BK101
Knowledge Base
Robots - Robotics - Autonomous Machines
Advancements in Robotics and Robots
 Robotics
is a device consisting of a piece of
machinery that has moving
parts that perform some function. A
mechanism that can be
programed to move
automatically.
Robotics
is a device consisting of a piece of
machinery that has moving
parts that perform some function. A
mechanism that can be
programed to move
automatically.
Ai - Half Man Half Robot - Bionic - Robot News
Automaton is a moving mechanical device made in imitation of a human being. A machine that performs a function according to a predetermined set of coded instructions, especially one capable of a range of programmed responses to different circumstances. Automaton is a self-operating machine, or a machine or control mechanism designed to follow automatically a predetermined sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions. Some automata, such as bellstrikers in mechanical clocks, are designed to give the illusion to the casual observer that they are operating under their own power.
Robot is a constructed replication of something that uses Robotics for the purpose of mimicking something else or achieving a task. Robots can be guided by an external control device or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to take on human form but most robots are machines designed to perform a task with no regard to how they look.
Robots don't take Jobs - Three Laws of Robotics - Ethical Robots
Animatronics refers to the use of robotic devices to emulate a human or an animal, or bring lifelike characteristics to an otherwise inanimate object. A robot designed to be a convincing imitation of a human is more specifically labeled as an android. Modern animatronics have found widespread applications in movie special effects and theme parks and have, since their inception, been primarily used as a spectacle of amusement. Animatronics is a multi-disciplinary field which integrates anatomy, robots, mechatronics, and puppetry resulting in lifelike animation. Animatronic figures are often powered by pneumatics, hydraulics, and/or by electrical means, and can be implemented using both computer control and human control, including teleoperation. Motion actuators are often used to imitate muscle movements and create realistic motions in limbs. Figures are covered with body shells and flexible skins made of hard and soft plastic materials and finished with details like colors, hair and feathers and other components to make the figure more life like.
Humanoid is something that has an appearance resembling a human without actually being one. The earliest recorded use of the term, in 1870, referred to indigenous peoples in areas colonized by Europeans. By the 20th century, the term came to describe fossils which were morphologically similar, but not identical, to those of the human skeleton.
Humanoid Robot is a robot with its body shape built to resemble the human body. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some forms of humanoid robots may model only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths.
Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans.
Android Robot is a humanoid robot or synthetic organism designed to look and act like a human, especially one with a body having a flesh-like resemblance. Historically, androids remained completely within the domain of science fiction where they are frequently seen in film and television. Only recently have advancements in robot technology allowed the design of functional and realistic humanoid robots. Human Operating System.
Uncanny Valley is a hypothesized relationship between the degree of an object's resemblance to a human being and the emotional response to such an object. The concept suggests that humanoid objects which imperfectly resemble actual human beings provoke uncanny or strangely familiar feelings of eeriness and revulsion in observers. "Valley" denotes a dip in the human observer's affinity for the replica, a relation that otherwise increases with the replica's human likeness.
Health Industry Robotics
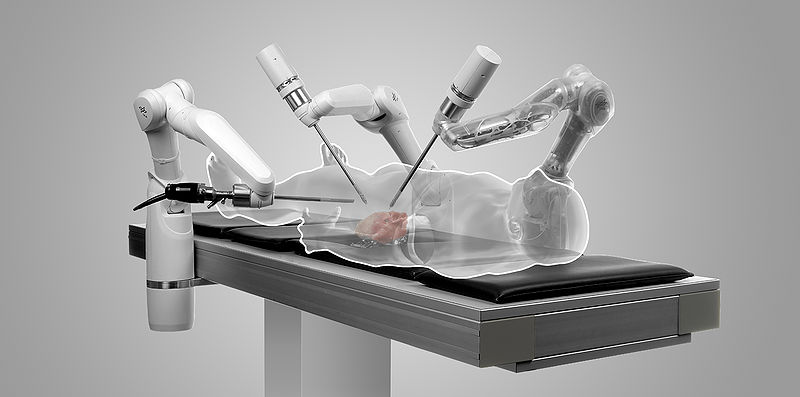 Robot-Assisted Surgery uses robotic systems to aid in
surgical procedures.
Robotically-assisted surgery was developed to overcome the limitations of
pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the
capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
Operating Robots
with Virtual Reality (youtube).
Robot-Assisted Surgery uses robotic systems to aid in
surgical procedures.
