BK101
Knowledge Base
Wind Energy
 Wind Turbine is a device that converts the wind's
kinetic energy into
electrical
power. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis types. The
smallest turbines are used for applications such as
battery charging for
auxiliary power for boats or caravans or to power traffic warning signs.
Slightly larger turbines can be used for making contributions to a
domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility
supplier via the electrical grid. Arrays of large turbines, known as
wind
farms, are becoming an increasingly important source of intermittent
renewable energy and are used by many countries as part of a strategy to
reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Wind Turbine Info-Graph (Motion Gif)
Wind Turbine is a device that converts the wind's
kinetic energy into
electrical
power. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis types. The
smallest turbines are used for applications such as
battery charging for
auxiliary power for boats or caravans or to power traffic warning signs.
Slightly larger turbines can be used for making contributions to a
domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility
supplier via the electrical grid. Arrays of large turbines, known as
wind
farms, are becoming an increasingly important source of intermittent
renewable energy and are used by many countries as part of a strategy to
reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Wind Turbine Info-Graph (Motion Gif)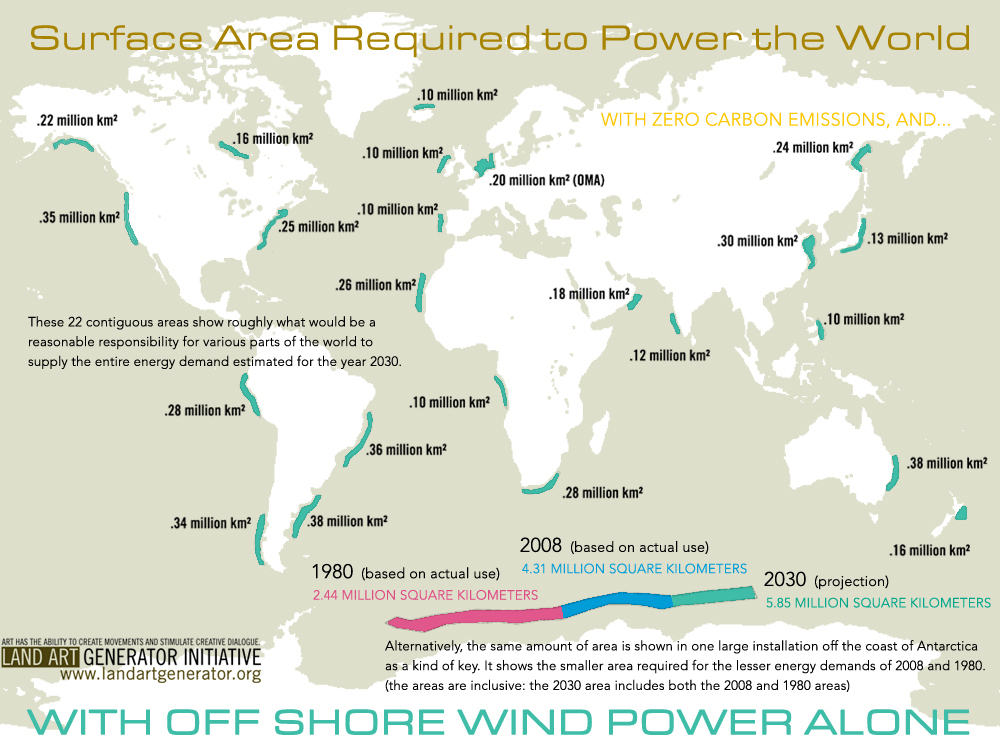 Wind Energy was producing energy for 6 million homes at the end of 2008,
Now it's up to 13 million as of 2012, providing about 3 percent of Americas energy needs.
In 2015, the United States, wind power accounts for about 4 percent of
overall electricity production (181.79
terawatt-hours) but supplies significant amounts
of power in various states and regions.
In May 2015, the Pacific Northwest’s Bonneville Power Administration
generated more than 40 percent of its electricity for its 13
million residents from wind energy alone.
