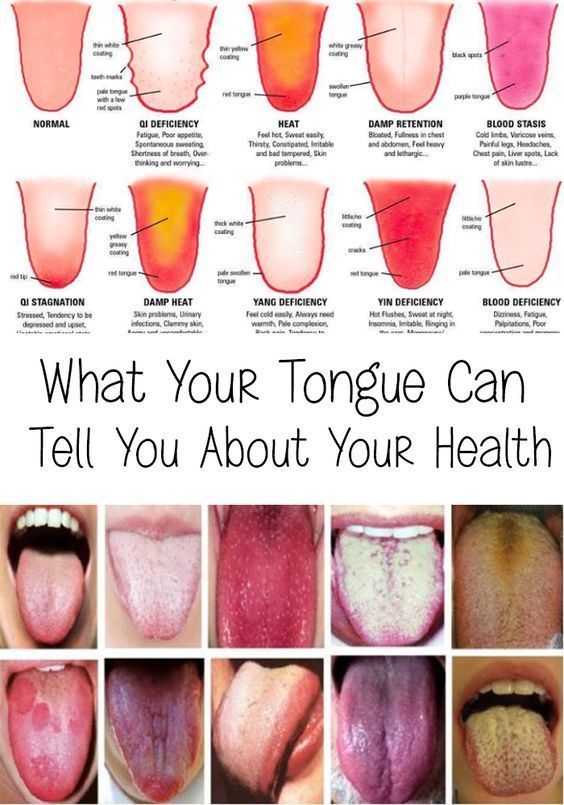 What Your Tongue Can Tell You About Your
Health. For clues about problems in your mouth, stick out your
tongue and look in the mirror. A healthy tongue should be pink and covered
with small nodules (papillae). Any deviation from your tongue's normal
appearance, or any pain, may be cause for concern.
Oral thrush – a yeast
infection that develops inside the mouth. It appears as white patches that
are often the consistency of cottage cheese. Leukoplakia – a condition in
which the cells in the mouth grow excessively, which leads to white
patches on the tongue and inside the mouth.
Oral lichen planus – a network
of raised white lines on your tongue that look similar to lace.
Vitamin
deficiency – “Folic acid and vitamin B-12 deficiencies may cause your
tongue to take on a reddish appearance.
Geographic tongue – This condition
causes a map-like pattern of reddish spots to develop on the surface of
your tongue.
Scarlet fever – an infection that causes the tongue to have a
strawberry-like (red and bumpy) appearance.
Kawasaki disease – a condition
that can also cause the tongue to have a strawberry-like appearance.
What Your Tongue Can Tell You About Your
Health. For clues about problems in your mouth, stick out your
tongue and look in the mirror. A healthy tongue should be pink and covered
with small nodules (papillae). Any deviation from your tongue's normal
appearance, or any pain, may be cause for concern.
Oral thrush – a yeast
infection that develops inside the mouth. It appears as white patches that
are often the consistency of cottage cheese. Leukoplakia – a condition in
which the cells in the mouth grow excessively, which leads to white
patches on the tongue and inside the mouth.
Oral lichen planus – a network
of raised white lines on your tongue that look similar to lace.
Vitamin
deficiency – “Folic acid and vitamin B-12 deficiencies may cause your
tongue to take on a reddish appearance.
Geographic tongue – This condition
causes a map-like pattern of reddish spots to develop on the surface of
your tongue.
Scarlet fever – an infection that causes the tongue to have a
strawberry-like (red and bumpy) appearance.
Kawasaki disease – a condition
that can also cause the tongue to have a strawberry-like appearance. Tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication and is used in the act of swallowing. It has importance in the digestive system and is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The four paired extrinsic muscles change the position of the tongue and are anchored to bone.