Robotically-assisted surgery was developed to overcome the limitations of
pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the
capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
Operating Robots
with Virtual Reality (youtube).Computer-Assisted Surgery represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for surgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions. CAS is also known as computer-aided surgery, computer-assisted intervention, image-guided surgery and surgical navigation, but these are terms that are more or less synonymous with CAS. CAS has been a leading factor in the development of robotic surgery. Augmented Reality.
Da Vinci Surgical Robot is a robotic surgical system made by the American company Intuitive Surgical. Approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000, it is designed to facilitate complex surgery using a minimally invasive approach, and is controlled by a surgeon from a console. The system is commonly used for prostatectomies, and increasingly for cardiac valve repair and gynecologic surgical procedures. Medical Device Warnings.
Telemedicine is the use of telecommunication and information technology to provide clinical health care from a distance. It helps eliminate distance barriers and can improve access to medical services that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities. It is also used to save lives in critical care and emergency situations.
Virtual Patient is used to describe interactive computer simulations used in health care education. The special focus is targeted on the simulation of clinical processes with virtual patients. Virtual patients combine scientific excellence, modern technologies and the innovative concept of game-based learning. Virtual patients allow the learner to take the role of a health care professional and develop clinical skills such as making diagnoses and therapeutic decisions. Virtual patients have also been considered computer-based simulations designed to complement clinical training. The use of virtual patient programmes is increasing in healthcare, partly in response to increasing demands on health care professionals and education of students but also because they allow opportunity for students to practice in a safe environment There are many different formats a virtual patient may take. However the overarching principle is that of interactivity - a virtual patient will have mechanisms for the learner to interact with the case and material or information is made available to the learner as they complete a range of learning activities. The interactivity is non-sequential. Remote Patient Monitoring - Telemetry - Remote Services.
Telepresence is the use of virtual reality technology, especially for remote control of machinery or for apparent participation in distant events. A sensation of being elsewhere, created by the use of virtual reality technology. Telepresence Robots.
Teleoperation indicates operation of a system or the electronic remote control of machine at a distance. It is similar in meaning to the phrase "remote control" but is usually encountered in research, academic and technical environments. It is most commonly associated with robotics and mobile robots but can be applied to a whole range of circumstances in which a device or machine is operated by a person from a distance. The term teleoperation is in use in research and technical communities as a standard term for referring to operation at a distance. This is as opposed to telepresence which is a less standard term and might refer to a whole range of existence or interaction that include a remote connotation.
Telecommand is a command sent to control a remote system or systems not directly connected (e.g. via wires) to the place from which the telecommand is sent. Telerobotics.
Robotic Arm for Extremity Amputations
Tele-Doctors (house calls anywhere) - Sensors
How Augmented Reality could change the future of Surgery - Nadine Hachach-Haram at TED Women 2017 (video and text)
Lifelike simulations that make real-life surgery safer: Peter Weinstock (video and interactive text)
Virtual Reality turns a patient's pre-procedural CT scans into 3-D images that the radiologist can virtually move and examine while wearing virtual reality-type glasses. By allowing the operator to manipulate routine, two-dimensional images in an open three-dimensional space, VR provides a look into a patients' organs and tissues that had not been possible outside of the human body, until now. As a result, the operator is armed with a deeper and intuitive understanding of spatial relationships, such as between an aneurysm and the surrounding arteries.
Surgical Theater is a 360-degree virtual reality reconstruction of the patient's anatomy.
Sound Waves Levitate multiple objects. Surgeons could perform a range of medical procedures all without touching the patient using a specialized array of mini-speakers to create an intricate sound field that 'traps' and manipulates selected objects in 'acoustic tweezers' for manipulation within tissue. Sound Waves.
Robotic Implants spur Tissue Regeneration inside the Body. Mechanical pull stimulates stunted hollow organs to grow, which could help treat defects like esophageal atresia and short bowel syndrome. An implanted, programmable medical robot can gradually lengthen tubular organs by applying traction forces -- stimulating tissue growth in stunted organs without interfering with organ function or causing apparent discomfort. (mechanostimulation).
Robot therapist Manipulative Massage Automation a single, 6-axis robotic arm capable of highly articulated movements.
Flexdex - Minimally Invasive Surgery.
Application of See One, Do One, Teach One Concept in Surgical Training. The traditional method of teaching in Surgery is known as “See One, Do One, Teach One.” However, many have argued that this method is no longer applicable mainly because of concerns for patient safety. Studies have shown that Learning is most efficient when learners are actively involved either physically or mentally in the learning process. This can be accomplished by writing notes or drawing diagrams while studying, asking residents appropriate questions, and engaging residents in surgery. The retention rate is greater the more multisensory and active a learning activity is. Accordingly, only 5% of information is retained when it is learned in a lecture format.
