BK101
Knowledge Base
Vitamins - Minerals - Supplements - Energy Bars
The word "Vitamin" means 'Vital to Life'
 Vitamin is an
organic compound and a vital
nutrient
that an organism requires in
limited amounts. An
organic chemical
compound
(or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot
synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained
through the diet; thus, the term "vitamin" is conditional upon the
circumstances and the particular organism. For example, ascorbic acid (one
form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal
organisms. Supplementation is important for the treatment of certain
health problems, but there could also be other factors involved when
determining the cause of a particular health problem, so please do your
research and get the advice of health professionals. Personalized Vitamins.
Vitamin is an
organic compound and a vital
nutrient
that an organism requires in
limited amounts. An
organic chemical
compound
(or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot
synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained
through the diet; thus, the term "vitamin" is conditional upon the
circumstances and the particular organism. For example, ascorbic acid (one
form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal
organisms. Supplementation is important for the treatment of certain
health problems, but there could also be other factors involved when
determining the cause of a particular health problem, so please do your
research and get the advice of health professionals. Personalized Vitamins.
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies
2.5 Million Kids Suffer Every Year from Vitamin Deficiencies - Malnourished - Food Security - Fortification - Testing.
The World Bank estimates that iron deficiency is a $50 billion drain on global GDP. Lucky Iron Fish are fish-shaped cast iron ingots used to provide dietary supplementation of iron to individuals living affected by iron-deficiency anaemia. The ingots are placed in a pot of boiling water to leach elemental iron into the water and food. Lucky Iron Fish.
Iron is required for life. Iron-containing proteins participate in transport, storage and use of oxygen. Iron proteins are involved in electron transfer.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when your body doesn't have enough iron to produce hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the part of red blood cells that gives blood its red color and enables the red blood cells to carry oxygenated blood throughout your body.
Iron Deficiency is the state in which a body has not enough (or not qualitatively enough) iron to supply its eventual needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key component of the hemoglobin protein, acting as a transport medium for electrons within the cells in the form of cytochromes, and facilitating oxygen enzyme reactions in various tissues. Too little iron can interfere with these vital functions and lead to morbidity and death. Total body iron averages approximately 3.8 g in men and 2.3 g in women. In blood plasma, iron is carried tightly bound to the protein transferrin. There are several mechanisms that control human iron metabolism and safeguard against iron deficiency. The main regulatory mechanism is situated in the gastrointestinal tract. When loss of iron is not sufficiently compensated by adequate intake of iron from the diet, a state of iron deficiency develops over time. When this state is uncorrected, it leads to iron deficiency anemia. Before anemia occurs, the medical condition of iron deficiency without anemia is called latent iron deficiency (LID) or Iron-deficient erythropoiesis (IDE). Untreated iron deficiency can lead to iron deficiency anemia, a common type of anemia. Anemia is a condition characterized by inadequate red blood cells (erythrocytes) or hemoglobin. Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body lacks sufficient amounts of iron, resulting in reduced production of the protein hemoglobin. Hemoglobin binds to oxygen, thus enabling red blood cells to supply oxygenated blood throughout the body. Children, pre-menopausal women (women of child-bearing age) and people with poor diet are most susceptible to the disease. Most cases of iron deficiency anemia are mild, but if not treated can cause problems like fast or irregular heartbeat, complications during pregnancy, and delayed growth in infants and children. Heavy Metals.
Zinc deficiency causes increased child mortality due to infectious diseases, because it prevents the immune system from working properly. Lack of iron increases the death rates of mothers and lowers the IQ of children.
Micronutrient Deficiency is a lack of one or more of the micronutrients required for plant or animal health. In humans and other animals they include both vitamin deficiencies and mineral deficiencies, whereas in plants the term refers to deficiencies of essential trace minerals.
Antinutrients - Malnutrition
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety of anaemias. Malabsorption syndrome occurs when something prevents the bowel from absorbing important nutrients and fluids, including proteins, fats, and vitamins. Malabsorption can be caused by conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, lactose intolerance, and intestinal damage. Risk factors include a family history of malabsorption or cystic fibrosis, excessive alcohol consumption, and travel to the Caribbean or Southeast Asia. Cooking Effects on Food Nutrients.
We Need More Vitamins as we Get Older.
Multivitamin, mineral supplement linked to less-severe, shorter-lasting illness symptoms. Older adults who took a daily multivitamin and mineral supplement with zinc and high amounts of vitamin C in a 12-week study experienced sickness for shorter periods and with less severe symptoms than counterparts in a control group receiving a placebo.
Personalized Diet - Vitamin Needs and Deficiency Testing
Have your Blood, Urine, Stool and DNA analyzed to determine your preferred food intake and the dosage that you need. Then after 1 month you do another full set of diagnostic tests to see if the diet is maximizing your physical energy and mental clarity, as well as producing all the necessary vital signs that signify good health. Eventually everyone will wear a device on their wrist that will measure their hydration levels, vitamin levels, blood sugar levels, ph, oxygen levels, protein levels, Triglyceride Levels and so on. This way they will know exactly what nutrition they need and when. And you will not have to wear the device all the time because you will learn from experience how much food and water you actually need each day.
Personalized Medicine - Nutrition Consulting - Calculate Nutrition Values
Nutrient Testing - Vitamin and Nutrition Lab Tests - Vitastiq
NASA to predict Vitamin Levels in Spaceflight Food and predict the degradation of vitamins in spaceflight food over time.
Epigenetics - Preventive Medicine - BMI
Cancer and Diet - Longevity Diet
Vitagene DNA Ancestry Test Kit can be used to help you create a fitness plan that's scientifically designed to work for you with customized meals and workouts that are optimized for your unique genetic makeup — just send in a cheek swab, and you're ready to go.
DNA will ultimately prove that Nutrition is a Science. We will be able to determine what Food Additives are poison and prove what are the exact amounts of the right foods that each individual person requires for maximum health and energy.
One X - The First Nutritional Biosensor for monitoring your skin antioxidants level.
Food Sensor (scan food to determine details of that food).
Custom Energy Bars - Make your own Energy Bars - Custom Nutrition Bars - Plumpy Nut (wiki) - Epic Bar - RX Bar.
 Individual Vitamins or Single Vitamin Supplements are better than
Multivitamins. Tailored Vitamins are Better than Multivitamins
because it's a better strategy to take just the vitamins a person needs
based on their age and diet. But remember that it's easy to overdose on
certain nutrients that can be toxic in large amounts.
Individual Vitamins or Single Vitamin Supplements are better than
Multivitamins. Tailored Vitamins are Better than Multivitamins
because it's a better strategy to take just the vitamins a person needs
based on their age and diet. But remember that it's easy to overdose on
certain nutrients that can be toxic in large amounts.When taking Vitamin Supplements you need to know the quality of the product. You need to know the amount of each vitamin and mineral that you need. You need to know the best time to take them. You need to know when not to combine them with other vitamins, minerals, foods or medications. You need to understand absorption rate and the difference between fat-soluble and water-soluble nutrients. You need to know when to take a break from vitamins and for how long.
Food Chemistry - Why Vitamins and Minerals Go Hand in Hand
I use to take only certain multi-vitamins that have a recommended dosage, or serving size, for taking several tablets a day. Then I only take one tablet a day even if they recommend 2 or more tablets a day. This way I’m only taking a low dosage of high quality vitamins. The vitamins will also last longer, which lowers the cost too. Some vitamins actually make me breakout. So I found these two Vitamins that work the best with no ill side effects when you take less the the recommended dosage. But now I take individual vitamins that are more tailor to my specific needs.