In Texas, record wind output in March met about 40 percent of
the demand for most of the state’s electric grid. In 2015,
Wind Power in the United States is generating nearly 75,000 megawatts
(MW).
Nameplate
Capacity is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power plant.
1,000-Year-Old
Windmills Still in Use Today | National Geographic (youtube) -
The Glaring
Engineering Mistake That Made Wind Turbines Inefficient | Massive
Engineering Mistakes (youtube).
Wind Energy was producing energy for 6 million homes at the end of 2008,
Now it's up to 13 million as of 2012, providing about 3 percent of Americas energy needs.
In 2015, the United States, wind power accounts for about 4 percent of
overall electricity production (181.79
terawatt-hours) but supplies significant amounts
of power in various states and regions.
In May 2015, the Pacific Northwest’s Bonneville Power Administration
generated more than 40 percent of its electricity for its 13
million residents from wind energy alone.
In Texas, record wind output in March met about 40 percent of
the demand for most of the state’s electric grid. In 2015,
Wind Power in the United States is generating nearly 75,000 megawatts
(MW).
Nameplate
Capacity is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power plant.
1,000-Year-Old
Windmills Still in Use Today | National Geographic (youtube) -
The Glaring
Engineering Mistake That Made Wind Turbines Inefficient | Massive
Engineering Mistakes (youtube).Info-Graph on right provided by Land Art Generator.
Energy Types - Renewable Energy Statistics - Batteries (backup power)
Wind Turbine has a 1.7-megawatt General Electric turbine, which rises 432 feet above the ground from the tip of a blade.
Takes 43 truckloads to pour close to 400 cubic yards of concrete. The concrete base is 9 feet deep and nearly 60 feet across.
When wind speeds are more than 45 mph, the blades will lock for safety.
More than 50,000 wind turbines in place across the U.S., wind power now accounts for 8 percent of the nation's energy-generating capacity — and experts predict that figure could rise to 20 percent by 2030.
December 2016, the 30-megawatt Block Island Wind Farm off of Rhode Island went into operation with five turbines.
 Roscoe Wind Farm in Roscoe, Texas, owned and operated by
E.ON Climate & Renewables is one of the world's largest capacity wind
farms with 634 wind turbines and a total installed capacity of 781.5 MW.
At the time of its completion in 2009, it was the largest wind farm in the
world, surpassing the nearby 735.5 MW Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center. In
2012, it was overtaken by California's 1,020 MW Alta Wind Energy Center.
Roscoe Wind Farm in Roscoe, Texas, owned and operated by
E.ON Climate & Renewables is one of the world's largest capacity wind
farms with 634 wind turbines and a total installed capacity of 781.5 MW.
At the time of its completion in 2009, it was the largest wind farm in the
world, surpassing the nearby 735.5 MW Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center. In
2012, it was overtaken by California's 1,020 MW Alta Wind Energy Center.
American Wind Energy Association - Fact Sheet Map by State
Denmark’s array of onshore and offshore wind farms met 116 percent of its national electricity demand on July 9, 2015, according to the energy tracking website energynet.dk. The next morning, after demand had peaked, the figure rose to 140 percent. Germany, Norway, and Sweden took the power surplus off Denmark’s hands, storing excess electricity in hydropower systems for later use. It’s a new record for Denmark, where wind farms met 39 percent of the country’s electricity needs in 2014, putting the nation of 5 million in the company of Scotland, Germany, and other countries that are producing more than a quarter of their power from renewable sources.
World's Largest Offshore Wind Farm Opens in English Channel. 100 turbines covering an area of 13.5 square miles, producing 300 megawatts, which is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of more than 200,000 British households.
Walney Extension is the Largest Offshore Wind Farm in the World. Off the coast of northwestern England stands 87 turbines that average 640 feet above mean sea level, each producing 8.25 megawatts on average, which totals 659 megawatts of power, enough to power almost 600,000 homes in the UK. The wind farm covers an area of water measuring 55.9 square miles, or 35,830 acres.