Disaster Relief Robots
 Rescue Robot
is a robot that has been designed for the purpose of rescuing people.
Common situations that employ rescue robots are mining accidents,
urban
disasters, hostage situations, and explosions. The benefits of rescue
robots to these operations include reduced personnel requirements, reduced
fatigue, and access to otherwise unreachable areas. Rescue robots in
development are being made with abilities such as searching,
reconnaissance and mapping, removing or shoring up rubble,
delivery of
supplies, medical treatment, and evacuation of casualties. Even with all
these ideas coming about there are still some technical challenges that
remain. Robin Murphy, a professor of computer science and engineering,
says that “Real disasters are infrequent, and every one is different. The
robots never get used exactly the way you think they will, and they keep
uncovering new bottlenecks and problems. So it’s an emerging technology.”
There are three main levels of challenges. First, the information
processing of the robot. Second, the mobility of the robot. Third, the
manipulation of the robot. Bringing these robots into real-world use and
being able to utilize them in all situations is so close to becoming a
reality. “We're just inches away” Murphy says, “a lot of software is just
waiting for the hardware to catch up”.
Rescue Robot
is a robot that has been designed for the purpose of rescuing people.
Common situations that employ rescue robots are mining accidents,
urban
disasters, hostage situations, and explosions. The benefits of rescue
robots to these operations include reduced personnel requirements, reduced
fatigue, and access to otherwise unreachable areas. Rescue robots in
development are being made with abilities such as searching,
reconnaissance and mapping, removing or shoring up rubble,
delivery of
supplies, medical treatment, and evacuation of casualties. Even with all
these ideas coming about there are still some technical challenges that
remain. Robin Murphy, a professor of computer science and engineering,
says that “Real disasters are infrequent, and every one is different. The
robots never get used exactly the way you think they will, and they keep
uncovering new bottlenecks and problems. So it’s an emerging technology.”
There are three main levels of challenges. First, the information
processing of the robot. Second, the mobility of the robot. Third, the
manipulation of the robot. Bringing these robots into real-world use and
being able to utilize them in all situations is so close to becoming a
reality. “We're just inches away” Murphy says, “a lot of software is just
waiting for the hardware to catch up”.Rescue Robot League is an international competition for urban search and rescue robots, in which robots compete to find victims in a simulated earthquake environment. The rescue robot league is run alongside Robocup Rescue Simulation, as part of the RoboCup robot competition. Robots perform 20 minute search and rescue missions in a test arena measuring approximately 10m by 6m, which features a number of obstacle zones designed to challenge autonomous operation, mobility during tele-operation, and object manipulation. Points are allocated based on the number of victims found, the detail with which victims were detected, and the quality with which the arena has been mapped.
The Robotics Challenge
Robots for Humanity (video)
4WD 100mm Mecanum Wheel Learning Arduino Kit C009 Robot Can Move In Every Direction Without Turning Its Wheel.
Flying Machines - Drones
Drones (types, rules and regulations) - Autonomous
Drone n Base: Race & Battle Drones at Home
Eyes in the Sky (Environmental Monitoring using Drones)
Radio Controlled - Remote Control - Remote
Telerobotics is the area of robotics concerned with the control of semi-autonomous robots from a distance, chiefly using Wireless network (like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, the Deep Space Network, and similar) or tethered connections. It is a combination of two major subfields, Teleoperation and Telepresence. Sensors - Telemetry.
Underwater Inspection Robots
Aquabotix - 2 Grobotics
Inspector Bots - Openrov
Submarines (scuba) - Oceans - Underwater Drones
Deepfield Robotics Robotic Ultra-Precise Weed Control (youtube) You can turn weed killing and pest control into a video game that anyone can play from around the world.
Manufacturing Robots
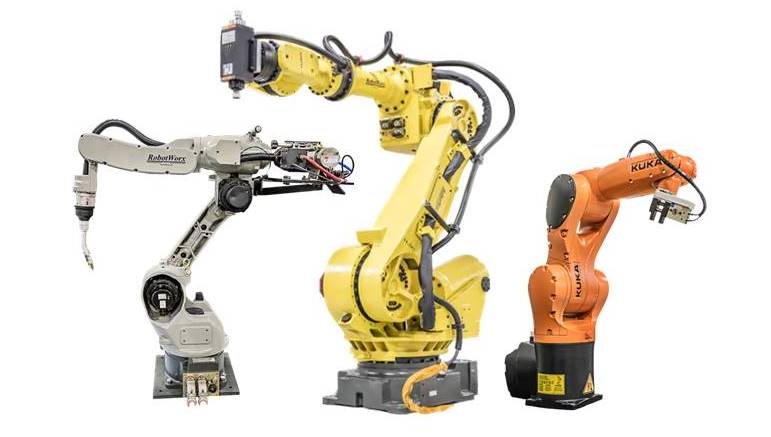 Industrial Robot is a robot system used for
manufacturing.
Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on
two or more axes. Typical applications of robots include welding,
painting, assembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging
and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all
accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can help in
material handling and provide
interfaces.
Industrial Robot is a robot system used for
manufacturing.
Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on
two or more axes. Typical applications of robots include welding,
painting, assembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging
and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all
accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can help in
material handling and provide
interfaces.Laboratory Robotics is the act of using robots in biology or chemistry labs. For example, pharmaceutical companies employ robots to move biological or chemical samples around to synthesize novel chemical entities or to test pharmaceutical value of existing chemical matter. Advanced laboratory robotics can be used to completely automate the process of science, as in the Robot Scientist project.
Robotic Process Automation is an emerging form of business process automation technology based on the notion of software robots or artificial intelligence (AI) workers. In traditional workflow automation tools, a software developer produces a list of actions to automate a task and interface to the back-end system using internal application programming interfaces (APIs) or dedicated scripting language. In contrast, RPA systems develop the action list by watching the user perform that task in the application's graphical user interface (GUI), and then perform the automation by repeating those tasks directly in the GUI. This can lower the barrier to use of automation in products that might not otherwise feature APIs for this purpose. RPA tools have strong technical similarities to graphical user interface testing tools. These tools also automate interactions with the GUI, and often do so by repeating a set of demonstration actions performed by a user. RPA tools differ from such systems including features that allow data to be handled in and between multiple applications, for instance, receiving email containing an invoice, extracting the data, and then typing that into a bookkeeping system.
Programming by Demonstration is an end-user development technique for teaching a computer or a robot new behaviors by demonstrating the task to transfer directly instead of programming it through machine commands.
Engineering Machines - 3D Printing
Biorobotics covers the fields of cybernetics, bionics and even genetic engineering as a collective study.
Cybernetics is used for exploring regulatory systems—their structures, constraints, and possibilities. Norbert Wiener defined cybernetics in 1948 as "the scientific study of control and communication in the animal and the machine. Universal Robots.
Collision Avoidance Using the Reflexxes Motion Libraries (youtube)
Artificial Robot Nervous System to Teach Robots How to Feel Pain (youtube)
Madeline the Robot Tamer (vimeo)
Quipt is a gesture-based control software that gives industrial robots basic spatial behaviors for interacting closely with people.
How to Tame Your Robot
Robotnik Summit XL OMNI - Mecanum Wheels | Омни боты (youtube)
Get a Grip with Soft Electronics (youtube) Soft Robotic Gripper Electroadhesion
SALTO - Berkeley's leaping robot (youtube)
Robots Sorting System sorts 200,000 packages a day in Chinese warehouse. (youtube)
Association for Computing Machinery
Artificial Muscles give soft Robots Superpowers. Origami-inspired muscles are both soft and strong, and can be made for less than $1. Origami-inspired artificial muscles are capable of lifting up to 1,000 times their own weight, simply by applying air or water pressure powered by a vacuum. They can generate about six times more force per unit area than mammalian skeletal muscle can and are also incredibly lightweight (water-soluble polymer PVA); a 2.6-gram muscle can lift a 3-kilogram object, muscles is that they're programmable and soft actuators are highly scalable.
Bionics - Electronic Physiological Functions
 Bionics
is the application of
biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design
of engineering systems and modern technology.
Bionics
is the application of
biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design
of engineering systems and modern technology.
Sensors - Bio-Mimicry - Self Healing
Bio-Robotics covers the fields of cybernetics, bionics and even genetic engineering.
Powered Exoskeleton is a wearable mobile machine that is powered by a system of electric motors, pneumatics, levers, hydraulics, or a combination of technologies that allow for limb movement with increased strength and endurance.
Exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton (endoskeleton) of, for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of animals with exoskeletons include insects such as grasshoppers and cockroaches, and crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters. The shells of certain sponges and the various groups of shelled molluscs, including those of snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus, are also exoskeletons. Some animals, such as the tortoise, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton.
Hybrid Assistive Limb is a powered exoskeleton suit designed to support and expand the physical capabilities of its users, particularly people with physical disabilities. There are two primary versions of the system: HAL 3, which only provides leg function, and HAL 5, which is a full-body exoskeleton for the arms, legs, and torso. Phantom Limb.