I use to take one tablet daily of GNC MEGA MEN Multivitamins
Nutrition Products (amazon) - Soy Nutrition - Get the Very First Caffeinated Bracelet
Do Multi-Vitamins make you Hungry? Does taking Vitamin Supplements increase Appetite? It does for me, but why? Here is one guess: Vitamin deficiencies that may cause loss of appetite. The following vitamin deficiencies may cause loss of appetite, along with numerous other symptoms. Vitamin B12 - Vitamin A - Vitamin B1 (thiamine) - Vitamin B6 - Biotin (rare and most commonly seen in infants).
You need to pay close attention to how you feel everyday, because if something that you're eating is giving you problems, you have to know when to stop eating that particular food, or stop taking that particular medicine or supplement. Do you notice any changes that may be an indicator that something is wrong physically or mentally? But knowing what exactly is making you feel discomfort is not that easy. You can stop one thing at a time if you can, but you may have to stop several things at once, which makes it harder to figure out the culprit, but it's not impossible.
Fortification
Fortification is the art or science of strengthening defenses with the addition of an ingredient for the purpose of enrichment.
Enrichment is the act of that significantly increases the value of something by making it more fuller or more meaningful or more rewarding.
Harvest Plus is breeding crops to increase their Nutritional Value. - Vertical Farming.
Bio-Fortification is the idea of breeding crops to increase their nutritional value. This can be done either through conventional selective breeding, or through genetic engineering. Biofortification differs from ordinary fortification because it focuses on making plant foods more nutritious as the plants are growing, rather than having nutrients added to the foods when they are being processed. This is an improvement on ordinary fortification when it comes to providing nutrients for the rural poor, who rarely have access to commercially fortified foods. As such, biofortification is seen as an upcoming strategy for dealing with deficiencies of micronutrients in the developing world. In the case of iron, WHO estimated that biofortification could help curing the 2 billion people suffering from iron deficiency-induced anemia. Research Programs.
Characterization of Selenium-Enriched Wheat by Agronomic Bio-Fortification
Food Fortification is the process of adding micronutrients (essential trace elements and vitamins) to food. Sometimes it's a purely commercial choice to provide extra nutrients in a food, while other times it is a public health policy which aims to reduce the number of people with dietary deficiencies within a population. Staple foods of a region can lack particular nutrients due to the soil of the region or from inherent inadequacy of a normal diet. Addition of micronutrients to staples and condiments can prevent large-scale deficiency diseases in these cases. Ideal Health - Elysiumhealth.
Soil Depletion - CO2 Decreasing Nutrients in Plants
The Secret behind Witchweed's devastating ability to Steal Nutrients from Crops. Hopes for developing a new method to control the parasitic Striga weed commonly known as 'witchweed,' the parasitic plant Striga hermonthica devastates crops in sub-Saharan Africa. Scientists have discovered a unique protein in Striga that helps sustain its high transpiration. Striga uses transpiration to effectively steal water and nutrients from its hosts, so this protein could provide a new target for controlling Striga.
Nutraceutical is a pharmaceutical-grade and standardized nutrient. Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that are purported to provide extra health benefits, pharmaceutical-grade nutritional supplements, or nutraceuticals, is a food containing health-giving additives and having medicinal benefit.
Functional Food are fortified or enriched during processing and then marketed as providing some benefit to consumers. Sometimes, additional complementary nutrients are added, such as vitamin D to milk. Functional food is a food given an additional function (often one related to health-promotion or disease prevention) by adding new ingredients or more of existing ingredients. The term may also apply to traits purposely bred into existing edible plants, such as purple or gold potatoes having enriched anthocyanin or carotenoid contents, respectively. Functional foods may be "designed to have physiological benefits and/or reduce the risk of chronic disease beyond basic nutritional functions, and may be similar in appearance to conventional food and consumed as part of a regular diet".
CGIAR is a global partnership that unites organizations engaged in research for a food secure future. CGIAR research is dedicated to reducing rural poverty, increasing food security, improving human health and nutrition, and ensuring sustainable management of natural resources.
 When and How Much?
When and How Much?
Dietary Reference Intake (wiki)
Recommended Allowances
Vitamins and Herbs - Nutrition Products (amazon)
Minerals is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms, other than carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur present in common organic molecules. The remaining elements are classed as minerals in the four groups of essential nutrients (the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids). The five major minerals in the human body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and magnesium. All of the remaining elements in a human body are called "trace elements". The trace elements that have a specific biochemical function in the human body are sulfur, iron, chlorine, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, iodine and selenium.
Minerals in Food - Dietary Minerals (wiki).
Dietary Supplement is intended to provide nutrients that may otherwise not be consumed in sufficient quantities. Supplements as generally understood include vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, or amino acids, among other substances. U.S. authorities define dietary supplements as foods, while elsewhere they may be classified as drugs or other products.
Dietary Element is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms, other than carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur present in common organic molecules. The remaining elements are classed as minerals in the four groups of essential nutrients (the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids).
Water-Soluble - Fat-Soluble - Dissolving Abilities
Soluble is something that is able to be dissolved.
Insoluble is something incapable of being dissolved. Insoluble can also mean that something is without hope of solution.
Solvent is a liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances. Solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid.
Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid or gaseous solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the physical and chemical properties of the solute and solvent as well as on temperature, pressure and presence of other chemicals (including changes to the pH) of the solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is measured as the saturation concentration, where adding more solute does not increase the concentration of the solution and begins to precipitate the excess amount of solute. Insolubility is the inability to dissolve in a solid, liquid or gaseous solvent. Most often, the solvent is a liquid, which can be a pure substance or a mixture. One may also speak of solid solution, but rarely of solution in a gas (see vapor–liquid equilibrium instead). Hydrophile.
Water-Soluble vitamins are easily dissolved in the body. The kidneys remove excess amounts of these vitamins so they can be excreted in the urine. Still, this doesn’t mean that you can take vitamins B and C in unlimited quantities.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins are absorbed in the lymph, transported in the blood, and can be stored in the liver and fatty tissues for use as needed. Fat-soluble vitamins are the ones you really need to be careful about. Because fat-soluble vitamins can be stored in the body, these vitamins can build up to toxic levels when consumed in excessive amounts. Fat-soluble vitamins are A, D, E, and K. Fat Soluble refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents.
Dissolve is to break up and become incorporated into a liquid so as to form a solution. To cause something to fade away or become soft, weaker or liquid and stop functioning or cohering as a unit.
Diffuse is to spread out and not be concentrated in one place. Dosage.
Dilute is to make a liquid thinner or weaker by adding water or another solvent to it. Dilution equation is the process of decreasing the concentration of a solute in a solution, usually simply by mixing with more solvent like adding more water to a solution. To dilute a solution means to add more solvent without the addition of more solute. The resulting solution is thoroughly mixed so as to ensure that all parts of the solution are identical.
Absorb is to become one with something. Take up mentally or take in something metaphorically. To devote oneself fully to a activity that consumes all of one's attention or time. To assimilate or take in.
Absorption is the process of absorbing nutrients into the body after digestion. A process in which one substance permeates, penetrates or pass through another liquid or solid.
Sublingual Vitamin means “beneath the tongue,” which is a way to take several vitamins and supplements where you simply place the tablet beneath the tongue and it dissolves and enters the bloodstream directly.
Solute is the dissolved matter in a solution; the component of a solution that changes its state.
Solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances like a liquid solution or other. Solution Problem Solving.
Vitamins can actually enhance the absorption of other nutrients. Vitamin C, for example, can enhance iron absorption from supplements and plant foods.
Synthetic Vitamins or Natural Vitamins?