World Wind Energy Association
Global Wind Energy Council
Types of Wind Turbines
Floating Wind Turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where bottom-mounted towers are not feasible. Locating wind farms out at sea can reduce visual pollution while providing better accommodation for fishing and shipping lanes. In addition, the wind is typically more consistent and stronger over the sea, due to the absence of topographic features that disrupt wind flow. Floating wind parks are wind farms that site several floating wind turbines closely together to take advantage of common infrastructure such as power transmission facilities.
Floating Wind & Current Hybrid Power
 Vertical Axis Wind Turbine are a type of wind turbine
where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind (but not
necessarily vertically) while the main components are located at the base
of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be
located close to the ground, facilitating service and repair. VAWTs do not
need to be pointed into the wind, which removes the need for wind-sensing
and orientation mechanisms. Major drawbacks for the early designs (Savonius,
Darrieus and giromill) included the significant torque variation or
"ripple" during each revolution, and the large bending moments on the
blades. Later designs addressed the torque ripple issue by sweeping the
blades helically.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine are a type of wind turbine
where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind (but not
necessarily vertically) while the main components are located at the base
of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be
located close to the ground, facilitating service and repair. VAWTs do not
need to be pointed into the wind, which removes the need for wind-sensing
and orientation mechanisms. Major drawbacks for the early designs (Savonius,
Darrieus and giromill) included the significant torque variation or
"ripple" during each revolution, and the large bending moments on the
blades. Later designs addressed the torque ripple issue by sweeping the
blades helically.Savonius Vertical Axis Wind Turbine are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT), used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft. The turbine consists of a number of aerofoils, usually—but not always—vertically mounted on a rotating shaft or framework, either ground stationed or tethered in airborne systems.
Vertical-axis wind turbine eggbeater pairs arrangement varying heights.
Magnetic Coupling is a coupling that transfers torque from one shaft, but using a magnetic field rather than a physical mechanical connection. Magnetic shaft couplings are most often used for liquid pumps and propeller systems, since a static, physical barrier can be placed between the two shafts to separate the fluid from the motor operating in air. Magnetic shaft couplings preclude the use of shaft seals, which eventually wear out and fail from the sliding of two surfaces against each another. Magnetic couplings are also used for ease of maintenance on systems that typically require precision alignment, when physical shaft couplings are used, since they allow a greater off axis error between the motor and driven shaft.
Electromagnetic Clutch operate electrically but transmit torque mechanically. This is why they used to be referred to as electro-mechanical clutches. Over the years, EM became known as electromagnetic versus electro-mechanical, referring more about their actuation method versus physical operation. Since the clutches started becoming popular over 60 years ago, the variety of applications and clutch designs has increased dramatically, but the basic operation remains the same today. Single-face clutches make up approximately 90% of all electromagnetic clutch sales. Electromagnetic clutches are most suitable for remote operation since no mechanical linkages are required to control their engagement, providing fast, smooth operation. However, because the activation energy dissipates as heat in the electromagnetic actuator when the clutch is engaged, there is a risk of overheating. Consequently, the maximum operating temperature of the clutch is limited by the temperature rating of the insulation of the electromagnet. This is a major limitation. Another disadvantage is higher initial cost.
Typhoon Turbine. Harvesting the energy from typhoons.
Airborne Wind Turbine is a design concept for a wind turbine with a rotor supported in the air without a tower, thus benefiting from more mechanical and aerodynamic options, the higher velocity and persistence of wind at high altitudes, while avoiding the expense of tower construction, or the need for slip rings or yaw mechanism. An electrical generator may be on the ground or airborne. Challenges include safely suspending and maintaining turbines hundreds of meters off the ground in high winds and storms, transferring the harvested and/or generated power back to earth, and interference with aviation. Airborne wind turbines may operate in low or high altitudes; they are part of a wider class of Airborne Wind Energy Systems (AWES) addressed by high-altitude wind power and crosswind kite power. When the generator is on the ground, then the tethered aircraft need not carry the generator mass or have a conductive tether. When the generator is aloft, then a conductive tether would be used to transmit energy to the ground or used aloft or beamed to receivers using microwave or laser. Kites and 'helicopters' come down when there is insufficient wind; kytoons and blimps may resolve the matter with other disadvantages. Also, bad weather such as lightning or thunderstorms, could temporarily suspend use of the machines, probably requiring them to be brought back down to the ground and covered. Some schemes require a long power cable and, if the turbine is high enough, a prohibited airspace zone. As of July 2015, no commercial airborne wind turbines are in regular operation.