Soft Robotics is the specific subfield of robotics dealing with constructing robots from highly compliant materials, similar to those found in living organisms. Soft robotics draws heavily from the way in which living organisms move and adapt to their surroundings. In contrast to robots built from rigid materials, soft robots allow for increased flexibility and adaptability for accomplishing tasks, as well as improved safety when working around humans. These characteristics allow for its potential use in the fields of medicine and manufacturing. Lifelike Robots.
Dynamic Hydrogel used to make 'Soft Robot' components and LEGO-like building blocks. A new type of hydrogel material could soon make assembling complex microfluidic or soft robotic devices as simple as putting together a LEGO set. Using a new type of dual polymer material capable of responding dynamically to its environment, Brown University researchers have developed a set of modular hydrogel components that could be useful in a variety of "soft robotic" and biomedical applications. The components, which are patterned by a 3D printer, are capable of bending, twisting or sticking together in response to treatment with certain chemicals.
Robotic Skins are made of elastic sheets embedded with sensors and remotely operated actuators, which work together to create the makeshift bots. Touch Bionics.
Robotics Skins” turn everyday objects into Robots (youtube)
Soft Robotic Muscles Created by CU Engineering Researchers. Liquefied Soft Artificial Muscle Electrically Activated to Mimic the Expansion and Contraction of Natural Muscles.
Better understanding of soft artificial muscles. Research sheds light on the underlying mechanics of soft filaments.
Peano-HASEL Actuators: Muscle-Mimetic, Electrohydraulic Transducers that Linearly Contract on Activation. Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic (HASEL).
Amputees Merge with their Bionic Leg. A smart artificial hand for amputees merges user and robotic control. Scientists from a European consortium led by Swiss Institutions, ETH Zurich and EPFL spin-off SensArs Neuroprosthetics, with clinical trials in collaboration with institutions in Belgrade, Serbia, successfully characterized and implemented bionic leg technology with three amputees.
Underactuation is a technical term used in robotics and control theory to describe mechanical systems that cannot be commanded to follow arbitrary trajectories in configuration space. This condition can occur for a number of reasons, the simplest of which is when the system has a lower number of actuators than degrees of freedom. In this case, the system is said to be trivially underactuated. The class of underactuated mechanical systems is very rich and includes such diverse members as automobiles, airplanes, and even animals.
Allen Zderad, uses Bionic Eye to see (youtube)
Body Builders Bionics (youtube)
How insects activate muscles to adapt to limbs removed. Adaptability explains why insects spread so widely and why they are the most abundant animal group on earth. Insects exhibit resilient and flexible locomotion, even with drastic changes in their body structure such as losing a limb.
Patient controls Prosthesis with own Thoughts. Radboud university medical center connects first click-on arm prosthesis to nerves.
Amputees can Learn to Control a Robotic arm with their Minds through Electrodes Implanted in the Brain.
The Force is Strong: Amputee Controls Individual Prosthetic Fingers. Luke Skywalker’s bionic hand made possible by ultrasound technology.
The First Dexterous and Sentient Hand Prosthesis has been successfully implanted. A Swedish patient with hand amputation has become the first recipient of an osseo-neuromuscular implant to control a dexterous hand prosthesis. In a pioneering surgery, titanium implants were placed in the two forearm bones (radius and ulnar), from which electrodes to nerves and muscle were extended to extract signals to control a robotic hand and to provide tactile sensations. This makes it the first clinically viable, dexterous and sentient prosthetic hand usable in real life.
Rewalk Robotics Mobility for Stroke Victims.
Brain Computer Interfaces (implants) - Hearing Aids
Neurorobotics is a combined study of neuroscience, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
Artificial Skin with Solar Cells could Power Prosthetics. Scientist creates graphene skin that's more sensitive than our own.
The Six Million Dollar Man is an American science fiction television series in 1973 about a former astronaut who was given superhuman strength due to bionic implants. A spin-off television series, The Bionic Woman, featuring the lead female character Jaime Sommers, ran from 1976 to 1978.
Advanced Artificial Limbs Mapped in the Brain. Neuroprosthetics have used functional MRI to show how the brain re-maps motor and sensory pathways following targeted motor and sensory reinnervation (TMSR), a neuroprosthetic approach where residual limb nerves are rerouted towards intact muscles and skin regions to control a robotic limb.
Neuroprosthetics or neural prostheses, are sometimes contrasted with a brain–computer interface, which connects the brain to a computer rather than a device meant to replace missing biological functionality. Neural prostheses are a series of devices that can substitute a motor, sensory or cognitive modality that might have been damaged as a result of an injury or a disease.