Natural Vitamins contain the isolate vitamin (used solely in synthetic vitamins), but they also contain a host of naturally occurring cofactors that assist in the absorption and bioavailability of the vitamin, including proteins, carbs, fats, bioflavonoids, enzymes, other vitamins and minerals, etc. These cofactors must be present for a vitamin or mineral to be used by the body. For example, to make naturally occurring vitamins, such as vitamin C, a manufacturer could use amla berries, one of the best sources for vitamin C found in nature. A full-spectrum extract is made by removing the non-nutritive fiber. Then the berries are filtered with water, ground up, and dried at low temperatures to concentrate the nutrients and their cofactors. No high heat, freezing, or chemical techniques are used in this natural process. This process would be repeated for other vegetables, fruits, oils, and yeasts to make a full spectrum natural multivitamin. There is a new standard for natural supplements under development known as the Naturally Occurring Standard (NOS). Products that meet this standard will have a label of approval from NOS proving they are naturally occurring, organic, fairly traded, and free of genetically engineered ingredients, synthetics, and nanoparticles.
Synthetic Vitamins or isolated nutrients are usually made Artificially in an industrial process. 90% of Vitamins are Synthetic. Synthetic nutrients do not include whole food supplements, which are made from concentrated, dehydrated whole foods. The production process of synthetic nutrients is very different to the way plants and animals create them. So despite having a similar structure, your body may react differently to synthetic nutrients. It's unclear how well synthetic nutrients are absorbed and used in the body. Some may be more easily absorbed, not others. This is because when you eat real food, you're not consuming single nutrients, but rather a whole range of vitamins, minerals, co-factors and enzymes that allow for optimal use by the body. Without these additional compounds, synthetic nutrients are unlikely to be used by the body in the same way as their natural counterparts. For example, studies show that natural vitamin E is absorbed twice as efficiently as synthetic vitamin E. Bio-Similar - Generic.
So should you take a synthetic vitamin or a natural vitamin? That is up to you. Try them both at different times and do some research. Your body should let you know which one is good and which manufacture is good.
New Chapter cultured whole-food vitamins & minerals and cultured organic herbal blends. Supplements are created from plants, herbs, fruits, vegetables, oils, and mushrooms. We strive to use organic and sustainable ingredients. We also believe in a holistic approach, meaning we focus on the best way to capture the beneficial nourishing qualities of a food.
Vitamin Benefits - Vitamin Deficiency Symptoms
 A Vitamin Benefits helps
formation and maintenance of teeth, bones, soft tissue, white blood
cells, the immune system and mucus membranes. Beta-carotene also acts as
an antioxidant, protecting cells from free radical damage.
A
Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are Dry
skin. Dry Eyes.
Eye problems are some of the most well-known issues
Night Blindness. Infertility and Trouble Conceiving. Delayed Growth.
Throat and Chest Infections. Poor Wound Healing. Acne and Breakouts.
A Vitamin Benefits helps
formation and maintenance of teeth, bones, soft tissue, white blood
cells, the immune system and mucus membranes. Beta-carotene also acts as
an antioxidant, protecting cells from free radical damage.
A
Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are Dry
skin. Dry Eyes.
Eye problems are some of the most well-known issues
Night Blindness. Infertility and Trouble Conceiving. Delayed Growth.
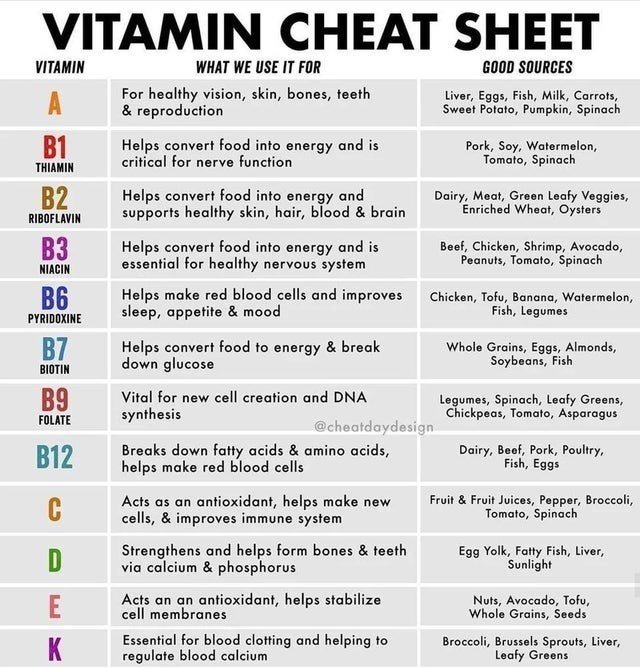
Throat and Chest Infections. Poor Wound Healing. Acne and Breakouts.B1 Vitamin or thiamin helps prevent complications in the nervous system, brain, muscles, heart, stomach, and intestines. It is also involved in the flow of electrolytes into and out of muscle and nerve cells. B1 Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are loss of Appetite. Fatigue. Fatigue may occur gradually or suddenly. Irritability. Irritability is the feeling of agitation and frustration. Reduced Reflexes. Tingling Sensation in Arms and Legs. Muscle Weakness. Blurry Vision. Nausea and Vomiting. B Complex Vitamins (wiki).
B2 Vitamin or Riboflavin, health benefits includes maintaining energy levels, protecting healthy skin and hair, promoting development and growth of reproductive organs, increased blood flow, prevent diseases, promoting healthy development of fetuses, protect the digestive tract, offers a powerful punch of antioxidants. B2 Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are dryness and cracking of the skin around the nose and mouth. Red, dry tongue – called magenta tongue. Skin rash. Anaemia. Weakness and fatigue. Vision problems - red, sore or watering eyes, blurred vision and sensitivity to light.
B3 Vitamin or Niacin, helps lowers LDL Cholesterol. Increases HDL Cholesterol. Lowers Triglycerides. May Help Prevent Heart Disease. May Help Treat Type 1 Diabetes. Boosts Brain Function. Improves skin Function. May Reduce Symptoms of Arthritis. B3 Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are thick, scaly pigmented rash on skin exposed to sunlight. Swollen mouth and bright red tongue. Vomiting and diarrhea. Headache. Apathy. Fatigue. Depression. Memory loss.
B5 or pantothenic acid can benefit arthritis, athletic performance, ADHD, skin problems, alcoholism, allergies, hair loss, asthma, heart problems, carpal tunnel syndrome, lung disorders, nerve damage, colitis, eyes. pantothenic-acid helps to create red blood cells. Create stress-related and sex hormones. Maintain a healthy digestive tract. Process other vitamins, particularly B2 (riboflavin). Synthesize cholesterol. B5 Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, may include symptoms such as fatigue, insomnia, depression, irritability, vomiting, stomach pains, burning feet, and upper respiratory infections.
B6 Vitamin helps support a healthier skin, detoxifying the liver, enhancing the health of blood vessels, improving cognitive function, relieving mood swings, curing anemia, supporting eye health, relieving the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. A coenzyme in many enzymatic reactions in metabolism. (pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine). B6 Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are Skin Rashes. Cracked and Sore Lips. Sore, Glossy Tongue. Mood Changes. Weakened Immune Function. Tiredness and Low Energy. Tingling and Pain in Hands and Feet. Seizures.
B7 Vitamin or Biotin can help strengthen hair and nails, improve the health of your skin. Supports your metabolism. Lowers cholesterol. B7 Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are red rashes on the skin, especially the face. Dry or scaly skin. Dry eyes. Brittle hair. Hair loss. Fatigue. Insomnia or difficulty sleeping. Loss of appetite. Biotin Deficiency (wiki).
B9 or Folate helps reduce Risk Of Heart Disease. Promotes Health And Function Of The Brain. Fosters Positive Mood And Can Prevent Depression. Has Anti-aging Properties. Promotes Health Pregnancy and Fetal Development. Reduces The Risk Of Cancer Development. Folate Promotes Liver Health. Help Manage Kidney Disease and Its Effects On The Body. Folate Vitamin Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are extreme tiredness (fatigue). Lack of energy (lethargy) Breathlessness. Feeling faint. Headaches. Pale skin. Noticeable heartbeats (palpitations). Less common symptoms of folate deficiency are fast heartbeat (tachycardia). Fast breathing (tachypnoea). Exfoliative dermatitis, a condition which makes the skin red and scaly. Heart murmur. Painful swallowing. A sore tongue (glossitis) and mouth ulcers. Petechiae. Angular stomatitis (fissures in the corners of the mouth).