Wind Lens is a modification on the wind turbine created by Professor Ohya from the Kyushu University as an attempt to be more efficient in production of electricity and less invasive to both humans and nature. While still in progress, the wind lens has a few changes in design which have led to impacts on how wind energy can be used and harnessed while changing how it impacts the world around us.
Dual-Rotor Wind Turbine
Coaxial Rotors or "coax rotors" are a pair of helicopter rotors mounted one above the other on concentric shafts, with the same axis of rotation, but turning in opposite directions (contra-rotation). This configuration is a feature of helicopters produced by the Russian Kamov helicopter design bureau.
Small Wind Turbines
Trinity Portable Wind Turbine
Wind Turbine for Home
Vortex Bladeless Wind Turbines
Vortex Bladeless
Crookes Radiometer also known as a light mill, consists of an airtight glass bulb, containing a partial vacuum. Inside are a set of vanes which are mounted on a spindle. The vanes rotate when exposed to light, with faster rotation for more intense light, providing a quantitative measurement of electromagnetic radiation intensity. The reason for the rotation was a cause of much scientific debate in the ten years following the invention of the device, but in 1879 the currently accepted explanation for the rotation was published. Today the device is mainly used in physics education as a demonstration of a heat engine run by light energy.
Wind Energy Resources
 Dyson
DysonWindtronics
Sauer Energy
Gold Wind Global
Urban Green Energy
Wind Spire Energy
Helix Wind
Solar Mill (youtube)
Wind Power Research Analysis
Hybrid Hydro Wind System
El Hierro is the smallest and farthest south and west of the Canary Islands.
Wind Spires
Wind Energy
Altestore
Wind Power
First Wind
Vibro Wind Panels jetsongreen.com
Sheer Wind
Down Draft Tower
Small Wind Certification
Airborne Wind Energy Association
Airborne Wind Energy System
Air Born Wind Turbine

Hosting Powered by Renewable Energy
Websites Powered by Renewable Energy
Birds and Windmills
Researchers estimate that 140,000 to 328,000 birds are killed every year in collisions with the turbines' spinning rotor blades and support towers. The risk to birds is highest at night, when the blades and towers are cloaked in darkness. Stopping or slowing their wind turbines temporarily when large numbers of birds are flying through the area, using automated bird migration forecasts and real-time tracking maps by Birdcast.
The Windmills of Your Mind - Noel Harrison (youtube - Released 1968
Round like a circle in a spiral, like a wheel within a wheel
Never ending or beginning on an ever spinning reel
Like a snowball down a mountain, or a carnival balloon
Like a carousel that's turning running rings around the moon
Like a clock whose hands are sweeping past the minutes of its face
And the world is like an apple whirling silently in space
Like the circles that you find in the windmills of your mind!
Like a tunnel that you follow to a tunnel of its own
Down a hollow to a cavern where the sun has never shone
Like a door that keeps revolving in a half forgotten dream
Or the ripples from a pebble someone tosses in a stream
Like a clock whose hands are sweeping past the minutes of its face
And the world is like an apple whirling silently in space
Like the circles that you find in the windmills of your mind!
Keys that jingle in your pocket, words that jangle in your head
Why did summer go so quickly, was it something that you said?
Lovers walking along a shore and leave their footprints in the sand
Is the sound of distant drumming just the fingers of your hand?
Pictures hanging in a hallway and the fragment of a song
Half remembered names and faces, but to whom do they belong?
When you knew that it was over you were suddenly aware
That the autumn leaves were turning to the color of her hair!
Like a circle in a spiral, like a wheel within a wheel
Never ending or beginning on an ever spinning reel
As the images unwind, like the circles that you find
In the windmills of your mind!