Prosthesis is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or congenital conditions. Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools.
Open Bionics 3d Printed Prosthetic Limbs
Open Bionics - Open Bionics - Limbitless Solutions
Orthotics externally applied device used to modify the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal system. An orthosis may be used to Control, guide, limit and/or immobilize an extremity, joint or body segment for a particular reason, Restrict movement in a given direction. Assist movement generally. Reduce weight bearing forces for a particular purpose. Aid rehabilitation from fractures after the removal of a cast. Otherwise correct the shape and/or function of the body, to provide easier movement capability or reduce pain.
Artificial Muscles power up with new Gel-Based Robotics.
Wearable Computing Ring Allows Users to Write Words and Numbers with Thumb. Technology provides eyes-free way to interact with smart devices.
UCLA scientists make Cells that enable the Sense of Touch. Researchers are the first to create sensory interneurons from stem cells.
A Prosthetic that Restores the Sense of where your Hand is. Researchers have developed a next-generation bionic hand that allows amputees to regain their proprioception. The results of the study are the culmination of ten years of robotics research.
Mind-Controlled Arm Prostheses.
Amart Artificial Hand for Amputees merges user and robotic control. Scientists have successfully tested new neuroprosthetic technology that combines robotic control with users' voluntary control, opening avenues in the new interdisciplinary field of shared control for neuroprosthetic technologies.
Even after long-term exposure, bionic touch does not remap the brain. A new study by neuroscientists demonstrates that the brain does not remap itself even with long-term bionic limb use, posing challenges for the development of realistic prosthetic limbs.
Seeing through a Robot's Eyes helps those with profound Motor Impairments. An interface system that uses augmented reality technology could help individuals with profound motor impairments operate a humanoid robot to feed themselves and perform routine personal care tasks such as scratching an itch and applying skin lotion. The web-based interface displays a 'robot's eye view' of surroundings to help users interact with the world through the machine.
Highly sensitive sensors show promise in enhancing human touch. Ultrathin crack-based sensors operate on a principle similar to a spider's sense organ and display remarkable sensitivity to movement. People rely on a highly tuned sense of touch to manipulate objects, but injuries to the skin and the simple act of wearing gloves can impair this ability. Surgeons, for example, find that gloves decrease their ability to manipulate soft tissues. Astronauts are also hampered by heavy spacesuits and find it difficult to work with equipment while wearing heavy gloves.
Mind-Controlled Arm Prostheses that 'feel' are now a part of everyday life. Our study shows that a prosthetic hand, attached to the bone and controlled by electrodes implanted in nerves and muscles, can operate much more precisely than conventional prosthetic hands. We further improved the use of the prosthesis by integrating tactile sensory feedback that the patients use to mediate how hard to grab or squeeze an object. Over time, the ability of the patients to discern smaller changes in the intensity of sensations has improved. The new concept of a neuromusculoskeletal prosthesis is unique in that it delivers several different features which have not been presented together in any other prosthetic technology in the world: It has a direct connection to a person's nerves, muscles, and skeleton. It is mind-controlled and delivers sensations that are perceived by the user as arising from the missing hand. It is self-contained; all electronics needed are contained within the prosthesis, so patients do not need to carry additional equipment or batteries. It is safe and stable in the long term; the technology has been used without interruption by patients during their everyday activities, without supervision from the researchers, and it is not restricted to confined or controlled environments.
Virtual Reality Reduces Phantom Pain in Paraplegics - Phantom Pain
Tech makes it possible to digitally communicate through human touch. Researchers have developed the first technology capable of sending digital information, such as a photo or password, by touching a surface with your finger. Instead of inserting a card or scanning a smartphone to make a payment, what if you could simply touch the machine with your finger? A prototype developed by Purdue University engineers would essentially let your body act as the link between your card or smartphone and the reader or scanner, making it possible for you to transmit information just by touching a surface.
Versatile new material family could build realistic prosthetics, futuristic army platforms. Researchers have developed a new family of polymers that can self-heal, have shape memory and are recyclable. Nature's blueprint for the human limb is a carefully layered structure with stiff bone wrapped in layers of different soft tissue, like muscle and skin, all bound to each other perfectly. Achieving this kind of sophistication using synthetic materials to build biologically inspired robotic parts or multicomponent, complex machines has been an engineering challenge.
Robots sense human touch using camera and shadows. Researchers have created a low-cost method for soft, deformable robots to detect a range of physical interactions, from pats to punches to hugs, without relying on touch at all. Instead, a USB camera located inside the robot captures the shadow movements of hand gestures on the robot's skin and classifies them with machine-learning software.