B12 supports your metabolism by helping it convert fats, carbohydrates, and proteins into energy. Nerve and mental function. Cardiovascular health Benefits helps keep the body's nerve and blood cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all cells. Vitamin B12 also helps prevent a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia that makes people tired and weak. Two steps are required for the body to absorb vitamin B12 from food. B12 Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are weakness, tiredness, or lightheadedness. Heart palpitations and shortness of breath. Pale skin. A smooth tongue. Constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite, or gas. Nerve problems like numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, and problems walking. Vision loss. B vitamins tend to boost energy, so take them in the morning; at night, they can lead to restlessness and insomnia.
C Vitamin may include protection against immune system deficiencies, cardiovascular disease, prenatal health problems, eye disease, and even skin wrinkling. A strong antioxidant that may reduce the risk of chronic diseases. May also help battle High Blood Pressure. Fights Heart Disease Risk Factors, Potentially Lowering Heart Disease Risk. Could Reduce Blood Uric Acid Levels and Help Prevent Gout Attacks. Vitamin C Deficiency Signs and Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are Rough, Bumpy Skin. Corkscrew-Shaped Body Hair. Bright Red Hair Follicles. Spoon-Shaped Fingernails With Red Spots or Lines. Dry, Damaged Skin. Easy Bruising. Slowly Healing Wounds. Painful, Swollen Joints. Symptoms include fatigue, depression, and connective tissue defects (eg, gingivitis, petechiae, rash, internal bleeding, impaired wound healing).
D3 Vitamin helps facilitate normal immune system function. Regulating the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Normal growth and development of bones and teeth. D3 Deficiency symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are getting sick or Infected Often. Fatigue and Tiredness. Bone and Back Pain. Depression. Impaired Wound Healing. Bone Loss. Hair Loss. Muscle Pain. More Vitamin D may improve memory but too much may slow reaction time.
E Vitamin supplements may prevent coronary heart disease, support immune function, prevent inflammation, promote eye health, and lower the risk of cancer. Vitamin E helps support the immune system, cell function, and skin health. It's an antioxidant, making it effective at combating the effects of free radicals produced by the metabolism of food and toxins in the environment. Vitamin E may be beneficial at reducing UV damage to skin. Vitamin E Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are disorientation and vision problems. Low levels of vitamin E can lead to: Muscle weakness: Vitamin E is essential to the central nervous system. It is among the body's main antioxidants, and a deficiency results in oxidative stress , which can lead to muscle weakness. Abetalipoproteinemia is a rare inherited disorder of fat metabolism that results in poor absorption of dietary fat and vitamin E. The vitamin E deficiency associated with this disease causes problems such as poor transmission of nerve impulses and muscle.
K Vitamin has benefits blood clotting and bone health. Vitamin K also seems to play an important role in preventing heart disease. Vitamin K activates a protein that helps prevent calcium from depositing in your arteries. Vitamin K1, also called phylloquinone, is mostly found in plant foods like leafy green vegetables. It makes up about 75–90% of all vitamin K consumed by humans. Vitamin K2 is found in fermented foods and animal products, and is also produced by gut bacteria. It has several subtypes called menaquinones (MKs) that are named by the length of their side chain. They range from MK-4 to MK-13. Because of differences in absorption and transport to tissues throughout the body, vitamin K1 and K2 could have profoundly different effects on your health. Vitamin K1 found in plants is poorly absorbed by the body. One study estimated that less than 10% of the K1 found in plants is actually absorbed. Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins are much better absorbed when eaten with dietary fat. Additionally, vitamin K2’s long side chain allows it to circulate in the blood longer than K1. Where vitamin K1 may stay in the blood for several hours, some forms of K2 can remain in the blood for days. Some researchers believe that the longer circulation time of vitamin K2 allows it to be better used in tissues located throughout the body. Vitamin K1 is primarily transported to and used by the liver. Vitamin K Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are easy bruising. Oozing from nose or gums. Excessive Bleeding from wounds, punctures, and injection or surgical sites. Heavy menstrual periods. Bleeding from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Blood in the urine and/or stool. Symptoms of deficiency include excessive bleeding that won’t stop easily, though this could also be caused by other things and should be evaluated by a physician. It typically only occurs in people with severe malnutrition or malabsorption, and sometimes in people taking the medication warfarin. Vitamin K Deficiency (wiki). Warfarin thins your blood, so it's important to eat about the same amount of vitamin K every day. Vitamin K normally helps your blood clot so wounds don't bleed too much. Warfarin works against vitamin K, making your blood clot more slowly. Vitamin K2 or menaquinone is one of three types of vitamin K, the other two being vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and K3 (menadione). K2 is both a tissue and bacterial product (derived from vitamin K1 in both cases) and is usually found in animal products or fermented foods.
Iodine a trace mineral, is present in certain vegetables and seafood and is essential for normal thyroid functioning. It's often added to salt to prevent iodine deficiency. Iodine health benefits includes supporting healthy metabolism, maintaining energy level, supporting hair and skin health, supporting fetus development, providing stronger immunity and hypothyroidism prevention. Iodine Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, are swelling in the neck. Unexpected Weight Gain. Unexpected weight gain is another sign of an iodine deficiency. Fatigue and Weakness. Hair loss. Dry, Flaky Skin. Feeling Colder Than Usual. Changes in Heart Rate. Trouble Learning and Remembering.
Minerals
Note: Even though the information of vitamin benefits and deficiency problems are true and have been documented, it does not prove or guarantee that the benefits will happen to you, because food and medicine is mostly relevant to a particular person. If you experience deficiency problems, you must know that there may be other factors involved and that something else may be causing you to experience abnormal health functions or causing a life threatening illness. You have to do your own research and not be totally dependent on information that may be relative. To accurately know how relevant something is to you, you have to be examined and tested, and you also need to learn as much as you possibly can. Knowledge is the Best Medicine.
Vitamins - Minerals
 Everyone should be aware of what Vitamins and Minerals are needed for Optimum Health and Energy Level.
Everyone should be aware of what Vitamins and Minerals are needed for Optimum Health and Energy Level.
Custom Vitamins - Custom Vitamins
Personalized Multi-Vitamin - Caplet or Capsule?
Your energy level comes from multiple sources and knowing these sources and how they react with one another is very crucial. The three major sources are eating healthy, good sound sleep and exercising. Other sources that can effect your energy levels are environment, allergies, medication and chemical imbalances to name a few. The word " Vitamin " means ' vital to life' and it comes from the Latin word vita (life) and the biochemical term amine (nitrogen-containing) though not all vitamins contain nitrogen. Vitamins are organic compounds that assist enzymes in converting food into energy, support your immune system and provide structures for your bones, skin and other tissues. With a few exceptions the body cannot manufacture or synthesize vitamins. They must be supplied in the diet or in dietary supplements. And eating lots of foods does not necessarily mean that you will get all your necessary vitamins and Dietary Minerals. Also sometimes vitamins can increase your Metabolism, which can affect your appetite, but not everyone has the same affect from vitamins. In order to fully optimize your vitamin and mineral needs you need to have blood and urine samples analyzed for your bodies exact vitamin and mineral usage. This is because everyone has different needs and also has different reactions to certain vitamins and minerals. Some people might need more of certain vitamins and minerals and some might need less of certain vitamins and minerals. Some vitamins and minerals might even be no good for you depending on your body’s sensitivity or allergic reaction. So Doctors must increase their training and knowledge about Nutrition and also know how to do a complete Blood Test in order to analyze a persons correct nutritional needs and also to see if there is any food allergies or adverse effects from certain vitamins, minerals, herbs or drugs.
Know which vitamins that should be taken together for maximum effect. Know which supplements that should not be taken together. Food Chemistry.
Organic Molecules in Biochemistry, Vitamins and Cofactors
Vitamin Benefits Chart (image) - Vitamin and Mineral Knowledge
Blood Type Diet are distinct diets for each blood type that is unsupported by scientific evidence.
Blood is a body fluid in humans and other animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Doppler Ultrasound gives doctors a way to see what’s going on inside your body without X-rays or injections. Instead, it turns sound waves into images. Your doctor can use it to check for issues with blood flow, such as clots in your veins or blockages in your arteries.
Antioxidants - Free Radicals
Antioxidant is a molecule that inhibits the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals, leading to chain reactions that may damage cells. Antioxidants such as thiols or ascorbic acid (vitamin C) terminate these chain reactions. The term "antioxidant" is mainly used for two different groups of substances: industrial chemicals which are added to products to prevent oxidation, and natural chemicals found in foods and body tissue which are said to have beneficial health effects. Antioxidants such as vitamin C could help reduce harmful effects from hexavalent chromium.
Free Radicals are atoms or groups of atoms with an odd unpaired number of electrons that can be formed when oxygen interacts with certain molecules. Once formed these highly reactive radicals can start a chain reaction, like dominoes. Unpaired electrons can cause damage to Cells, Proteins and even DNA as these highly reactive atoms travel through the body seeking to pair up with other electrons. When we oxidize our food to produce energy there's a number of free radicals that are produced that are side products of that action and many of these are quite toxic. Free radicals may be formed through natural human physiological processes as well as from the environment. They may be the result of diet, stress, smoking, alcohol, exercise, inflammation, drugs or exposure to sunlight and air pollutants. While there are many types of free radicals that can be formed, the most common in aerobic (oxygen breathing) organisms are oxygen free radicals, often referred to as Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), which include superoxides, hydroxyl anions, hydrogen peroxide and singlet oxygen.
Oxidative Stress is essentially an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the ability of the body to counteract or detoxify their harmful effects through neutralization by antioxidants. Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated, e.g. O2− (superoxide radical), OH (hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling. In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of ADHD, cancer, Parkinson's disease, Lafora disease, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, heart failure, myocardial infarction, fragile X syndrome, sickle-cell disease, lichen planus, vitiligo, autism, infection, chronic fatigue syndrome, and depression and seems to be characteristic of individuals with Asperger syndrome. However, reactive oxygen species can be beneficial, as they are used by the immune system as a way to attack and kill pathogens. Short-term oxidative stress may also be important in prevention of aging by induction of a process named mitohormesis. Oxygen - Ph.
Superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide anion with the chemical formula O−2. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen anion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature. Whereas molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, the addition of a second electron fills one of its two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism.
Amidogen is a radical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH2. A member of the amino group, it may be regarded as an ammonia (NH3) molecule which has had one of its hydrogen atoms removed. NH2 as a functional group is common in nature, as it forms part of many compounds, e.g. the phenethylamines. The free radical is present in solutions of ammonia because, like water, ammonia undergoes molecular autoionisation to form its acid and base conjugates.
Phytochemical are chemical compounds produced by plants, generally to help them thrive or thwart competitors, predators, or pathogens.
Omega Fatty Acids - Brain Food - Blending - Juicing - Natural Plants - Micro-Greens
Diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, that is, the increased production of Urine. Dehydration.
Nutraceutical is a pharmaceutical-grade and standardized nutrient.
Can combined Exercise and Nutritional intervention improve Muscle Mass and Function?
Smart Antioxidant-Containing Polymer responds to Body Chemistry, Environment. Oxidants found within living organisms are byproducts of metabolism and are essential to wound-healing and immunity. However, when their concentrations become too high, inflammation and tissue damage can occur. Engineers have now developed and tested a new drug-delivery system that senses high oxidant levels and responds by administering just the right amount of antioxidant to restore this delicate balance.
Phenols
Phenols are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
Polyphenol are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments. Polyphenols are a structural class of mainly natural, but also synthetic or semisynthetic, organic chemicals characterized by the presence of large multiples of phenol structural units. The number and characteristics of these phenol structures underlie the unique physical, chemical, and biological (metabolic, toxic, therapeutic, etc.) properties of particular members of the class. Examples include tannic acid. The historically important chemical class of tannins is a subset of the polyphenols. The name derives from the Ancient Greek word πολύς (polus, meaning "many, much") and the word phenol which refers to a chemical structure formed by attaching to an aromatic benzenoid (phenyl) ring, an hydroxyl (-OH) group akin to that found in alcohols (hence the -ol suffix). The term polyphenol appears to have been in use since 1894. Both natural phenols and the larger polyphenols play important roles in the ecology of most plants. Their effects in plant tissues can be divided into the following categories: Release and suppression of growth hormones such as auxin. UV screens to protect against ionizing radiation and to provide coloration (plant pigments). Deterrence of herbivores (sensory properties). Prevention of microbial infections (phytoalexins). Signaling molecules in ripening and other growth processes. The most abundant polyphenols are the condensed tannins, found in virtually all families of plants. Larger polyphenols are often concentrated in leaf tissue, the epidermis, bark layers, flowers and fruits but also play important roles in the decomposition of forest litter, and nutrient cycles in forest ecology. Generally foods contain complex mixtures of polyphenols. The most important food sources are commodities widely consumed in large quantities such as fruit and vegetables, green tea, black tea, red wine, coffee, chocolate, olives, and extra virgin olive oil. Herbs and spices, nuts and algae are also potentially significant for supplying certain polyphenols. Some polyphenols are specific to particular food (flavanones in citrus fruit, isoflavones in soya, phloridzin in apples); whereas others, such as quercetin, are found in all plant products such as fruit, vegetables, cereals, leguminous plants, tea, and wine. Some polyphenols are considered antinutrients, compounds that interfere with the absorption of essential nutrients, especially iron and other metal ions, but also by binding to digestive enzymes and other proteins, particularly in ruminants. Phenolic and carotenoid compounds with antioxidant properties in vegetables have been found to be retained significantly better through steaming than through frying. Polyphenols in wine, beer and various nonalcoholic juice beverages can be removed using finings, substances that are usually added at or near the completion of the processing of brewing. Many polyphenolic extracts, such as from grape skin, grape seeds, olive pulp or maritime pine bark, are sold as ingredients in functional foods, dietary supplements, and cosmetics without proof of effect or legal health claims. Some polyphenol ingredients have self-affirmed GRAS status in the United States. There are no recommended Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) levels established for polyphenols. The diverse structures and uncertain metabolic fate of phenolic compounds following digestion prevent understanding about their potential health effects. Specifically, because the presumed antioxidant role of polyphenols in vivo cannot be established, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued labeling guidance to manufacturers that polyphenols cannot be mentioned as antioxidant nutrients unless physiological evidence exists to verify such a qualification and a DRI value has been established. Further, because purported health claims for specific polyphenol-enriched foods remain unproven, health statements about polyphenols on product labels are prohibited by the FDA. Compared with the effects of polyphenols in vitro, the possible functions in vivo remain unknown due to 1) the absence of validated in vivo biomarkers; 2) long-term studies failing to demonstrate effects with a mechanism of action, sensitivity and specificity or efficacy; and 3) invalid applications of high, unphysiological test concentrations in the in vitro studies, which are subsequently irrelevant for the design of in vivo experiments. Traditional medicine. Herbal teas contain soluble polyphenols which impart astringent effects thought to have medicinal properties. In the Ayurveda system of folk medicine, the pomegranate and its polyphenol-rich peel are assumed to be useful for therapy. With respect to food and beverages, the cause of astringency is not fully understood, but it is measured chemically as the ability of a substance to precipitate proteins. Longevity.