Robotics Education
 Roboticist is a person who designs, builds,
programs, and
experiments with
robots. Since robotics is a highly interdisciplinary field, roboticists
often have backgrounds in a number of disciplines including
computer
science, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering,
physics,
human–computer interaction and interaction design. Roboticists often work
for university, industry, and government research labs, but may also work
for startup companies and other entrepreneurial firms. Amateur Robotics is
also a growing hobby all over the world.
Robotics Education.
Roboticist is a person who designs, builds,
programs, and
experiments with
robots. Since robotics is a highly interdisciplinary field, roboticists
often have backgrounds in a number of disciplines including
computer
science, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering,
physics,
human–computer interaction and interaction design. Roboticists often work
for university, industry, and government research labs, but may also work
for startup companies and other entrepreneurial firms. Amateur Robotics is
also a growing hobby all over the world.
Robotics Education.Open Robotics we support the development, distribution, and adoption of open software and hardware for use in robotics research, education, and product development.
Locorobo-Master Programming Robotics
Robotics Trends
Cloud Robotics
Boston Dynamics
µTug: Micro robot pulls 2000 times its weight on glass (youtube)
Revolve Robotics
kubi
Festo Automation
Kiva Systems
KOOV: all-in-one Coding & Robotics design Kit.
Anki toy robot that is also a programming platform.
Fect Robotics Toys
Romotive
RoboSimian
Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2014)
Petman, Atlas (youtube)
Robot Restaurant
Another great reason why we need to improve education is to make sure that students learn about human relationships and the relationships and interactions that we have with machines, technology and robots. Techno-Stress.
Grade-school students teach a robot to help themselves learn geometry
 Lost in Space STS-117 B9 Robot Presentation Video (youtube)
Lost in Space STS-117 B9 Robot Presentation Video (youtube)
Janken (rock-paper-scissors) Robot with 100% winning rate (youtube)
Nano-Robotics
Learning Code
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence (body smart)
Engineering Machines
Information Stations
Artificial Intelligence
3D Printing
Computers
Software - Hardware
Technology News
Technology Apps and Accessories
Virtual Reality
Science Kits
The Media Equation is a general communication theory that claims that people tend to treat computers and other media as if they were either real people or real places. The effects of this phenomenon on people experiencing these media are often profound, leading them to behave and to respond to these experiences in unexpected ways, most of which they are completely unaware.
Robot Competitions
Battle-Bots
Robo-Cup
The Robotics Challenge
Robot Events
Robo Games
MIT Zero Robotics
Robot Hall of Fame
Robot Festival
Vacation Ideas
Robot Building Kits
Robot Building Kits
Robotics Electronic Kits
Robotics Parts
Science Kits and Tools
Antbo: An Insect Robot Anyone Can Build
DRONOID Modular Drone for Kids & Adults
Tinkerbots Robotics Wheeler Set
Personal Home Robots
Jibo: The World's First Family Robot
Buddy: Family's Companion Robot
Leka Robotic Toy for Exceptional Children with motor, cognitive, social, and emotional disorders.
Could Robots have the same beneficial qualities as owning a Pet?
Musio Robot
Baxter
Baxter Robot (wiki)
Baxter Robot Video
Aido: Next Gen Home Robot
Voice-Activated Assistants
Charli-2 (youtube)
Robit - The World's Most Affordable Home Robot
Romela
Human Operating System
Saffir Autonomous Humanoid
i robot
Robotic
Tamaggo Panoramic Videos
Rp-7i Robot
Cobot (wiki)
irobot Virtual Robots
Alpha 2, the First Humanoid Robot for the Family!
Riley Mobile Companion
Zenbo Asus
Moorebot
Nao Robot (wiki)
Robelf - multi-camera home security robot Moving Monitor.
Home Monitoring
Robot News
Alter: a new type of robot has its own neural network Takashi Ikegami (University of Tokyo) (youtube)
Boston Dynamics - Atlas uses its whole body -- legs, arms, torso -- to perform a sequence of dynamic maneuvers that form a gymnastic routine. We created the maneuvers using new techniques that streamline the development process. First, an optimization algorithm transforms high-level descriptions of each maneuver into dynamically-feasible reference motions. Then Atlas tracks the motions using a model predictive controller that smoothly blends from one maneuver to the next. Using this approach, we developed the routine significantly faster than previous Atlas routines, with a performance success rate of about 80%.