Wine polyphenols could fend off bacteria that cause cavities and gum disease. Health benefits of polyphenols have been attributed to the fact that these compounds are antioxidants, meaning they likely protect the body from harm caused by free radicals. However, recent work indicates polyphenols might also promote health by actively interacting with bacteria in the gut. That makes sense because plants and fruits produce polyphenols to ward off infection by harmful bacteria and other pathogens. two wine polyphenols in isolation -- caffeic and p-coumaric acids -- were generally better than the total wine extracts at cutting back on the bacteria's ability to stick to the cells. When combined with the Streptococcus dentisani, which is believed to be an oral probiotic, the polyphenols were even better at fending off the pathogenic bacteria. The researchers also showed that metabolites formed when digestion of the polyphenols begins in the mouth might be responsible for some of these effects.
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. A hydroxide attached to a strongly electropositive center may itself ionize, liberating a hydrogen cation (H+), making the parent compound an acid. The corresponding electrically neutral compound •HO is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently-bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxyl group. Hydroxide ion and hydroxyl group are nucleophiles and can act as a catalyst in organic chemistry. Many inorganic substances which bear the word "hydroxide" in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxyl groups.
Lectin
Lectin are carbohydrate-binding proteins, macromolecules that are highly specific for sugar moieties. Lectins perform recognition on the cellular and molecular level and play numerous roles in biological recognition phenomena involving cells, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lectins also mediate attachment and binding of bacteria and viruses to their intended targets. Lectins are ubiquitous in nature and are found in many foods. Some foods such as beans and grains need to be cooked or fermented to reduce lectin content, but the lectins consumed in a typical balanced diet are not harmful. Some lectins are beneficial, such as CLEC11A which promotes bone growth, while others may be powerful toxins such as ricin. Lectins may be disabled by specific mono- and oligosaccharides, which bind to ingested lectins from grains, legume, nightshade plants and dairy; binding can prevent their attachment to the carbohydrates within the cell membrane. The selectivity of lectins means that they are very useful for analyzing blood type, and they are also used in some genetically engineered crops to transfer traits, such as resistance to pests and resistance to herbicides. Lectins serve many different biological functions in animals, from the regulation of cell adhesion to glycoprotein synthesis and the control of protein levels in the blood. They also may bind soluble extracellular and intercellular glycoproteins. Some lectins are found on the surface of mammalian liver cells that specifically recognize galactose residues. It is believed that these cell-surface receptors are responsible for the removal of certain glycoproteins from the circulatory system. Another lectin is a receptor that recognizes hydrolytic enzymes containing mannose-6-phosphate, and targets these proteins for delivery to the lysosomes. I-cell disease is one type of defect in this particular system. Lectins also are known to play important roles in the immune system. Within the innate immune system lectins such as the MBL, the mannose-binding lectin, help mediate the first-line defense against invading microorganisms. Other lectins within the immune system are thought to play a role in self-nonself discrimination and they likely modulate inflammatory and autoreactive processes. Intelectins (X-type lectins) were shown to bind microbial glycans and may function in the innate immune system as well. Lectins are ubiquitous in nature and all foods – plant and animal – contain some type of the proteins. Because some lectins can be harmful if poorly cooked or consumed in great quantities, or when absorbed into the bloodstream by individuals with ‘leaky gut syndrome’, reduced-lectin diets have been proposed. Since lectins are present to some degree in all plant and animal foods, a lectin-free diet is impossible. Individuals eliminating any food groups need to be deliberate about consuming adequate nutrients, and may also require dietary supplementation to maintain health.
List of Life-Supporting Minerals with illustrative Biological Functions
Sodium: nerve function, osmotic pressure balance, and charge stability of cell. Vitamin Benefits.
Potassium: nerve function, osmotic pressure balance, and charge stability of cell.
Magnesium: plant photosynthesis, structure stabilizer. Micronutrients are cofactors for enzymes. 300 enzymes require Magnesium (350 mg a day). ATP.
Manganese: activator of certain enzymes, plant photosynthesis Iron: oxygen transport and storage, electron transport catalyst.
Calcium: skeletal structure forming (teeth, bones), control signal trigger.
Vanadium: catalyst for oxygen reactions, possibly involved in oxygen transport.
Chromium is a mineral that is required by the body in small amounts. As it forms a part of a compound in the body known as Glucose Tolerance Factor (GTF). Chromium is essential for metabolic processes that regulate blood sugar, and helps insulin transport glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy. Chromium Deficiency (wiki) - Chromium Toxicity (wiki).
Cobalt: cell division, a constituent of vitamin B12.
Nickel: hydrogen activation, catalytic protection from toxic superoxide.
Copper: respiratory chain electron transport catalyst, catalytic protection from toxic superoxide.
Zinc: super acid catalyst, enzyme activator, blood pH control.
Molybdenum: nitrogen fixation in plants, oxygen atom transfer catalyst.
Tungsten: oxygen atom transfer catalyst.
Iron: transport, storage and use of oxygen and electron transfer.
Selenium is important for reproduction, thyroid gland function, DNA production, and protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals and from infection. Selenium acts as a Powerful Antioxidant. May Reduce the Risk of Certain Cancers. May Protect Against Heart Disease. Helps Prevent Mental Decline. Is Important for Thyroid Health. Boosts the Immune System. May Help Reduce Asthma Symptoms. Selenium is an essential micronutrient. Antioxidants like selenium help reduce oxidative stress by keeping free radical numbers in check and helps defend the body from chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. Selenium: the biological role and antioxidant activity. Selenium Side Effects, but not necessarily the cause, may be nausea, vomiting; lack of energy, feeling irritable or very tired. hair loss, mild rash, brittle or painful fingernails, or white streaks on the nails; tremors, feeling light-headed; muscle tenderness; flushing (warmth, redness, or tingly feeling);metallic taste, bad breath, strong body odor; Selenium Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, may experience fatigue, hair loss, weight gain, joint and muscle pain. Signs that indicate problems like Kashin-Beck disease or Keshen disease may also develop. Arsenic.
Choline and other vitamins, such as B12 and folate, helps with a process that's important for DNA synthesis. Helps to maintain a healthy nervous system. This nutrient is required to make acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter. Choline Deficiency Symptoms, but not necessarily the cause, may result in fat and cholesterol buildup in your liver Inadequate Choline intake can also lead to fatty liver or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The most common symptoms of choline deficiency are fatty liver and/or hemorrhagic kidney necrosis. Consuming choline rich foods usually relieve these deficiency.
Trace Element is a chemical element whose concentration is very low, or a measured detectable amount of an element that is low. The exact definition depends on the field of science.
Elements Chart - Vitals
Customized Diets
Emergency Food
Meal Replacement Powder
Energy Drink for Workouts
GNC Puredge (amazon)
Soylent
You need larger amounts of macro-minerals or major minerals. They include calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride and sulfur. You only need small amounts of trace minerals. They include iron, manganese, copper, iodine, zinc, cobalt, fluoride and selenium.
Heavy Metals can have a Toxic Buildup when Over Consumed
Metal Toxicity or metal poisoning is the toxic effect of certain metals in certain forms and doses on life. Some metals are toxic when they form poisonous soluble compounds. Certain metals have no biological role, i.e. are not essential minerals, or are toxic when in a certain form. In the case of lead, any measurable amount may have negative health effects. Often heavy metals are thought as synonymous, but lighter metals may also be toxic in certain circumstances, such as beryllium and lithium. Not all heavy metals are particularly toxic, and some are essential, such as iron. The definition may also include trace elements when in abnormally high doses may be toxic. An option for treatment of metal poisoning may be chelation therapy, which is a technique which involves the administration of chelation agents to remove metals from the body. Toxic metals sometimes imitate the action of an essential element in the body, interfering with the metabolic process resulting in illness. Many metals, particularly heavy metals are toxic, but some heavy metals are essential, and some, such as bismuth, have a low toxicity. Most often the definition of toxic metals includes at least cadmium, manganese, lead, mercury and the radioactive metals. Metalloids (arsenic, polonium) may be included in the definition. Radioactive metals have both radiological toxicity and chemical toxicity. Metals in an oxidation state abnormal to the body may also become toxic: chromium(III) is an essential trace element, but chromium(VI) is a carcinogen. Toxicity is a function of solubility. Insoluble compounds as well as the metallic forms often exhibit negligible toxicity. The toxicity of any metal depends on its ligands. In some cases, organometallic forms, such as methylmercury and tetraethyl lead, can be extremely toxic. In other cases, organometallic derivatives are less toxic such as the cobaltocenium cation. Decontamination for toxic metals is different from organic toxins: because toxic metals are elements, they cannot be destroyed. Toxic metals may be made insoluble or collected, possibly by the aid of chelating agents, or through Bioremediation. Alternatively, they can be diluted into a sufficiently large reservoir, such as the sea, because immediate toxicity is a function of concentration rather than amount. Toxic metals can Bioaccumulate in the body and in the food chain. Therefore, a common characteristic of toxic metals is the chronic nature of their toxicity. This is particularly notable with radioactive heavy metals such as radium, which imitates calcium to the point of being incorporated into human bone, although similar health implications are found in lead or mercury poisoning. The exceptions to this are barium and aluminium, which can be removed efficiently by the kidneys.
Body Burden - Food Additives - Hormones - Toxins
Arsenic and Lead Are in Your Fruit Juice: What You Need to Know. CR finds concerning levels of heavy metals in almost half of tested juices. Here’s how to protect yourself and your family, including juices marketed for children. “In some cases, drinking just 4 ounces a day—or half a cup—is enough to raise concern, ”test focused on cadmium, lead, mercury, and inorganic arsenic risk for Lowered IQ, behavioral problems (such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), type 2 diabetes, and cancer, among other health issues. Twenty-four national, store, and private-label brands were represented: 365 Everyday Value (Whole Foods), Apple & Eve, Big Win (Rite Aid), Capri Sun, Clover Valley (Dollar General), Great Value (Walmart), Gerber, Good2Grow, Gold Emblem (CVS), Goya, Honest Kids, Juicy Juice, Looza, Market Pantry (Target), Minute Maid, Mott’s, Nature’s Own, Ocean Spray, Old Orchard, R.W. Knudsen, Simply Balanced (Target), Trader Joe’s, Tree Top, and Welch’s. Selenium.
Aluminium phosphide poisoning. Aluminum has no known biological role and its classification into toxic metals is controversial. Acute aluminium phosphide poisoning (AAlPP) is a large, though under-reported, problem in the Indian subcontinent. Aluminium phosphide (AlP), which is readily available as a fumigant for stored cereal grains, sold under various brand names such as QuickPhos and Celphos, is highly toxic, especially when consumed from a freshly opened container. Death results from profound shock, myocarditis and multi-organ failure. Aluminium phosphide has a fatal dose of between 0.15 and 0.5 grams (0.0053 and 0.0176 oz). It has been reported to be the most common cause of suicidal death in North India. The very high toxicity of aluminium phosphide is attributed to the phosphine content and is not related to aluminium. Calcium phosphide and zinc phosphide are similar poisons.
Arsenic Poisoning is a medical condition caused by elevated levels of arsenic in the body. The dominant basis of arsenic poisoning is from ground water that naturally contains high concentrations of arsenic. A 2007 study found that over 137 million people in more than 70 countries are probably affected by arsenic poisoning from drinking water. Arsenic (consumer reports). AS3MT Arsenite Methyltransferase (Arsenic Antidote Hidden In Our Genes). Arsenic is a chemical element with symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form is important to industry.
Beryllium poisoning is illness resulting from the toxic effect of Beryllium in its elemental form or in various chemical compounds. The toxicity of beryllium depends upon the duration, intensity and frequency of exposure (features of dose), as well as the form of beryllium and the route of exposure (i.e. inhalation, dermal, ingestion). According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), beryllium and beryllium compounds are Category 1 carcinogens; they are carcinogenic to both animals and humans.
Cadmium poisoning. Cadmium is an extremely toxic metal commonly found in industrial workplaces. Due to its low permissible exposure limit, overexposures may occur even in situations where trace quantities of cadmium are found. Cadmium is used extensively in electroplating, although the nature of the operation does not generally lead to overexposures. Cadmium is also found in some industrial paints and may represent a hazard when sprayed. Operations involving removal of cadmium paints by scraping or blasting may pose a significant hazard. Cadmium is also present in the manufacturing of some types of batteries. Exposures to cadmium are addressed in specific standards for the general industry, shipyard employment, construction industry, and the agricultural industry.
Copper toxicity also called copperiedus, refers to the consequences of an excess of copper in the body. Copperiedus can occur from eating acid foods cooked in uncoated copper cookware, or from exposure to excess copper in drinking water, as a side-effect of estrogen birth control pills, or other environmental sources. It can also result from the genetic condition Wilson's disease. Metal Working.
Iron poisoning is an Iron overload caused by a large excess of iron intake and usually refers to an acute overload rather than a gradual one. The term has been primarily associated with young children who consumed large quantities of iron supplement pills, which resemble sweets and are widely used, including by pregnant women—see overnutrition (approximately 3 grams is lethal for a 2 year old). Targeted packaging restrictions in the US for supplement containers with over 250 mg elemental iron have existed since 1978, and recommendations for unit packaging have reduced the several iron poisoning fatalities per year to almost nil since 1998. No known cases of iron poisoning have been identified that are associated with iron mining.
Lead poisoning is a medical condition in humans and other vertebrates caused by increased levels of the heavy metal lead in the body. Lead interferes with a variety of body processes and is toxic to many organs and tissues including the heart, bones, intestines, kidneys, and reproductive and nervous systems. It interferes with the development of the nervous system and is therefore particularly toxic to children, causing potentially permanent learning and behavior disorders. Symptoms include abdominal pain, confusion, headache, anemia, irritability, and in severe cases seizures, coma, and death. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include memory problems, inability to have children, and tingling in the hands and feet. It causes almost 10% of intellectual disability of otherwise unknown cause and can result in behavioral problems. Some of the effects are permanent. In severe cases anemia, seizures, coma, or death may occur. Water.
Lithium poisoning. Lithium is used in some medications, specifically to treat bipolar disorder. The level of "sufficient" medication is thought by many physicians to be close to toxic tolerance for kidney function. Therefore, the patient is often monitored for this purpose.
Manganism or manganese poisoning is a toxic condition resulting from chronic exposure to Manganese and first identified in 1837 by James Couper.
Mercury poisoning is a disease caused by exposure to Mercury or its compounds. Mercury (chemical symbol Hg) is a heavy metal occurring in several forms, all of which can produce toxic effects in high enough doses. Its zero oxidation state Hg0 exists as vapor or as liquid metal, its mercurous state Hg22+ exists as inorganic salts, and its mercuric state Hg2+ may form either inorganic salts or organomercury compounds; the three groups vary in effects. Toxic effects include damage to the brain, kidney, and lungs. Mercury poisoning can result in several diseases, including acrodynia (pink disease), Hunter-Russell syndrome, and Minamata disease. Symptoms typically include sensory impairment (vision, hearing, speech), disturbed sensation and a lack of coordination. The type and degree of symptoms exhibited depend upon the individual toxin, the dose, and the method and duration of exposure.