Boston Dynamics Robots Dancing (youtube) - The anthropomorphic Atlas, Spot the robot dog, and even Handle, a box moving robot, danced to the classic song "Do You Love Me" by the Contours. "First they dance for us, then they start killing us".
COWAROBOT R1: Robotic Suitcase, Autonomous Navigation, High-tech Security. There are probably more practicable uses for this technology besides just a suitcase.
Lifelike Robots. A self-contained soft actuator three times stronger than natural muscle, without the need of externals, signals a breakthrough in Soft Robotics.
FenSens Smart Wireless Parking Sensor - Installs in less than 5 min, no wires, and hands-free App .
3D-Printed Robot wave-propelled that can swim, climb and crawl. 3D printed wave producing robot (SAW).
Let's all Pull Together: Team of µTug Microrobots Pulls a Car (microTug microrobots).
Everybot RS500 Robotic Spin Mop
Peeqo - The GIF Bot (youtube)
Transparent Gel Robot that Can Snatch Fish Right Up (youtube)
Now you can "build your own" bio-bot Optogenetic skeletal muscle-powered adaptive biological machines.
Uncanny Lover: Building a Sex Robot | Robotica | The New York Times (youtube) - Sex Dolls with AI will replace most prostitutes. RealDoll could be used for practice and education.
Three-dimensionally printed biological machines powered by skeletal muscle.
Robo-Thread (youtube) - MIT engineers have developed a magnetically steerable, thread-like robot that can actively glide through narrow, winding pathways, such as the labyrinthine vasculature of the brain.
Engineers have designed a microfluidic device they call a "tree-on-a-chip," which mimics the pumping mechanism of trees and plants. The more sugar there is in the phloem, the more water flows from xylem to phloem to balance out the sugar-to-water gradient, in a passive process known as osmosis. The resulting water flow flushes nutrients down to the roots. Trees and plants are thought to maintain this pumping process as more water is drawn up from their roots. engineers have previously attempted to design tree-inspired microfluidic pumps, fabricating parts that mimic xylem and phloem. Hosoi envisions that the tree-on-a-chip pump may be built into a small robot to produce hydraulically powered motions, without requiring active pumps or parts.
Physicists take first step toward Cell-Sized Robots. An electricity-conducting, environment-sensing, shape-changing machine the size of a human cell. A robot exoskeleton that can rapidly change its shape upon sensing chemical or thermal changes in its environment. And, they claim, these microscale machines – equipped with electronic, photonic and chemical payloads – could become a powerful platform for robotics at the size scale of biological microorganisms, with the computational power of the spaceship Voyager onto an object the size of a cell. The machines move using a motor called a bimorph. A bimorph is an assembly of two materials – in this case, graphene and glass – that bends when driven by a stimulus like heat, a chemical reaction or an applied voltage. The shape change happens because, in the case of heat, two materials with different thermal responses expand by different amounts over the same temperature change.
Bimorph is a cantilever used for actuation or sensing which consists of two active layers. It can also have a passive layer between the two active layers. In contrast, a piezoelectric unimorph has only one active (i.e. piezoelectric) layer and one passive (i.e. non-piezoelectric) layer. The term is most commonly used with piezoelectric bimorphs. In actuator applications, one active layer contracts and the other expands if voltage is applied, thus the bimorph bends. In sensing applications, bending the bimorph produces voltage which can for example be used to measure displacement or acceleration. This mode can also be used for energy harvesting. A bimetal could be regarded as a thermally activated bimorph. The first theory about the bending of thermally activated bimorphs was given by Stoney. Newer developments also enabled electrostatically activated bimorphs for the use in Microelectromechanical systems.
First walking robot that can explore its environment randomly and go home automatically, without GPS or mapping.
AntBot, the brand-new robot designed by CNRS and Aix-Marseille University (AMU) researchers at ISM, copies the desert ants' exceptional navigation capacities. It is equipped with an optical compass used to determine its heading by means of polarized light, and by an optical movement sensor directed to the sun to measure the distance covered. Armed with this information, AntBot has been shown to be able, like the desert ants, to explore its environment and to return on its own to its base, with precision of up to 1 cm after having covered a total distance of 14 meters. Weighing only 2.3 kg, this robot has six feet for increased mobility, allowing it to move in complex environments, precisely where deploying wheeled robots and drones can be complicated (disaster areas, rugged terrain, exploration of extraterrestrial soils, etc.).
What happens when a Gorilla meets a Robot that looks like a small Ape? Animals can be fooled just like Humans can.
Alpha Silverback Gorilla Welcomes Spy Gorilla To The Family | BBC Earth (youtube).