Silver poisoning or Argyria or argyrosis is a condition caused by inappropriate exposure to chemical compounds of the element Silver, or to silver dust. The most dramatic symptom of argyria is that the skin turns blue or bluish-grey. It may take the form of generalized argyria or local argyria. Generalized argyria affects large areas over much of the visible surface of the body. Local argyria shows in limited regions of the body, such as patches of skin, parts of the mucous membrane or the conjunctiva. Precious Metals (rare earth).
Thallium poisoning. Thallium and its compounds are often highly toxic.Contact with skin is dangerous, and adequate ventilation should be provided when melting this metal. Many thallium(I) compounds are highly soluble in water and are readily absorbed through the skin.[citation needed] Exposure to them should not exceed 0.1 mg per m2 of skin in an 8-hour time-weighted average (40-hour work week). Thallium is a suspected human carcinogen.
Tin poisoning refers to the toxic effects of Tin and its compounds. Cases of poisoning from tin metal, its oxides, and its salts are "almost unknown"; on the other hand certain organotin compounds are almost as toxic as cyanide.
Zinc toxicity. Even though Zinc is an essential requirement for a healthy body, excess zinc can be harmful, and cause zinc toxicity. Such toxicity levels have been seen to occur at ingestion of greater than 225 mg of Zinc. Excessive absorption of zinc can suppress copper and iron absorption. The free zinc ion in solution is highly toxic to bacteria, plants, invertebrates, and even vertebrate fish.
Hexavalent Chromium is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the salt sodium dichromate. Hexavalent chromium compounds are genotoxic carcinogens.
Metallome - Metabolomics - Metabolite
Vitamins Vaporizer - Vitastik
Glutamine is an a-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. Glutamine is an amino acid (a building block for proteins), found naturally in the body. Glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid in the body. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Glutamine is produced in the muscles and is distributed by the blood to the organs that need it. Glutamine might help gut function, the immune system, and other essential processes in the body, especially in times of stress. It is also important for providing "fuel" (nitrogen and carbon) to many different cells in the body. Glutamine is needed to make other chemicals in the body such as other amino acids and glucose (sugar). After surgery or traumatic injury, nitrogen is necessary to repair the wounds and keep the vital organs functioning. About one third of this nitrogen comes from glutamine. New research is now showing that L-glutamine benefits the body in the following ways: Improves gastrointestinal health, Helps leaky gut and ulcers, Boosts brain health, Improves IBS and diarrhea, Promotes muscle growth and decreases muscle wasting, Improves athletic performance and recovery from endurance exercise. L-glutamine is synthesized by the body from glutamic acid or glutamate. If the body is unable to produce enough it needs to get it directly from your diet. L-glutamine can be found in animal proteins such as meats and dairy, along with plant-based protein sources such as beans, raw spinach, parsley and red cabbage. It’s worth noting, though, that animal proteins are not as easily digestible as plant proteins. The foods with the most L-glutamine benefits include: Bone broth, Grass-fed beef, Spirulina, Chinese cabbage, Cottage cheese, Asparagus, Broccoli rabe, Wild-caught fish (cod and salmon), Venison, Turkey.
As we Age our Vitamins and Mineral needs changes as we get Older
Certain Vitamins are harder to absorb by the body when you get older. One in two persons aged 65 and above has suboptimal levels of vitamin D in the blood and one in four older adults has suboptimal vitamin B12 levels. Vitamin Deficiency in Later Life.
Your body needs more of certain vitamins and minerals as you hit your 40s and beyond. Nutrients that become especially important as you age include protein, vitamin D, calcium and vitamin B12. Summary: Older adults generally need fewer calories. However, their nutrient needs are just as high or higher than when they were younger. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics says older adults should pay special attention to their intake of calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B-12, potassium, and fiber.
Vitamin D. This nutrient, made by the body from sunshine, helps you take in calcium and phosphorus, so it’s key for healthy bones and teeth. Older adults don’t make it as well, so supplements can help make you less likely to have bone loss and broken bones. Higher dosages of vitamin D (because dietary consumption and sun exposure decline with age) and vitamin B12 (which is not as well absorbed in older people). They also often exclude iron, because many older adults do not need extra amounts and high levels may be harmful. Personalized Vitamins.
Calcium. Plays in making your bones stronger, calcium is found in dairy products like milk and yogurt. Women -- especially those who are likely to have osteoporosis -- may think about taking calcium supplements. But talk to your doctor first.
Vitamin B12. This is important for keeping blood cells and nerve cells healthy. Aging affects how well you take in and use B12 from foods, so if you’re over 50, it’s probably best to get your B12 from supplements and B12-fortified foods like cereals, as well as foods that are rich in it, like meat, low-fat dairy, and fish. Vitamin B12 Once you turn 40 (and definitely after turning 50), vitamin B12 should be on your radar. It's essential for normal blood and brain function, Kirkpatrick says. And while children and younger adults are likely to get the B12 they need from food—it's in meat and animal products including chicken, fish, dairy, and eggs—B12 is more poorly absorbed as the body ages, typically starting around 50 because that's when stomach acid levels deplete.
Folate. This helps prevent anemia. Spinach, beans, peas, oranges, fortified cereals, and enriched breads can have it.
B6. This helps your metabolism and immune system. You can get it in fortified cereals and soy products, as well as organ meats and whole grains.
Vitamin C. Oranges, right? (And red and green bell peppers, along with other vegetables and fruits.) It may help protect you from cataracts, help wound healing, and possibly lower your odds of having certain kinds of cancer.
Magnesium. Among other things, it helps keep your blood pressure and blood sugar levels steady. It’s also good for your bones. You can get it from nuts, spinach, and dairy products, and it’s used to fortify some breakfast cereals. Experts aren’t sure how well it works as a supplement. Minerals.
Probiotics. Gut health is also very important for your immune system. Some studies show that probiotics -- living organisms like those found in yogurt -- help prevent some types of diarrhea and ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.
Coenzyme Q10. Also called coQ10, this is made naturally in your body and found in most body tissues. It may help your immune system work better.
Melatonin. A hormone released mostly at night, it’s believed to help you fall asleep.
Fish oil. The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings a week of salmon and other types of fish with omega-3 fatty acids. In supplement form, though, no studies have shown that it protects against heart disease. Omega-3s also may help with symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Omega-3s. Technically not a vitamin, omega-3 fatty acids still deserve a place on this list because of their myriad health benefits—and especially because they help counteract some of the negative changes that come with aging, like increased heart disease risk and cognitive decline. Research has shown that omega-3s help lower blood pressure and LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and play a role in keeping memory and thinking sharp. In fact, a recent study found that people with higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids in their blood had larger brains and performed better on memory tests, planning activities, and abstract thinking, compared with individuals with lower levels—which suggests that omega-3 fatty acids play a role in maintaining brain health in addition to the other known benefits. Though you can get omega-3s from foods like fish, walnuts, flaxseeds, and leafy vegetables, taking a supplement is a good way to make sure you're getting enough. Either way, aim for 500 mg if you're healthy, 800 to 1,000 mg if you have heart disease, and 2,000 to 4,000 mg if you have high triglyceride levels. And be sure to ask your doctor about the right dose if you're taking anticoagulant drugs, which can have serious side effects.
Potassium plays a key role in keeping blood pressure in check, no matter your age. In postmenopausal women, research has linked higher intake of potassium from food to decreased risk of stroke—though "high" intake was considered approximately 3.1 g, which is still lower than the recommended 4.7 g per day. And the benefits were seen in those getting as little as 2 g per day.
Zinc eaten at levels found in Bio-Fortified Crops reduces 'wear and tear' on DNA
Vitamin D deficiency increases risk of chronic headache
Amino Acids - Hormones.
